Mastering Crop Health: Essential Guide to Pest, Disease, and Soil Management for Farmers and Growers

In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, maintaining optimal crop health is paramount for farmers and growers alike. At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges that come with managing pests, diseases, and soil conditions across various crops and fields. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to master crop health management, leveraging both traditional methods and cutting-edge technology.
Understanding the Foundations of Crop Health
Before delving into specific management strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental factors that contribute to crop health:
- Soil Quality: The foundation of plant growth and development
- Water Management: Ensuring optimal hydration without oversaturation
- Nutrient Balance: Providing essential elements for plant health
- Pest and Disease Control: Protecting crops from harmful organisms
- Environmental Conditions: Managing the impact of weather and climate
Soil Management: The Cornerstone of Crop Health
Healthy soil is the bedrock of successful crop production. Let’s explore the key aspects of soil management:
Soil Structure and Composition
Understanding your soil’s structure and composition is crucial for optimal plant growth. We recommend regular soil testing to assess:
- Soil texture (sand, silt, clay ratios)
- Organic matter content
- pH levels
- Nutrient composition
With this information, you can make informed decisions about soil amendments and fertilization strategies.
Soil pH Management
Soil pH plays a vital role in nutrient availability and plant health. Most crops prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range (6.0-7.0). Here are some tips for managing soil pH:
- Use lime to raise pH in acidic soils
- Apply sulfur to lower pH in alkaline soils
- Consider crop-specific pH requirements
- Monitor pH levels regularly throughout the growing season
Organic Matter and Soil Health
Increasing organic matter in your soil can significantly improve its overall health and fertility. Consider these practices:
- Implement crop rotation to diversify organic inputs
- Use cover crops to add biomass and protect soil
- Incorporate compost or well-rotted manure
- Practice minimal tillage to preserve soil structure
Water Management: Balancing Hydration and Drainage
Effective water management is critical for crop health and yield optimization. Here’s how to ensure your plants receive the right amount of water:
Irrigation Strategies
Choosing the right irrigation method can significantly impact water use efficiency and crop health:
- Drip irrigation for precise water delivery
- Sprinkler systems for broader coverage
- Furrow irrigation for row crops
- Subsurface irrigation for reduced evaporation
Monitoring Soil Moisture
Regular monitoring of soil moisture helps prevent both water stress and oversaturation. Consider using:
- Soil moisture sensors
- Tensiometers
- Remote sensing technology for large-scale monitoring
At Farmonaut, our satellite-based monitoring system provides real-time insights into soil moisture levels across your fields, enabling precise irrigation management. Learn more about our crop monitoring solutions.
Drainage Solutions
Proper drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging and root diseases. Consider these drainage improvements:
- Install tile drainage systems in poorly drained fields
- Create surface drainage channels
- Implement raised bed planting in heavy soils
Pest and Disease Management: Protecting Your Crops
Effective pest and disease control is crucial for maintaining crop health and maximizing yields. Let’s explore integrated pest management (IPM) strategies and disease prevention techniques.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various strategies to minimize pesticide use and environmental impact:
- Prevention: Use resistant varieties and maintain crop hygiene
- Monitoring: Regular scouting and pest population tracking
- Biological Control: Encourage natural predators and beneficial insects
- Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, intercropping, and sanitation
- Chemical Control: Targeted application of pesticides as a last resort
Common Crop Pests and Control Strategies
Let’s examine some widespread pests and effective management techniques:
Aphids
These small, soft-bodied insects can quickly multiply and damage crops by sucking sap and transmitting viruses.
- Encourage natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings
- Use insecticidal soaps or neem oil for organic control
- Apply systemic insecticides for severe infestations
Spider Mites
These tiny arachnids can cause significant damage to leaves, especially in hot, dry conditions.
- Maintain proper irrigation to prevent water stress
- Release predatory mites for biological control
- Apply miticides when populations exceed economic thresholds
Cutworms
These nocturnal caterpillars can sever young plants at the soil line.
- Use protective collars around seedlings
- Apply diatomaceous earth around plant bases
- Consider targeted insecticide applications for severe infestations
Disease Management Strategies
Preventing and managing crop diseases requires a multifaceted approach:
- Crop Rotation: Disrupt disease cycles by alternating crops
- Resistant Varieties: Choose cultivars with built-in disease resistance
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infected plant material
- Environmental Control: Manage humidity and leaf wetness in greenhouses
- Fungicide Application: Use preventative or curative treatments as needed
Common Crop Diseases and Their Management
Powdery Mildew
This fungal disease affects a wide range of crops, causing white, powdery growths on leaves and stems.
- Improve air circulation between plants
- Apply potassium bicarbonate or sulfur-based fungicides
- Use resistant varieties when available
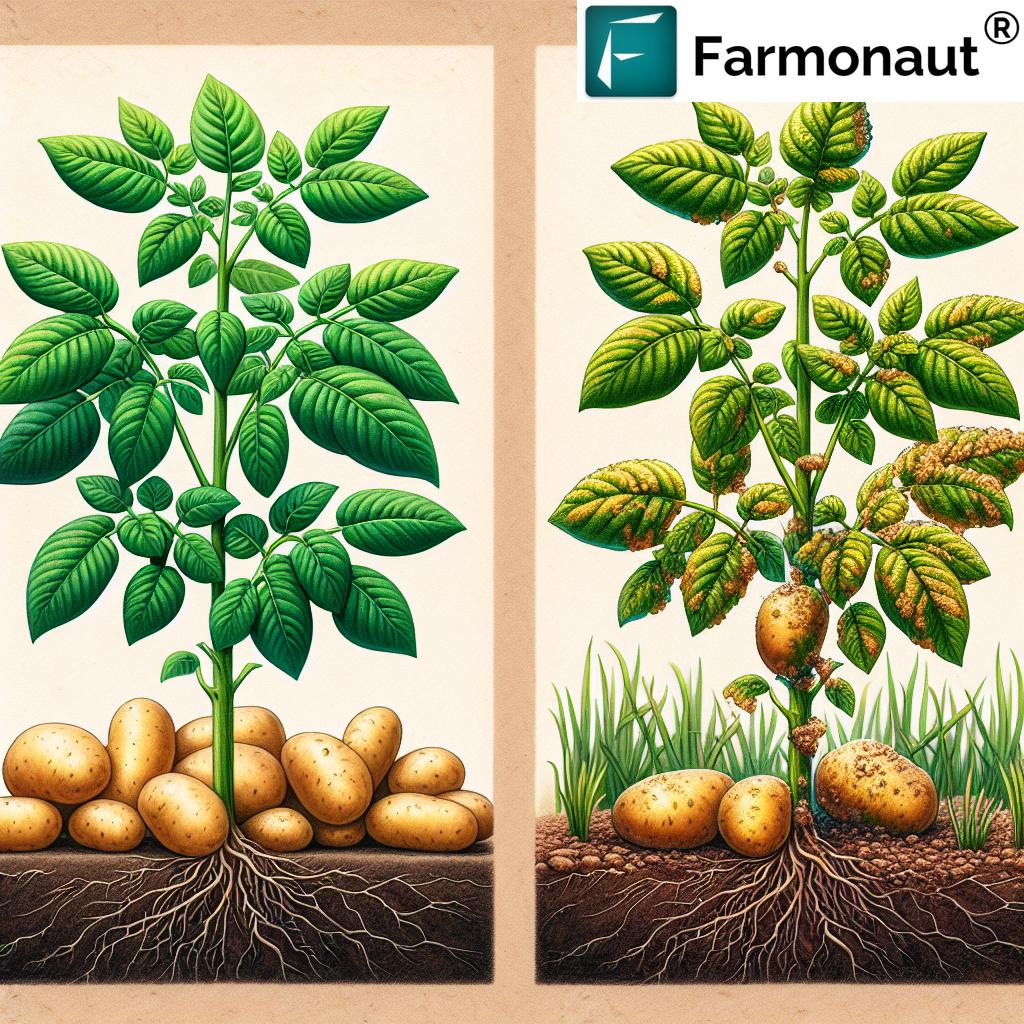
Late Blight
A devastating disease for potato and tomato crops, caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans.
- Plant certified disease-free seed potatoes
- Apply protective fungicides during high-risk periods
- Remove and destroy infected plants immediately
Fusarium Wilt
This soil-borne fungal disease affects various crops, causing wilting and yellowing of leaves.
- Practice crop rotation with non-susceptible plants
- Use resistant cultivars when available
- Solarize soil in severely infected areas
Leveraging Technology for Advanced Crop Health Management
At Farmonaut, we believe in harnessing the power of technology to revolutionize crop health management. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers farmers and growers unprecedented insights into their fields’ conditions.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Our advanced satellite imagery provides real-time data on:
- Vegetation health indices (e.g., NDVI)
- Soil moisture levels
- Crop stress detection
- Yield prediction
This information enables proactive decision-making and targeted interventions to optimize crop health and productivity. Explore our satellite-based crop monitoring solutions.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI system analyzes satellite data, weather forecasts, and historical trends to provide personalized crop management recommendations, including:
- Optimal planting dates
- Irrigation scheduling
- Fertilizer application timing
- Pest and disease risk alerts
Comparison: Traditional Scouting vs. Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Monitoring
| Aspect | Traditional Scouting | Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Limited to accessible areas | Comprehensive field-wide coverage |
| Frequency | Periodic, labor-intensive | Continuous, real-time updates |
| Data Analysis | Manual, potentially subjective | AI-powered, objective analysis |
| Early Detection | May miss early-stage issues | Detects subtle changes in crop health |
| Resource Efficiency | Time and labor-intensive | Time-saving, cost-effective |
| Historical Data | Limited by manual record-keeping | Comprehensive historical data for trend analysis |
By integrating Farmonaut’s technology with traditional farming practices, growers can achieve unprecedented levels of precision in crop health management.
Crop-Specific Health Management Strategies
While general principles apply across crops, certain plants have unique requirements and challenges. Let’s explore health management strategies for some common crops:
Soybean Health Management
Soybeans are a crucial global crop, requiring careful management to maximize yields:
- Soil Preparation: Ensure well-drained soils with pH 6.0-6.8
- Pest Management: Monitor for soybean aphids and spider mites
- Disease Control: Implement strategies to prevent sudden death syndrome and white mold
- Nutrient Management: Focus on nitrogen fixation and phosphorus availability
Potato Crop Health
Potatoes are susceptible to various pests and diseases, requiring vigilant management:
- Soil Health: Maintain well-drained, slightly acidic soils (pH 5.8-6.5)
- Disease Prevention: Implement strategies to control late blight and early blight
- Pest Control: Monitor for Colorado potato beetles and aphids
- Storage Management: Proper curing and storage conditions to prevent post-harvest diseases
Fruit Tree Health
Orchards require long-term management strategies for optimal health and productivity:
- Pruning: Regular pruning for air circulation and light penetration
- Pest Management: Implement IPM strategies for codling moths, aphids, and scale insects
- Disease Control: Monitor and treat for fire blight, apple scab, and brown rot
- Soil and Nutrient Management: Maintain proper pH and nutrient levels for tree health
Sustainable Practices for Long-Term Crop Health
Implementing sustainable practices not only promotes crop health but also ensures the long-term viability of agricultural operations:
Conservation Tillage
Reducing tillage helps preserve soil structure, retain moisture, and promote beneficial soil microorganisms. Consider:
- No-till planting
- Strip-till methods
- Mulch-till practices
Cover Cropping
Planting cover crops between main crop seasons offers numerous benefits:
- Improved soil structure and organic matter content
- Reduced erosion and nutrient leaching
- Natural weed suppression
- Enhanced biodiversity and beneficial insect habitat
Precision Agriculture Techniques
Leveraging technology for precise resource management:
- Variable-rate fertilizer application
- Site-specific pest management
- Precision irrigation systems
Our satellite-based monitoring system at Farmonaut supports these precision agriculture techniques by providing detailed, field-specific data. Learn how our technology can enhance your precision agriculture efforts.
Weather Monitoring and Climate Adaptation
As climate patterns become increasingly unpredictable, adapting to weather conditions is crucial for maintaining crop health:
Weather Monitoring Tools
Utilize advanced weather monitoring systems to make informed decisions:
- On-site weather stations
- Satellite-based weather forecasting
- Crop-specific climate models
Farmonaut’s platform integrates real-time weather data with crop health information, enabling farmers to anticipate and mitigate weather-related risks. Explore our weather API for developers.
Climate Adaptation Strategies
Implement long-term strategies to adapt to changing climate conditions:
- Diversify crop varieties and planting dates
- Improve water management and storage systems
- Adopt heat and drought-tolerant crop varieties
- Implement agroforestry practices for microclimate management
Continuous Learning and Improvement
The field of agriculture is constantly evolving, with new research and technologies emerging regularly. To stay at the forefront of crop health management:
- Attend agricultural workshops and conferences
- Participate in farmer networks and discussion groups
- Collaborate with local agricultural extension services
- Engage in on-farm trials and experiments
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in their continuous learning journey. Our platform not only provides valuable data but also offers insights and recommendations based on the latest agricultural research.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to Crop Health
Mastering crop health management requires a comprehensive understanding of soil health, water management, pest and disease control, and environmental factors. By combining traditional agricultural wisdom with cutting-edge technology, farmers and growers can optimize their crop health strategies for improved yields, sustainability, and profitability.
Remember, every field is unique, and successful crop health management often involves tailoring general principles to your specific conditions. Regular monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and a willingness to adapt are key to long-term success in agriculture.
At Farmonaut, we’re dedicated to empowering farmers with the tools and information they need to excel in crop health management. Our satellite-based monitoring system, AI-powered advisory services, and commitment to continuous innovation make us your ideal partner in navigating the complexities of modern agriculture.
Ready to take your crop health management to the next level? Explore our solutions and start your journey towards precision agriculture today.
FAQs: Crop Health Management
1. How often should I scout my fields for pests and diseases?
Regular scouting is crucial for early detection of issues. We recommend scouting at least once a week during the growing season, and more frequently during critical growth stages or when pest pressure is high. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can complement physical scouting with daily remote sensing data for comprehensive coverage.
2. What are the signs of nutrient deficiency in crops?
Common signs include yellowing leaves (chlorosis), stunted growth, and unusual coloration of leaves. Specific symptoms can vary by nutrient and crop type. Our satellite imagery can detect early signs of stress, potentially indicating nutrient deficiencies before they become visible to the naked eye.
3. How can I improve soil health in my fields?
Implement practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, minimal tillage, and organic matter incorporation. Regular soil testing and pH management are also crucial. Farmonaut’s soil moisture monitoring can help you optimize irrigation and prevent issues related to over or under-watering.
4. What is the best way to manage water in drought conditions?
Implement efficient irrigation systems, use drought-tolerant crop varieties, and practice soil moisture conservation techniques like mulching. Our satellite-based soil moisture monitoring can help you make precise irrigation decisions, even in drought conditions.
5. How can technology help in pest and disease management?
Technologies like satellite imaging, AI-powered advisory systems, and weather forecasting can provide early warnings of pest and disease risks. Farmonaut’s platform integrates these technologies to offer comprehensive crop health monitoring and predictive analytics for proactive management.
6. What are some sustainable alternatives to chemical pesticides?
Consider biological control agents, companion planting, pheromone traps, and cultural practices like crop rotation. Our AI advisory system can suggest integrated pest management strategies tailored to your specific crop and conditions.
7. How does climate change affect crop health management?
Climate change can alter pest and disease patterns, affect water availability, and impact crop growth cycles. Adapting to these changes requires flexible management strategies and robust monitoring systems. Farmonaut’s platform helps farmers track and respond to changing environmental conditions in real-time.
8. What role does crop rotation play in maintaining soil and plant health?
Crop rotation helps break pest and disease cycles, improves soil structure, and balances nutrient use. Our platform can help you plan effective rotation strategies based on historical field data and crop-specific requirements.
9. How can I effectively manage weeds without overusing herbicides?
Implement integrated weed management strategies including mechanical control, cover cropping, and precision herbicide application. Farmonaut’s satellite imagery can help identify areas of weed pressure for targeted treatment.
10. What are the benefits of precision agriculture in crop health management?
Precision agriculture allows for targeted resource application, reducing waste and environmental impact while optimizing crop health and yield. Farmonaut’s technology enables precision agriculture by providing detailed, field-specific data for informed decision-making.