Effective Organic and Chemical Control Strategies for Leafminers in Citrus and Vegetable Crops

As agricultural experts, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges that farmers face when dealing with pests like leafminers. These tiny yet destructive insects can wreak havoc on a wide range of crops, particularly citrus fruits and vegetables. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective strategies for controlling leafminers, from organic methods to chemical treatments, and how our satellite-based technology can help in early detection and management of infestations.
Understanding Leafminers: A Microscopic Menace
Leafminers are the larvae of various species of insects, primarily flies and moths, that feed on the internal tissues of leaves. The most common leafminers affecting agricultural crops belong to the genus Liriomyza (flies) and Phyllocnistis citrella (moths), the latter specifically targeting citrus plants.
The Life Cycle of Leafminers
To effectively control leafminers, it’s crucial to understand their life cycle:
- Egg Stage: Adult females lay eggs inside leaf tissue.
- Larval Stage: Upon hatching, larvae (often called maggots) begin feeding on the leaf’s internal tissues, creating distinctive tunnels or mines.
- Pupal Stage: After feeding, larvae exit the leaf to pupate in the soil or on the leaf surface.
- Adult Stage: Adult flies or moths emerge to mate and lay eggs, continuing the cycle.
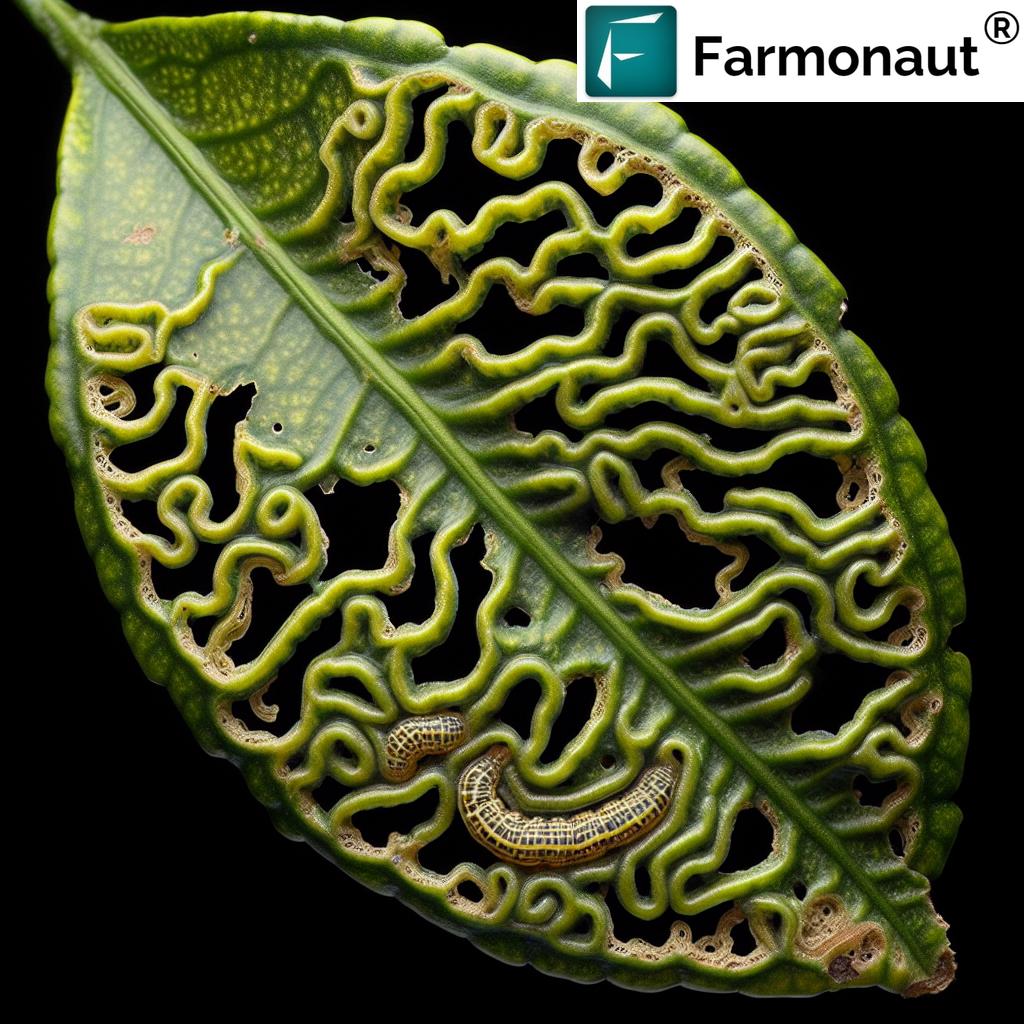
Identifying Leafminer Damage
Leafminer infestation can be identified by the following signs:
- Serpentine tunnels or blotch mines on leaves
- Distorted or curled leaves
- Premature leaf drop
- Reduced photosynthesis and plant vigor
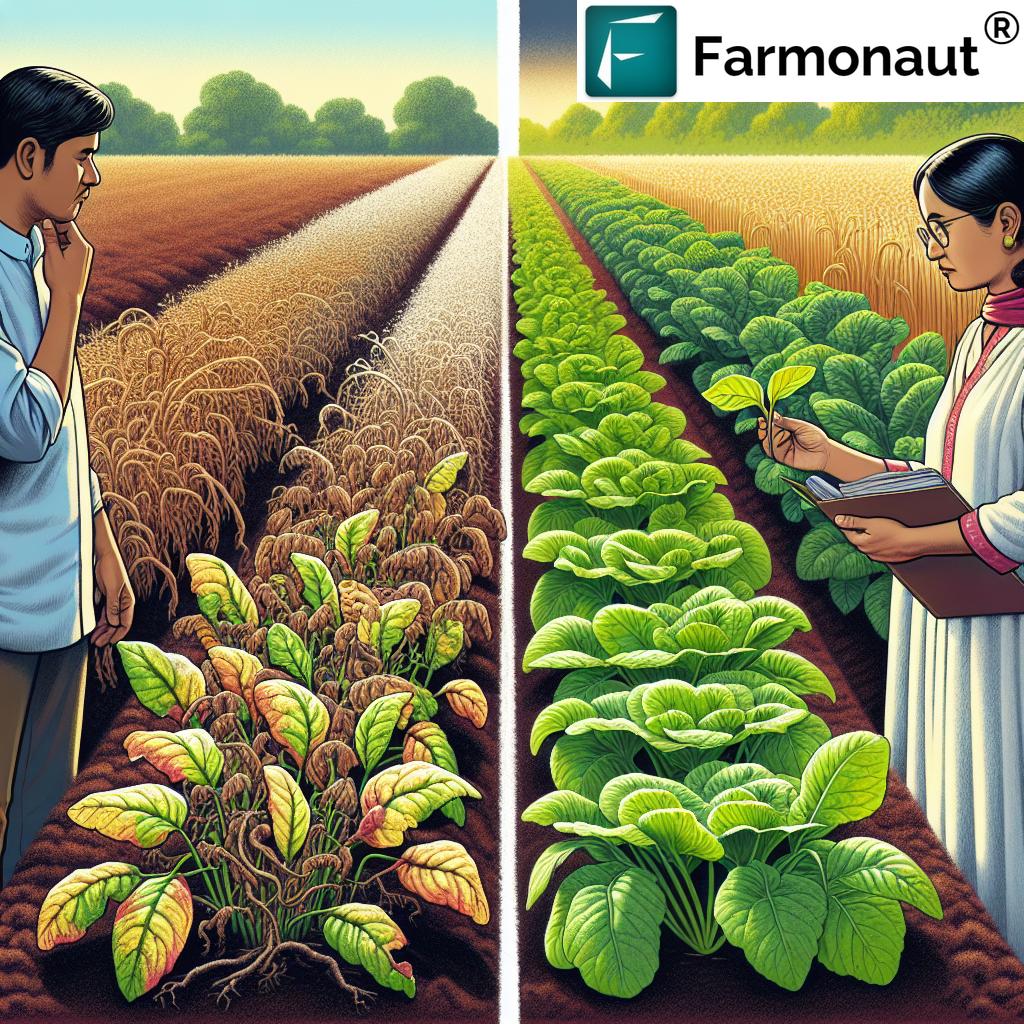
The Impact of Leafminers on Crops
Leafminers can cause significant damage to a variety of crops, including:
- Citrus: Lemons, oranges, limes, and other citrus fruits
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, beans, and leafy greens
- Ornamental Plants: Various flowering and foliage plants
- Fresh Herbs: Basil, cilantro, and other culinary herbs
The damage caused by leafminers can lead to reduced crop yield, lower fruit quality, and increased susceptibility to diseases. In severe cases, entire crops can be lost, making effective control strategies crucial for farmers and gardeners alike.
Early Detection: The Key to Effective Leafminer Control
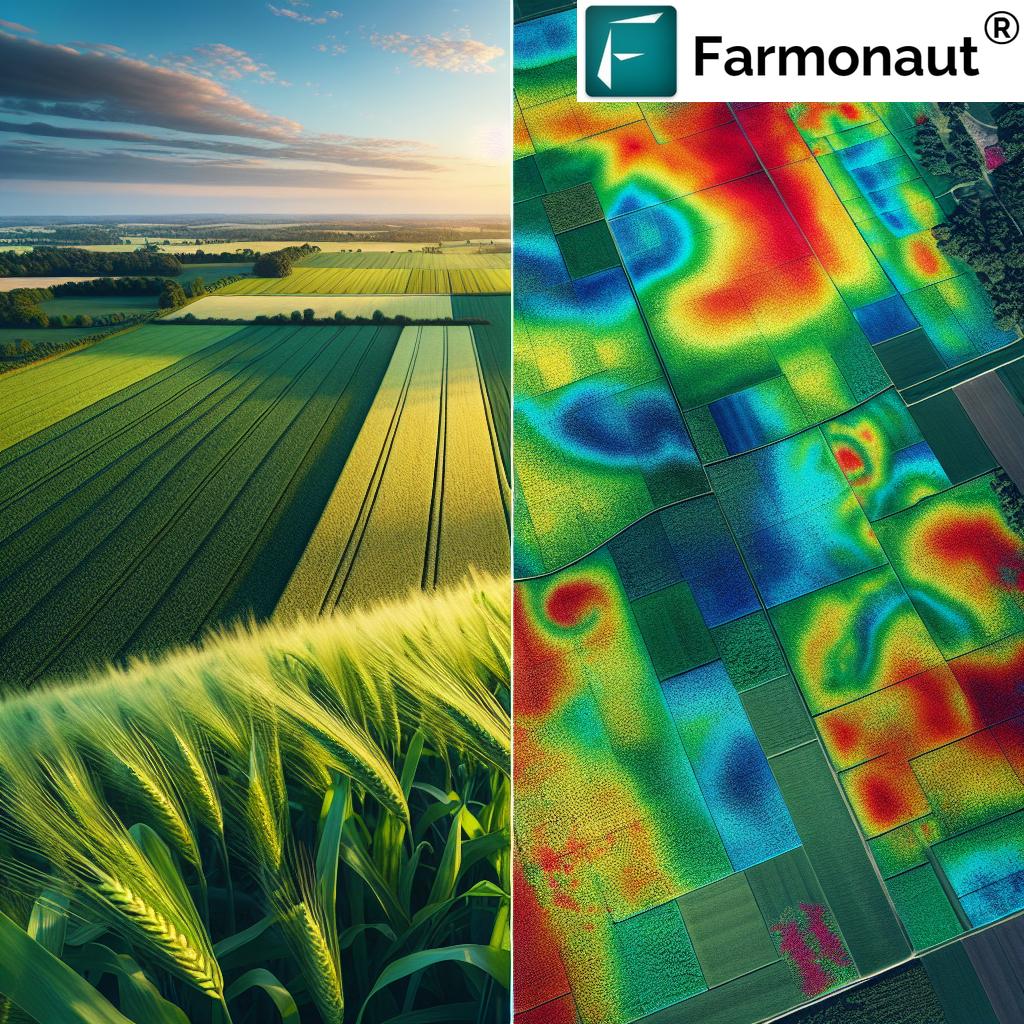
At Farmonaut, we believe that early detection is paramount in managing leafminer infestations. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers a revolutionary approach to pest detection, allowing farmers to identify potential problems before they escalate.
Traditional vs. Satellite-Based Detection
| Feature | Traditional Leafminer Detection | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Slow (manual field inspection) | Rapid (real-time satellite imagery) |
| Accuracy | Variable (depends on inspector’s expertise) | High (AI-powered analysis) |
| Coverage Area | Limited (time-consuming for large fields) | Extensive (entire fields at once) |
| Cost-effectiveness | Low (labor-intensive) | High (automated and scalable) |
Our satellite system can quickly identify potential leafminer infestations across large areas, enabling timely and targeted treatment strategies for citrus and vegetable crops. By leveraging this technology, farmers can stay one step ahead of these persistent pests.
To learn more about how our satellite-based crop monitoring can help you detect and manage leafminer infestations, visit Farmonaut’s Crop Monitoring Platform.
Integrated Pest Management: A Holistic Approach to Leafminer Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to controlling leafminers. This strategy combines various methods to manage pest populations effectively while minimizing environmental impact. Let’s explore the key components of an IPM strategy for leafminers:
1. Cultural Control Methods
Cultural control methods focus on creating an environment that is less favorable for leafminers:
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can disrupt the life cycle of leafminers, especially those species that specialize in specific plant types.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infested leaves or plants to reduce the population of leafminers in your field.
- Proper Irrigation: Avoid over-watering, as moist conditions can attract adult leafminers.
- Resistant Varieties: When available, choose plant varieties that are less susceptible to leafminer attacks.
2. Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural predators and parasitoids to manage leafminer populations:
- Parasitoid Wasps: Species like Diglyphus isaea and Dacnusa sibirica are effective against leafminers in the genus Liriomyza.
- Predatory Insects: Encourage the presence of natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings in your field.
- Nematodes: Certain species of beneficial nematodes can help control leafminer pupae in the soil.
Our satellite monitoring system can help identify areas where natural predator populations may be thriving, allowing for targeted conservation efforts to boost biological control.
3. Organic Control Methods
For farmers practicing organic agriculture or those looking to reduce chemical use, several organic control methods are available:
- Neem Oil: This natural insecticide can disrupt the feeding and reproductive cycles of leafminers.
- Spinosad: Derived from soil bacteria, spinosad is effective against leafminers and is approved for organic use.
- Diatomaceous Earth: This fine powder can deter adult leafminers and damage the larvae as they exit the leaf to pupate.
- Sticky Traps: Yellow sticky traps can capture adult leafminers, reducing the population over time.
4. Chemical Control
While we advocate for integrated and organic approaches, there are situations where chemical control may be necessary, especially in severe infestations:
- Systemic Insecticides: These are absorbed by the plant and can effectively control leafminer larvae feeding inside the leaves.
- Contact Insecticides: These target adult leafminers and can be effective when timed correctly.
- Growth Regulators: Insect growth regulators disrupt the molting process of leafminer larvae.
Important Note: Always follow label instructions and local regulations when using any pesticides. Our satellite monitoring can help you apply these treatments more precisely, reducing overall chemical use.
Precision Application: Leveraging Satellite Technology for Targeted Treatment

At Farmonaut, we’re revolutionizing the way farmers approach pest control. Our satellite-based technology allows for precise identification of leafminer-affected areas, enabling targeted treatment strategies. Here’s how our system enhances leafminer control efforts:
- Early Detection: Our satellites can detect subtle changes in plant health before visible symptoms appear, allowing for proactive treatment.
- Precise Mapping: We generate detailed maps of affected areas, helping farmers focus their control efforts where they’re needed most.
- Resource Optimization: By targeting only affected areas, farmers can reduce the use of pesticides and save on labor costs.
- Monitoring Effectiveness: Our continuous monitoring allows farmers to track the effectiveness of their control measures over time.
To explore how our satellite technology can enhance your leafminer control strategies, visit our Satellite API page.
Crop-Specific Strategies for Leafminer Control
Different crops may require tailored approaches to leafminer control. Let’s explore strategies for some commonly affected crops:
Citrus Crops
Citrus leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella) is a significant pest in citrus orchards worldwide. Here are some specific strategies for citrus crops:
- Pruning: Regular pruning can help remove infested leaves and improve air circulation, reducing humidity that attracts leafminers.
- Pheromone Traps: These can disrupt mating cycles and reduce populations over time.
- Targeted Spraying: Focus on new flushes of growth, as these are most susceptible to leafminer attack.
- Beneficial Insects: Encourage populations of parasitic wasps like Ageniaspis citricola, which specifically target citrus leafminers.
Vegetable Crops
Vegetable crops, especially tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens, are often targeted by leafminers in the genus Liriomyza. Consider these strategies:
- Row Covers: Physical barriers can prevent adult leafminers from laying eggs on young plants.
- Companion Planting: Certain plants like marigolds and chrysanthemums can repel leafminers.
- Vertical Gardening: Growing plants vertically can make it harder for leafminers to move between plants.
- Regular Monitoring: Inspect plants frequently, especially the undersides of leaves, for early signs of infestation.
Ornamental Plants
Ornamental plants in landscapes and greenhouses can also fall victim to leafminers. Here are some tailored strategies:
- Quarantine: Isolate new plants to prevent the spread of leafminers to established plantings.
- Proper Spacing: Adequate spacing between plants improves air circulation and makes it harder for leafminers to spread.
- Foliar Sprays: Regular applications of neem oil or insecticidal soaps can deter leafminers.
- Selective Pruning: Remove heavily infested parts of plants to prevent further spread.
The Role of Technology in Modern Leafminer Control
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of integrating technology into pest management strategies. Our advanced tools can significantly enhance your leafminer control efforts:
Satellite Imagery and AI Analysis
Our satellite imagery, combined with AI-powered analysis, can detect early signs of leafminer infestation across vast areas. This technology allows for:
- Early detection of stress patterns indicative of leafminer activity
- Mapping of infestation hotspots for targeted treatment
- Monitoring the effectiveness of control measures over time
Mobile Apps for On-the-Go Monitoring
Our mobile apps for Android and iOS allow farmers to access real-time data on their crops, including potential leafminer infestations, directly from their smartphones.
Weather Integration for Optimal Treatment Timing
Our Weather API provides accurate forecasts, helping farmers time their leafminer control measures for maximum effectiveness.
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Leafminer Management
At Farmonaut, we believe in promoting sustainable agricultural practices that not only control pests like leafminers but also contribute to overall ecosystem health. Here are some sustainable approaches to consider:
1. Biodiversity Enhancement
Increasing biodiversity in and around your fields can help naturally control leafminer populations:
- Polyculture: Growing multiple crop species together can confuse and deter leafminers.
- Hedgerows and Flower Strips: These provide habitat for beneficial insects that prey on leafminers.
- Cover Crops: Planting cover crops between main crop cycles can break the leafminer life cycle and improve soil health.
2. Soil Health Management
Healthy soil leads to stronger plants that are more resistant to leafminer attacks:
- Composting: Add organic matter to improve soil structure and nutrient content.
- Reduced Tillage: Minimize soil disturbance to preserve beneficial soil organisms.
- Balanced Fertilization: Avoid over-fertilization, which can make plants more attractive to leafminers.
3. Water Management
Proper irrigation practices can help deter leafminers and create a less favorable environment for their development:
- Drip Irrigation: This method reduces leaf wetness, making the environment less attractive to leafminers.
- Timing: Water early in the day to allow leaves to dry, reducing humidity that leafminers prefer.
- Mulching: Use organic mulches to retain soil moisture and reduce the need for frequent watering.
Economic Considerations in Leafminer Control
While effective leafminer control is crucial for crop health, it’s important to consider the economic aspects of various control strategies. At Farmonaut, we help farmers make cost-effective decisions:
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Before implementing any control measure, consider:
- The potential crop loss if left untreated
- The cost of the control method (including labor and materials)
- The expected efficacy of the treatment
- Long-term benefits vs. short-term gains
Threshold-Based Decision Making
Establish economic thresholds for leafminer populations to guide treatment decisions:
- Monitor leafminer populations regularly
- Determine the level of infestation that justifies intervention
- Use our satellite monitoring to track infestation levels across your fields
Precision Agriculture for Cost Reduction
Our satellite-based monitoring system can help reduce costs by:
- Identifying specific areas that need treatment, reducing overall pesticide use
- Optimizing the timing of interventions for maximum effectiveness
- Reducing labor costs associated with manual scouting
Future Trends in Leafminer Control
As technology continues to advance, we at Farmonaut are excited about the future of leafminer control. Here are some emerging trends and technologies to watch:
1. Gene Editing for Pest Resistance
CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies may lead to the development of crop varieties with enhanced resistance to leafminers.
2. Drone-Based Pest Control
Precision application of treatments using drones could revolutionize the way we manage leafminer infestations in large fields.
3. IoT Sensors for Real-Time Monitoring
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors placed throughout fields could provide continuous, real-time data on pest populations and plant health.
4. AI-Powered Predictive Models
Advanced AI algorithms could predict leafminer outbreaks based on historical data, weather patterns, and current field conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How do I know if my plants have leafminers?
A: Look for serpentine tunnels or blotch mines on leaves, which are the most common signs of leafminer infestation. You may also notice distorted or curled leaves and premature leaf drop.
Q2: Are leafminers harmful to humans?
A: Leafminers do not directly harm humans. They primarily affect plant health and crop yield.
Q3: Can leafminers infest indoor plants?
A: Yes, leafminers can infest indoor plants, especially if they are brought in from outside or if windows are left open.
Q4: How quickly can leafminers damage a crop?
A: Leafminer damage can occur rapidly, with visible signs appearing within a few days of infestation. Severe damage can occur within 1-2 weeks if left untreated.
Q5: Are organic control methods effective against leafminers?
A: Yes, many organic control methods can be effective, especially when used as part of an integrated pest management strategy. Neem oil, spinosad, and biological controls like parasitic wasps can all help manage leafminer populations.
Q6: How can Farmonaut’s satellite technology help with leafminer control?
A: Our satellite technology can detect early signs of stress in plants caused by leafminer infestations, allowing for early intervention. It also helps in mapping affected areas for targeted treatment, reducing overall pesticide use and improving cost-effectiveness.
Q7: Are there any natural predators of leafminers?
A: Yes, several natural predators feed on leafminers, including parasitic wasps, birds, and some species of ants and beetles. Encouraging these natural predators can be an effective part of a biological control strategy.
Q8: How often should I monitor my crops for leafminers?
A: Regular monitoring is key. We recommend checking your crops at least weekly during the growing season, and more frequently if you’ve had previous leafminer issues or if conditions are favorable for their development.
Q9: Can crop rotation help control leafminers?
A: Yes, crop rotation can be an effective cultural control method for leafminers. By changing the crop planted in a particular field each season, you can disrupt the life cycle of leafminers that specialize in certain plant types.
Q10: Are there any specific weather conditions that favor leafminer infestations?
A: Leafminers tend to thrive in warm, humid conditions. They are often more problematic during spring and early summer, or in greenhouse environments where temperatures are consistently warm.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage leafminer infestations and other crop health issues, visit our website or contact our team of agricultural experts.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Leafminer Control
Effective leafminer control requires a multifaceted approach that combines traditional methods with cutting-edge technology. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the tools and knowledge they need to protect their crops from these persistent pests.
By integrating cultural, biological, and chemical control methods with our advanced satellite monitoring system, farmers can achieve more effective and sustainable leafminer management. Our technology enables early detection, precise treatment, and ongoing monitoring, all of which contribute to healthier crops and improved yields.
Remember, the key to successful leafminer control lies in:
- Early detection and intervention
- Implementing an integrated pest management strategy
- Utilizing sustainable and environmentally friendly practices
- Leveraging technology for precision and efficiency
- Continuous learning and adaptation of control strategies
As we look to the future, Farmonaut remains dedicated to innovating and improving our services to meet the evolving challenges of pest control in agriculture. Together, we can create a more resilient and productive farming ecosystem.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can help you in your fight against leafminers and other agricultural challenges, explore our services and subscribe to our platform:
Join us in revolutionizing agriculture and taking control of leafminer infestations with precision and efficiency.