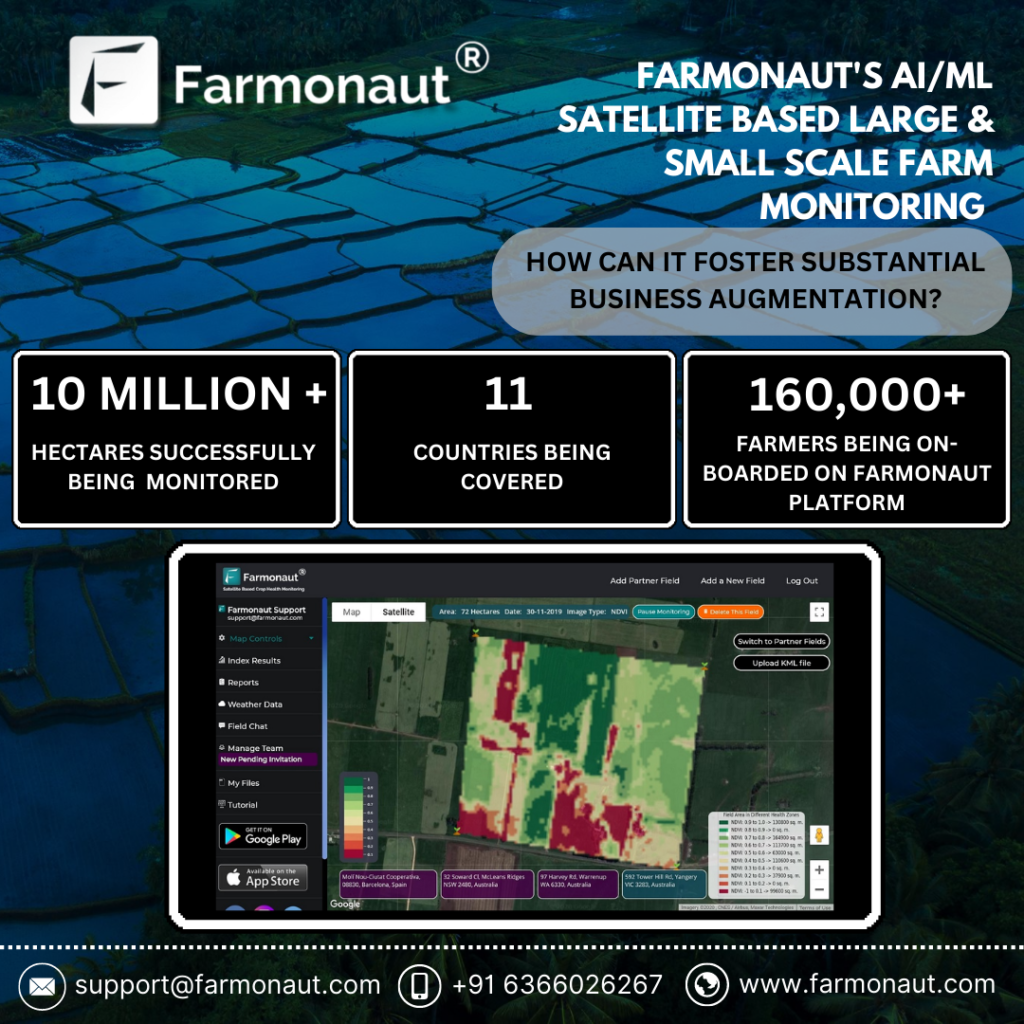
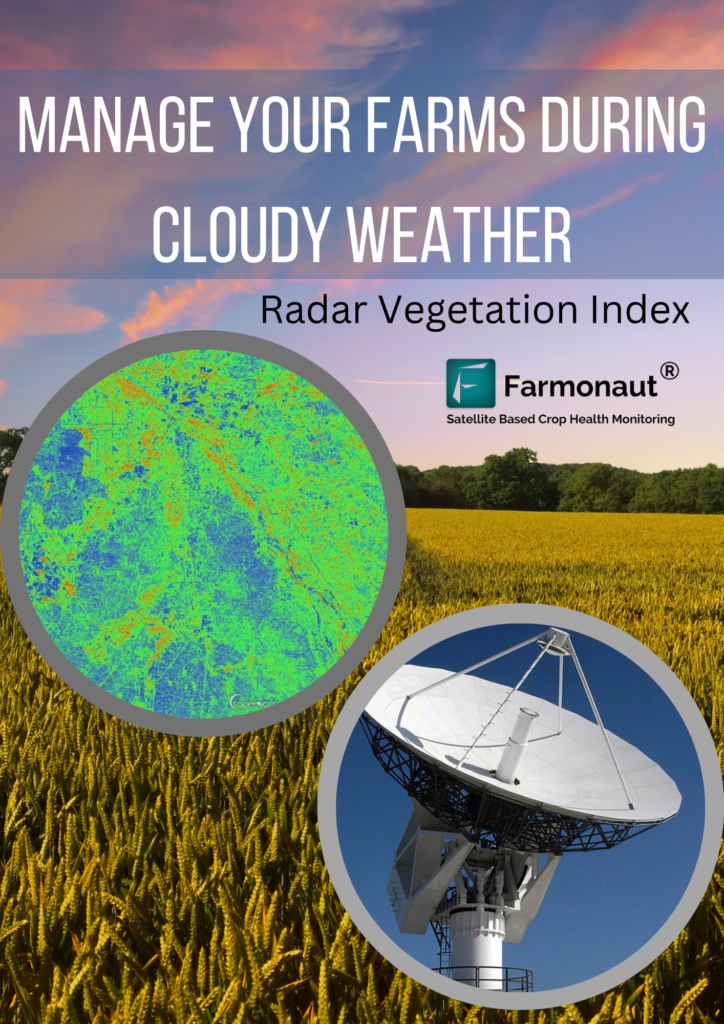
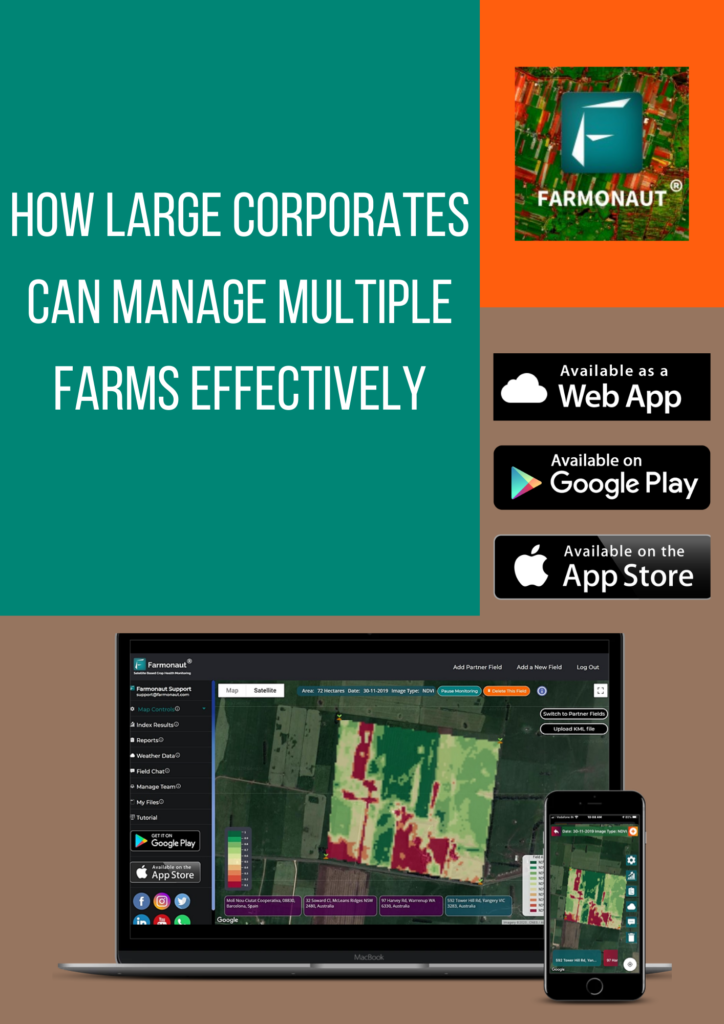
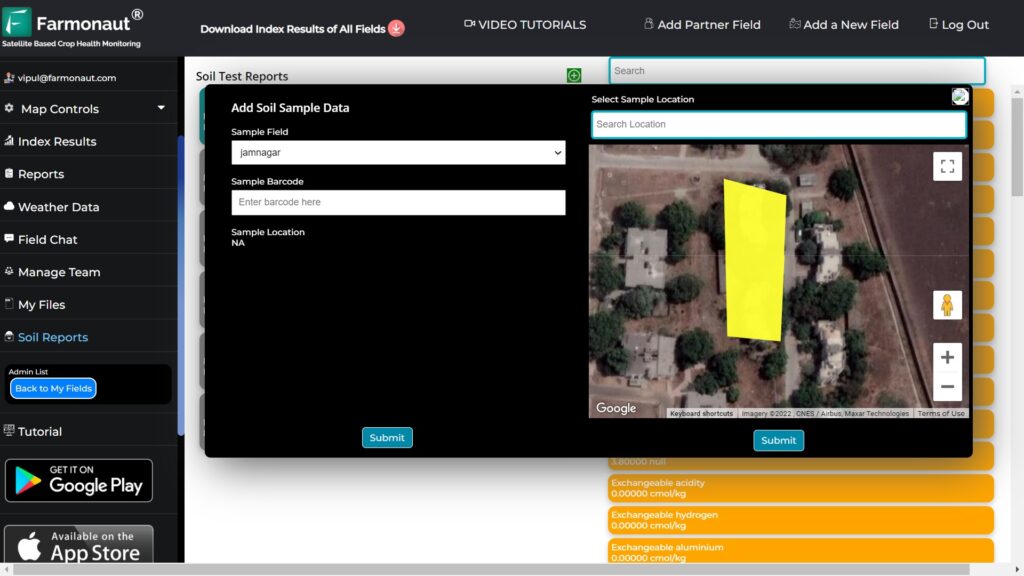
Introduction Sugarcane, a tall, perennial grass of the genus Saccharum, is primarily cultivated for sugar production. It is a robust tropical plant that contributes to about 70% of the world’s sugar production and has a great potential for biomass and biofuel production. It is the most important source of sugar production in India, with about 359 million tonnes produced annually. In the 2022-23 sugar season, approximately 360 million tons of sugar is anticipated to be procured by sugar mills. The Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) for sugarcane, as approved for the same period, is Rs. 305 per quintal. The average sugarcane yield in India ranges from 80 to 100 tonnes per hectare. Uttar Pradesh leads as the highest sugarcane-producing state, followed by Maharashtra and Karnataka The current agriculture scenario in the sugarcane sector is rapidly evolving with the integration of satellite technology. Satellite-based monitoring systems enable efficient and effective monitoring of sugarcane plantations, allowing for the delineation of field boundaries, tracking of crop growth across vast areas, and monitoring of soil moisture levels. Challenges Affecting India’s Sugarcane Sector The sugarcane sector in India faces several challenges, including stagnating production, price regulations, unstable sugarcane market, and water scarcity. Some of the key challenges faced by the sector are: Stagnating Production: Sugarcane production in India has stagnated in the last 20 years, with farmers producing around 70 tonnes per hectare. By 2030, they will need to produce around 100-110 tonnes per hectare to meet the increasing demand for sugar. Price Regulations: Sugar, being an essential commodity, is controlled through various regulatory mechanisms in India, including minimum prices. However, the sugar price for consumers is not regulated, making sugar manufacturers vulnerable. Unstable Sugarcane Market: The unstable sugarcane market poses a significant challenge for the sector, as it affects the prices paid to farmers and the overall profitability of sugarcane cultivation. Water Scarcity: India is facing an increasing lack of water, which can impact crop yields and the overall sustainability of sugarcane cultivation. Low Yield of Sugarcane: Despite being the largest producer of sugarcane in the world, India’s yield per hectare is extremely low compared to some of the major sugarcane-producing countries. This leads to low overall production and results in a short supply of sugarcane to sugar mills Economic and Social Injustices: Sugarcane farmers in India are dealing with various economic and social injustices. A majority of those dependent on sugarcane farming are small and marginal farmers, and the cultivation of the crop is their primary source of income. These farmers are vulnerable to price fluctuations and face economic and social injustices Source: Indian Council of Agriculture Research Source: Indian Council of Agriculture Research Transforming the landscape of Precision Agriculture with Farmonaut Sugarcane farming in India faces numerous challenges, impacting both yield and sustainability. Thankfully, innovative solutions like Farmonaut can equip farmers with the tools and insights to overcome these hurdles and cultivate sweeter success. Let’s explore how Farmonaut can address key challenges in the sugarcane industry: 1. Fluctuating Sugar Prices: Market Intelligence: Farmonaut provides real-time market data and analysis, empowering farmers to make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and selling their sugarcane based on anticipated price trends. 2. Water Scarcity: Precision Irrigation: Farmonaut leverages satellite imagery, soil moisture sensors, and weather data to recommend customized irrigation schedules, optimizing water usage and minimizing wastage. Drought-Resistant Varieties: The platform provides information on high-yielding, drought-resistant sugarcane varieties suitable for specific regions, helping farmers adapt to water scarcity. 3. Climate Change: Climate-Smart Practices: Farmonaut offers guidance on adopting climate-resilient practices like cover cropping, mulching, and integrated pest management, mitigating the impact of extreme weather events. Crop Monitoring: Satellite imagery and on-field sensors enable real-time crop health monitoring, allowing farmers to identify and address climate-related stresses promptly. 4. Pest and Disease Management: Targeted Application: The platform guides farmers in applying fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides only where and when necessary, reducing the cost of inputs and environmental impact. 5. Yield Optimization: Data-Driven Insights: Farmonaut analyzes farm data to identify yield-limiting factors like soil deficiencies, inadequate irrigation, or pest infestations, guiding farmers towards corrective actions. Precision Agriculture: The platform recommends optimal planting densities, fertilizer application rates, and harvesting times based on specific field conditions, maximizing yield potential. Effective Methods for Managing Sugarcane Farm Losses: Case Study Understanding the Impact on Production Loss A conducted study revealed that 50% of agricultural losses can be directly attributed to the deficiencies in water and nitrogen. Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU) reports that regions, including Tamil Nadu and nearby states, witness approximately 20% loss in sugarcane yield. TNAU additionally notes a 15% decrease in sugar yield, attributing the losses to insects like borers, sucking pests, and soil-dwelling insects.. The complexity of the problem deepens as the research identifies an extensive array of approximately 200 insect species affecting sugarcane. Optimize Operations with Farmonaut Management Farmonaut Technologies provides satellite-based services to help farmers manage their sugarcane farms more effectively. By utilizing satellite images and data, farmers can address issues such as water deficiency, pest and disease infestations, and declining yields. The technology allows for early detection of these problems, enabling farmers to take necessary actions to mitigate losses and improve crop health. Additionally, Farmonaut’s services include crop health monitoring, water stress assessment, and crop area and yield estimation, all of which are crucial for optimizing farming practices and increasing yields. The innovative technological interventions for sugarcane improvement, production, and management have helped the industry progress towards a more sustainable and self-reliant future. Exploring Success: Case Studies of Successful and Satisfied Farmer (Mr. Ashok Shinde : Shree Datta Shetkari Sahakari Sakhar Karkhana Ltd.) Mr. Ashok Shinde, a sugarcane farmer from Maharashtra, has effectively utilized Farmonaut Services to address irrigation challenges and monitor crop health. By leveraging NDMI, NDWI, and evapotranspiration data, he optimized his irrigation strategies, leading to improved yields. The reports generated by Farmonaut Services also provided valuable insights into crop health, temperature, pests, and diseases, enabling Mr. Shinde to take proactive measures to control pest and disease intrusions. In addition to addressing irrigation