Revolutionizing Kenyan Agriculture: How Digital Platforms and Cold Storage Are Empowering Smallholder Farmers
“A Nairobi-based agritech startup boosts smallholder farmers’ incomes by over 15% through digital market access.”
In the heart of East Africa, a revolution is taking place in the agricultural sector. We are witnessing a remarkable transformation as digital platforms and innovative cold storage solutions reshape the landscape for smallholder farmers in Kenya. This blog post delves into the groundbreaking changes occurring in Kenyan agriculture, exploring how technology is bridging gaps, enhancing efficiency, and empowering those at the grassroots level of food production.
The Dawn of Digital Agriculture in Kenya
Kenya, a country where agriculture forms the backbone of the economy, is experiencing a paradigm shift. Agritech startups in Africa are at the forefront of this change, introducing solutions that address long-standing challenges faced by smallholder farmers. These innovations are not just incremental improvements; they represent a complete overhaul of how agricultural supply chains function.
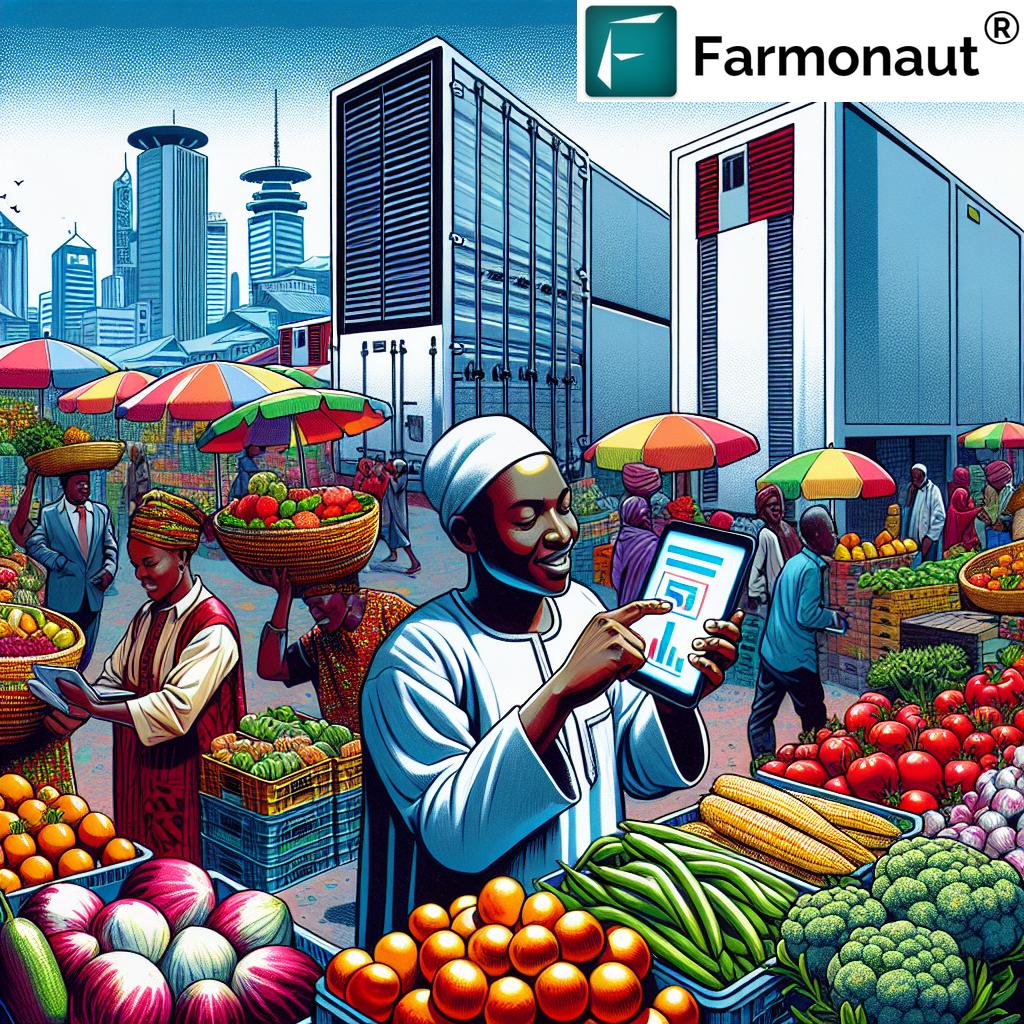

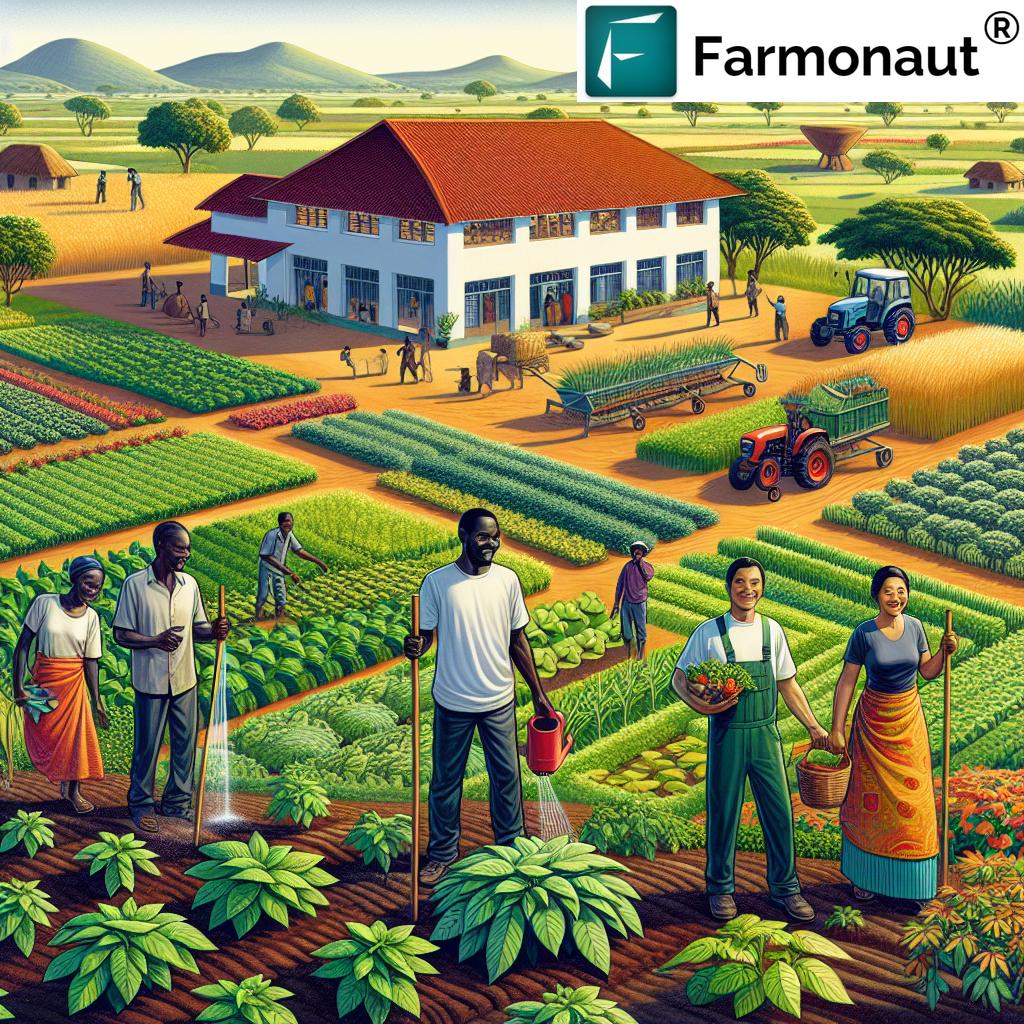
At the heart of this revolution is a Nairobi-based company that has pioneered an approach to agricultural supply chain innovation. By leveraging digital technology, this startup has created a platform that connects rural farmers directly with urban traders, effectively eliminating middlemen and streamlining the entire process from farm to market.
Enhancing Smallholder Farmer Market Access
One of the most significant challenges faced by smallholder farmers in Kenya has been limited access to markets. Traditional supply chains often involve multiple intermediaries, each taking a cut of the profits and leaving farmers with minimal returns for their hard work. The introduction of digital platforms is changing this narrative dramatically.
- Direct connection to urban markets
- Real-time price information
- Reduced dependency on intermediaries
- Increased bargaining power for farmers
These digital platforms are not just marketplaces; they are comprehensive ecosystems that provide farmers with valuable insights, from market trends to best practices in crop management. By leveraging data and analytics, these platforms empower farmers to make informed decisions about what to grow, when to harvest, and how to price their produce.
The Impact on Farmer Incomes
The results of this digital revolution are tangible and significant. Reports indicate that farmers using these platforms have seen their incomes increase by over 15%. This boost in income is not just a statistic; it represents real change in the lives of smallholder farmers across Kenya.
Consider the case of a tomato farmer in rural Kenya. Previously, this farmer might have been at the mercy of local traders, often forced to accept low prices due to lack of alternatives. Now, with access to a digital platform, the same farmer can:
- Compare prices across different markets
- Negotiate directly with urban buyers
- Plan harvests based on market demand
- Reduce losses through better market timing
This newfound empowerment is transforming the economic landscape of rural Kenya, one farm at a time.
Reducing Food Waste Through Innovation
“Innovative cold storage integration allows Kenyan farmers to extend harvest-to-sale periods, stabilizing prices and demand.”
Another critical aspect of this agricultural revolution is the focus on reducing food waste in agriculture. Post-harvest losses have long been a significant issue in Kenya, with some estimates suggesting that up to 30% of produce is lost before it reaches the market. The integration of cold storage solutions is addressing this challenge head-on.
The Role of Cold Storage
Cold storage facilities are game-changers in the fight against food waste. By providing cold storage for perishable goods, these innovations allow farmers to:
- Extend the shelf life of their produce
- Wait for better market prices
- Reduce the urgency to sell immediately after harvest
- Maintain the quality of their goods for longer periods
This flexibility is particularly crucial for farmers dealing with highly perishable goods like fruits and vegetables. The ability to store produce safely for extended periods means farmers are no longer forced to sell at rock-bottom prices during peak harvest times.
Optimizing Agricultural Logistics
The success of these digital platforms and cold storage solutions hinges on efficient agricultural logistics optimization. The startup at the center of this revolution is not just connecting farmers to markets; it’s reimagining the entire supply chain.
Key aspects of this logistics optimization include:
- Efficient transport routes
- Real-time tracking of goods
- Coordinated delivery schedules
- Quality control measures throughout the supply chain
By streamlining these processes, the platform ensures that produce reaches urban markets quickly and in optimal condition. This efficiency not only reduces waste but also ensures that farmers receive better prices for their goods.
Fostering Urban-Rural Agricultural Linkages
One of the most profound impacts of this digital revolution is the strengthening of urban-rural agricultural linkages. For too long, there has been a disconnect between urban consumers and rural producers. Digital platforms are bridging this gap, creating a more integrated and efficient food system.
Benefits of stronger urban-rural linkages include:
- Increased awareness of rural farming challenges among urban consumers
- Better understanding of urban market demands by farmers
- More direct feedback loops between producers and consumers
- Enhanced food traceability and transparency
These connections are not just economic; they’re reshaping the social fabric of Kenya, creating a more cohesive and interconnected society.
Sustainable Agriculture in Kenya
The integration of digital platforms and cold storage solutions is not just about economic gains; it’s a significant step towards sustainable agriculture in Kenya. By reducing waste and optimizing resource use, these innovations are helping to create a more environmentally friendly agricultural sector.
Key sustainability aspects include:
- Reduced carbon footprint from food waste
- More efficient use of water and land resources
- Decreased reliance on chemical preservatives
- Promotion of local food systems
These sustainability gains are crucial in the face of climate change and growing environmental concerns. They demonstrate that economic progress and environmental stewardship can go hand in hand.
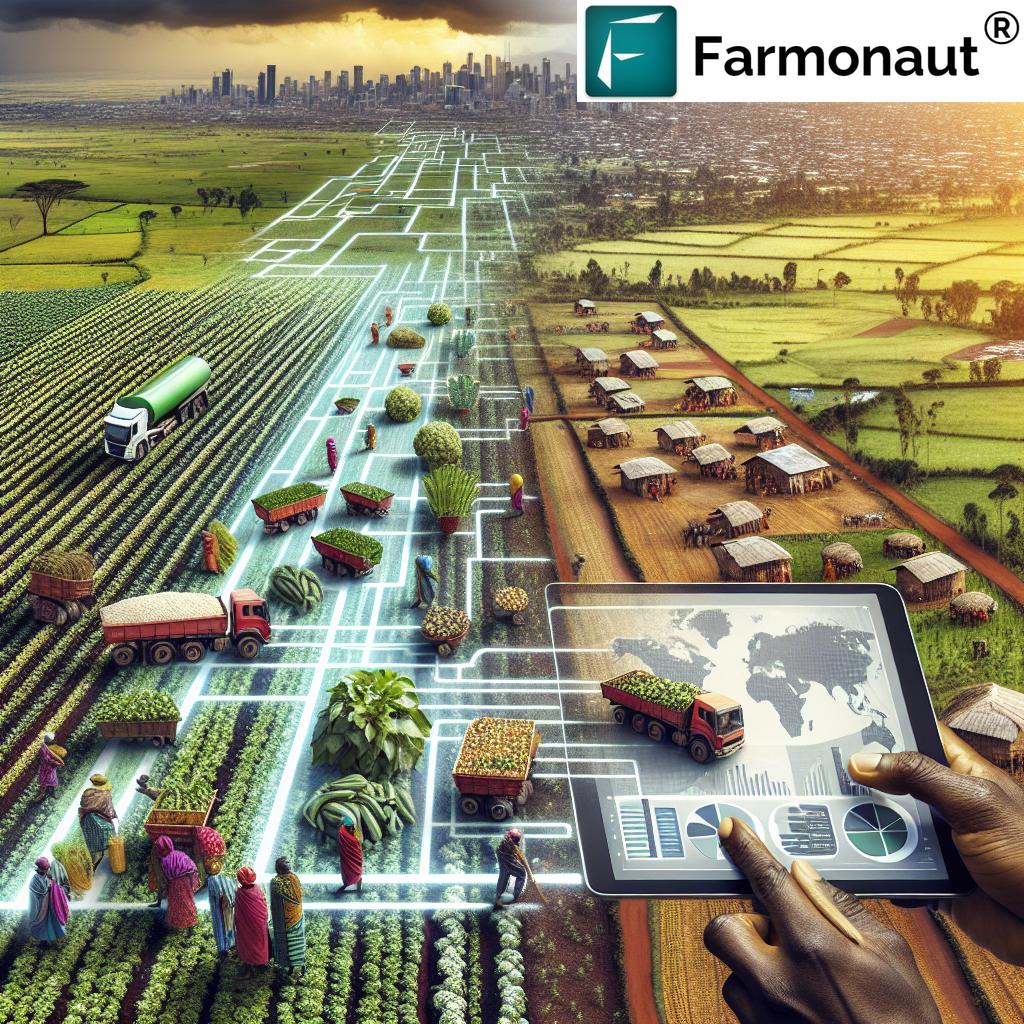

The Role of Technology in Agricultural Transformation
At the core of this agricultural revolution is technology. Digital platforms for farmers are not just convenience tools; they are powerful engines of change. These platforms leverage various technologies to create comprehensive solutions:
- Mobile applications for easy access
- Cloud computing for data storage and analysis
- Artificial Intelligence for market predictions and crop management advice
- Blockchain for ensuring transparency and traceability
The integration of these technologies creates a robust ecosystem that supports farmers at every stage of their agricultural journey.
Empowering Smallholder Farmers
The true measure of success for these innovations is their impact on smallholder farmers. These are the individuals who form the backbone of Kenyan agriculture, yet have historically been the most vulnerable to market fluctuations and climate challenges.
Digital platforms and cold storage solutions are empowering smallholder farmers in several ways:
- Providing access to broader markets
- Offering financial services and credit opportunities
- Delivering educational resources and best practices
- Enabling better planning and risk management
This empowerment is not just economic; it’s about giving farmers the tools and knowledge to take control of their futures.
The Future of Kenyan Agriculture
As we look to the future, the potential for further growth and innovation in Kenyan agriculture is immense. The success of digital platforms and cold storage solutions has laid the groundwork for even more transformative changes.
Potential future developments include:
- Integration of IoT devices for precision agriculture
- Expansion of cold chain infrastructure to more remote areas
- Development of specialized financial products for smallholder farmers
- Increased use of renewable energy in agricultural operations
These advancements will continue to drive the sector towards greater efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the progress in Kenyan agriculture is remarkable, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges that remain. These include:
- Limited digital literacy in some rural areas
- Infrastructure gaps, particularly in remote regions
- The need for ongoing farmer education and support
- Ensuring equitable access to technology across all farmer demographics
However, these challenges also present opportunities for further innovation and development. They drive the continuous improvement of platforms and solutions, ensuring that the benefits of digital agriculture reach all corners of Kenya.
The Role of Farmonaut in Agricultural Innovation
In the context of this agricultural revolution, companies like Farmonaut are playing a crucial role. While not directly involved in the marketplace or cold storage aspects, Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions complement the digital transformation of Kenyan agriculture.
Farmonaut offers:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- AI-based advisory systems
- Resource management tools
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions
These technologies align perfectly with the goals of improving agricultural productivity, reducing waste, and empowering smallholder farmers. By providing advanced satellite imagery and data analysis, Farmonaut enables farmers to make more informed decisions about their crops and resources.
For more information on Farmonaut’s solutions, visit their web app or check out their mobile apps:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s technology into their own solutions, the company offers a robust API. Detailed documentation is available in their API Developer Docs.
Impact of Digital Platforms on Kenyan Agriculture
| Metric | Before Digital Platforms | After Digital Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Farmer Income (% increase) | Baseline | 15%+ |
| Post-Harvest Losses (% reduction) | 30% | 15% |
| Time between Harvest and Sale (days) | 1-2 | 5-7 |
| Direct Farmer-Retailer Communication | Low | High |
| Carbon Footprint from Food Waste (estimated tons CO2e) | High | Medium |
| Market Access for Smallholder Farmers (% increase) | Baseline | 50%+ |
| Price Stability | Low | Medium |
Conclusion
The digital revolution in Kenyan agriculture, spearheaded by innovative startups and complemented by companies like Farmonaut, is reshaping the future of food production and distribution in East Africa. By addressing key challenges such as market access, post-harvest losses, and supply chain inefficiencies, these digital platforms and cold storage solutions are not just improving livelihoods; they’re building a more resilient and sustainable agricultural sector.
As we look to the future, the potential for further growth and innovation is immense. With continued investment in technology, infrastructure, and farmer education, Kenya is poised to become a model for agricultural transformation across Africa and beyond. The journey towards a fully digitized and efficient agricultural sector is ongoing, but the foundations laid by these innovations promise a brighter, more prosperous future for Kenya’s smallholder farmers and the entire agricultural ecosystem.
FAQs
- How do digital platforms benefit smallholder farmers in Kenya?
Digital platforms provide direct market access, real-time price information, and reduced dependency on intermediaries, leading to increased income and better decision-making for farmers. - What role does cold storage play in reducing food waste?
Cold storage extends the shelf life of produce, allowing farmers to store goods longer, wait for better prices, and reduce post-harvest losses. - How are urban-rural agricultural linkages being strengthened?
Digital platforms create direct connections between rural farmers and urban buyers, fostering better understanding of market demands and supply capabilities. - What technologies are driving this agricultural revolution?
Key technologies include mobile applications, cloud computing, AI for market predictions, and blockchain for transparency and traceability. - How does Farmonaut contribute to agricultural innovation?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based farm management solutions, including crop health monitoring and AI advisory systems, complementing the digital transformation of agriculture.