Stink Bug Invasion: Protecting Fruits and Crops from Pentatomidae Pests
In the world of agriculture, we face numerous challenges in our quest to produce bountiful harvests. Among these challenges, pest infestations remain a persistent threat to crop health and yield. Today, we’re diving deep into the world of one particular family of pests that has been causing significant concern for farmers worldwide: the Pentatomidae, commonly known as stink bugs.
Understanding the Pentatomidae Family
The Pentatomidae family is a diverse group of insects belonging to the order Hemiptera. These bugs are characterized by their shield-shaped bodies and the distinctive odor they emit when disturbed, hence their common name “stink bugs.” Within this family, there are numerous genera and species that pose threats to various crops.
Some of the most problematic pentatomids in agriculture include:
- Brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys)
- Green stink bug (Chinavia hilaris)
- Rice stink bug (Oebalus pugnax)
- Brown stink bug (Euschistus servus)
These pests are not just a nuisance; they can cause significant damage to a wide variety of crops, including:
- Fruits: apple, peach, nectarine, pear, apricot, cherry, raspberry
- Vegetables: tomato, pea
- Field crops: soy, wheat, rice, cotton, alfalfa, corn
- Tree nuts: pecan
The Impact of Stink Bug Infestations
Stink bugs can cause significant economic losses for farmers due to their feeding habits. These pests use their piercing-sucking mouthparts to feed on plant tissues, particularly developing fruits and seeds. This feeding activity can result in:
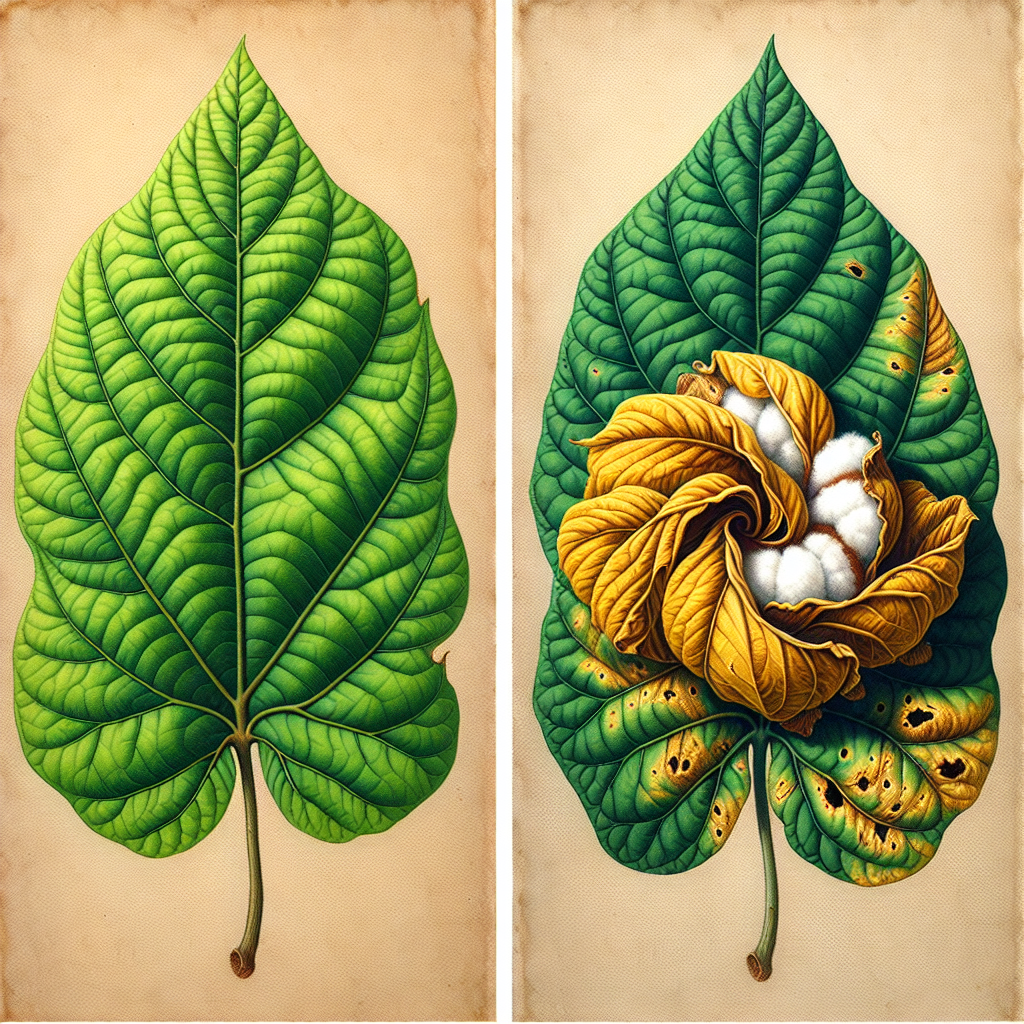
- Discoloration and deformities in fruits
- Reduced crop quality and marketability
- Yield losses in field crops
- Transmission of plant pathogens
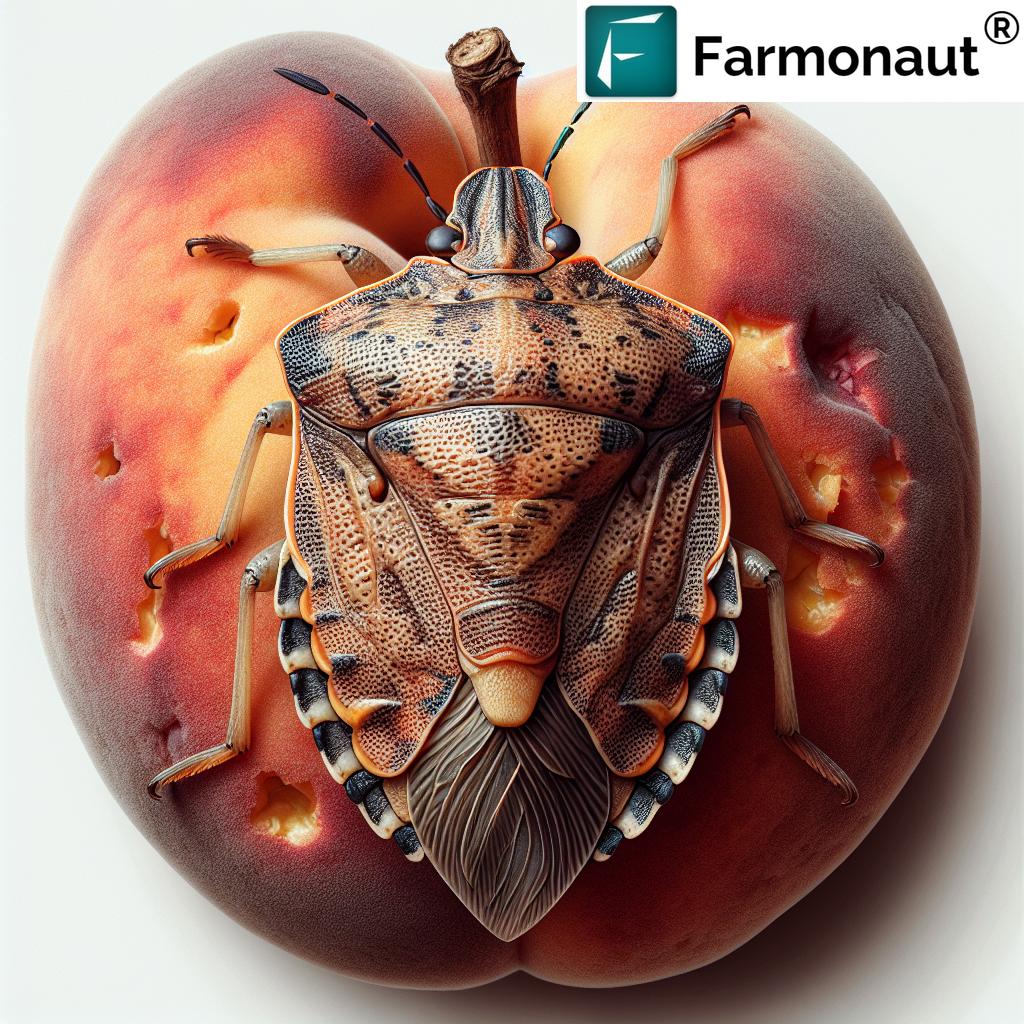
For example, in peach orchards, stink bug feeding can cause a condition known as “cat-facing,” where the fruit develops unsightly depressions and scarring. In cotton fields, their feeding can lead to boll damage and reduced fiber quality.

Detecting Stink Bug Infestations
Early detection of stink bug infestations is crucial for effective management. Here’s a comparison of different detection methods:
| Method | Coverage area | Frequency | Cost | Accuracy | Early detection capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional scouting | Limited | Weekly | High (labor-intensive) | Moderate | Limited |
| Drone imagery | Medium | As needed | Moderate | Good | Moderate |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Large | Daily to weekly | Low | High | Excellent |
As you can see, the Farmonaut Satellite System offers significant advantages in terms of coverage area, frequency of updates, cost-effectiveness, and early pest detection capabilities. This allows for timely intervention and more effective pest management strategies.
Stink Bug Control Strategies
Managing stink bug populations requires an integrated approach. Here are some strategies we recommend:
1. Cultural Control
- Crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles
- Proper sanitation practices to remove overwintering sites
- Use of trap crops to lure stink bugs away from main crops
2. Biological Control
- Encouraging natural predators like parasitic wasps
- Use of entomopathogenic fungi
3. Chemical Control
While we always advocate for integrated pest management, sometimes chemical interventions are necessary. Conventional insecticides can be effective, but their use should be carefully timed and targeted to minimize impacts on beneficial insects.
4. Protection Measures
- Physical barriers like netting for high-value crops
- Pheromone traps for monitoring and mass trapping
The Role of Technology in Stink Bug Management
At Farmonaut, we’re leveraging cutting-edge technology to revolutionize pest management strategies. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can detect early signs of stress in crops, which may indicate pest pressure. By integrating this data with our AI-powered advisory system, we can provide timely alerts and recommendations for pest control.
To learn more about how our technology can help you manage stink bug infestations and other agricultural challenges, visit our Farmonaut app or explore our API services.
Understanding Stink Bug Behavior
To effectively manage stink bug populations, it’s crucial to understand their behavior and life cycle. These insects have several unique characteristics that make them particularly challenging pests:
Defense Mechanism
One of the most distinctive features of stink bugs is their ability to secrete a foul-smelling substance as a defense mechanism. This malodor is produced by glands located on their thorax. When threatened, stink bugs release this odor to deter predators. While this characteristic gives them their common name, it also makes them unpleasant for humans to handle, complicating control efforts.
Life Cycle and Seasonal Patterns
Stink bugs typically go through five nymphal stages before reaching adulthood. Understanding their life cycle is crucial for timing control measures effectively:
- Egg stage: Females lay clusters of barrel-shaped eggs on the undersides of leaves.
- Nymphal stages: Nymphs go through five instars, gradually developing wings and adult coloration.
- Adult stage: Adults are capable of flight and can disperse widely.
In many regions, stink bugs overwinter as adults in protected areas such as under tree bark or in buildings. They become active in spring, moving into crops as temperatures warm. Understanding these seasonal patterns is crucial for implementing timely control measures.
The Economic Impact of Stink Bug Damage
The economic consequences of stink bug infestations can be severe. Here’s a breakdown of the potential impacts across different crop types:
Fruit Crops
In fruit orchards, stink bug damage can lead to significant losses. For example:
- Apple and pear orchards can see up to 50% crop damage in severe infestations.
- Peach and nectarine growers may face losses of 10-20% due to cosmetic damage making fruits unmarketable.
- Cherry and apricot crops can suffer yield reductions and quality issues.
Field Crops
Stink bugs can also have a significant impact on field crops:
- Soy fields may experience yield losses of up to 30% in heavily infested areas.
- Cotton quality can be severely impacted, with damaged bolls leading to reduced fiber quality.
- Corn may suffer from reduced kernel quality and yield losses.
Vegetables
Vegetable crops are not immune to stink bug damage:
- Tomato fruits can become unmarketable due to feeding damage.
- Pea crops may suffer reduced yield and quality.
Given these potential losses, implementing effective monitoring and control strategies is crucial for protecting crop yields and quality.
Innovative Approaches to Stink Bug Management
As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, new and innovative approaches to pest management are emerging. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of these developments, integrating cutting-edge technology with traditional agricultural practices to provide comprehensive solutions for farmers.
Satellite-Based Monitoring
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system offers several advantages for stink bug management:
- Early Detection: By analyzing multispectral imagery, we can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate pest pressure before visible symptoms appear.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Our system can monitor vast areas of farmland, providing a comprehensive view of pest distribution and movement.
- Timely Updates: With frequent satellite passes, we can provide regular updates on crop health, allowing for rapid response to emerging pest issues.
To experience the benefits of our satellite monitoring system, download our app for Android or iOS.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI advisory system takes pest management to the next level:
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing satellite data, weather patterns, and historical pest information, our AI can provide tailored pest management recommendations for each farm.
- Predictive Modeling: We’re developing models to predict stink bug outbreaks based on environmental conditions, helping farmers prepare proactively.
- Integration with IPM Strategies: Our system can suggest optimal timing for various control measures, integrating seamlessly with existing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs.
Blockchain for Traceability
While not directly related to pest control, our blockchain-based traceability system can play a role in managing the impacts of stink bug damage:
- Quality Assurance: By tracking produce from farm to consumer, we can help identify and isolate affected batches, minimizing the spread of damaged produce.
- Consumer Confidence: Transparent tracking can help maintain consumer confidence even when pest issues arise, by demonstrating rigorous quality control measures.
The Future of Stink Bug Management
As we look to the future, several emerging technologies and approaches hold promise for improving stink bug management:
1. Gene Editing
CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies could potentially be used to develop crop varieties with enhanced resistance to stink bug feeding.
2. Precision Agriculture
Advances in precision agriculture, including the use of drones and IoT sensors, will allow for even more targeted pest control measures.
3. Biopesticides
The development of new, environmentally friendly biopesticides could provide additional tools for managing stink bug populations without relying on conventional chemical insecticides.
4. Climate Modeling
As climate change alters pest distributions and behavior, advanced climate modeling integrated with pest monitoring systems will become increasingly important for predicting and managing outbreaks.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continuously improving our services to provide farmers with the most effective tools for pest management.
Implementing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approach
While individual control methods can be effective, the most successful stink bug management strategies typically involve an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach. IPM combines various control methods to manage pest populations in an environmentally sensitive and economically sound manner. Here’s how to implement an IPM strategy for stink bug control:
1. Monitoring and Identification
- Regularly scout fields for stink bug presence and damage.
- Use Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system for large-scale, frequent assessments.
- Correctly identify the specific stink bug species present, as control measures may vary.
2. Prevention
- Implement crop rotation strategies to disrupt pest life cycles.
- Maintain field hygiene by removing crop residues that can harbor overwintering bugs.
- Use trap crops to attract stink bugs away from main crops.
3. Cultural Control
- Adjust planting dates to avoid peak stink bug activity periods.
- Manage weeds that can serve as alternative hosts for stink bugs.
- Consider intercropping with plants that repel stink bugs or attract their natural predators.
4. Biological Control
- Encourage natural predators like birds, spiders, and predatory insects.
- Consider releasing parasitic wasps that target stink bug eggs.
- Use entomopathogenic fungi in suitable conditions.
5. Physical and Mechanical Control
- Use row covers or netting to protect high-value crops.
- Employ pheromone traps for monitoring and mass trapping.
- Consider vacuum harvesting in some crops to remove stink bugs.
6. Chemical Control
- Use chemical interventions only when other methods have failed and pest populations exceed economic thresholds.
- Choose selective insecticides that minimize impact on beneficial insects.
- Rotate insecticide classes to prevent resistance development.
- Time applications based on pest life cycle and crop stage for maximum effectiveness.
7. Evaluation and Adjustment
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your IPM strategy.
- Use Farmonaut’s AI advisory system to analyze results and suggest improvements.
- Adjust your approach based on changing pest pressures, environmental conditions, and new research findings.
By implementing a comprehensive IPM strategy, farmers can effectively manage stink bug populations while minimizing environmental impacts and preserving the long-term productivity of their land.
Case Studies: Successful Stink Bug Management
While we don’t have specific case studies to share, we can discuss general examples of successful stink bug management strategies that have been implemented in various regions:
Orchard IPM in the Pacific Northwest
Fruit growers in Washington state have successfully managed brown marmorated stink bug populations through a combination of monitoring, biological control, and targeted insecticide applications. By using pheromone traps for early detection and encouraging natural predators, they’ve been able to reduce reliance on broad-spectrum insecticides.
Trap Cropping in Vegetable Production
Some vegetable farmers have found success using trap crops like sunflowers or sorghum to draw stink bugs away from high-value crops like tomatoes. This approach, combined with targeted control measures on the trap crops, has helped reduce overall pesticide use while protecting the main crop.
Precision Agriculture in Soybean Fields
Large-scale soybean producers have utilized precision agriculture techniques, including satellite and drone monitoring, to identify stink bug hotspots within fields. This allows for targeted treatment of affected areas rather than blanket application of insecticides, reducing costs and environmental impact.
These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of integrated approaches that combine multiple management strategies. At Farmonaut, we aim to support such holistic pest management efforts through our advanced monitoring and advisory systems.
Leveraging Farmonaut’s Technology for Stink Bug Management
Our suite of technologies at Farmonaut offers powerful tools for managing stink bug infestations effectively. Here’s how our various services can be integrated into your pest management strategy:
1. Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our satellite monitoring system provides several advantages for stink bug management:
- Early Detection: By analyzing vegetation health indices like NDVI, we can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate pest pressure before visible symptoms appear.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Our system can monitor vast areas of farmland, providing a comprehensive view of pest distribution and movement.
- Frequent Updates: With regular satellite passes, we can provide timely updates on crop health, allowing for rapid response to emerging pest issues.
2. Jeevn AI Advisory System
Our AI-powered advisory system takes pest management to the next level:
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing satellite data, weather patterns, and historical pest information, our AI can provide tailored pest management recommendations for each farm.
- Predictive Modeling: We’re developing models to predict stink bug outbreaks based on environmental conditions, helping farmers prepare proactively.
- Integration with IPM Strategies: Our system can suggest optimal timing for various control measures, integrating seamlessly with existing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs.
3. Weather API
Our Weather API provides crucial data for pest management:
- Precise Forecasts: Accurate weather predictions help in timing pest control measures effectively.
- Historical Data: Long-term weather data can be used to understand pest population trends and predict future outbreaks.
- Microclimate Information: Detailed local weather data can help identify conditions favorable for stink bug activity.
4. Mobile App
Our mobile app, available for Android and iOS, puts powerful pest management tools in your pocket:
- Real-time Alerts: Receive notifications about potential pest threats based on our satellite and AI analysis.
- Field-level Insights: Access detailed information about crop health and pest pressure for each of your fields.
- Management Tools: Log pest sightings, track control measures, and monitor their effectiveness over time.
By leveraging these technologies, farmers can implement more effective, data-driven strategies for managing stink bug populations and protecting their crops.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about stink bug management:
Q: How can I tell if my crop has a stink bug infarctation?
A: Look for signs such as discolored, dimpled, or deformed fruits, puncture marks on leaves or stems, and of course, the presence of the insects themselves. Our satellite monitoring system can also detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate pest pressure.
Q: Are there any natural predators of stink bugs?
A: Yes, several natural predators can help control stink bug populations, including birds, spiders, and predatory insects like assassin bugs and praying mantises. Some parasitic wasps also target stink bug eggs.
Q: How effective are organic control methods for stink bugs?
A: Organic control methods can be effective when used as part of an integrated pest management strategy. These may include cultural practices, biological controls, and OMRI-listed insecticides. The effectiveness can vary depending on the specific situation and pest pressure.
Q: Can stink bugs develop resistance to insecticides?
A: Like many pests, stink bugs can potentially develop resistance to insecticides over time, especially if the same products are used repeatedly. This is why it’s important to rotate insecticide classes and integrate other control methods into your pest management strategy.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help me manage stink bug infestations?
A: Our satellite monitoring system can detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate pest pressure. Our AI advisory system can then provide tailored recommendations for pest management based on this data, along with weather information and historical pest trends. This allows for more timely and targeted interventions.
Q: Are stink bugs harmful to humans?
A: While stink bugs can be a nuisance when they enter homes or buildings, they do not bite humans or spread diseases. However, their presence in large numbers can be distressing, and their odor when crushed can be unpleasant.
Q: How do weather conditions affect stink bug populations?
A: Weather plays a significant role in stink bug behavior and population dynamics. Warm temperatures generally increase activity and reproductive rates, while harsh winters can reduce overwintering populations. Our Weather API can provide detailed climate data to help predict and manage stink bug activity.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage stink bug infestations and other agricultural challenges, please visit our website or contact our support team.
Conclusion
Managing stink bug infestations is a complex but crucial task for farmers and agricultural professionals. By understanding the behavior and life cycle of these pests, implementing integrated pest management strategies, and leveraging advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, it’s possible to effectively control stink bug populations and minimize crop damage.
Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, adaptability, and a willingness to embrace new technologies and techniques. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in this endeavor by providing cutting-edge tools and insights for more effective, sustainable agriculture.
To learn more about how our services can help you manage stink bugs and other agricultural challenges, explore our subscription options below:
Together, we can work towards a future of more resilient, productive, and sustainable agriculture.