Maximizing Agricultural Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Land Utilisation, Suitability, and Productivity

In today’s world, where food security and sustainable agriculture are paramount concerns, understanding and optimizing land utilisation for agriculture has become more critical than ever. As we navigate the complexities of feeding a growing global population while preserving our planet’s resources, it’s essential to delve deep into the concepts of land suitability, land categorisation, and the identification of highly productive land. In this comprehensive guide, we at Farmonaut will explore these crucial aspects of modern agriculture, shedding light on how technology and data-driven insights are revolutionizing the way we approach farming.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Land Utilisation in Agriculture
- The Importance of Land Categorisation
- Decoding Land Cover Types
- The Role of Land Grade Maps in Agriculture
- Assessing Land Suitability for Optimal Crop Production
- Identifying and Maximizing Highly Productive Land
- Technological Advancements in Agricultural Land Management
- Farmonaut’s Contribution to Precision Agriculture
- FAQs
1. Understanding Land Utilisation in Agriculture
Land utilisation in agriculture refers to the way we use land resources for farming purposes. It’s a critical concept that helps us understand how much land is used for agriculture globally and how efficiently we’re using these resources. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately 38% of the Earth’s land surface is used for agriculture. This includes both cropland and pastures for livestock.
Efficient land utilisation is crucial for several reasons:
- Food Security: Proper land use ensures we can produce enough food to feed the world’s growing population.
- Environmental Conservation: Optimizing land use can help reduce deforestation and preserve natural habitats.
- Economic Stability: Agriculture is a significant economic driver in many countries, making efficient land use vital for economic stability.
- Sustainable Development: Proper land utilisation contributes to sustainable development goals, balancing human needs with environmental conservation.
At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of efficient land utilisation. Our satellite-based farm management solutions provide farmers with real-time data on their land, helping them make informed decisions about crop placement, resource allocation, and overall farm management.
2. The Importance of Land Categorisation
Land categorisation is a fundamental concept in agriculture that involves classifying land based on its characteristics and potential for different uses. This process is crucial for effective land management and agricultural planning.
The main categories of agricultural land typically include:
- Arable Land: Suitable for growing crops
- Pasture Land: Used for grazing livestock
- Permanent Crop Land: Land used for crops that occupy the area for long periods
- Forest Land: Areas covered with trees, which can sometimes be used for agroforestry
- Other Land: Including built-up areas, barren land, etc.
Land categorisation helps in:
- Optimizing Land Use: By understanding the potential of different land types, we can make better decisions about how to use each area.
- Resource Allocation: It helps in allocating resources more efficiently based on the land’s potential.
- Policy Making: Governments use land categorisation data to formulate agricultural policies and land use regulations.
- Conservation Efforts: It aids in identifying areas that need protection or conservation.
At Farmonaut, our advanced satellite imagery and AI-driven analysis help in accurate land categorisation. This information is crucial for our users to make informed decisions about crop selection and land management strategies.
3. Decoding Land Cover Types
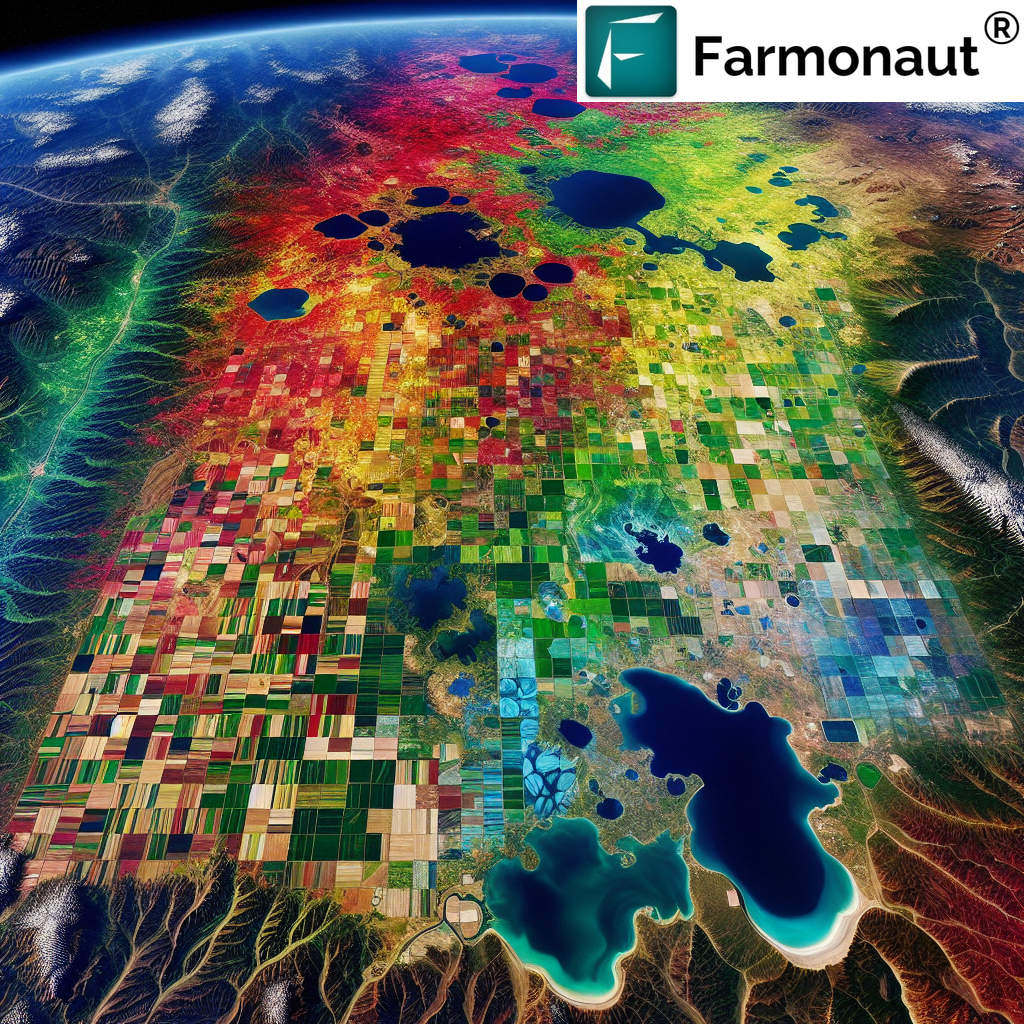
Land cover type refers to the physical material at the surface of the earth. It includes various categories such as grass, asphalt, trees, bare ground, water, etc. Understanding land cover types is crucial in agriculture for several reasons:
- Crop Suitability: Different crops thrive in different land cover types.
- Water Management: Land cover affects water retention and runoff patterns.
- Soil Health: The type of land cover influences soil composition and health.
- Biodiversity: Land cover types play a role in supporting various ecosystems.
- Climate Impact: Different land covers have varying effects on local and global climate patterns.
Common agricultural land cover types include:
- Cropland: Areas used for growing crops
- Grassland: Natural or managed areas dominated by grasses
- Forest: Areas covered with trees, which can sometimes be used for agroforestry
- Wetlands: Areas where water covers the soil or is present at or near the surface for significant periods
- Bare Soil: Exposed soil areas, which may be transitional or permanent
At Farmonaut, we use advanced satellite imagery and machine learning algorithms to accurately identify and map different land cover types. This information is crucial for our users to make informed decisions about land use and crop selection.
4. The Role of Land Grade Maps in Agriculture
A land grade map is a valuable tool in agriculture that classifies land based on its agricultural potential. These maps take into account various factors such as soil quality, climate, topography, and drainage to categorize land into different grades.
The importance of land grade maps in agriculture includes:
- Informed Decision Making: Farmers can make better decisions about crop selection and land use based on the land grade.
- Resource Allocation: It helps in allocating resources more efficiently, focusing efforts on areas with the highest potential.
- Land Valuation: Land grade maps are often used in land valuation for buying, selling, or leasing agricultural land.
- Policy Making: Governments use these maps for agricultural policy formulation and land use planning.
- Conservation Efforts: They help identify prime agricultural land that should be protected from non-agricultural development.
At Farmonaut, we integrate land grade information into our satellite-based farm management system. This allows our users to visualize their land’s potential and make data-driven decisions about crop selection and management practices.
5. Assessing Land Suitability for Optimal Crop Production
Land suitability assessment is a crucial process in agriculture that determines how well a piece of land is suited for a specific use, such as growing a particular crop. This assessment takes into account various factors including soil characteristics, climate, topography, and socio-economic conditions.
Key factors considered in land suitability assessment include:
- Soil Properties: Texture, depth, pH, nutrient content, and organic matter
- Climate: Temperature, rainfall, humidity, and growing season length
- Topography: Slope, aspect, and elevation
- Water Availability: Both natural precipitation and irrigation potential
- Socio-economic Factors: Market access, labor availability, and local agricultural practices
The benefits of conducting land suitability assessments include:
- Optimized Crop Selection: Farmers can choose crops that are best suited to their land conditions.
- Increased Productivity: By matching crops to suitable land, yields can be significantly improved.
- Resource Efficiency: It helps in more efficient use of water, fertilizers, and other inputs.
- Risk Reduction: Understanding land suitability can help mitigate risks associated with crop failure.
- Sustainable Land Use: It promotes sustainable land use practices by aligning agricultural activities with land capabilities.
At Farmonaut, we utilize advanced satellite imagery and AI algorithms to provide detailed land suitability assessments. Our platform integrates this information with real-time crop health monitoring, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about crop selection and management practices.
6. Identifying and Maximizing Highly Productive Land
Highly productive land is a valuable resource in agriculture, capable of producing high crop yields with minimal inputs. Identifying and maximizing the use of such land is crucial for sustainable agriculture and food security.
Characteristics of highly productive land often include:
- Rich, fertile soil with good structure and nutrient content
- Adequate and reliable water supply
- Favorable climate conditions for crop growth
- Gentle slopes or flat terrain for easy cultivation
- Good drainage to prevent waterlogging
Strategies for maximizing highly productive land include:
- Crop Rotation: This practice helps maintain soil fertility and prevents pest and disease buildup.
- Precision Agriculture: Using technology to apply inputs precisely where and when they’re needed.
- Soil Conservation: Implementing practices like contour plowing and cover cropping to prevent soil erosion.
- Efficient Irrigation: Using modern irrigation techniques to optimize water use.
- Integrated Pest Management: Combining biological, cultural, and chemical methods to manage pests effectively.
At Farmonaut, we provide tools that help farmers identify and maximize their highly productive land. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system allows for early detection of issues, enabling timely interventions to maintain high productivity.
7. Technological Advancements in Agricultural Land Management
The agricultural sector has seen significant technological advancements in recent years, revolutionizing the way we manage and utilize agricultural land. These technologies are helping farmers make more informed decisions, increase productivity, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Key technological advancements include:
- Satellite Imagery: Provides real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical metrics.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Analyzes vast amounts of data to provide actionable insights.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connects various farm devices for real-time monitoring and automated actions.
- Drones: Offers detailed aerial imagery and can be used for precision application of inputs.
- GPS and GIS Technologies: Enables precise mapping and navigation for various farm operations.
- Blockchain: Ensures transparency and traceability in the agricultural supply chain.
These technologies offer numerous benefits:
- Improved Decision Making: Farmers can make data-driven decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
- Resource Optimization: Precision application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides reduces waste and environmental impact.
- Increased Productivity: Early detection of issues and optimized farming practices lead to higher yields.
- Risk Mitigation: Advanced weather forecasting and crop monitoring help farmers prepare for and mitigate risks.
- Sustainability: Efficient resource use and reduced environmental impact promote sustainable farming practices.
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of these technological advancements. Our platform integrates satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain technology to provide comprehensive farm management solutions.
8. Farmonaut’s Contribution to Precision Agriculture
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide. Our advanced satellite-based farm management solutions leverage cutting-edge technology to provide valuable insights and tools for efficient farm management.
Key features of Farmonaut’s platform include:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: We use multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI-driven personalized farm advisory tool delivers real-time insights, weather forecasts, and expert crop management strategies.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: We enable traceability solutions for various industries, particularly agriculture, ensuring transparency and security in supply chains.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Our tools help agribusinesses manage their logistics more efficiently, reducing operational costs.
- Carbon Footprinting: We offer carbon footprint tracking to help agribusinesses monitor and reduce their environmental impact.
Here’s how Farmonaut’s Satellite System compares to drone and IoT-based farm monitoring:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large (entire farms) | Medium | Small (point-based) |
| Frequency of Data | Daily to weekly | On-demand | Real-time |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium |
| Maintenance Required | Minimal | Regular | Regular |
| Weather Dependency | Low | High | Low |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Moderately scalable | Limited scalability |
To learn more about our services or to start using Farmonaut, visit our app or check out our API documentation. You can also download our mobile app for Android or iOS.
For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data into their systems, please refer to our API developer documentation.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
FAQs
Q1: What is land utilisation in agriculture?
A1: Land utilisation in agriculture refers to how land resources are used for farming purposes. It involves understanding how much land is used for agriculture globally and how efficiently these resources are being used.
Q2: Why is land categorisation important in agriculture?
A2: Land categorisation is important because it helps in optimizing land use, allocating resources efficiently, informing policy-making, and guiding conservation efforts. It allows farmers and policymakers to make informed decisions about how to best use different types of land.
Q3: What are land cover types and why are they important in agriculture?
A3: Land cover types refer to the physical material at the surface of the earth, such as grass, asphalt, trees, bare ground, or water. In agriculture, understanding land cover types is crucial for determining crop suitability, managing water resources, maintaining soil health, and supporting biodiversity.
Q4: What is a land grade map?
A4: A land grade map is a tool that classifies land based on its agricultural potential. It takes into account factors such as soil quality, climate, topography, and drainage to categorize land into different grades. These maps are valuable for informed decision-making, resource allocation, and land valuation in agriculture.
Q5: How does Farmonaut contribute to precision agriculture?
A5: Farmonaut contributes to precision agriculture by providing advanced satellite-based farm management solutions. These include satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, blockchain-based product traceability, and tools for fleet and resource management. These technologies help farmers make data-driven decisions, optimize resource use, and increase productivity.
Q6: How does satellite-based monitoring compare to drone and IoT-based monitoring?
A6: Satellite-based monitoring, like that offered by Farmonaut, generally covers larger areas and is less weather-dependent than drone monitoring. It’s also more scalable and has lower initial setup and maintenance costs compared to both drone and IoT-based systems. However, IoT systems can provide real-time data, while satellite data is typically updated daily to weekly.
Q7: What is land suitability assessment?
A7: Land suitability assessment is the process of determining how well a piece of land is suited for a specific use, such as growing a particular crop. It considers factors like soil properties, climate, topography, water availability, and socio-economic conditions to optimize crop selection and management practices.
Q8: How can farmers identify and maximize highly productive land?
A8: Highly productive land can be identified by characteristics such as rich, fertile soil, adequate water supply, favorable climate, and good drainage. To maximize its use, farmers can employ strategies like crop rotation, precision agriculture techniques, soil conservation practices, efficient irrigation, and integrated pest management.
Q9: What technological advancements are shaping agricultural land management?
A9: Key technological advancements include satellite imagery, artificial intelligence and machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), drones, GPS and GIS technologies, and blockchain. These technologies are improving decision-making, optimizing resource use, increasing productivity, mitigating risks, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Q10: How can I start using Farmonaut’s services?
A10: You can start using Farmonaut’s services by visiting our website and signing up for an account. We offer various subscription packages tailored to different needs. You can also download our mobile app for Android or iOS for on-the-go access to our services.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into land utilisation, suitability, and productivity in agriculture. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering farmers with the tools and knowledge they need to maximize their agricultural potential while promoting sustainable practices. For more information or to start your journey with Farmonaut, visit our website or contact our team today.