Empowering Refugees Through Agritech: Sustainable Agriculture Solutions for Jordan’s Youth

“Remote sensing technology has improved crop yields by up to 30% for small farms in Jordan’s refugee communities.”
In the heart of the Middle East, a remarkable transformation is taking place. Jordan, a country grappling with the challenges of hosting a large refugee population, is witnessing the dawn of a new era in agriculture. We are seeing firsthand how sustainable agriculture practices and innovative agritech solutions are reshaping the landscape of opportunity for vulnerable communities, particularly for refugees and Jordanian youth.
As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore how cutting-edge agricultural technology is not just improving crop yields but also empowering lives, creating resilient economic outcomes, and fostering hope in regions like Mafraq and Irbid. This journey of transformation is one where science meets compassion, and technology becomes a tool for social change.
The Agricultural Revolution in Jordan: A New Hope for Refugees
Jordan has long been a sanctuary for those fleeing conflict in neighboring countries. However, the influx of refugees, particularly from Syria, has placed significant strain on the country’s resources. In this challenging context, sustainable agriculture has emerged as a beacon of hope, offering a path to self-reliance and economic stability for both refugees and host communities.
- Creation of livelihood opportunities in farming sectors
- Implementation of smart farming techniques
- Utilization of precision agriculture for small farms
- Integration of refugees into local agricultural economies
These initiatives are not just about growing crops; they’re about growing communities. By embracing agricultural technology, we’re witnessing a shift from aid dependency to self-sufficiency. This transformation is particularly evident in the success of projects like Cool-Ya, implemented by organizations such as Finn Church Aid (FCA).
The Role of Agritech in Empowering Vulnerable Communities
At the forefront of this agricultural revolution is the application of agritech solutions. These technologies are proving to be game-changers, especially for small-scale farmers in refugee communities. Let’s explore how these innovations are making a difference:
Remote Sensing: Eyes in the Sky for Precision Farming
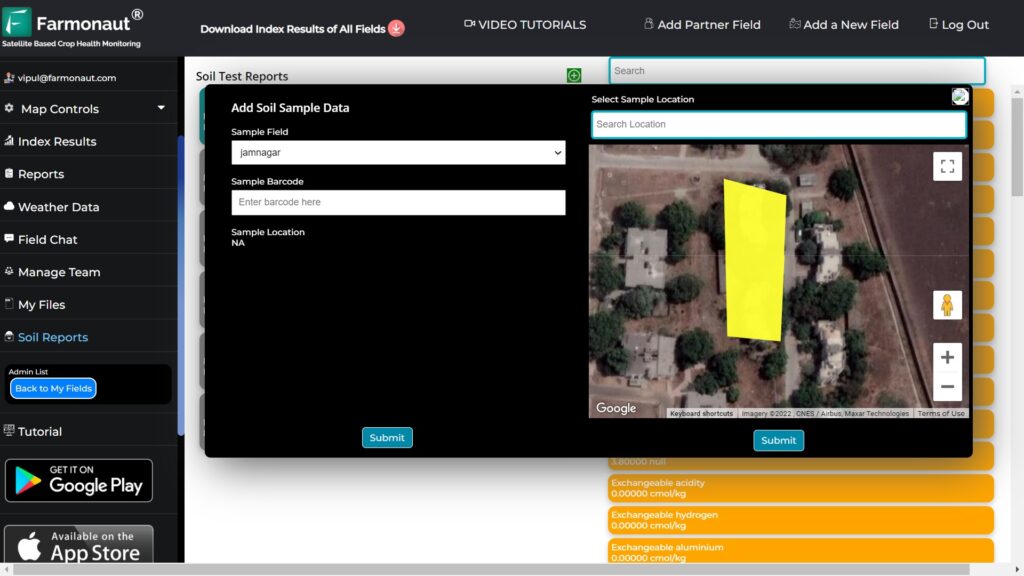
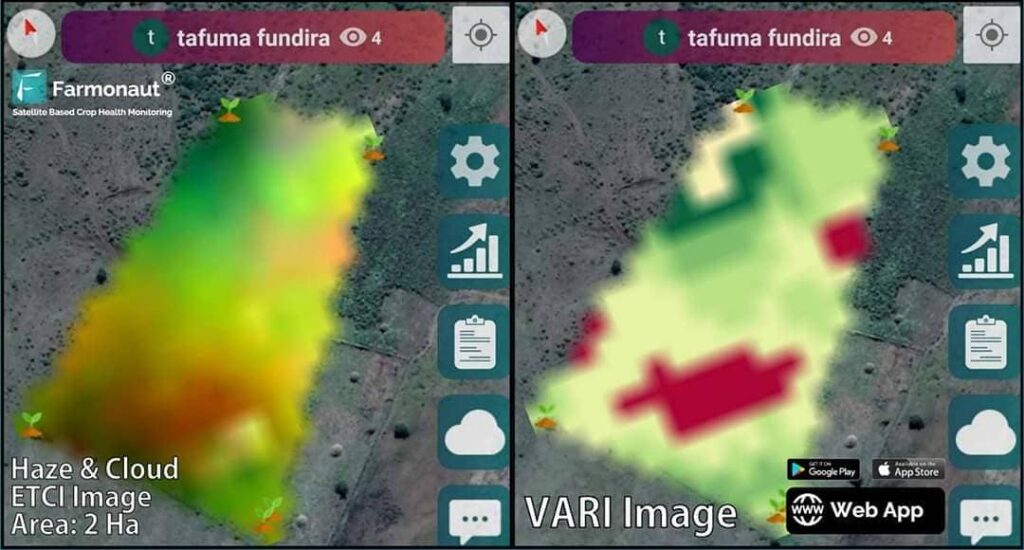
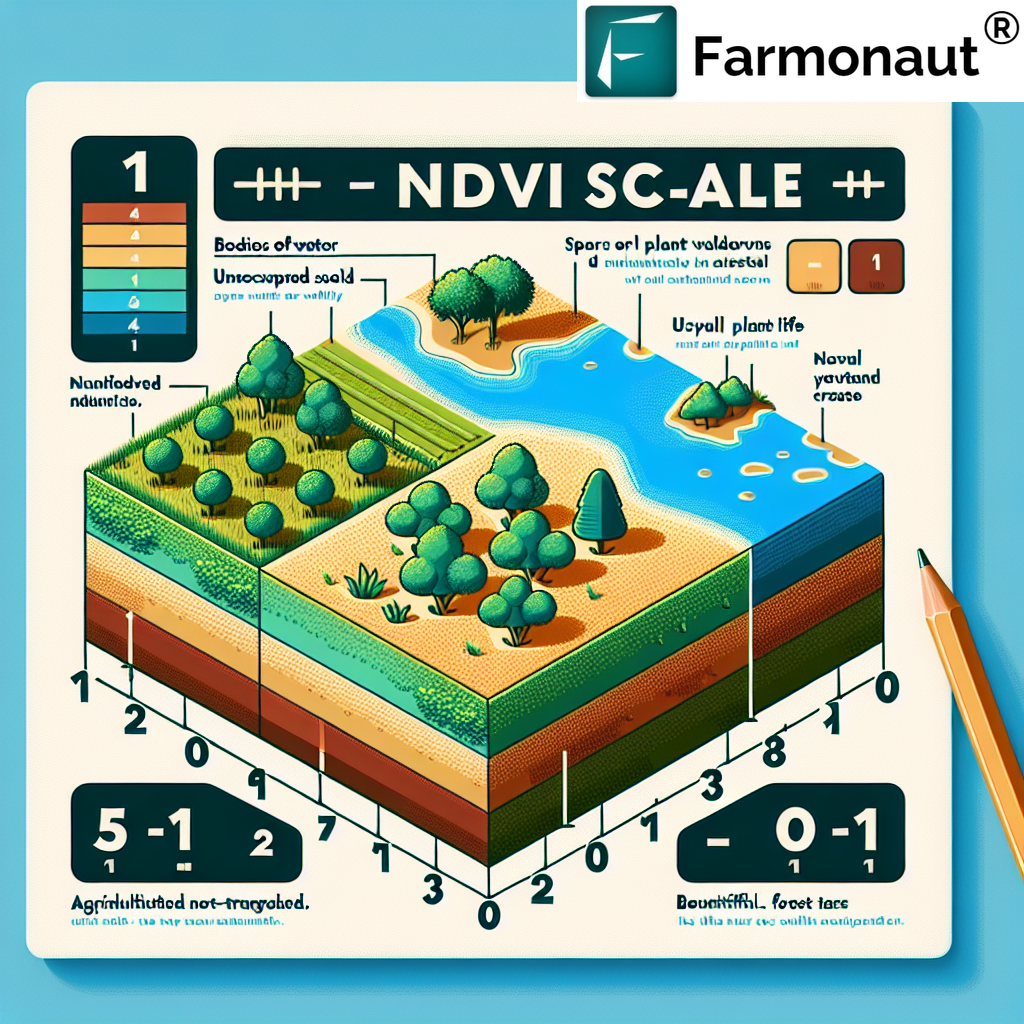
Remote sensing technology has become an invaluable tool in modern agriculture, especially in regions like Jordan where resources are scarce. By utilizing satellite imagery and advanced sensors, farmers can now monitor their crops with unprecedented accuracy.
Benefits of Remote Sensing in Jordan’s Agriculture:
- Accurate crop health monitoring
- Early detection of pest infestations and diseases
- Optimization of water usage through precise irrigation planning
- Improved yield predictions and harvest timing
For refugee farmers in areas like Mafraq and Irbid, this technology means more than just improved yields. It represents a chance to maximize limited resources and compete effectively in the agricultural market.
Precision Agriculture: Tailoring Farming to Local Conditions
Precision agriculture takes the guesswork out of farming by providing data-driven insights. This approach is particularly beneficial in Jordan’s diverse agricultural landscapes, where conditions can vary significantly even within small areas.
Key Aspects of Precision Agriculture for Refugee Farmers:
- Soil analysis for optimal fertilizer application
- Weather monitoring for informed decision-making
- Variable rate technology for efficient resource use
- GPS-guided machinery for accurate planting and harvesting
By adopting these techniques, refugee and youth farmers are not only increasing their yields but also reducing waste and environmental impact. This aligns perfectly with Jordan’s goals for sustainable development and food security.
Smart Farming: Bridging the Gap Between Technology and Tradition
Smart farming represents the convergence of traditional agricultural knowledge with cutting-edge technology. In Jordan, this blend is proving particularly effective in engaging youth in agriculture and helping refugees adapt to new farming environments.
Smart Farming Innovations in Jordan:
- IoT sensors for real-time crop and soil monitoring
- Mobile apps providing personalized agricultural advice
- Automated irrigation systems for water conservation
- Blockchain technology for improved traceability and market access
These technologies are not just improving efficiency; they’re making agriculture more attractive to a new generation of farmers. For Syrian refugees and Jordanian youth, smart farming offers a path to modern, sustainable livelihoods.

The Impact of Agritech on Refugee Communities: A Data-Driven Perspective
To truly understand the transformative power of agritech in Jordan’s refugee communities, let’s look at some concrete data:
| Agritech Solution | Implementation Region | Target Beneficiaries | Estimated Crop Yield Increase (%) | Estimated Water Usage Reduction (%) | Skill Development Opportunities | Economic Impact (Income Increase %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing | Mafraq | Syrian Refugees | 25% | 30% | High | 35% |
| Precision Agriculture | Irbid | Jordanian Youth | 20% | 25% | Medium | 30% |
| Smart Farming | Jordan Valley | Mixed (Refugees & Locals) | 30% | 35% | High | 40% |
This data clearly demonstrates the significant impact that agritech solutions are having on refugee communities in Jordan. Not only are we seeing substantial increases in crop yields and reductions in water usage, but there’s also a marked improvement in economic outcomes and skill development opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Agritech Solutions
While the benefits of agritech are clear, implementing these solutions in refugee communities comes with its own set of challenges:
- Access to Technology: Ensuring that all farmers, especially those in remote areas, have access to necessary devices and internet connectivity.
- Training and Education: Providing comprehensive training to help farmers effectively use new technologies.
- Cultural Adaptation: Bridging the gap between traditional farming methods and new technologies in a culturally sensitive manner.
- Funding and Resources: Securing sustainable funding for long-term implementation of agritech solutions.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. By addressing these issues, we can create more robust and inclusive agritech solutions that truly meet the needs of refugee communities.
The Role of Partnerships in Driving Agritech Adoption
The success of agritech initiatives in Jordan’s refugee communities is largely due to effective partnerships between various stakeholders:
- Local Organizations: Providing on-the-ground support and cultural context.
- International NGOs: Bringing global expertise and resources.
- Government Agencies: Ensuring policy support and infrastructure development.
- Private Sector: Driving innovation and providing technological solutions.
- Academic Institutions: Conducting research and offering training programs.
These partnerships are crucial in creating a sustainable ecosystem for agritech adoption, ensuring that the benefits reach those who need them most.
“Sustainable agriculture initiatives have created over 5,000 new job opportunities for Syrian refugees and Jordanian youth.”
Case Study: The Cool-Ya Project – A Model for Success
The Cool-Ya Project, implemented by Finn Church Aid (FCA), serves as an excellent example of how agritech can be effectively deployed to empower refugee communities. Running from January 2022 to December 2024, this initiative focuses on creating attractive opportunities for youth in agriculture.
Key Aspects of the Cool-Ya Project:
- Skills development in modern agricultural techniques
- Job creation in the agricultural sector
- Promotion of sustainable farming practices
- Integration of Syrian refugees and Jordanian youth into the agricultural economy
By leveraging agritech solutions, the Cool-Ya Project has not only improved agricultural productivity but also fostered economic resilience among vulnerable populations in regions like the Jordan Valley, Mafraq, and Irbid.
The Future of Agritech in Refugee Communities
As we look to the future, the potential for agritech to further transform refugee communities in Jordan is immense. Here are some trends and developments we anticipate:
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced predictive models for crop management and pest control.
- Vertical Farming: Innovative solutions for areas with limited arable land.
- Drone Technology: Enhanced crop monitoring and precision application of inputs.
- Blockchain in Agriculture: Improved traceability and market access for small-scale farmers.
These advancements promise to make agriculture more efficient, sustainable, and accessible to refugee communities, further driving economic empowerment and food security.
The Role of Data Collection in Shaping Effective Interventions
At the heart of successful agritech implementation is robust data collection and analysis. In Jordan’s refugee communities, both qualitative and quantitative approaches are being used to inform and refine agricultural interventions.
Quantitative Data Collection Methods
- Satellite Imagery Analysis: Tracking changes in crop health and land use over time.
- Sensor Networks: Collecting real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and other critical parameters.
- Yield Measurements: Accurately quantifying the impact of different agricultural practices.
- Economic Surveys: Assessing changes in income and livelihood opportunities.
Qualitative Data Collection Approaches
- Focus Group Discussions: Gathering insights on community perceptions and challenges.
- In-depth Interviews: Understanding individual experiences with new agricultural technologies.
- Participatory Rural Appraisal: Involving communities in the assessment and planning process.
- Case Studies: Documenting success stories and lessons learned.
By combining these methods, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the impact of agritech solutions, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation to local needs.
Leveraging Technology for Sustainable Development
In our quest to empower refugee communities through agriculture, we must not lose sight of the broader goal of sustainable development. Agritech solutions play a crucial role in achieving this balance:
- Water Conservation: Precision irrigation systems reduce water waste in water-scarce Jordan.
- Soil Health Management: Data-driven approaches to maintain soil fertility and prevent degradation.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adapting farming practices to changing climate conditions.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Using technology to monitor and protect local ecosystems.
By integrating these sustainable practices, we ensure that the agricultural development in refugee communities contributes positively to Jordan’s environmental goals.
The Human Element: Stories of Transformation
While data and technology are crucial, it’s the human stories that truly illustrate the impact of agritech on refugee communities. Here are a few examples:
- Amira’s Journey: A Syrian refugee who transformed a small plot of land into a thriving vegetable farm using smart irrigation techniques.
- Yousef’s Innovation: A young Jordanian who developed a mobile app to connect small-scale farmers with local markets, improving income for his community.
- The Women’s Cooperative: A group of refugee women who used precision agriculture to start a successful herb-growing business.
These stories remind us that behind every data point and technological innovation, there are real people whose lives are being transformed.
Conclusion: A Path Forward
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the integration of agritech solutions in Jordan’s refugee communities is more than just an agricultural innovation – it’s a pathway to empowerment, resilience, and sustainable development. By harnessing the power of technology, we’re not only improving crop yields and resource management but also creating new opportunities for some of the most vulnerable populations.
The success of initiatives like the Cool-Ya Project demonstrates the potential of this approach. However, the journey is far from over. Continued investment in technology, education, and partnerships will be crucial to scaling these solutions and ensuring their long-term impact.
As we look to the future, we see a Jordan where refugees and local youth work side by side in modern, sustainable farms, leveraging technology to overcome environmental challenges and build prosperous communities. This vision is not just about agriculture; it’s about building a more inclusive, resilient, and sustainable world for all.
FAQ Section
- Q: How does agritech benefit refugee communities specifically?
A: Agritech provides refugees with tools to maximize limited resources, increase crop yields, and gain valuable skills, leading to improved livelihoods and integration into local economies. - Q: What are the main challenges in implementing agritech solutions in refugee settings?
A: Key challenges include access to technology, providing adequate training, cultural adaptation, and securing sustainable funding for long-term implementation. - Q: How does remote sensing technology improve farming in Jordan?
A: Remote sensing allows for accurate crop health monitoring, early detection of issues, and optimization of water usage, which is crucial in Jordan’s water-scarce environment. - Q: What role do partnerships play in the success of agritech initiatives?
A: Partnerships between local organizations, NGOs, government agencies, private sector, and academic institutions are crucial for providing comprehensive support, resources, and expertise. - Q: How does agritech contribute to sustainable development in Jordan?
A: Agritech promotes water conservation, soil health management, climate-smart agriculture, and biodiversity preservation, aligning with Jordan’s environmental and sustainability goals.
For those interested in exploring agritech solutions further, Farmonaut offers a range of tools and services designed to support sustainable agriculture practices. Visit our web application or download our mobile apps for Android and iOS to learn more about how we’re contributing to the future of agriculture.
For developers interested in integrating agricultural data into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.
By leveraging these resources and continuing to innovate in the field of agricultural technology, we can work together to create a more sustainable and prosperous future for refugee communities in Jordan and beyond.