Rising Trends in Carbon Market, Carbon Management & Footprinting: Farmonaut’s Sustainable Solution
In an era where environmental responsibility is paramount, the significance of carbon management and footprinting cannot be overstated. As businesses worldwide navigate the path towards sustainability, measuring and reducing carbon emissions have become pivotal objectives. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this green revolution, offering innovative solutions that empower organizations to transform sustainability into a strategic asset. Today, we’re excited to share insights from our interview with Akash Omar, Co-founder of Farmonaut®. We’ll explore cutting-edge trends reshaping how companies address their carbon impact, from the dynamic carbon market to groundbreaking technological solutions. Let’s delve into the world of carbon management and discover how Farmonaut is revolutionizing agricultural practices through our advanced satellite-based farm management solutions.The Evolving Landscape of Carbon Management
As we step into a new era of environmental consciousness, the carbon management landscape is rapidly evolving. Here are some key trends we’ve observed:- Increased corporate commitment to carbon neutrality
- Growing importance of carbon disclosure and reporting
- Rise of carbon pricing mechanisms
- Integration of carbon management into business strategies
- Emergence of innovative carbon capture technologies
The Role of Technology in Carbon Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology plays a crucial role in driving effective carbon management strategies. Our web app, which harnesses the power of remote sensing technology, is a prime example of how innovative solutions can revolutionize sustainability efforts.Farmonaut’s Web App: A Game-Changer in Soil Organic Carbon Mapping
Our web app creates detailed Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) images, providing agri-businesses with actionable insights. Here’s how it works:- Remote sensing technology captures high-resolution imagery of agricultural fields
- Advanced algorithms process the data to generate color-coded maps
- Maps highlight organic matter concentration in fields
- Regions rich in SOC display in vibrant green
- Areas with lower SOC concentrations appear in red
The Importance of Soil Organic Carbon
Understanding the importance of soil organic matter is crucial for effective agricultural management and carbon sequestration efforts. Soil organic carbon plays a vital role in:- Improving soil structure and water retention
- Enhancing nutrient availability for plants
- Supporting beneficial soil microorganisms
- Increasing soil fertility and productivity
- Mitigating climate change through carbon sequestration
The Carbon Market: Opportunities and Challenges
The carbon market has emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. It provides economic incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promotes the adoption of cleaner technologies. However, navigating this market can be complex. Here’s an overview of the current state of the carbon market:Types of Carbon Markets
- Compliance Markets: Regulated by governments, these markets require companies to comply with emission reduction targets.
- Voluntary Markets: These allow companies and individuals to voluntarily offset their emissions by investing in carbon reduction projects.
Key Players in the Carbon Market
- Emitters: Companies and organizations that produce greenhouse gas emissions
- Project Developers: Entities that create and implement emission reduction projects
- Verifiers: Third-party organizations that validate emission reduction claims
- Traders: Intermediaries who facilitate the buying and selling of carbon credits
- Regulators: Government bodies that oversee and enforce carbon market rules
Challenges in the Carbon Market
While the carbon market offers significant potential, it also faces several challenges:- Lack of standardization across different markets and jurisdictions
- Difficulty in accurately measuring and verifying emission reductions
- Price volatility and market instability
- Concerns about the additionality and permanence of carbon offset projects
- Potential for double-counting of emission reductions
Carbon Footprinting: A Crucial Step Towards Sustainability
Carbon footprinting is an essential tool for organizations looking to understand and reduce their environmental impact. It involves measuring the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product.The Carbon Footprinting Process
- Defining Boundaries: Determine the scope of activities to be included in the footprint calculation.
- Data Collection: Gather information on energy use, transportation, waste production, and other relevant activities.
- Emission Calculation: Convert activity data into greenhouse gas emissions using standardized emission factors.
- Analysis and Reporting: Interpret the results and identify areas for potential emission reductions.
- Setting Targets: Establish emission reduction goals based on the footprint analysis.
- Implementing Reduction Strategies: Develop and execute plans to reduce emissions.
- Monitoring and Verification: Continuously track progress and verify emission reductions.
Farmonaut’s Contribution to Carbon Footprinting
Our technology plays a crucial role in the carbon footprinting process for agricultural businesses. By providing accurate data on soil organic carbon levels and changes over time, we enable farmers and agribusinesses to:- Quantify the carbon sequestration potential of their agricultural practices
- Monitor the effectiveness of carbon reduction strategies
- Provide verifiable data for carbon offset projects
- Contribute to more accurate and comprehensive carbon footprint calculations
The Role of Soil in Carbon Sequestration
Understanding the role of soil organic matter in carbon sequestration is crucial for developing effective climate change mitigation strategies. Soil is one of the largest carbon sinks on the planet, with the potential to store vast amounts of carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere.How Soil Sequesters Carbon
The process of soil carbon sequestration involves:- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Biomass Production: Carbon is incorporated into plant biomass.
- Organic Matter Input: Plant residues and root exudates add organic matter to the soil.
- Decomposition: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter, storing some carbon in stable forms.
- Aggregation: Soil particles bind together, protecting organic carbon from rapid decomposition.
Factors Affecting Soil Carbon Sequestration
- Climate conditions (temperature and precipitation)
- Soil type and texture
- Land use and management practices
- Vegetation type and productivity
- Soil microbial activity
Innovative Approaches to Carbon Management in Agriculture
Agriculture plays a significant role in both carbon emissions and sequestration. Innovative approaches to carbon management in this sector are crucial for addressing climate change. Here are some cutting-edge strategies:1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses technology to optimize resource use and minimize waste. This approach can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with agricultural inputs. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system is a prime example of precision agriculture technology, providing farmers with detailed insights for more efficient and sustainable farming practices.2. Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage practices, such as no-till or reduced tillage, help maintain soil structure and prevent the release of stored carbon. Our soil organic carbon mapping technology can help farmers monitor the effectiveness of these practices over time.3. Cover Cropping
Planting cover crops between main crop cycles can increase carbon inputs to the soil and improve soil health. Farmonaut’s technology can track the impact of cover cropping on soil organic carbon levels, providing valuable data for farmers and researchers.4. Agroforestry
Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes can significantly increase carbon sequestration. Our satellite imagery can help monitor tree growth and estimate carbon storage in agroforestry systems.5. Biochar Application
Biochar, a form of charcoal produced from plant matter, can be added to soils to increase carbon storage. Our soil organic carbon mapping can help track the long-term effects of biochar application on soil carbon levels.The Future of Carbon Management: Trends and Predictions
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the landscape of carbon management:- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies will play an increasingly important role in carbon measurement, reporting, and verification.
- Blockchain for Carbon Tracking: Blockchain technology will enhance transparency and traceability in carbon markets.
- Nature-Based Solutions: There will be a growing focus on leveraging natural ecosystems for carbon sequestration.
- Carbon Removal Technologies: Direct air capture and other carbon removal technologies will become more prevalent.
- Integration of Carbon Management into ESG Frameworks: Carbon performance will become a key component of corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategies.
Farmonaut’s Comprehensive Suite of Agricultural Solutions
While our soil organic carbon mapping technology is a cornerstone of our offerings, Farmonaut provides a comprehensive suite of solutions for modern agriculture. Here’s an overview of our key technologies:1. Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.2. Jeevn AI Advisory System
This AI-driven personalized farm advisory tool delivers real-time insights, weather forecasts, and expert crop management strategies. Jeevn AI analyzes satellite data and other inputs to generate customized advice, improving farm productivity and efficiency.3. Blockchain-Based Product Traceability
Our blockchain integration enables traceability solutions for various industries, particularly agriculture. This ensures that every stage of the product’s journey, from farm to consumer, is transparent and secure, enhancing trust and reducing fraud in supply chains.4. Fleet and Resource Management
We provide tools for fleet management, enabling agribusinesses to manage their logistics more efficiently. This helps reduce operational costs by optimizing vehicle usage, ensuring safety, and improving the overall management of agricultural machinery.5. Carbon Footprinting
To help agribusinesses monitor and reduce their environmental impact, we offer carbon footprint tracking. This feature provides real-time data on emissions, allowing businesses to take steps towards sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations.How Farmonaut Compares to Other Farm Monitoring Systems
While there are various farm monitoring systems available, Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach offers several advantages over drone and IoT-based systems. Here’s a comparison:| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Systems | IoT-based Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (thousands of hectares) | Limited (typically less than 100 hectares per flight) | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (every few days, depending on satellite revisit time) | As needed, but requires manual flights | Continuous, but limited to sensor locations |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (drone purchase, training) | High (sensors, network infrastructure) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (automated data collection and processing) | High (requires skilled operators) | Medium (requires maintenance of sensor network) |
| Weather Dependency | Low (can penetrate clouds with radar satellites) | High (cannot fly in poor weather) | Low (but sensors can be damaged in extreme conditions) |
| Data Consistency | High (standardized data collection) | Variable (depends on flight conditions) | High (but limited to sensor locations) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by operational capacity | Requires additional hardware for scaling |
Getting Started with Farmonaut
Ready to revolutionize your agricultural practices and contribute to a more sustainable future? Here’s how you can get started with Farmonaut:- Visit our website at https://farmonaut.com/app_redirect to access our web application.
- Download our mobile app:
- For Android: Google Play Store
- For iOS: Apple App Store
- Explore our API documentation at https://farmonaut.com/farmonaut-satellite-weather-api-developer-docs/ for integration with your existing systems.
- For developers interested in leveraging our satellite and weather data, check out our API at https://sat.farmonaut.com/api.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
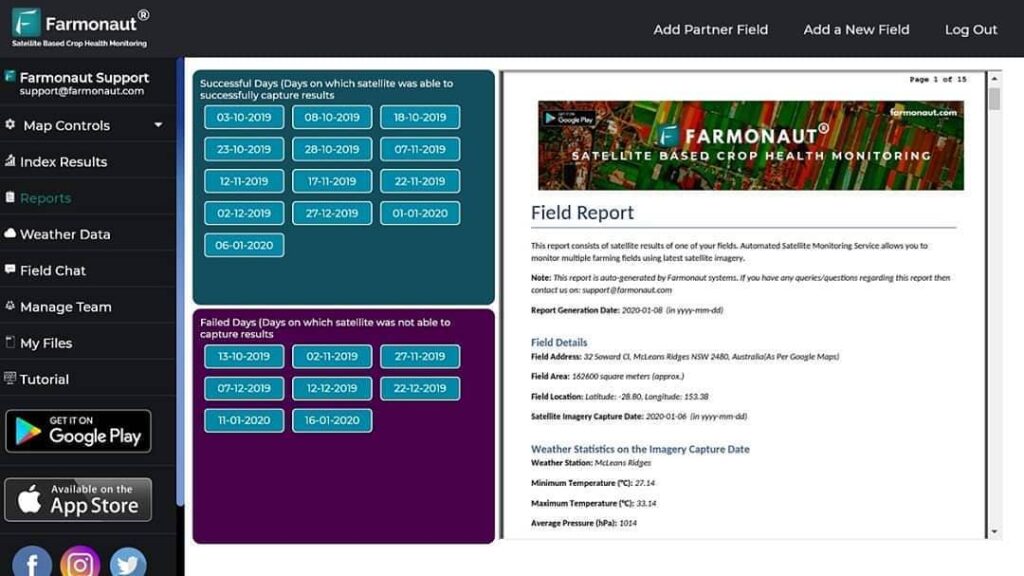
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is soil organic carbon (SOC)?
A1: Soil organic carbon refers to the carbon component of organic matter in soil. It plays a crucial role in soil health, fertility, and carbon sequestration.Q2: How does Farmonaut’s technology measure soil organic carbon?
A2: Farmonaut uses remote sensing technology and advanced algorithms to analyze satellite imagery, creating detailed maps of soil organic carbon concentration in agricultural fields.Q3: Why is carbon management important in agriculture?
A3: Carbon management in agriculture is crucial for mitigating climate change, improving soil health, and enhancing crop productivity. It also opens up opportunities for farmers to participate in carbon markets.Q4: How often is Farmonaut’s satellite data updated?
A4: The frequency of updates depends on satellite revisit times and can range from daily to weekly, depending on the specific location and service package.Q5: Can Farmonaut’s technology be used for carbon credit verification?
A5: Yes, Farmonaut’s detailed soil organic carbon mapping can provide valuable data for verifying carbon sequestration in agricultural soils, supporting carbon credit projects.Q6: How does Farmonaut compare to on-ground soil testing?
A6: While on-ground testing provides precise point measurements, Farmonaut offers comprehensive, large-scale mapping of soil organic carbon. Our technology complements traditional soil testing methods, providing a broader perspective and enabling more efficient targeted sampling.Q7: Is Farmonaut’s technology suitable for small-scale farmers?
A7: Absolutely! Farmonaut is designed to be accessible and affordable for farmers of all scales, from small holdings to large agricultural operations.Q8: How can businesses integrate Farmonaut’s data into their existing systems?
A8: Farmonaut provides APIs that allow businesses to integrate our satellite and weather data into their existing systems. Detailed documentation is available on our website.Q9: What other agricultural insights does Farmonaut provide besides soil organic carbon?
A9: Farmonaut offers a range of insights including crop health monitoring, soil moisture levels, weather forecasts, and personalized farm advisory through our Jeevn AI system.Q10: How does Farmonaut contribute to sustainable agriculture?
A10: By providing detailed insights into soil health and crop conditions, Farmonaut enables farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and implement sustainable farming practices that promote carbon sequestration and environmental conservation.Conclusion
As we navigate the challenges of climate change and environmental sustainability, the importance of effective carbon management and footprinting cannot be overstated. At Farmonaut, we’re proud to be at the forefront of this critical effort, providing innovative solutions that empower farmers, agribusinesses, and organizations to make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future. Our advanced satellite-based technology, combined with AI and blockchain capabilities, offers a comprehensive suite of tools for modern agriculture. From detailed soil organic carbon mapping to crop health monitoring and personalized advisory services, we’re committed to making precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide. As we look to the future, we remain dedicated to continuous innovation, staying ahead of emerging trends in carbon management and agricultural technology. By harnessing the power of data and technology, we believe we can play a significant role in addressing global challenges such as food security, climate change mitigation, and sustainable resource management. We invite you to join us on this journey towards a more sustainable and productive agricultural future. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer, a large agribusiness, or an organization interested in carbon management, Farmonaut has the tools and expertise to support your goals. Together, we can cultivate change, one field at a time. For more information about our products and services, or to start your journey with Farmonaut, visit our website or download our mobile app today. Let’s work together to revolutionize agriculture and build a more sustainable world.
Rising Trends in Carbon Market, Carbon Management & Footprinting: Farmonaut’s Sustainable Solution
In an era where environmental responsibility is paramount, the significance of carbon management and footprinting cannot be overstated. As businesses worldwide navigate the path towards sustainability, measuring and reducing carbon emissions have become pivotal objectives. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this green revolution, offering innovative solutions that empower organizations to transform sustainability into a strategic asset.
Today, we’re excited to share insights from our interview with Akash Omar, Co-founder of Farmonaut®. We’ll explore cutting-edge trends reshaping how companies address their carbon impact, from the dynamic carbon market to groundbreaking technological solutions. Let’s delve into the world of carbon management and discover how Farmonaut is revolutionizing agricultural practices through our advanced satellite-based farm management solutions.
The Evolving Landscape of Carbon Management
As we step into a new era of environmental consciousness, the carbon management landscape is rapidly evolving. Here are some key trends we’ve observed:
- Increased corporate commitment to carbon neutrality
- Growing importance of carbon disclosure and reporting
- Rise of carbon pricing mechanisms
- Integration of carbon management into business strategies
- Emergence of innovative carbon capture technologies
These trends underscore the growing recognition that effective carbon management is not just an environmental imperative but also a business necessity. Companies that proactively address their carbon footprint are better positioned to mitigate risks, capitalize on opportunities, and build long-term resilience.
The Role of Technology in Carbon Management
At Farmonaut, we believe that technology plays a crucial role in driving effective carbon management strategies. Our web app, which harnesses the power of remote sensing technology, is a prime example of how innovative solutions can revolutionize sustainability efforts.
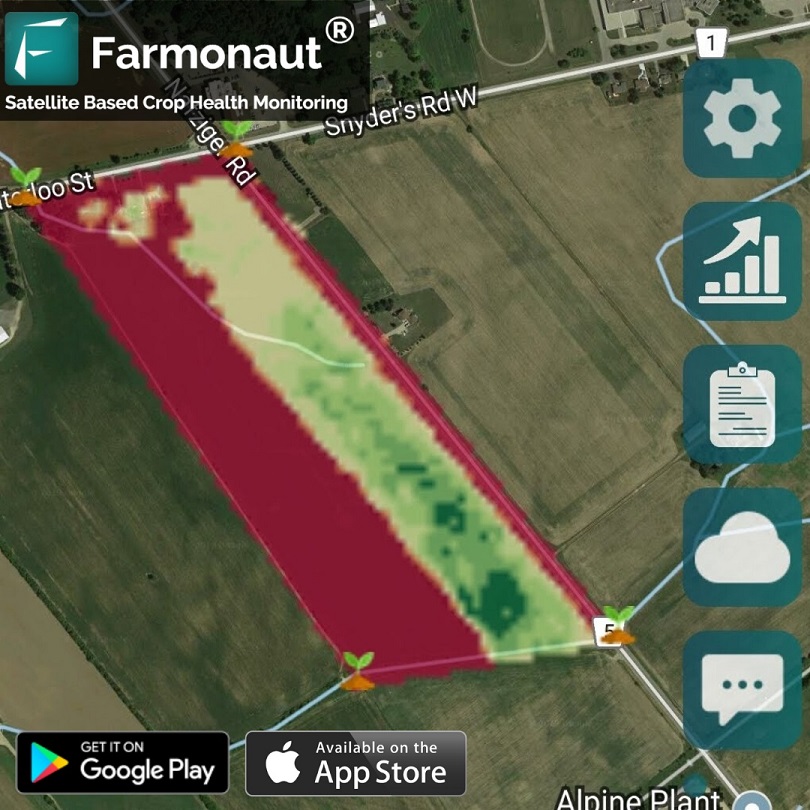
Farmonaut’s Web App: A Game-Changer in Soil Organic Carbon Mapping
Our web app creates detailed Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) images, providing agri-businesses with actionable insights. Here’s how it works:
- Remote sensing technology captures high-resolution imagery of agricultural fields
- Advanced algorithms process the data to generate color-coded maps
- Maps highlight organic matter concentration in fields
- Regions rich in SOC display in vibrant green
- Areas with lower SOC concentrations appear in red
This visual representation allows farmers and agricultural professionals to quickly identify areas that may require intervention or special attention. But we don’t stop there. Our solution also tracks SOC changes over time, providing invaluable data for informed decision-making.
The Importance of Soil Organic Carbon
Understanding the importance of soil organic matter is crucial for effective agricultural management and carbon sequestration efforts. Soil organic carbon plays a vital role in:
- Improving soil structure and water retention
- Enhancing nutrient availability for plants
- Supporting beneficial soil microorganisms
- Increasing soil fertility and productivity
- Mitigating climate change through carbon sequestration
By providing detailed insights into SOC levels, our technology empowers farmers to make informed decisions that not only optimize crop yields but also contribute to global carbon sequestration efforts.
The Carbon Market: Opportunities and Challenges
The carbon market has emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. It provides economic incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promotes the adoption of cleaner technologies. However, navigating this market can be complex. Here’s an overview of the current state of the carbon market:
Types of Carbon Markets
- Compliance Markets: Regulated by governments, these markets require companies to comply with emission reduction targets.
- Voluntary Markets: These allow companies and individuals to voluntarily offset their emissions by investing in carbon reduction projects.
Key Players in the Carbon Market
- Emitters: Companies and organizations that produce greenhouse gas emissions
- Project Developers: Entities that create and implement emission reduction projects
- Verifiers: Third-party organizations that validate emission reduction claims
- Traders: Intermediaries who facilitate the buying and selling of carbon credits
- Regulators: Government bodies that oversee and enforce carbon market rules
Challenges in the Carbon Market
While the carbon market offers significant potential, it also faces several challenges:
- Lack of standardization across different markets and jurisdictions
- Difficulty in accurately measuring and verifying emission reductions
- Price volatility and market instability
- Concerns about the additionality and permanence of carbon offset projects
- Potential for double-counting of emission reductions
At Farmonaut, we’re working to address some of these challenges through our innovative technology. Our satellite-based monitoring system provides accurate, verifiable data on carbon sequestration in agricultural soils, contributing to the integrity and effectiveness of carbon offset projects in the agricultural sector.
Carbon Footprinting: A Crucial Step Towards Sustainability
Carbon footprinting is an essential tool for organizations looking to understand and reduce their environmental impact. It involves measuring the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product.
The Carbon Footprinting Process
- Defining Boundaries: Determine the scope of activities to be included in the footprint calculation.
- Data Collection: Gather information on energy use, transportation, waste production, and other relevant activities.
- Emission Calculation: Convert activity data into greenhouse gas emissions using standardized emission factors.
- Analysis and Reporting: Interpret the results and identify areas for potential emission reductions.
- Setting Targets: Establish emission reduction goals based on the footprint analysis.
- Implementing Reduction Strategies: Develop and execute plans to reduce emissions.
- Monitoring and Verification: Continuously track progress and verify emission reductions.
Farmonaut’s Contribution to Carbon Footprinting
Our technology plays a crucial role in the carbon footprinting process for agricultural businesses. By providing accurate data on soil organic carbon levels and changes over time, we enable farmers and agribusinesses to:
- Quantify the carbon sequestration potential of their agricultural practices
- Monitor the effectiveness of carbon reduction strategies
- Provide verifiable data for carbon offset projects
- Contribute to more accurate and comprehensive carbon footprint calculations
This data-driven approach not only supports more effective carbon management but also opens up new opportunities for farmers to participate in carbon markets and benefit from sustainable agricultural practices.
The Role of Soil in Carbon Sequestration
Understanding the role of soil organic matter in carbon sequestration is crucial for developing effective climate change mitigation strategies. Soil is one of the largest carbon sinks on the planet, with the potential to store vast amounts of carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere.
How Soil Sequesters Carbon
The process of soil carbon sequestration involves:
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Biomass Production: Carbon is incorporated into plant biomass.
- Organic Matter Input: Plant residues and root exudates add organic matter to the soil.
- Decomposition: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter, storing some carbon in stable forms.
- Aggregation: Soil particles bind together, protecting organic carbon from rapid decomposition.
Factors Affecting Soil Carbon Sequestration
- Climate conditions (temperature and precipitation)
- Soil type and texture
- Land use and management practices
- Vegetation type and productivity
- Soil microbial activity
At Farmonaut, our technology helps farmers and researchers understand these factors better by providing detailed, real-time data on soil organic carbon levels. This information is crucial for developing and implementing effective carbon sequestration strategies in agriculture.
Innovative Approaches to Carbon Management in Agriculture
Agriculture plays a significant role in both carbon emissions and sequestration. Innovative approaches to carbon management in this sector are crucial for addressing climate change. Here are some cutting-edge strategies:
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses technology to optimize resource use and minimize waste. This approach can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with agricultural inputs. Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system is a prime example of precision agriculture technology, providing farmers with detailed insights for more efficient and sustainable farming practices.
2. Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage practices, such as no-till or reduced tillage, help maintain soil structure and prevent the release of stored carbon. Our soil organic carbon mapping technology can help farmers monitor the effectiveness of these practices over time.
3. Cover Cropping
Planting cover crops between main crop cycles can increase carbon inputs to the soil and improve soil health. Farmonaut’s technology can track the impact of cover cropping on soil organic carbon levels, providing valuable data for farmers and researchers.
4. Agroforestry
Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes can significantly increase carbon sequestration. Our satellite imagery can help monitor tree growth and estimate carbon storage in agroforestry systems.
5. Biochar Application
Biochar, a form of charcoal produced from plant matter, can be added to soils to increase carbon storage. Our soil organic carbon mapping can help track the long-term effects of biochar application on soil carbon levels.
The Future of Carbon Management: Trends and Predictions
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the landscape of carbon management:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies will play an increasingly important role in carbon measurement, reporting, and verification.
- Blockchain for Carbon Tracking: Blockchain technology will enhance transparency and traceability in carbon markets.
- Nature-Based Solutions: There will be a growing focus on leveraging natural ecosystems for carbon sequestration.
- Carbon Removal Technologies: Direct air capture and other carbon removal technologies will become more prevalent.
- Integration of Carbon Management into ESG Frameworks: Carbon performance will become a key component of corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategies.
At Farmonaut, we’re continuously innovating to stay ahead of these trends. Our technology not only addresses current needs in carbon management but is also designed to adapt to future developments in this rapidly evolving field.
Farmonaut’s Comprehensive Suite of Agricultural Solutions
While our soil organic carbon mapping technology is a cornerstone of our offerings, Farmonaut provides a comprehensive suite of solutions for modern agriculture. Here’s an overview of our key technologies:
1. Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
2. Jeevn AI Advisory System
This AI-driven personalized farm advisory tool delivers real-time insights, weather forecasts, and expert crop management strategies. Jeevn AI analyzes satellite data and other inputs to generate customized advice, improving farm productivity and efficiency.
3. Blockchain-Based Product Traceability
Our blockchain integration enables traceability solutions for various industries, particularly agriculture. This ensures that every stage of the product’s journey, from farm to consumer, is transparent and secure, enhancing trust and reducing fraud in supply chains.
4. Fleet and Resource Management
We provide tools for fleet management, enabling agribusinesses to manage their logistics more efficiently. This helps reduce operational costs by optimizing vehicle usage, ensuring safety, and improving the overall management of agricultural machinery.
5. Carbon Footprinting
To help agribusinesses monitor and reduce their environmental impact, we offer carbon footprint tracking. This feature provides real-time data on emissions, allowing businesses to take steps towards sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations.
How Farmonaut Compares to Other Farm Monitoring Systems
While there are various farm monitoring systems available, Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach offers several advantages over drone and IoT-based systems. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Systems | IoT-based Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (thousands of hectares) | Limited (typically less than 100 hectares per flight) | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (every few days, depending on satellite revisit time) | As needed, but requires manual flights | Continuous, but limited to sensor locations |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (drone purchase, training) | High (sensors, network infrastructure) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (automated data collection and processing) | High (requires skilled operators) | Medium (requires maintenance of sensor network) |
| Weather Dependency | Low (can penetrate clouds with radar satellites) | High (cannot fly in poor weather) | Low (but sensors can be damaged in extreme conditions) |
| Data Consistency | High (standardized data collection) | Variable (depends on flight conditions) | High (but limited to sensor locations) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by operational capacity | Requires additional hardware for scaling |
Getting Started with Farmonaut
Ready to revolutionize your agricultural practices and contribute to a more sustainable future? Here’s how you can get started with Farmonaut:
- Visit our website at https://farmonaut.com/app_redirect to access our web application.
- Download our mobile app:
- For Android: Google Play Store
- For iOS: Apple App Store
- Explore our API documentation at https://farmonaut.com/farmonaut-satellite-weather-api-developer-docs/ for integration with your existing systems.
- For developers interested in leveraging our satellite and weather data, check out our API at https://sat.farmonaut.com/api.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is soil organic carbon (SOC)?
A1: Soil organic carbon refers to the carbon component of organic matter in soil. It plays a crucial role in soil health, fertility, and carbon sequestration.
Q2: How does Farmonaut’s technology measure soil organic carbon?
A2: Farmonaut uses remote sensing technology and advanced algorithms to analyze satellite imagery, creating detailed maps of soil organic carbon concentration in agricultural fields.
Q3: Why is carbon management important in agriculture?
A3: Carbon management in agriculture is crucial for mitigating climate change, improving soil health, and enhancing crop productivity. It also opens up opportunities for farmers to participate in carbon markets.
Q4: How often is Farmonaut’s satellite data updated?
A4: The frequency of updates depends on satellite revisit times and can range from daily to weekly, depending on the specific location and service package.
Q5: Can Farmonaut’s technology be used for carbon credit verification?
A5: Yes, Farmonaut’s detailed soil organic carbon mapping can provide valuable data for verifying carbon sequestration in agricultural soils, supporting carbon credit projects.
Q6: How does Farmonaut compare to on-ground soil testing?
A6: While on-ground testing provides precise point measurements, Farmonaut offers comprehensive, large-scale mapping of soil organic carbon. Our technology complements traditional soil testing methods, providing a broader perspective and enabling more efficient targeted sampling.
Q7: Is Farmonaut’s technology suitable for small-scale farmers?
A7: Absolutely! Farmonaut is designed to be accessible and affordable for farmers of all scales, from small holdings to large agricultural operations.
Q8: How can businesses integrate Farmonaut’s data into their existing systems?
A8: Farmonaut provides APIs that allow businesses to integrate our satellite and weather data into their existing systems. Detailed documentation is available on our website.
Q9: What other agricultural insights does Farmonaut provide besides soil organic carbon?
A9: Farmonaut offers a range of insights including crop health monitoring, soil moisture levels, weather forecasts, and personalized farm advisory through our Jeevn AI system.
Q10: How does Farmonaut contribute to sustainable agriculture?
A10: By providing detailed insights into soil health and crop conditions, Farmonaut enables farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and implement sustainable farming practices that promote carbon sequestration and environmental conservation.
Conclusion
As we navigate the challenges of climate change and environmental sustainability, the importance of effective carbon management and footprinting cannot be overstated. At Farmonaut, we’re proud to be at the forefront of this critical effort, providing innovative solutions that empower farmers, agribusinesses, and organizations to make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Our advanced satellite-based technology, combined with AI and blockchain capabilities, offers a comprehensive suite of tools for modern agriculture. From detailed soil organic carbon mapping to crop health monitoring and personalized advisory services, we’re committed to making precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide.
As we look to the future, we remain dedicated to continuous innovation, staying ahead of emerging trends in carbon management and agricultural technology. By harnessing the power of data and technology, we believe we can play a significant role in addressing global challenges such as food security, climate change mitigation, and sustainable resource management.
We invite you to join us on this journey towards a more sustainable and productive agricultural future. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer, a large agribusiness, or an organization interested in carbon management, Farmonaut has the tools and expertise to support your goals.
Together, we can cultivate change, one field at a time.
For more information about our products and services, or to start your journey with Farmonaut, visit our website or download our mobile app today. Let’s work together to revolutionize agriculture and build a more sustainable world