Satellite Monitoring: Combating Amazon Deforestation and Advancing Sustainable Agriculture in Brazil
“Brazil’s carbon emissions have increased by 73% since 2019, primarily due to Amazon deforestation.”
As we delve into the critical issue of Amazon deforestation and its impact on sustainable agriculture in Brazil, it’s crucial to understand the gravity of the situation. The Amazon rainforest, often called the “lungs of the Earth,” is facing unprecedented threats from deforestation, largely driven by agricultural expansion and weakening environmental protections. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the complex interplay between politics, agriculture, and conservation in Brazil’s Amazon region, and how innovative satellite monitoring technologies are offering hope in the fight against deforestation.
The Current State of Amazon Deforestation
Brazil’s Amazon rainforest is at a tipping point. Recent years have seen a significant surge in deforestation rates, with alarming consequences for biodiversity, climate change, and sustainable agriculture. Let’s break down the key factors contributing to this crisis:
- Political Pressure: Various Brazilian states are pushing to loosen environmental protections, primarily due to pressure from cattle ranchers and soybean producers.
- Legislative Changes: New laws in states like Acre, Rondonia, and Mato Grosso are facilitating illegal land clearing and dismantling conservation units.
- Economic Interests: The drive for short-term economic gains is overshadowing long-term sustainability concerns.
- Carbon Emissions: Deforestation is now Brazil’s largest source of carbon emissions, threatening global climate goals.
The situation is particularly dire in states like Acre, where recent legislation has opened up protected lands for privatization, effectively legalizing the status of illegal settlers in conservation areas. This move has not only sparked controversy but has also led to a measurable increase in deforestation activities.
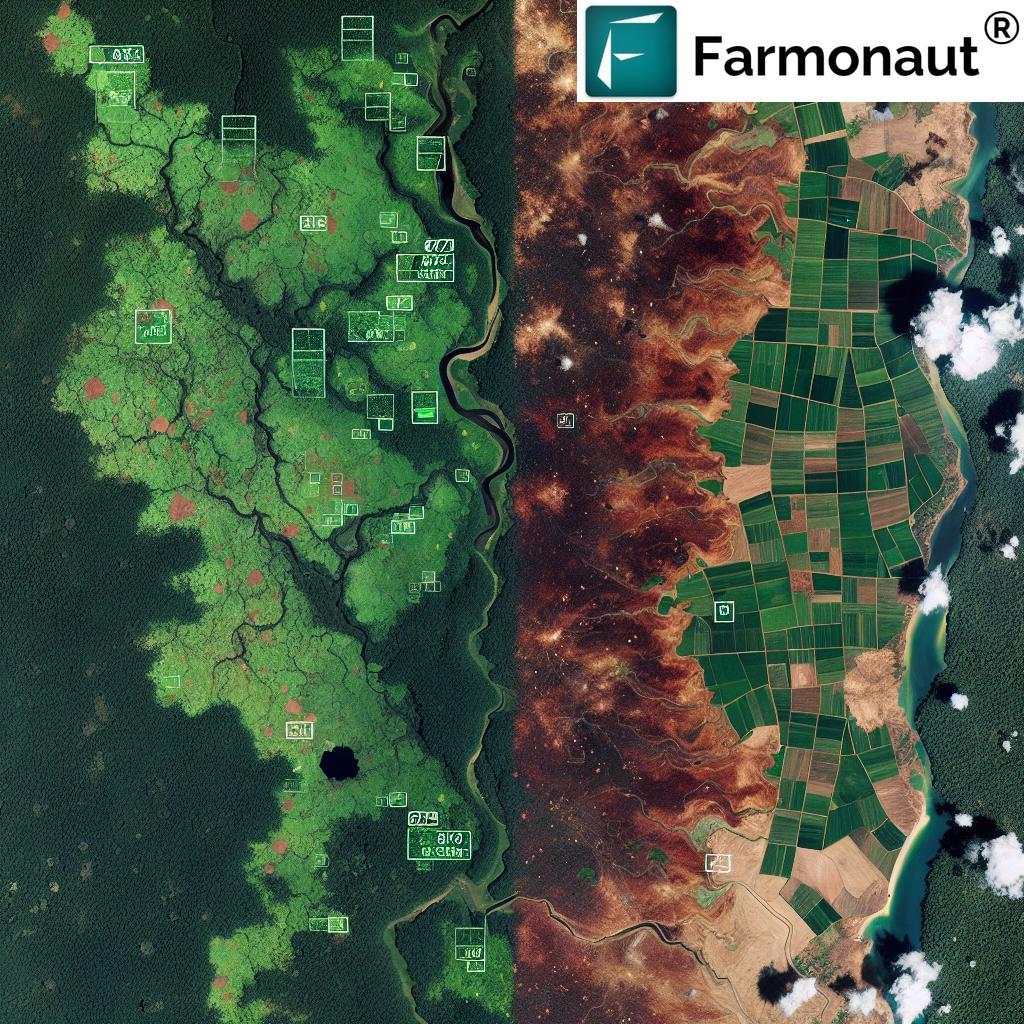
The Role of Satellite Monitoring in Combating Deforestation
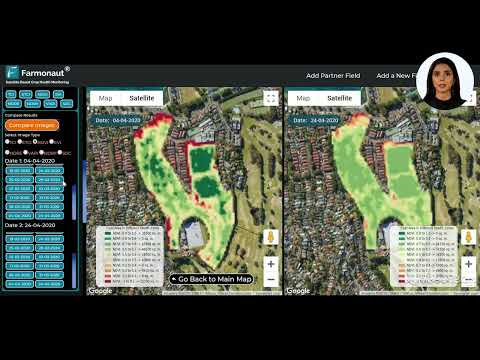
In the face of these challenges, satellite monitoring technology emerges as a powerful tool in the fight against deforestation. Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this technological revolution, offering advanced satellite-based solutions that can help track and prevent illegal deforestation.
“Satellite monitoring can detect deforestation with up to 95% accuracy, aiding in rainforest conservation efforts.”
Here’s how satellite monitoring is making a difference:
- Real-time Detection: Satellite imagery allows for near-real-time detection of deforestation activities, enabling rapid response from authorities.
- Precision Mapping: High-resolution satellite images provide detailed maps of forest cover, helping to identify areas at risk of deforestation.
- Trend Analysis: By comparing images over time, we can track deforestation trends and predict future high-risk areas.
- Support for Enforcement: Satellite data provides crucial evidence for law enforcement agencies to combat illegal logging and land clearing.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to leveraging our satellite technology to support sustainable agriculture and forest conservation efforts. Our platform offers valuable insights that can help policymakers, environmentalists, and farmers make informed decisions about land use and conservation strategies.
The Impact of Deforestation on Sustainable Agriculture
While short-term economic gains drive much of the deforestation in the Amazon, the long-term consequences for agriculture are severe. Deforestation leads to:
- Soil Degradation: Clearing forests exposes soil to erosion, reducing its fertility and productivity over time.
- Altered Rainfall Patterns: Deforestation disrupts local and regional climate patterns, potentially leading to droughts or floods that harm agricultural output.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The Amazon’s rich biodiversity plays a crucial role in pest control and pollination, both essential for sustainable agriculture.
- Increased Carbon Emissions: As forests are cleared, massive amounts of carbon are released into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and its impacts on agriculture.
To address these challenges, we at Farmonaut are developing innovative solutions that promote sustainable agriculture while preserving forest cover. Our satellite monitoring technology can help farmers optimize their land use, reduce the need for expansion into forested areas, and implement more sustainable farming practices.
Case Study: Acre State’s Environmental Protection Rollback
The situation in Acre State serves as a stark example of the current challenges facing the Amazon. Recent legislation in Acre has:
- Allowed for the privatization of approximately 347 square miles of protected land.
- Attempted to legalize the status of illegal settlers in conservation units.
- Received endorsement from agribusiness groups, promoting the idea that forests hinder economic development.
The consequences of this legislation have been swift and severe. Satellite imagery has shown a threefold increase in illegal clearing within months of the law’s introduction. This rapid acceleration of deforestation underscores the urgent need for robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms.
The Soy Moratorium: A Crumbling Agreement
The Soy Moratorium, once a beacon of hope in the fight against deforestation, is now facing significant challenges. This agreement, which halted the trade of soybeans cultivated on recently deforested land, is unraveling as authorities in states like Rondonia and Mato Grosso dismantle the legal framework that supported it.
Critics argue that the moratorium exceeds existing anti-deforestation laws, while proponents of agricultural expansion see its dismantling as necessary for economic growth. However, the environmental costs of this shift could be catastrophic.
The Role of Technology in Promoting Sustainable Agriculture
In the face of these challenges, technology offers a ray of hope. Advanced agricultural technologies, including those offered by Farmonaut, can play a crucial role in promoting sustainable farming practices while reducing the pressure on forested lands. Here’s how:
- Precision Agriculture: Satellite monitoring allows farmers to optimize their use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time data on crop health enables early detection of issues, minimizing crop losses and the need for expansion.
- Land Use Optimization: Satellite imagery helps identify the most suitable areas for agriculture, reducing the need to clear new land.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain-based traceability solutions can ensure that agricultural products are sourced from areas free from recent deforestation.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making these technologies accessible to farmers of all scales, from small-holders to large agribusinesses. By democratizing access to precision agriculture tools, we aim to promote more sustainable farming practices across Brazil and beyond.
The Global Implications of Amazon Deforestation
The impact of Amazon deforestation extends far beyond Brazil’s borders. As one of the world’s largest carbon sinks, the Amazon rainforest plays a critical role in regulating global climate patterns. Its destruction has severe consequences for the entire planet:
- Climate Change Acceleration: Deforestation releases massive amounts of stored carbon, contributing significantly to global warming.
- Biodiversity Loss: The Amazon is home to countless species, many still undiscovered. Deforestation threatens this irreplaceable biodiversity.
- Disrupted Water Cycles: The Amazon generates its own rainfall through transpiration. Deforestation disrupts this cycle, potentially affecting weather patterns across South America and beyond.
- Economic Ripple Effects: The loss of ecosystem services provided by the Amazon could have far-reaching economic consequences globally.
These global implications underscore the need for international cooperation and support in preserving the Amazon rainforest. Technologies like satellite monitoring can play a crucial role in this global effort by providing accurate, real-time data on deforestation activities.

Comparative Analysis of Deforestation Impacts in Brazilian States
| State Name | Estimated Annual Deforestation Rate (km²/year) | Primary Drivers of Deforestation | Recent Legislative Changes Affecting Forest Protection | Estimated Carbon Emissions from Deforestation (million tons CO2/year) | Potential Satellite Monitoring Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acre | 500 | Cattle ranching, illegal logging | Privatization of protected lands, legalization of illegal settlements | 25 | Real-time deforestation alerts, land use change detection |
| Rondonia | 1,200 | Soybean cultivation, cattle ranching | Dismantling of conservation units, weakening of Soy Moratorium | 60 | Monitoring of agricultural expansion, fire detection |
| Mato Grosso | 1,500 | Large-scale agriculture, cattle ranching | Relaxation of environmental licensing requirements | 75 | Crop health monitoring, precision agriculture support |
This comparative analysis highlights the varying impacts of deforestation across different Brazilian states. It’s clear that while the drivers and scale of deforestation may differ, the overall trend is alarming across the Amazon region. Satellite monitoring technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, can play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by providing accurate, timely data to support conservation efforts and promote sustainable agriculture.
The Way Forward: Balancing Agriculture and Conservation
As we confront the challenges of Amazon deforestation and its impact on sustainable agriculture, it’s clear that a multifaceted approach is needed. Here are some key strategies that can help balance agricultural needs with forest conservation:
- Strengthening Environmental Policies: Robust, enforceable policies are needed to protect the Amazon and discourage illegal deforestation.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Techniques like agroforestry and precision farming can increase yields without expanding into forested areas.
- Leveraging Technology: Satellite monitoring and other advanced technologies can support both conservation efforts and agricultural productivity.
- International Cooperation: Given the global importance of the Amazon, international support and cooperation are crucial for its preservation.
- Economic Incentives: Developing economic models that value standing forests can help shift the balance away from deforestation.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to being part of this solution. Our satellite monitoring technology not only helps detect and prevent deforestation but also supports farmers in implementing more sustainable and productive agricultural practices.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The challenges facing the Amazon rainforest and sustainable agriculture in Brazil are significant, but not insurmountable. By leveraging advanced technologies like satellite monitoring, implementing strong environmental policies, and promoting sustainable farming practices, we can work towards a future where agriculture thrives without compromising our vital forest ecosystems.
We invite policymakers, farmers, environmentalists, and technology providers to join us in this crucial effort. Together, we can combat Amazon deforestation, advance sustainable agriculture, and protect one of the world’s most valuable natural resources for generations to come.
FAQs
- Q: How does satellite monitoring help prevent deforestation?
A: Satellite monitoring provides real-time data on forest cover changes, allowing for quick detection of illegal deforestation activities. This enables authorities to respond rapidly and enforce conservation laws more effectively. - Q: Can sustainable agriculture practices really help reduce deforestation?
A: Yes, sustainable agriculture practices like precision farming and agroforestry can significantly increase crop yields on existing farmland, reducing the need to clear new areas for agriculture. - Q: What role do international agreements play in protecting the Amazon?
A: International agreements can provide financial incentives for forest conservation, set global standards for sustainable production, and create pressure for countries to maintain their forest cover. - Q: How can individual consumers contribute to reducing Amazon deforestation?
A: Consumers can support products certified as deforestation-free, reduce meat consumption (as cattle ranching is a major driver of deforestation), and support organizations working to protect the Amazon. - Q: What are the long-term consequences of continued Amazon deforestation?
A: Continued deforestation could lead to a tipping point where the Amazon can no longer sustain itself, potentially transforming into a savanna. This would have catastrophic consequences for biodiversity, global climate regulation, and local and global weather patterns.
For more information on how satellite monitoring can support sustainable agriculture and forest conservation, visit our API page or check out our API Developer Docs.