Understanding and Controlling Armyworms and Cutworms: Protecting Crops from Moth Larvae Damage

In the world of agriculture, we often face numerous challenges that threaten our crops and livelihoods. Among these challenges, moth larvae, particularly armyworms and cutworms, pose a significant threat to various plants and crops. As experts in agricultural technology and pest management, we at Farmonaut understand the importance of addressing these issues effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of these destructive insects, their impact on agriculture, and how modern technology can help in their control.
Understanding Moths and Their Larvae
Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera, which also includes butterflies. The suborder Noctuoidea, particularly the family Noctuidae, contains many species that are agricultural pests. These moths, often referred to as owlet moths, are the parents of some of the most destructive agricultural pests: armyworms and cutworms.
The Life Cycle of Moth Pests
Understanding the life cycle of these pests is crucial for effective control. The cycle typically involves four stages:
- Egg: Adult moths lay eggs on plant leaves or soil.
- Larva: The eggs hatch into caterpillars, which are the destructive stage.
- Pupa: After several molts, the caterpillar enters the pupal stage.
- Adult: The pupa transforms into an adult moth, ready to mate and lay eggs.
It’s the larval stage that causes the most damage to crops, as these caterpillars have voracious appetites and can quickly defoliate plants.
Armyworms: The Marching Menace
Armyworms get their name from their behavior of moving in large groups, like an army, as they feed on crops. These pests can cause significant damage in a short period, often overnight.
Types of Armyworms
- Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
- Beet Armyworm (Spodoptera exigua)
- True Armyworm (Mythimna unipuncta)
Each species has its preferred host plants, but they can adapt to feed on various crops when their primary food source is scarce.
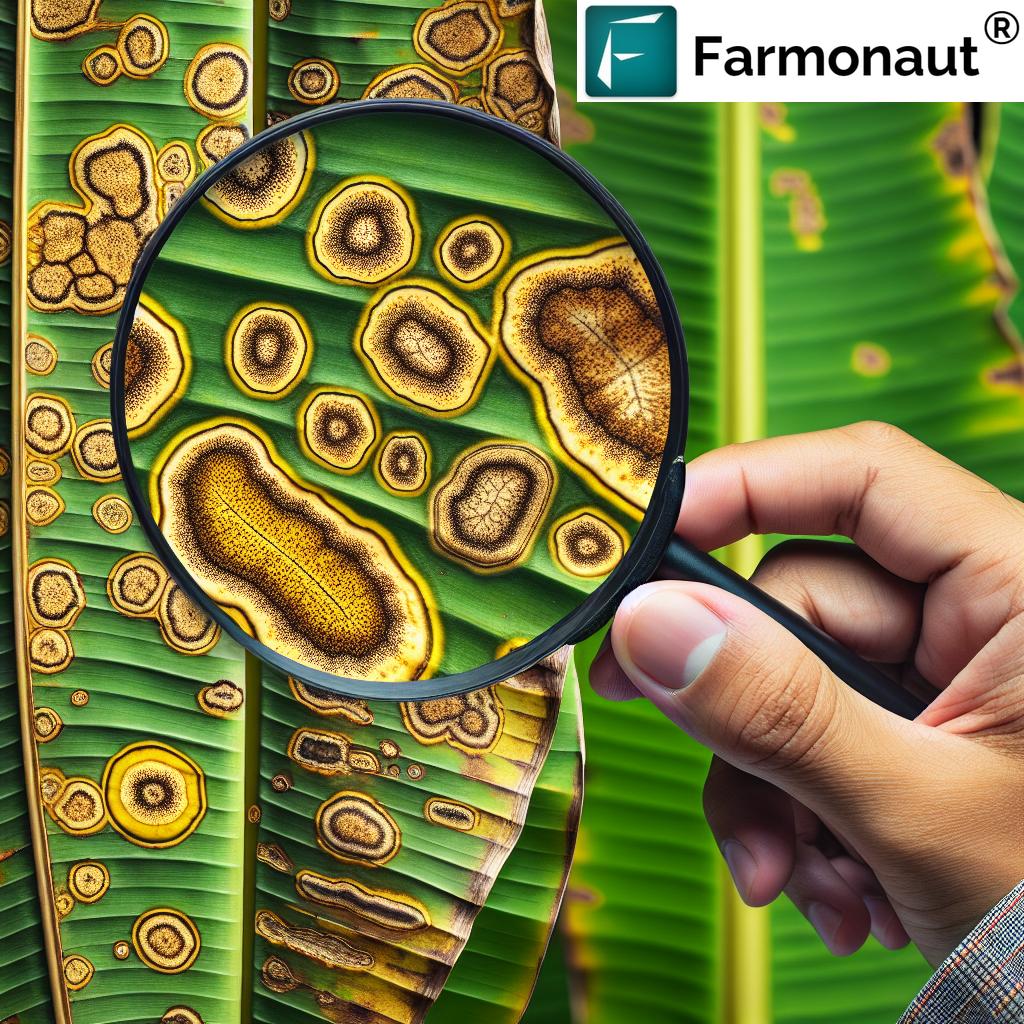
Identifying Armyworm Damage
Armyworm damage is characterized by:
- Irregular holes in leaves
- Skeletonized leaves (only veins remaining)
- Complete defoliation in severe cases
- Circular patches of destroyed crops in fields

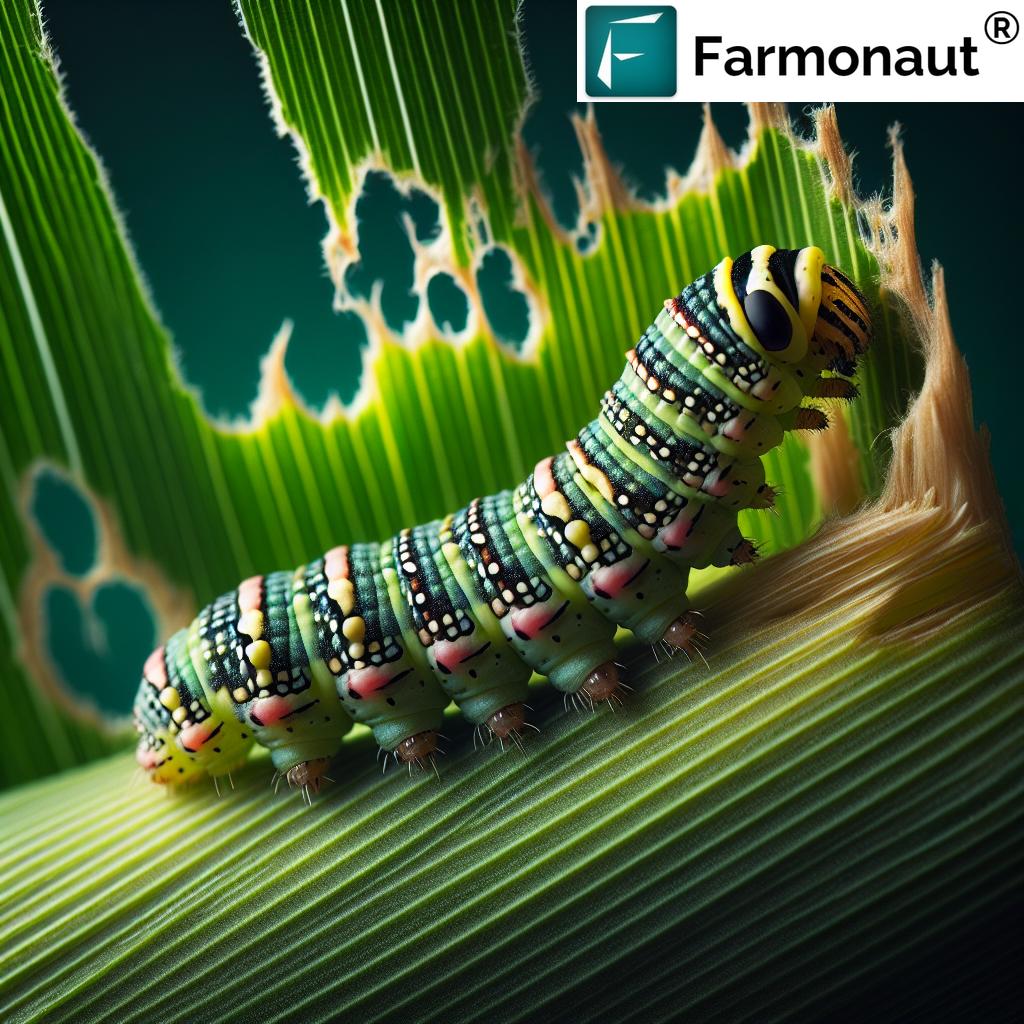
Cutworms: The Silent Killers
Cutworms are another group of moth larvae that can cause significant damage to crops. Unlike armyworms, cutworms tend to be solitary feeders, but their impact can be just as devastating.
Types of Cutworms
- Black Cutworm (Agrotis ipsilon)
- Variegated Cutworm (Peridroma saucia)
- Glassy Cutworm (Apamea devastator)
Identifying Cutworm Damage
Cutworm damage is often characterized by:
- Young plants cut off at or near the soil surface
- Irregular holes in leaves and stems
- Wilting or dying plants, especially in newly planted fields
The Economic Impact of Armyworms and Cutworms
The damage caused by these pests can have severe economic consequences for farmers and the agricultural industry as a whole. Some impacts include:
- Reduced crop yields
- Increased production costs due to pest control measures
- Potential loss of entire crops in severe infestations
- Negative effects on food security, especially in developing regions
At Farmonaut, we understand the gravity of these issues and are committed to providing solutions that help farmers mitigate these risks effectively.
Traditional Methods of Pest Control
Historically, farmers have used various methods to control armyworms and cutworms:
- Chemical Pesticides: While effective, these can have negative environmental impacts and may lead to pest resistance over time.
- Biological Control: Using natural predators or pathogens to control pest populations.
- Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, tillage, and adjusting planting dates to avoid peak pest seasons.
- Physical Barriers: Such as collars around young plants to prevent cutworm damage.
While these methods have their merits, they often require significant labor and can be challenging to implement effectively over large areas.
Farmonaut’s Innovative Approach to Pest Management
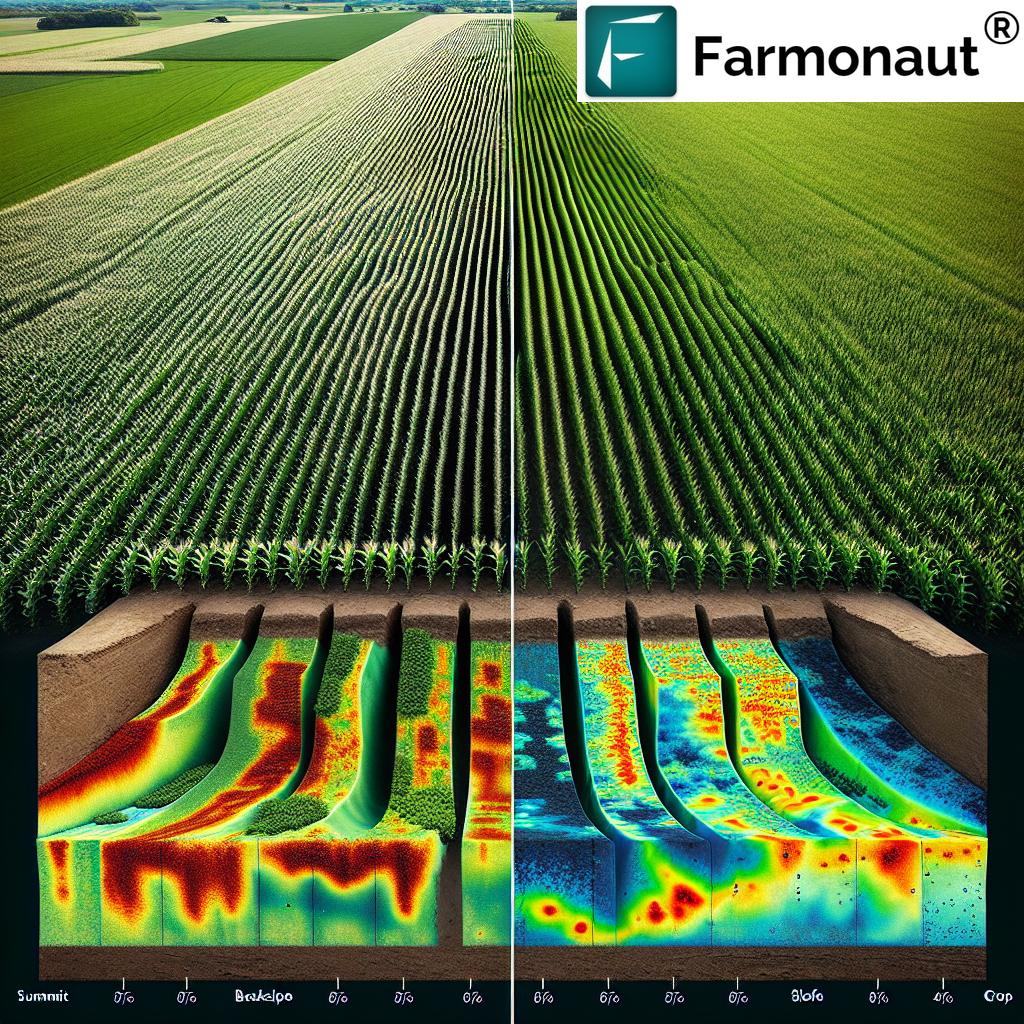
At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced technology to revolutionize pest management in agriculture. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers several advantages over traditional scouting methods:
| Feature | Traditional Scouting | Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based System |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Slow, manual process | Rapid, automated detection |
| Accuracy | Varies based on scout’s experience | High accuracy using AI and multispectral imagery |
| Coverage Area | Limited to physically scouted areas | Large-scale coverage of entire fields |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Labor-intensive and costly for large areas | Highly cost-effective, especially for large farms |
How Farmonaut’s Technology Works
- Satellite Imagery: We use high-resolution satellite imagery to monitor crop health across vast areas.
- AI Analysis: Our advanced AI algorithms analyze the imagery to detect signs of pest infestation, including changes in crop health indicative of armyworm or cutworm damage.
- Early Warning System: Farmers receive alerts when potential pest issues are detected, allowing for timely intervention.
- Precision Treatment: By identifying specific areas of infestation, we enable targeted pest control measures, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticide application.
To learn more about our satellite-based monitoring system, visit Farmonaut’s App.
Integrating Farmonaut’s Technology with Traditional Pest Control Methods
While our technology provides a significant advantage in early detection and monitoring, it’s most effective when integrated with traditional pest control methods. Here’s how farmers can combine these approaches:
- Targeted Scouting: Use Farmonaut’s alerts to guide in-person field inspections, focusing on areas flagged by our system.
- Precision Application: Apply pesticides or biological controls only to affected areas, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Timing Optimization: Use our weather forecasting and pest prediction models to time interventions for maximum effectiveness.
- Data-Driven Crop Planning: Utilize historical pest data from our system to inform crop rotation and planting decisions.
Case Study: Armyworm Control in Maize Fields
While we don’t provide specific case studies, we can discuss a hypothetical scenario to illustrate the potential of our technology:
A large maize farm in the Midwest was struggling with recurring armyworm infestations. By implementing Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, they were able to:
- Detect early signs of armyworm activity before visible damage occurred
- Reduce scouting time by 75% by focusing on high-risk areas identified by our system
- Decrease pesticide use by 40% through targeted application
- Improve crop yields by 15% due to timely interventions
This example demonstrates the potential impact of integrating advanced technology with traditional farming practices.
The Future of Pest Management in Agriculture
As we look to the future, the role of technology in pest management will only grow. At Farmonaut, we’re continually innovating to stay ahead of evolving challenges:
- Machine Learning Advancements: Improving our AI models to detect an even wider range of pests and diseases with greater accuracy.
- Integration with IoT Devices: Combining satellite data with ground-based sensors for even more precise monitoring.
- Predictive Analytics: Developing models to forecast pest outbreaks based on historical data and environmental factors.
- Automated Drone Scouting: Integrating drone technology for close-up inspections of flagged areas.
To stay updated on our latest innovations, check out our API documentation.
Sustainable Pest Management Practices
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to promoting sustainable agriculture. Our technology supports several eco-friendly pest management practices:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Our system supports the core principles of IPM by providing accurate, timely data for decision-making.
- Reduced Pesticide Use: By enabling targeted applications, we help reduce overall pesticide use in agriculture.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: Less reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides helps preserve beneficial insects and natural pest predators.
- Water Conservation: Our soil moisture monitoring helps optimize irrigation, indirectly supporting pest management by promoting healthy, resilient crops.
Empowering Farmers with Knowledge
We believe that knowledge is power in the fight against agricultural pests. That’s why we offer comprehensive resources to help farmers understand and manage armyworms, cutworms, and other moth larvae:
- Educational Webinars: Regular online sessions covering pest identification, lifecycle, and management strategies.
- In-App Guides: Detailed information on pest species and control methods available within our mobile app.
- Community Forums: A platform for farmers to share experiences and strategies for dealing with moth larvae infestations.
- Expert Consultations: Access to agricultural experts for personalized advice on pest management.
Download our app for Android from the Google Play Store or for iOS from the App Store to access these resources.
The Global Impact of Effective Pest Management
The battle against armyworms, cutworms, and other moth larvae is not just about protecting individual farms; it’s about ensuring global food security and sustainable agricultural practices. By leveraging technology to combat these pests effectively, we can:
- Increase global crop yields
- Reduce food waste due to pest damage
- Minimize the environmental impact of agriculture
- Support the livelihoods of farmers worldwide
- Contribute to more resilient and sustainable food systems
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How can I tell if my crops are infested with armyworms or cutworms?
A: Look for signs such as irregular holes in leaves, plants cut off at the base, or circular patches of damage in fields. Our satellite monitoring system can also help detect early signs of infestation before visible damage occurs.
Q: Are organic methods effective against these pests?
A: Yes, organic methods can be effective. These include biological controls (like predatory insects), cultural practices (crop rotation), and organic pesticides. Our system can help you time these interventions for maximum effectiveness.
Q: How often should I scout my fields for these pests?
A: Traditional recommendations vary, but with Farmonaut’s continuous monitoring, you can receive alerts as soon as potential issues are detected, allowing for more timely and targeted scouting.
Q: Can climate change affect armyworm and cutworm populations?
A: Yes, climate change can influence pest populations and distribution. Warmer temperatures may lead to increased reproduction rates and expanded geographical ranges for some species. Our predictive models take climate factors into account.
Q: How does Farmonaut’s technology differentiate between different types of pest damage?
A: Our AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets of pest damage patterns. While we can’t always distinguish between specific species, we can identify areas showing signs of pest activity, which can then be verified through targeted scouting.
Conclusion
The battle against armyworms, cutworms, and other destructive moth larvae is ongoing, but with the right tools and knowledge, it’s a battle we can win. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering farmers with cutting-edge technology and data-driven insights to protect their crops and livelihoods.
By combining our satellite-based monitoring system with traditional pest management practices, we can create a more resilient, sustainable, and productive agricultural system. Together, we can ensure food security for generations to come while minimizing our impact on the environment.
To learn more about how Farmonaut can help you protect your crops from moth larvae and other pests, visit our API documentation or subscribe to our services below:
Together, we can revolutionize pest management and secure a brighter future for agriculture worldwide.