Unlocking Sustainable Agriculture: How Farmonaut’s Organic Certification Standards Drive Environmental Impact
“Organic certification standards can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 40% compared to conventional farming methods.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on organic farming and sustainable agriculture practices! At Farmonaut, we’re passionate about revolutionizing the agricultural landscape through innovative technology and data-driven insights. In this blog post, we’ll explore the world of organic certification standards and their profound impact on environmental sustainability. Join us as we delve into the benefits of organic farming, the latest industry trends, and how these practices contribute to a healthier planet and a more secure food future.
The Foundation of Organic Farming
Organic farming is more than just a method of food production; it’s a holistic approach to agriculture that prioritizes environmental stewardship, biodiversity, and soil health. At its core, organic farming seeks to work in harmony with nature rather than against it. This philosophy aligns perfectly with Farmonaut’s mission to make precision agriculture accessible and sustainable for farmers worldwide.
Let’s explore the key principles that form the foundation of organic farming:
- Soil Health: Organic farmers focus on building and maintaining healthy soil through practices like crop rotation, composting, and the use of natural fertilizers.
- Biodiversity: Encouraging a diverse ecosystem on the farm helps control pests naturally and promotes overall environmental health.
- Non-GMO Approach: Organic certification standards prohibit the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), ensuring that crops are grown from traditional or naturally bred seeds.
- Chemical-Free: Synthetic pesticides and fertilizers are replaced with natural alternatives, reducing harmful impacts on the environment and human health.
- Animal Welfare: In organic livestock production, animals are raised with a focus on their natural behaviors and well-being.
These principles form the bedrock of organic certification standards, which we’ll explore in more detail throughout this post. But first, let’s take a look at how Farmonaut’s technology supports these organic practices.
Farmonaut: Empowering Organic Farmers with Cutting-Edge Technology
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making precision agriculture accessible to all farmers, including those practicing organic methods. Our satellite-based farm management solutions provide valuable tools for organic farmers to optimize their operations while adhering to strict certification standards.
Here’s how our technology supports organic farming practices:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Our advanced satellite imagery helps organic farmers monitor crop health without the need for chemical inputs. By providing real-time data on vegetation health (NDVI) and soil moisture levels, we enable farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation and natural pest management strategies.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI-driven personalized farm advisory tool delivers tailored insights for organic crop management. By analyzing satellite data and other inputs, Jeevn AI generates customized advice that aligns with organic farming principles, improving productivity while maintaining environmental integrity.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Transparency is crucial in the organic industry. Our blockchain technology ensures that every stage of an organic product’s journey, from farm to consumer, is transparent and secure. This builds trust and reduces the risk of fraud in organic supply chains.
- Carbon Footprinting: Organic farms often have a lower carbon footprint than conventional operations. Our carbon footprint tracking feature allows organic farmers to monitor and report on their emissions, supporting their sustainability goals and compliance with environmental regulations.
By leveraging these technologies, organic farmers can enhance their practices, improve yields, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Now, let’s dive deeper into the world of organic certification standards and their environmental impact.
Organic Certification Standards: Ensuring Quality and Trust
Organic certification standards are the backbone of the organic industry, providing consumers with assurance that the products they purchase meet strict guidelines for production and processing. These standards cover every aspect of farming, from soil management to animal welfare, and are designed to promote environmental sustainability and product integrity.
Key aspects of organic certification standards include:
- Soil Management: Standards require practices that build soil health, such as crop rotation and the use of compost and natural fertilizers.
- Pest and Disease Control: Organic farmers must use natural methods to manage pests and diseases, avoiding synthetic pesticides and herbicides.
- Seed and Plant Stock: Only non-GMO seeds and planting materials are allowed in organic production.
- Livestock Management: Animals must be raised in conditions that allow for natural behaviors, with access to the outdoors and organic feed.
- Processing and Handling: Strict regulations govern how organic products are processed and handled to maintain their integrity.
- Record Keeping: Detailed records must be kept to demonstrate compliance with organic standards.
These standards are enforced through regular audits and inspections, ensuring that certified organic products maintain their quality and environmental benefits throughout the supply chain.
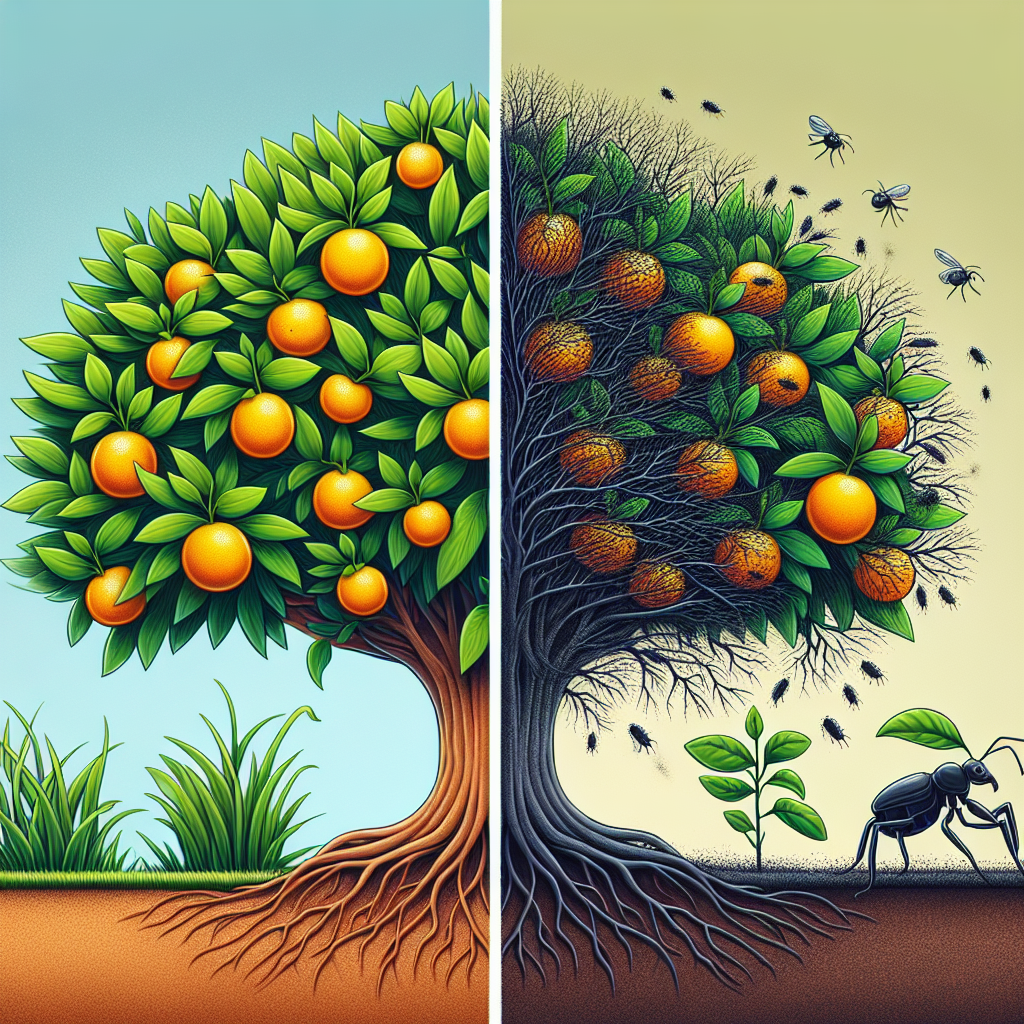
The Environmental Impact of Organic Farming
One of the most compelling reasons to support organic farming is its positive environmental impact. By eschewing synthetic chemicals and prioritizing natural ecosystem balance, organic farming practices contribute significantly to environmental conservation and climate change mitigation.
Let’s explore some of the key environmental benefits of organic farming:
- Soil Health: Organic farming practices, such as crop rotation and the use of natural fertilizers, help build healthy soil structures. This improves soil fertility, reduces erosion, and enhances the soil’s ability to sequester carbon.
- Biodiversity: By avoiding synthetic pesticides and herbicides, organic farms create habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. This increased biodiversity contributes to natural pest control and pollination.
- Water Conservation: Healthy soil structure in organic farms improves water retention, reducing the need for irrigation and helping to conserve water resources.
- Reduced Pollution: The absence of synthetic chemicals in organic farming means fewer pollutants in our waterways and ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Organic farming practices can help mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production and use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to support these environmental benefits through our technology. Our satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems help organic farmers optimize their practices, further enhancing the positive environmental impact of organic agriculture.
Non-GMO Food Production: A Cornerstone of Organic Farming
One of the defining characteristics of organic farming is the prohibition of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This commitment to non-GMO food production is rooted in the organic philosophy of working with natural systems and preserving genetic diversity.
Here’s why non-GMO production is crucial in organic farming:
- Preserving Biodiversity: By using traditional and naturally bred seeds, organic farmers help maintain a diverse gene pool, which is crucial for long-term food security and ecosystem resilience.
- Reducing Chemical Inputs: Many GMO crops are engineered to be resistant to certain herbicides, which can lead to increased chemical use. Organic farming’s non-GMO approach naturally aligns with reduced chemical inputs.
- Supporting Seed Sovereignty: Non-GMO practices allow farmers to save and replant seeds, promoting seed diversity and reducing dependence on patented seed varieties.
- Meeting Consumer Demand: Many consumers prefer non-GMO products, and organic certification provides assurance that products are GMO-free.
Farmonaut’s satellite technology and AI advisory system support non-GMO production by helping organic farmers optimize their natural pest management and crop rotation strategies, reducing the perceived need for GMO solutions.
Organic Livestock Management: Prioritizing Animal Welfare
Organic certification standards extend beyond crop production to include comprehensive guidelines for livestock management. These standards prioritize animal welfare, natural behaviors, and the use of organic feed, resulting in more ethical and environmentally friendly animal husbandry practices.
Key aspects of organic livestock management include:
- Access to Outdoors: Organic standards require that animals have access to the outdoors and pasture, allowing them to engage in natural behaviors.
- Organic Feed: Livestock must be fed 100% organic feed, which is produced without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers.
- No Routine Antibiotics: Preventive use of antibiotics is prohibited, promoting natural disease resistance and reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
- Humane Treatment: Organic standards emphasize humane handling and transportation practices, as well as appropriate living conditions for each species.
- Natural Breeding: Artificial hormones for growth or reproduction are not allowed in organic livestock production.
These practices not only improve animal welfare but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the farm ecosystem. Farmonaut’s technology can assist organic livestock farmers by providing insights into pasture health and helping optimize grazing rotations through satellite imagery analysis.
Organic Viticulture: Cultivating Sustainable Wines
The world of organic wine production, or organic viticulture, is a fascinating subset of organic farming that deserves special attention. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of their food and drink choices, organic wines are gaining popularity.
Organic viticulture involves:
- Natural Pest Management: Using beneficial insects and natural predators to control pests in vineyards.
- Soil Health: Emphasizing cover crops and natural fertilizers to maintain soil fertility and structure.
- Biodiversity: Encouraging diverse plant life in and around vineyards to create a balanced ecosystem.
- Minimal Intervention: Using traditional winemaking techniques with minimal additives in the cellar.
Farmonaut’s satellite technology can be particularly useful in organic viticulture, helping vintners monitor vine health, optimize irrigation, and detect early signs of disease without relying on chemical interventions.
Organic Export Regulations: Ensuring Global Standards
As the global demand for organic products continues to grow, understanding and navigating organic export regulations becomes increasingly important. These regulations ensure that organic products maintain their integrity across international borders and meet the standards of importing countries.
Key aspects of organic export regulations include:
- Certification Equivalency: Many countries have agreements recognizing each other’s organic standards, facilitating international trade.
- Documentation: Detailed records and certificates are required to prove organic status throughout the supply chain.
- Labeling Requirements: Specific labeling rules must be followed to market products as organic in different countries.
- Inspection and Verification: Products may be subject to additional inspections at borders to verify organic status.
Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability solutions can play a crucial role in meeting these export regulations by providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of a product’s organic journey from farm to international markets.
Climate Change and Agriculture: Organic Farming as a Mitigation Strategy
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, but organic farming practices offer promising strategies for both mitigation and adaptation. By focusing on soil health, biodiversity, and reduced chemical inputs, organic farming can play a crucial role in addressing climate change concerns in agriculture.
Here’s how organic farming contributes to climate change mitigation:
- Carbon Sequestration: Organic farming practices, such as cover cropping and reduced tillage, help sequester carbon in the soil, reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Reduced Emissions: By avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, organic farms produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production and use of these chemicals.
- Energy Efficiency: Organic farms often use less energy than conventional farms, particularly in terms of fertilizer and pesticide production.
- Resilience: The focus on soil health and biodiversity in organic systems can make farms more resilient to extreme weather events associated with climate change.
Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting feature allows organic farmers to track and report on their emissions, helping them quantify their contribution to climate change mitigation and identify areas for further improvement.
Organic Industry Trends: Innovation and Growth
“The global organic food market is projected to reach $380 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 14.5%.”
The organic industry is dynamic and constantly evolving, with new trends emerging as consumer preferences shift and technology advances. Some of the key trends we’re observing include:
- Regenerative Organic: Going beyond sustainable to actively improve soil health and ecosystem function.
- Urban Organic Farming: Bringing organic practices to cities through vertical farming and rooftop gardens.
- Organic Aquaculture: Expanding organic certification to fish and seafood production.
- Tech-Enabled Organic Farming: Integrating precision agriculture technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, into organic farming practices.
- Organic Plant-Based Products: Meeting the growing demand for organic, plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy.
These trends highlight the organic industry’s commitment to innovation and adaptation, ensuring that organic practices remain relevant and impactful in a changing world.
Comparative Analysis: Organic vs. Conventional Farming Practices
To better understand the impact of organic farming, let’s compare organic and conventional practices across key sustainability metrics:
| Farming Practice | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming | Environmental Impact | Long-term Sustainability Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pesticide Use | Natural pest control methods | Synthetic pesticides | Low | 9 |
| Soil Health Management | Crop rotation, compost, natural fertilizers | Synthetic fertilizers, monoculture | Low | 8 |
| Biodiversity Support | Encourages diverse ecosystems | Often reduces biodiversity | Low | 9 |
| Water Conservation | Improved soil structure retains water | Often requires more irrigation | Medium | 7 |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower emissions, carbon sequestration | Higher emissions from inputs | Low | 8 |
| Animal Welfare Standards | Prioritizes natural behaviors | Varies, often less stringent | Medium | 8 |
| GMO Policy | No GMOs allowed | GMOs often used | Medium | 7 |
| Crop Rotation Practices | Regular rotation to maintain soil health | Less emphasis on rotation | Low | 9 |
This comparison illustrates the significant environmental benefits of organic farming practices across various aspects of agricultural production.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Organic Farming
While organic farming is rooted in traditional practices, modern technology plays an increasingly important role in optimizing these methods for maximum sustainability and productivity. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this intersection between organic principles and cutting-edge technology.
Here’s how our technology supports and advances organic farming:
- Precision Resource Management: Our satellite-based monitoring helps organic farmers precisely manage water and natural inputs, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Early Disease Detection: Advanced imaging can detect early signs of crop stress or disease, allowing for timely intervention with organic methods.
- Optimized Crop Rotation: AI-driven insights can help farmers plan optimal crop rotations to maintain soil health and natural pest control.
- Traceability and Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures the integrity of organic supply chains, building consumer trust.
By embracing these technological advancements, organic farmers can enhance their practices, improve yields, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability more effectively than ever before.
Challenges and Solutions in Organic Farming
While organic farming offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges and developing innovative solutions is crucial for the continued growth and success of the organic industry.
Some key challenges and potential solutions include:
- Yield Gaps:
- Challenge: Organic yields can sometimes be lower than conventional yields.
- Solution: Improving organic farming techniques through research and technology, such as Farmonaut’s precision agriculture tools, can help close this gap.
- Pest and Disease Management:
- Challenge: Managing pests and diseases without synthetic pesticides can be difficult.
- Solution: Developing more effective biological controls and using technology for early detection and targeted interventions.
- Cost of Certification:
- Challenge: The cost of organic certification can be prohibitive for small farmers.
- Solution: Developing group certification models and providing support through cooperatives or government programs.
- Market Access:
- Challenge: Small organic farmers may struggle to access larger markets.
- Solution: Creating digital platforms and blockchain-based traceability systems to connect farmers directly with consumers and retailers.
By addressing these challenges head-on, we can continue to improve and expand organic farming practices, making them more accessible and effective for farmers worldwide.
The Future of Organic Farming: Innovations and Opportunities
As we look to the future, the organic farming sector is poised for exciting developments and innovations. Here are some areas where we anticipate significant growth and opportunity:
- Vertical Organic Farming: Bringing organic practices to urban environments through technologically advanced vertical farming systems.
- Organic Hydroponics and Aquaponics: Developing organic standards for soilless growing systems to increase efficiency and sustainability.
- AI and Machine Learning in Organic Pest Management: Using advanced algorithms to predict and manage pest outbreaks without chemical interventions.
- Blockchain for Organic Supply Chain Transparency: Enhancing traceability and consumer trust through blockchain technology.
- Bioengineering for Organic-Compliant Crop Improvements: Exploring gene editing techniques that align with organic principles to develop more resilient crops.
At Farmonaut, we’re excited to be part of this future, continuously innovating our technology to support the growth and evolution of organic farming practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To help you better understand organic farming and Farmonaut’s role in supporting sustainable agriculture, we’ve compiled answers to some frequently asked questions:
- What makes a product certified organic?
A product is certified organic when it has been produced according to strict organic standards and verified by an accredited certification body. This includes using natural inputs, avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, and adhering to specific animal welfare standards for livestock.
- How does Farmonaut support organic farmers?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven advisory services, and blockchain-based traceability solutions that help organic farmers optimize their practices, improve yields, and ensure transparency in their supply chains.
- Can organic farming feed the world?
While there are challenges, many experts believe that with continued innovation and support, organic farming can play a significant role in global food security. Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can help bridge the yield gap between organic and conventional farming.
- How does organic farming contribute to climate change mitigation?
Organic farming practices, such as building healthy soils and reducing synthetic inputs, can help sequester carbon, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and create more resilient agricultural systems in the face of climate change.
- What is the difference between organic and biodynamic farming?
While both organic and biodynamic farming avoid synthetic inputs, biodynamic farming goes further by viewing the farm as a holistic, self-sustaining ecosystem and incorporates spiritual and astrological considerations into farming practices.
Conclusion: Embracing Organic Farming for a Sustainable Future
As we’ve explored throughout this blog post, organic farming and its associated certification standards play a crucial role in driving environmental sustainability in agriculture. From soil health and biodiversity to climate change mitigation and animal welfare, the benefits of organic practices are far-reaching and significant.
At Farmonaut, we’re proud to support the organic farming community with our innovative technology solutions. By combining the wisdom of traditional organic practices with cutting-edge satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain technology, we’re helping to shape the future of sustainable agriculture.
We encourage farmers, consumers, and industry professionals alike to consider the impact of their agricultural choices and to explore the possibilities of organic farming. Whether you’re a seasoned organic producer looking to optimize your operations or a curious consumer wanting to make more informed food choices, remember that every decision counts in our collective journey towards a more sustainable and resilient food system.
Join us in unlocking the full potential of sustainable agriculture. Together, we can cultivate a healthier planet and a more secure food future for generations to come.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can support your organic farming journey, explore our range of satellite-based farm management solutions:
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their own systems, check out our API and API Developer Docs.
Let’s cultivate a sustainable future, one farm at a time!