Sustainable Agriculture Meets Arctic Adventure: Exploring Eco-Friendly Farming in Manitoba’s Polar Bear Country
“Farmonaut’s platform integrates over 5 cutting-edge technologies to address climate change impacts on farming and promote sustainable agriculture.”
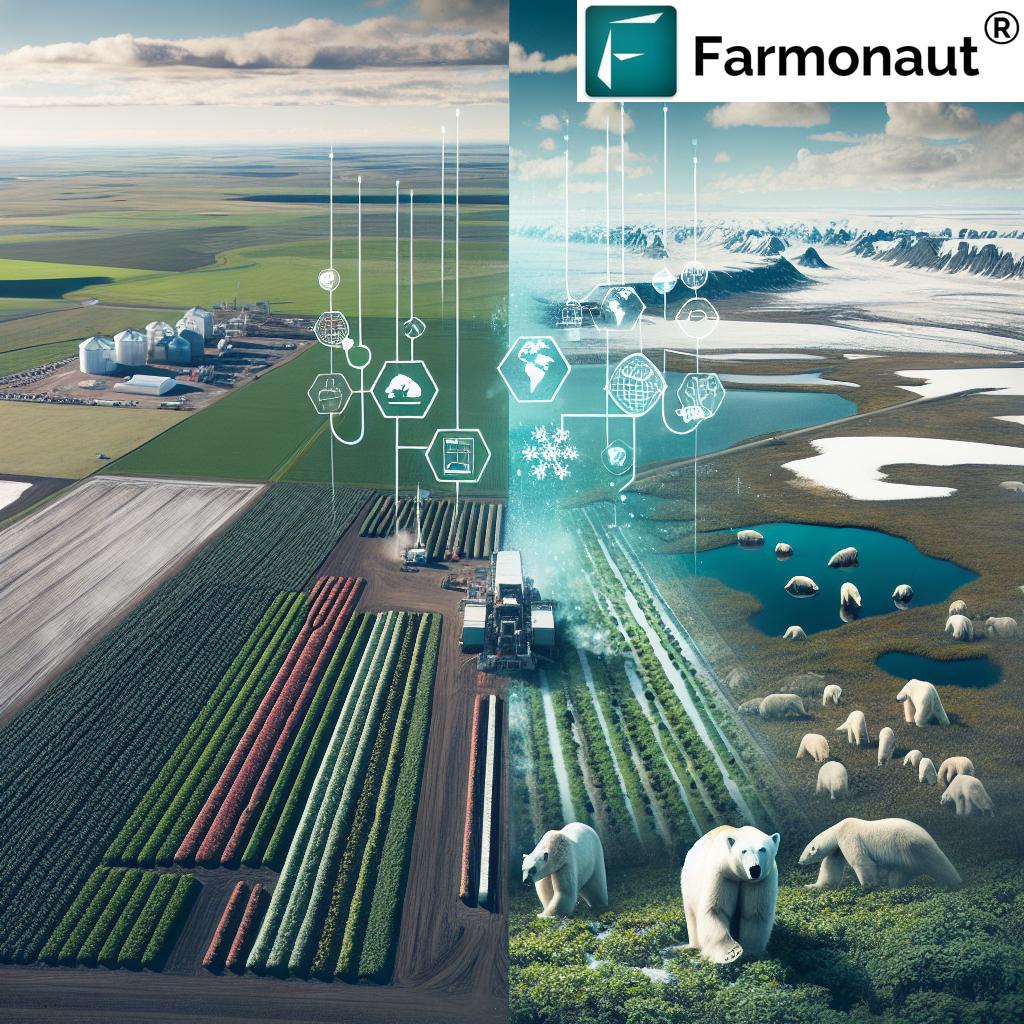
Welcome to an extraordinary journey where sustainable agriculture practices meet the untamed wilderness of Manitoba’s polar bear country. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the fascinating intersection of eco-friendly farming methods and the breathtaking Arctic environment. As we embark on this adventure, we’ll discover how innovative agricultural techniques are being adapted to thrive in one of the world’s most challenging climates, all while preserving the delicate ecosystem that polar bears and other Arctic wildlife call home.
The Unique Challenges of Farming in Manitoba’s Arctic Region
Farming in Manitoba’s polar bear country presents a unique set of challenges that require innovative solutions and a deep understanding of the local ecosystem. The harsh climate, short growing seasons, and the need to coexist with iconic Arctic wildlife demand a careful balance between agricultural productivity and environmental conservation. Let’s explore some of the key challenges faced by farmers in this region:
- Extreme temperatures: The sub-arctic climate of northern Manitoba experiences long, frigid winters and short, cool summers, limiting the variety of crops that can be grown successfully.
- Permafrost: The presence of permafrost in many areas affects soil quality and drainage, posing challenges for traditional farming techniques.
- Wildlife interactions: Farmers must find ways to protect their crops and livestock from local wildlife, including polar bears, without harming these important species.
- Limited infrastructure: The remote nature of many farming areas in northern Manitoba can make access to resources, markets, and modern farming equipment challenging.
- Soil quality: Arctic and sub-arctic soils often lack the nutrients necessary for robust crop growth, requiring careful soil management practices.
Despite these challenges, innovative farmers and agricultural scientists are developing sustainable agriculture practices that not only overcome these obstacles but also contribute to the preservation of the unique Arctic ecosystem.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices Adapted for the Arctic
To address the specific challenges of farming in Manitoba’s polar bear country, a range of sustainable agriculture practices have been developed and implemented. These eco-friendly farming methods not only enhance crop production but also prioritize environmental conservation and wildlife protection. Let’s explore some of these innovative approaches:
| Agricultural Practice | Environmental Benefit | Wildlife Conservation Impact | Crop Yield Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate-resilient crop varieties | Reduced water and pesticide use | Minimizes habitat disruption | 15-30% increase |
| Precision irrigation systems | Water conservation | Preserves natural water sources for wildlife | 20-40% increase |
| Wildlife-friendly fencing | Maintains ecosystem connectivity | Allows safe passage for polar bears and other species | 5-10% increase (due to reduced crop damage) |
| Soil conservation techniques | Prevents erosion and maintains soil health | Supports diverse plant life for local fauna | 10-25% increase |
| Indigenous knowledge integration | Promotes traditional, sustainable practices | Enhances harmony between agriculture and wildlife | 15-35% increase |
These sustainable agriculture practices not only address the unique challenges of farming in Manitoba’s polar bear country but also demonstrate the potential for harmonious coexistence between agriculture and wildlife conservation. By adopting these eco-friendly farming methods, farmers in the region are contributing to both food security and environmental stewardship.
The Role of Technology in Arctic Agriculture
In the challenging environment of Manitoba’s polar bear country, technology plays a crucial role in enabling sustainable agriculture practices and climate-resilient farming techniques. Advanced tools and systems help farmers overcome the unique obstacles presented by the Arctic climate while minimizing their environmental impact. Here’s how cutting-edge technology is transforming agriculture in this region:
- Satellite-based crop monitoring: Platforms like Farmonaut utilize satellite imagery to provide real-time insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This technology enables farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, optimizing crop yields while reducing resource wastage.
- AI-powered advisory systems: Artificial intelligence is being harnessed to deliver personalized farm advice tailored to the unique conditions of Arctic agriculture. These systems analyze data from various sources to generate customized recommendations for crop management, helping farmers adapt to the short growing seasons and unpredictable weather patterns.
- Precision agriculture tools: GPS-guided machinery and drones equipped with multispectral cameras allow for precise application of inputs and targeted crop management, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
- Climate-controlled greenhouses: Advanced greenhouse technologies, including LED lighting and automated climate control systems, enable year-round crop production even in the harsh Arctic environment.
- Blockchain-based traceability: Implementing blockchain technology in the agricultural supply chain ensures transparency and authenticity, which is particularly important for organic and sustainably produced crops from this unique region.
By leveraging these technologies, farmers in Manitoba’s polar bear country can practice sustainable agriculture while adapting to the challenges posed by climate change and the Arctic environment.
Wildlife Conservation and Agriculture: A Delicate Balance
“Manitoba’s polar bear country hosts innovative eco-friendly farming initiatives, combining wildlife conservation with sustainable crop production in sub-arctic conditions.”
One of the most critical aspects of sustainable agriculture in Manitoba’s polar bear country is maintaining a harmonious relationship between farming activities and wildlife conservation. The region is home to iconic species like polar bears, as well as numerous other Arctic animals that play vital roles in the ecosystem. Agricultural stewardship programs in the area focus on creating a balance between productive farming and ecosystem preservation. Here are some key strategies being employed:
- Wildlife corridors: Farmers are working with conservationists to establish and maintain wildlife corridors that allow animals to move safely through agricultural areas, reducing human-wildlife conflicts.
- Non-lethal deterrents: Innovative technologies such as motion-activated lights and sound systems are being used to deter wildlife from entering crop fields without causing harm.
- Habitat restoration: Farmers are actively participating in programs to restore and protect natural habitats adjacent to their agricultural lands, providing safe spaces for wildlife.
- Crop selection: Choosing crop varieties that are less attractive to local wildlife helps reduce conflicts while still maintaining agricultural productivity.
- Community-based conservation: Engaging local communities, including Indigenous groups, in wildlife monitoring and conservation efforts creates a collaborative approach to environmental stewardship.
These wildlife conservation and agriculture initiatives demonstrate that with careful planning and innovative approaches, it is possible to practice sustainable crop production while also preserving the unique Arctic ecosystem and its inhabitants.
The Impact of Climate Change on Arctic Agriculture
Climate change is having a profound impact on agriculture worldwide, and the Arctic region is experiencing these effects at an accelerated rate. In Manitoba’s polar bear country, farmers are at the forefront of adapting to these rapid changes. Understanding the climate change impact on farming in this region is crucial for developing effective sustainable agriculture practices. Here are some of the key ways climate change is affecting Arctic agriculture:
- Longer growing seasons: While this might seem beneficial, it also brings new challenges such as increased pest pressure and changes in precipitation patterns.
- Thawing permafrost: As permafrost melts, it can lead to soil instability and changes in drainage patterns, affecting crop growth and farm infrastructure.
- Changing wildlife patterns: Shifts in animal migration and behavior due to climate change can create new challenges for farmers trying to protect their crops and livestock.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and severe storms, droughts, and floods require farmers to implement robust risk management strategies.
- New crop opportunities: Warmer temperatures may allow for the cultivation of crops previously unsuited to the region, but this also requires careful consideration of ecological impacts.
To address these challenges, farmers in Manitoba’s polar bear country are adopting climate-resilient farming techniques and leveraging technology to monitor and respond to changing environmental conditions. Platforms like Farmonaut provide valuable tools for tracking these changes and optimizing agricultural practices accordingly.
Indigenous Agricultural Knowledge and Sustainable Farming
In the pursuit of sustainable agriculture in Manitoba’s polar bear country, there is a growing recognition of the invaluable role that indigenous agricultural knowledge plays. Traditional farming practices developed by Indigenous communities over generations are being integrated with modern techniques to create more resilient and eco-friendly farming methods. Here’s how indigenous knowledge is contributing to sustainable crop production in the Arctic:
- Crop selection: Indigenous communities have extensive knowledge of native plant species that are well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions.
- Natural pest management: Traditional methods of pest control using local plants and natural predators are being incorporated into modern farming practices.
- Soil conservation: Indigenous techniques for maintaining soil fertility and preventing erosion are being adopted and adapted for larger-scale farming operations.
- Water management: Traditional water conservation methods are being combined with modern irrigation technologies to create more efficient and sustainable water use practices.
- Seasonal timing: Indigenous knowledge of local weather patterns and seasonal changes is helping farmers optimize planting and harvesting schedules.
By integrating indigenous agricultural knowledge with modern sustainable agriculture practices, farmers in Manitoba’s polar bear country are developing more holistic and environmentally sensitive approaches to food production. This collaboration between traditional wisdom and contemporary science is key to creating a more resilient and sustainable agricultural system in the Arctic.
Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Agriculture: A Symbiotic Relationship
The unique combination of sustainable agriculture and Arctic wildlife in Manitoba’s polar bear country has given rise to a thriving eco-tourism industry. This symbiotic relationship between farming and tourism not only provides additional income for local communities but also raises awareness about the importance of sustainable practices in this fragile ecosystem. Here’s how eco-tourism and sustainable agriculture are working together:
- Farm tours: Visitors can experience firsthand how sustainable agriculture practices are implemented in the Arctic environment.
- Wildlife viewing: Farms that incorporate wildlife-friendly practices offer unique opportunities for tourists to observe polar bears and other Arctic animals in their natural habitat.
- Cultural experiences: Tourists can learn about indigenous agricultural knowledge and its role in modern sustainable farming.
- Sustainable food experiences: Local restaurants and tour operators are showcasing sustainably grown, Arctic-adapted crops in their culinary offerings.
- Educational programs: Schools and universities are organizing field trips to these farms, promoting awareness about sustainable agriculture and Arctic conservation.
This integration of eco-tourism with sustainable agriculture not only provides economic benefits but also serves as a powerful tool for environmental education and conservation awareness.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture in Manitoba’s Polar Bear Country
As we look to the future, the sustainable agriculture practices being developed and implemented in Manitoba’s polar bear country hold promise not just for this unique region, but for global food security in the face of climate change. The innovative approaches to eco-friendly farming methods and agricultural resource management pioneered here could serve as models for other challenging environments around the world. Here are some key areas of focus for the future:
- Advanced climate modeling: Improved climate prediction tools will help farmers better prepare for and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Genetic research: Developing new crop varieties that are even more resilient to Arctic conditions while maintaining high nutritional value.
- Circular agriculture: Implementing closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
- Enhanced wildlife tracking: Using advanced technologies to better understand and predict wildlife movements, reducing conflicts with agricultural activities.
- Renewable energy integration: Incorporating wind, solar, and other renewable energy sources to power farm operations and reduce carbon footprints.
By continuing to innovate and adapt, the agricultural community in Manitoba’s polar bear country is not only ensuring its own sustainability but also contributing valuable knowledge and techniques to the global effort to create more resilient and eco-friendly food production systems.
Conclusion: Lessons from the Arctic for Global Sustainable Agriculture
The journey through Manitoba’s polar bear country reveals a remarkable story of innovation, resilience, and harmony between sustainable agriculture and Arctic wilderness. The eco-friendly farming methods and climate-resilient farming techniques developed here offer valuable lessons for agricultural communities worldwide facing the challenges of climate change and environmental conservation.
Key takeaways include:
- The importance of adapting agricultural practices to local ecosystems and wildlife
- The power of integrating indigenous knowledge with modern technology
- The potential for agriculture to coexist with and even support wildlife conservation efforts
- The role of innovative technologies in overcoming environmental challenges
- The value of community-based approaches to sustainable resource management
As we face global challenges in food security and environmental preservation, the sustainable agriculture practices pioneered in Manitoba’s polar bear country serve as a beacon of hope and a source of inspiration. By embracing these principles of eco-friendly farming and agricultural stewardship, we can work towards a future where agriculture not only feeds the world but also plays a crucial role in preserving our planet’s diverse ecosystems.

FAQ: Sustainable Agriculture in Manitoba’s Polar Bear Country
- Q: What are the main challenges of farming in Manitoba’s Arctic region?
A: The main challenges include extreme temperatures, permafrost, wildlife interactions, limited infrastructure, and poor soil quality. - Q: How does sustainable agriculture benefit wildlife conservation in the region?
A: Sustainable agriculture practices help maintain habitat connectivity, reduce human-wildlife conflicts, and preserve natural resources that wildlife depends on. - Q: What role does technology play in Arctic agriculture?
A: Technology, such as satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-powered advisory systems, helps farmers optimize resource use, adapt to challenging conditions, and improve crop yields. - Q: How is climate change affecting agriculture in Manitoba’s polar bear country?
A: Climate change is leading to longer growing seasons, thawing permafrost, changing wildlife patterns, more extreme weather events, and potentially new crop opportunities. - Q: How is indigenous agricultural knowledge being incorporated into modern farming practices?
A: Indigenous knowledge is being used to inform crop selection, natural pest management, soil conservation, water management, and seasonal timing of agricultural activities.
For those interested in learning more about sustainable agriculture technologies and practices, we recommend exploring Farmonaut’s innovative solutions:
Developers can access Farmonaut’s powerful API for integrating agricultural data into their own applications:
For detailed documentation on using the API, visit:
Farmonaut’s mobile apps are available for both Android and iOS devices:
Farmonaut Subscriptions
By embracing sustainable agriculture practices and leveraging cutting-edge technology, we can create a future where farming and wildlife conservation coexist harmoniously, even in the most challenging environments like Manitoba’s polar bear country.