Effective Thrips Control: Organic and Chemical Treatments for Protecting Tomato Plants and Flowers
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges that farmers face when it comes to protecting their crops from pests. One of the most persistent and damaging pests in agriculture is the thrips. These tiny insects can cause significant damage to a wide range of plants, including tomatoes and flowers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective methods for thrips control, covering both organic and chemical treatments to help you protect your valuable crops.
Understanding Thrips: A Tiny Pest with a Big Impact
Thrips are minute insects, typically measuring less than 1/20 of an inch in length. Despite their small size, they can cause extensive damage to plants, particularly in warm and dry conditions. These pests are known for their rapid reproduction cycle, which can lead to quick population explosions if left unchecked.
The Life Cycle of Thrips
To effectively control thrips, it’s essential to understand their life cycle:
- Egg stage: Female thrips lay their eggs within plant tissues.
- Larval stage: Upon hatching, the larvae begin feeding on plant cells.
- Pupal stage: The thrips enter a non-feeding stage, often in soil or leaf litter.
- Adult stage: Mature thrips emerge and continue feeding and reproducing.
Each stage of the thrips life cycle presents unique challenges for control, making it crucial to implement a comprehensive management strategy.
The Impact of Thrips on Crops
Thrips can cause significant damage to a variety of crops, but they are particularly problematic for tomato plants and flowers. Let’s examine how these pests affect different types of plants:
Thrips Damage on Tomato Plants
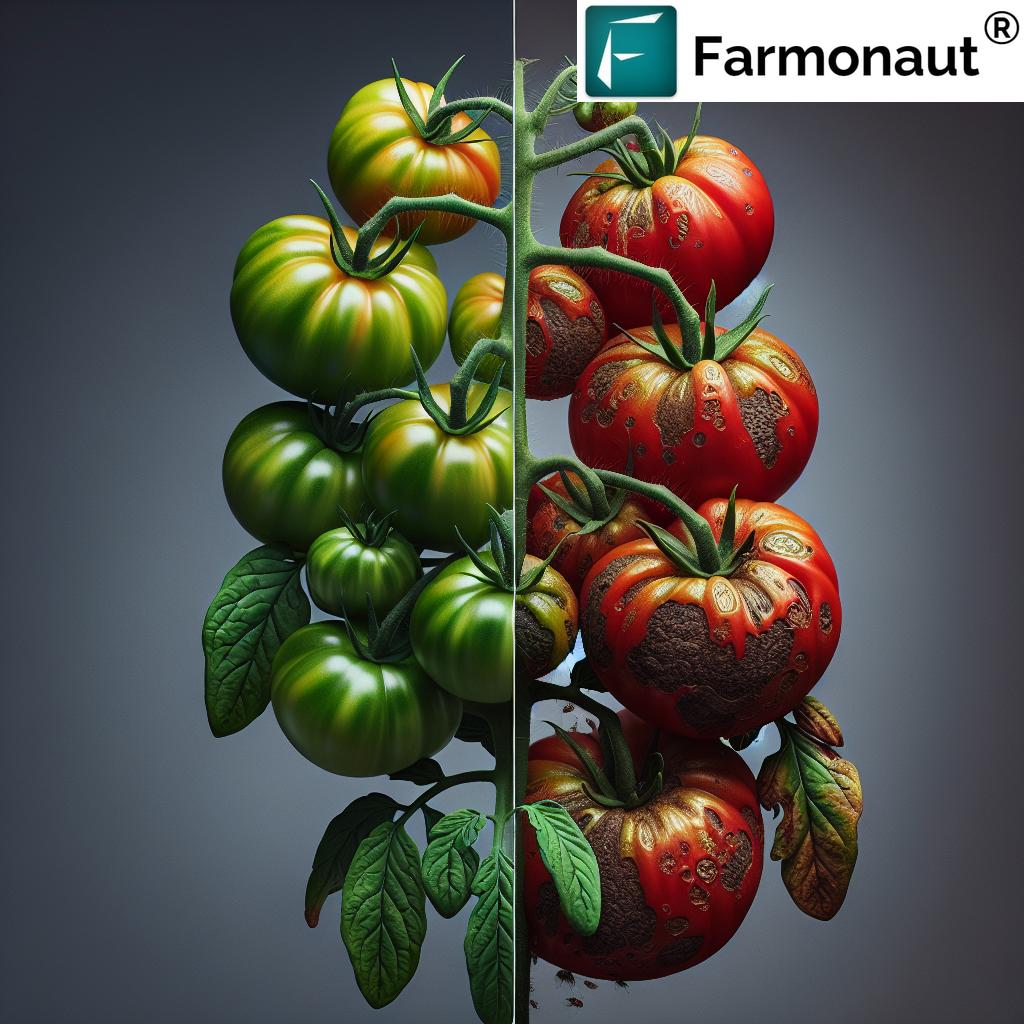
Tomato plants are highly susceptible to thrips infestations. The damage caused by these pests can manifest in several ways:
- Silvery or bronzed patches on leaves
- Stunted growth and distorted leaves
- Scarring on fruits
- Transmission of viruses, such as Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV)
The impact of thrips on tomato crops can be severe, leading to reduced yield and lower fruit quality. In cases of heavy infestation, entire crops may be lost.
Thrips Damage on Flowers
Flowers are another favorite target for thrips. The damage they cause to ornamental plants can be particularly devastating:
- Discoloration and distortion of petals
- Streaking or spotting on flower surfaces
- Premature wilting of flowers
- Reduced plant vigor and overall aesthetics
For commercial flower growers, thrips infestations can result in significant economic losses due to unsaleable products.
Early Detection: The Key to Effective Thrips Control
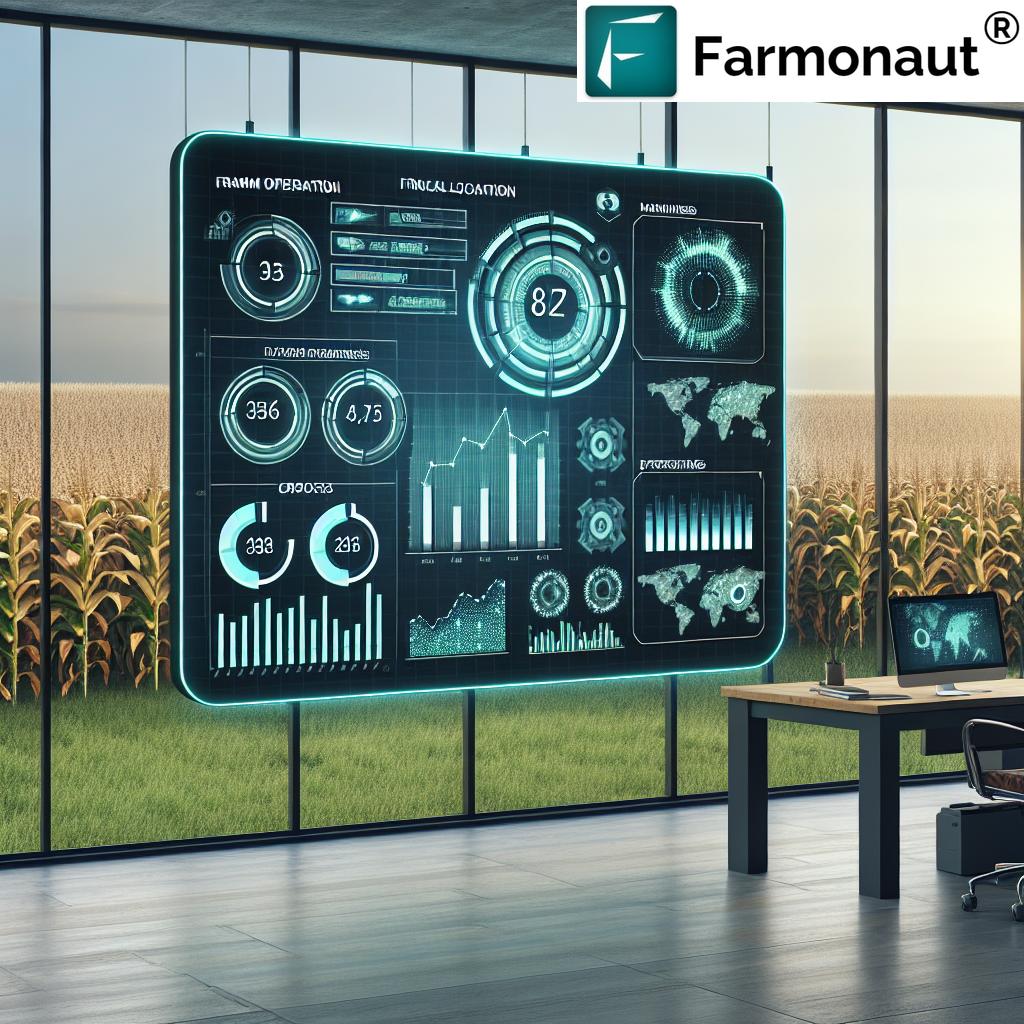
Identifying thrips infestations early is crucial for implementing timely and effective control measures. At Farmonaut, we’ve developed advanced technologies to aid in early pest detection, including thrips. Let’s compare traditional methods with our innovative satellite-based system:
| Detection Method | Detection Speed | Coverage Area | Labor Required | Early Warning Capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Scouting | Slow | Limited | High | Low |
| Sticky Traps | Moderate | Localized | Moderate | Moderate |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Fast | Extensive | Low | High |
Our satellite-based monitoring system provides farmers with a significant advantage in detecting thrips infestations early. By analyzing multispectral imagery, we can identify subtle changes in plant health that may indicate the presence of pests, including thrips. This early warning system allows for prompt intervention, potentially saving crops before significant damage occurs.
Organic Treatments for Thrips Control
For farmers looking to implement organic pest management strategies, there are several effective methods for controlling thrips without resorting to synthetic chemicals:
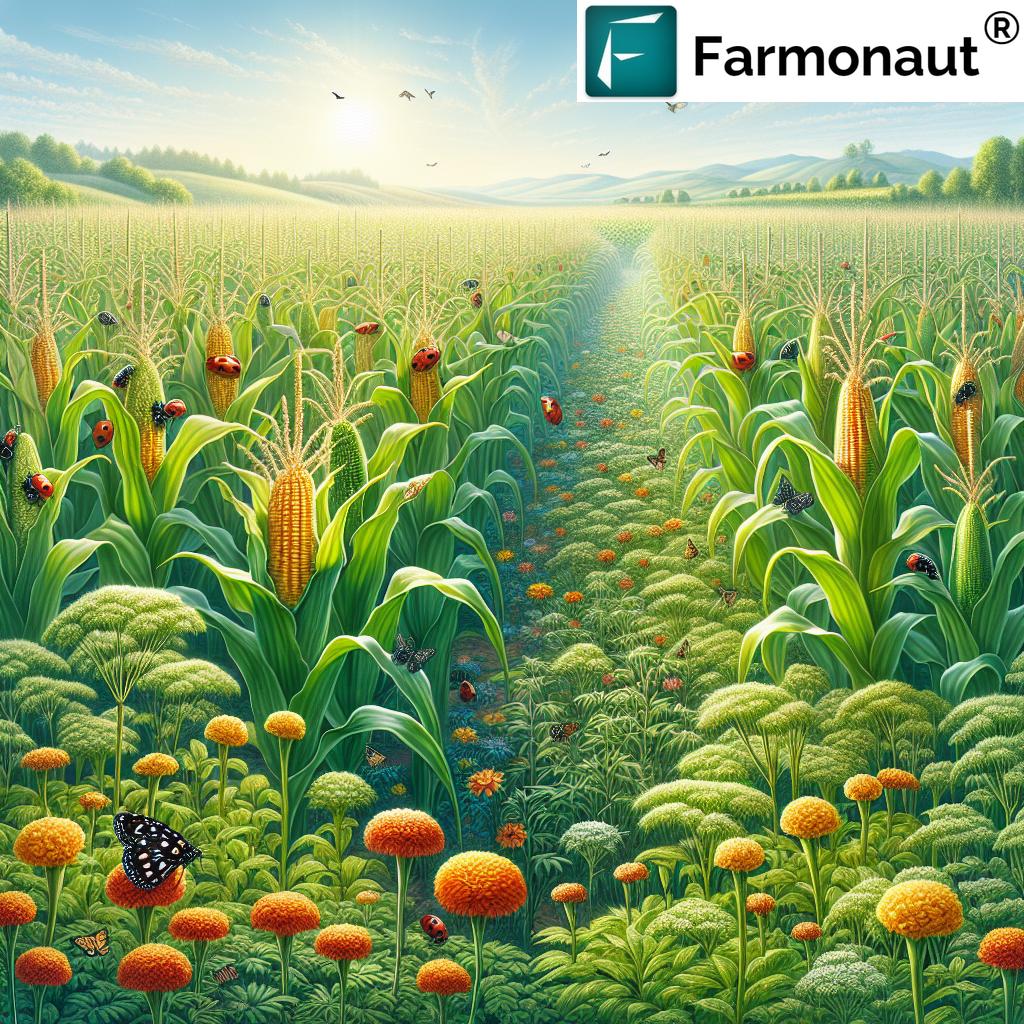
1. Biological Control Using Natural Enemies
Introducing natural predators of thrips can be an effective organic control method. Some beneficial insects that prey on thrips include:
- Predatory mites (e.g., Amblyseius swirskii)
- Minute pirate bugs (Orius spp.)
- Lacewings (Chrysoperla spp.)
These natural enemies can help keep thrips populations in check, reducing the need for other interventions.
2. Cultural Control Methods
Implementing good cultural practices can significantly reduce the risk of thrips infestations:
- Crop rotation to disrupt thrips life cycles
- Removal of weeds and plant debris that may harbor thrips
- Use of reflective mulches to deter thrips from landing on plants
- Proper irrigation to maintain plant health and resilience
3. Physical Barriers
Creating physical barriers can prevent thrips from reaching your crops:
- Install fine mesh screens on greenhouse vents
- Use row covers to protect susceptible plants
- Implement sticky traps to capture adult thrips
4. Organic Insecticides
When other methods are insufficient, organic insecticides can be used as a last resort:
- Neem oil
- Spinosad
- Pyrethrin-based products
- Insecticidal soaps
These organic treatments can be effective when used correctly and in conjunction with other control methods.
Chemical Treatments for Thrips Control
While organic methods are preferable, there are situations where chemical treatments may be necessary for effective thrips control, especially in cases of severe infestations:
1. Systemic Insecticides
Systemic insecticides are absorbed by the plant and distributed throughout its tissues, providing long-lasting protection against thrips:
- Imidacloprid
- Thiamethoxam
- Acephate
These products can be effective but should be used judiciously to prevent the development of resistance.
2. Contact Insecticides
Contact insecticides kill thrips upon direct exposure:
- Pyrethroids
- Organophosphates
- Carbamates
These insecticides require thorough coverage of the plant for maximum effectiveness.
3. Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs)
IGRs disrupt the thrips life cycle by preventing them from reaching maturity:
- Diflubenzuron
- Azadirachtin
These products are often less harmful to beneficial insects and can be integrated into IPM programs.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Thrips Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to thrips control. This strategy combines various methods to achieve effective pest management while minimizing environmental impact and reducing the risk of pesticide resistance.
Key Components of an IPM Strategy for Thrips:
- Monitoring: Regular scouting and use of our satellite-based detection system to identify thrips infestations early.
- Prevention: Implementing cultural and physical control methods to reduce the likelihood of infestations.
- Biological Control: Introducing and encouraging natural enemies of thrips.
- Chemical Control: Using targeted applications of insecticides only when necessary, based on established economic thresholds.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of pest populations, treatments, and their effectiveness to inform future management decisions.
By adopting an IPM approach, farmers can achieve more sustainable and effective thrips control over the long term.
The Role of Technology in Thrips Management

At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating advanced technology into pest management strategies. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system plays a crucial role in early detection and management of thrips infestations:
1. Early Detection
Our satellite imagery can detect subtle changes in plant health that may indicate the presence of thrips before visible symptoms appear. This early warning system allows farmers to take proactive measures to prevent widespread infestations.
2. Precision Application
By identifying specific areas of infestation, our technology enables targeted application of treatments, reducing overall pesticide use and minimizing environmental impact.
3. Monitoring Treatment Efficacy
Post-treatment satellite imagery helps assess the effectiveness of control measures, allowing for timely adjustments to management strategies.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Our AI-powered advisory system, Jeevn AI, analyzes satellite data along with other environmental factors to provide personalized recommendations for thrips management.
To learn more about how our technology can enhance your thrips management strategy, visit Farmonaut’s App or explore our API services.
Case Studies: Successful Thrips Management with Farmonaut
While we don’t provide specific case studies, our technology has been successfully implemented by numerous farmers worldwide to manage thrips and other pest infestations effectively. Our satellite-based monitoring system has helped growers:
- Detect thrips infestations up to two weeks earlier than traditional scouting methods
- Reduce pesticide use by up to 30% through targeted applications
- Improve crop yields by preventing widespread thrips damage
- Save time and labor costs associated with manual pest scouting
The Future of Thrips Control
As we look to the future, the management of thrips and other agricultural pests will continue to evolve. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments:
Emerging Technologies
- Advanced AI algorithms for even more accurate pest detection
- Integration of drone technology for closer, on-demand crop inspection
- Development of new, environmentally friendly biopesticides
- Genetic engineering of crop varieties with enhanced thrips resistance
Sustainable Practices
We’re also focusing on promoting sustainable agricultural practices that naturally suppress thrips populations:
- Enhancing biodiversity in agricultural landscapes
- Developing push-pull strategies using companion planting
- Improving soil health to boost plant resilience against pests
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Thrips Control
Effective thrips management requires a multifaceted approach that combines traditional methods with cutting-edge technology. At Farmonaut, we’re dedicated to providing farmers with the tools and knowledge they need to protect their crops from these persistent pests.
By integrating our satellite-based monitoring system with a comprehensive IPM strategy, farmers can achieve superior thrips control while minimizing environmental impact and reducing costs. Whether you’re growing tomatoes, managing ornamental flowers, or cultivating other susceptible crops, our technology can help you stay ahead of thrips infestations and ensure healthy, productive plants.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can transform your approach to pest management, download our app from the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store. For developers interested in integrating our technology into their own solutions, check out our API documentation.
FAQs: Thrips Control and Management
-
Q: How can I tell if my plants have a thrips infestation?
A: Look for silvery or bronzed patches on leaves, distorted growth, and tiny, slender insects. Our satellite monitoring can also detect early signs of infestation before visible symptoms appear.
-
Q: Are organic methods effective against severe thrips infestations?
A: Organic methods can be effective, especially when used preventatively or for minor infestations. For severe cases, a combination of organic and conventional methods may be necessary.
-
Q: How often should I monitor my crops for thrips?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. With traditional methods, weekly inspections are recommended. Our satellite monitoring provides continuous oversight, alerting you to potential issues in real-time.
-
Q: Can thrips develop resistance to insecticides?
A: Yes, thrips can develop resistance to frequently used insecticides. This is why we recommend an IPM approach that includes rotating different control methods.
-
Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology improve thrips management?
A: Our satellite-based system provides early detection, enables precise treatment application, and offers data-driven insights for more effective and sustainable pest management.
Ready to revolutionize your approach to thrips control? Subscribe to Farmonaut today and take the first step towards more effective, sustainable pest management: