Mastering Crop Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Plant Diseases, Pests, and Disorders in Agriculture and Horticulture

In the ever-evolving world of agriculture and horticulture, understanding and managing plant diseases, pests, and disorders is crucial for ensuring healthy crops and maximizing yields. At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of this knowledge and its application in modern farming practices. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore a wide range of common plant health issues and provide insights into their identification, prevention, and management.
The Importance of Plant Health in Agriculture
Maintaining plant health is fundamental to successful crop production. Healthy plants are more resistant to diseases and pests, use resources more efficiently, and ultimately produce higher yields. However, various factors can compromise plant health, including:
- Pathogens (bacteria, fungi, viruses)
- Insect pests
- Nutrient deficiencies
- Environmental stressors
- Genetic disorders
Understanding these threats and implementing effective management strategies is essential for sustainable agriculture. Let’s delve into some of the most common plant health issues faced by farmers and horticulturists.
Common Leaf Diseases and Disorders
1. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of crops, including cucurbits, grapes, and apples. It appears as a white, powdery coating on leaves, stems, and sometimes fruits.
- Symptoms: White, powdery spots on leaves and stems
- Causes: Fungal spores spread by wind
- Management: Proper plant spacing, resistant varieties, fungicides when necessary
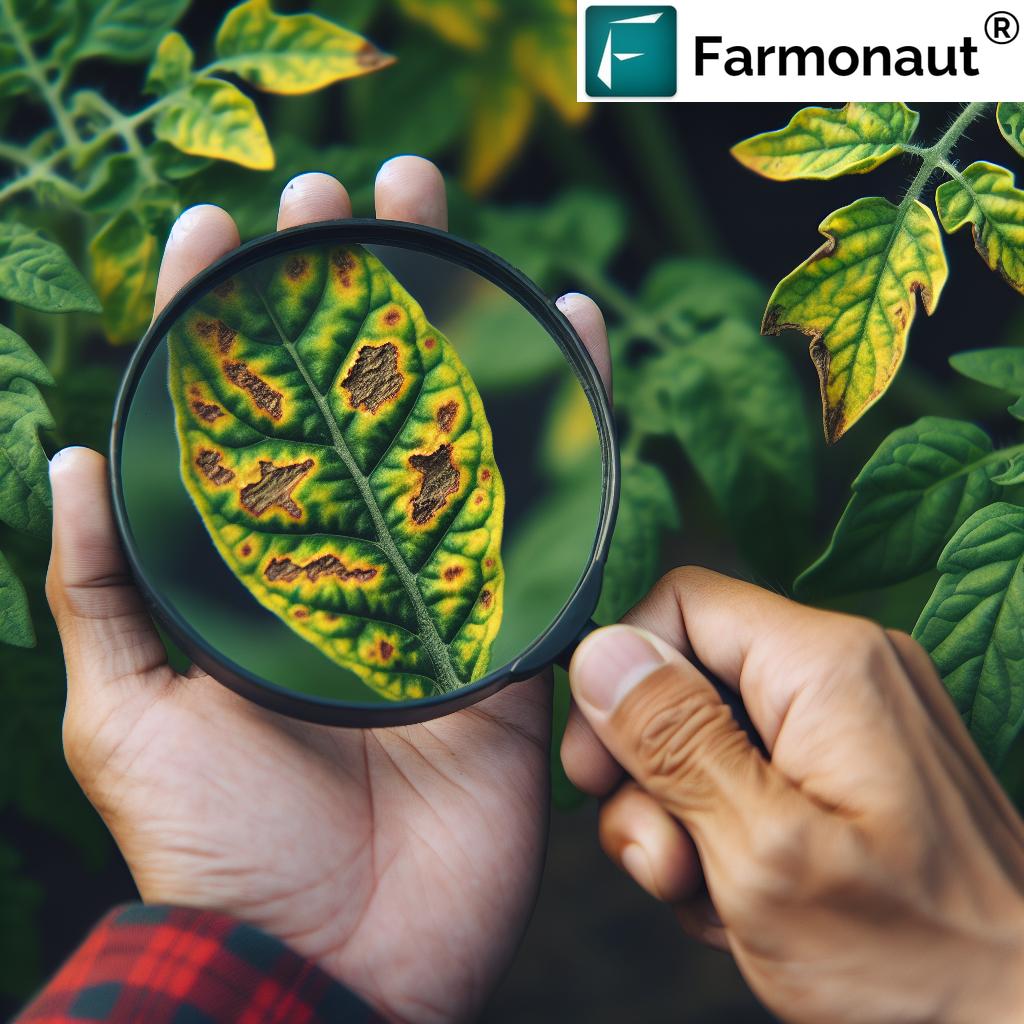
2. Leaf Spot Diseases
Leaf spot diseases can be caused by various fungi and bacteria. They manifest as distinct spots on leaves, often leading to defoliation if left untreated.
- Symptoms: Circular or irregular spots on leaves, often with a yellow halo
- Causes: Various pathogens, often spread by water splash or wind
- Management: Crop rotation, proper sanitation, fungicides or bactericides as needed
3. Mosaic Viruses
Mosaic viruses affect many crops, causing distinctive mottled patterns on leaves. Common examples include Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) and Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV).
- Symptoms: Mottled light and dark green patterns on leaves, stunted growth
- Causes: Viruses transmitted by insects or through mechanical means
- Management: Use of virus-free seeds, control of insect vectors, removal of infected plants
4. Leaf Curl
Leaf curl can be caused by various factors, including viral infections, insect damage, or environmental stress.
- Symptoms: Curling, twisting, or distortion of leaves
- Causes: Viruses, aphids, mites, or environmental factors
- Management: Depends on the cause – may include pest control, virus management, or adjusting growing conditions
Fruit and Vegetable Specific Diseases
1. Citrus Canker
Citrus canker is a serious bacterial disease affecting citrus fruits, causing lesions on leaves, stems, and fruits.
- Symptoms: Raised, brown lesions surrounded by an oily, water-soaked margin and yellow ring
- Causes: Bacterium Xanthomonas axonopodis
- Management: Quarantine measures, removal of infected trees, copper-based sprays
2. Tomato Blight
Both early and late blight are significant diseases in tomato cultivation.
- Symptoms: Dark spots on leaves, stems, and fruits; can lead to rapid plant death
- Causes: Fungi (Alternaria solani for early blight, Phytophthora infestans for late blight)
- Management: Crop rotation, resistant varieties, fungicides, proper plant spacing
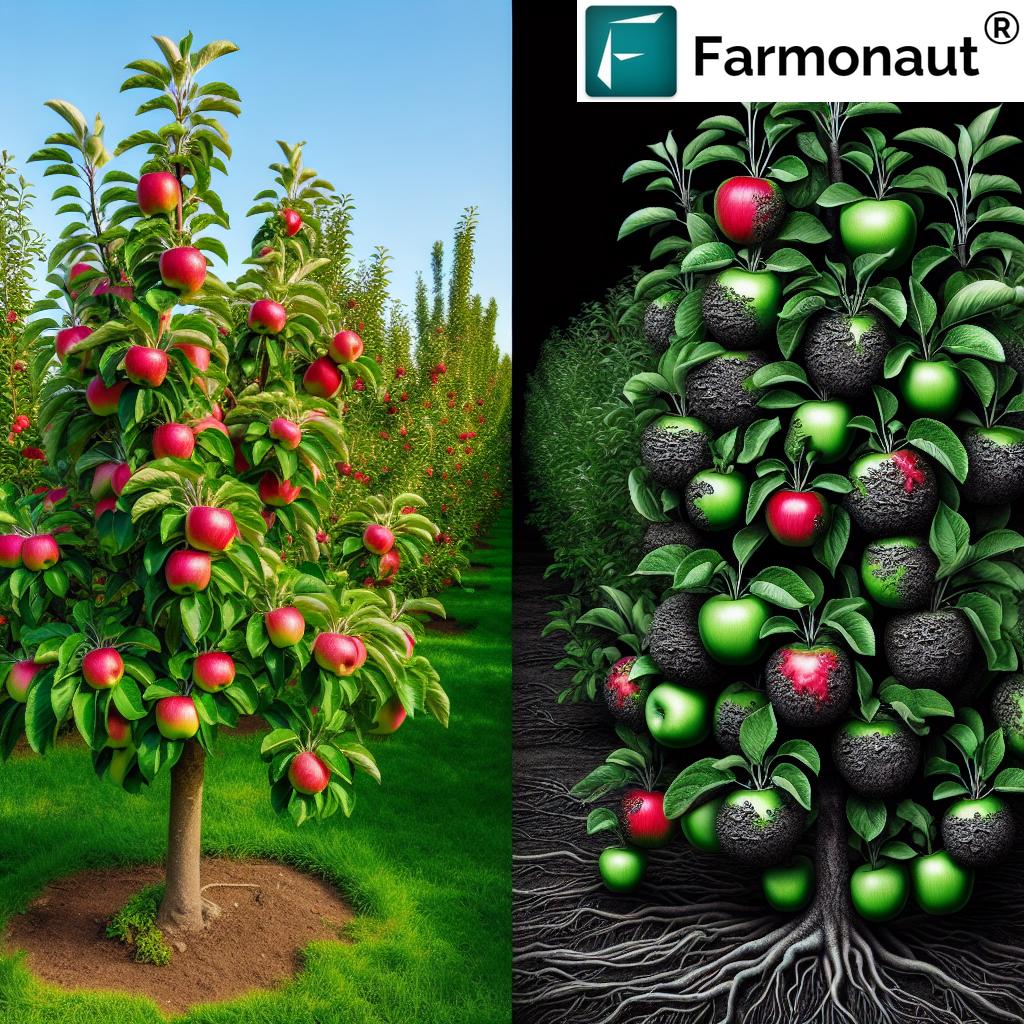
3. Apple Scab
Apple scab is a fungal disease that affects apple and pear trees, causing unsightly lesions on fruits and leaves.
- Symptoms: Olive-green to black scab-like lesions on leaves and fruits
- Causes: Fungus Venturia inaequalis
- Management: Resistant varieties, proper pruning for air circulation, fungicide applications
4. Banana Sigatoka
Sigatoka diseases, including Yellow Sigatoka and Black Sigatoka, are major threats to banana production worldwide.
- Symptoms: Yellow or black streaks on leaves, leading to leaf necrosis
- Causes: Fungi (Mycosphaerella musicola for Yellow Sigatoka, M. fijiensis for Black Sigatoka)
- Management: Resistant varieties, leaf pruning, fungicide applications
Common Crop Pests
1. Aphids
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap and can transmit viruses.
- Symptoms: Curled leaves, stunted growth, sticky honeydew on leaves
- Management: Beneficial insects, insecticidal soaps, neem oil
2. Scale Insects
Scale insects, including armored scales, are small, immobile pests that attach themselves to plant parts and suck sap.
- Symptoms: Small, bump-like structures on stems and leaves, yellowing of leaves
- Management: Horticultural oils, pruning of infested parts, biological controls
3. Fruit Flies
Fruit flies are a major pest for many fruit crops, laying eggs in ripening fruits.
- Symptoms: Small punctures in fruits, maggots inside fruits
- Management: Traps, proper sanitation, bagging of fruits, insecticides
4. Codling Moth
The codling moth is a significant pest of apples and pears.
- Symptoms: “Wormy” apples with tunnels to the core
- Management: Pheromone disruption, timely insecticide applications, orchard sanitation
Nutrient Deficiencies and Disorders
1. Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen is crucial for leaf growth and overall plant vigor.
- Symptoms: Yellowing of older leaves, stunted growth
- Management: Application of nitrogen-rich fertilizers, cover crops
2. Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency often occurs in alkaline soils or overwatered conditions.
- Symptoms: Interveinal chlorosis, particularly in young leaves
- Management: Iron supplements, adjusting soil pH
3. Blossom End Rot
Blossom end rot is a physiological disorder often seen in tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants.
- Symptoms: Dark, sunken areas at the blossom end of fruits
- Causes: Calcium deficiency, often due to irregular watering
- Management: Consistent watering, calcium supplements, mulching
Emerging Threats in Crop Protection
1. Fall Armyworm
The fall armyworm has become a significant threat to crops worldwide, particularly in maize production.
- Symptoms: Ragged leaf edges, holes in leaves, damage to corn ears
- Management: Early detection, targeted insecticides, biological controls
2. Citrus Greening (Huanglongbing)
Citrus greening is a devastating bacterial disease affecting citrus crops globally.
- Symptoms: Mottled leaves, misshapen and bitter fruits, tree decline
- Causes: Bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter, spread by psyllids
- Management: Vector control, removal of infected trees, quarantine measures
Sustainable Pest and Disease Management Strategies
At Farmonaut, we advocate for integrated pest management (IPM) approaches that combine various strategies to manage pests and diseases effectively while minimizing environmental impact:
- Cultural practices: Crop rotation, proper plant spacing, sanitation
- Biological control: Encouraging beneficial insects, using microbial pesticides
- Chemical control: Judicious use of pesticides when necessary
- Resistant varieties: Planting disease-resistant crop varieties
- Monitoring and early detection: Regular field scouting and use of advanced technologies
The Role of Technology in Crop Protection
Modern agriculture increasingly relies on technology for effective crop protection. At Farmonaut, we leverage satellite imagery and AI to provide farmers with valuable insights:
- Early detection of crop stress and potential disease outbreaks
- Monitoring of crop health over large areas
- Precision application of treatments based on real-time data
- Historical analysis to predict and prevent recurring issues
Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers significant advantages over traditional scouting methods:
| Feature | Traditional Scouting | Farmonaut’s Satellite Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Limited to physically accessible areas | Entire field or farm, regardless of size |
| Frequency | Periodic, labor-intensive | Regular updates based on satellite passes |
| Early Detection | May miss early signs of stress | Can detect subtle changes in crop health |
| Cost-effectiveness | Labor and time-intensive | Automated and efficient |
| Data Analysis | Manual, subject to human error | AI-powered, consistent and objective |
| Historical Tracking | Limited by record-keeping | Comprehensive historical data available |
To learn more about how Farmonaut can help you protect your crops, visit our application page or explore our API services.
Case Studies: Successful Crop Protection Strategies
While we don’t include specific case studies or success stories, we can highlight general scenarios where effective crop protection strategies have made a significant difference:
- Implementing IPM in apple orchards to manage codling moth populations
- Using resistant varieties and cultural practices to control powdery mildew in vineyard
- Combining biological controls and targeted spraying to manage aphids in vegetable crops
- Leveraging satellite monitoring for early detection of crop stress in large-scale farming operations
Future Trends in Crop Protection
The field of crop protection is continually evolving. Some emerging trends include:
- Gene editing for disease resistance
- Nanotechnology in pest control
- AI and machine learning for pest and disease prediction
- Drone technology for precision application of treatments
- Climate-smart agriculture practices for pest and disease management
Conclusion
Effective crop protection is a cornerstone of successful agriculture and horticulture. By understanding common plant diseases, pests, and disorders, and implementing integrated management strategies, farmers and growers can significantly improve their crop health and yields. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting these efforts through our advanced satellite-based monitoring systems and AI-driven insights.
For more information on how our technology can enhance your crop protection strategies, download our app from the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store.
FAQs
- Q: How often should I scout my fields for pests and diseases?
A: Regular scouting is crucial, typically weekly during the growing season. However, with Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can get continuous updates on crop health. - Q: Are organic methods effective for pest and disease control?
A: Yes, many organic methods can be highly effective when used as part of an integrated pest management strategy. - Q: How can I differentiate between nutrient deficiencies and disease symptoms?
A: This can be challenging, but generally, nutrient deficiencies show patterns across the plant, while diseases often appear as localized symptoms. Our AI-powered system can help in accurate identification. - Q: Is climate change affecting pest and disease patterns?
A: Yes, climate change is altering pest and disease distributions and life cycles. This makes monitoring and adaptable management strategies even more crucial. - Q: How can small-scale farmers benefit from advanced crop protection technologies?
A: Farmonaut offers affordable solutions scalable to farms of all sizes, making advanced crop protection accessible to small-scale farmers.
For more detailed information on our satellite and weather API services, please refer to our developer documentation.
Ready to take your crop protection to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut’s services: