Georgia’s Agricultural Landscape: USDA Leadership and US Market Trends Shaping the Future of Farming
“The USDA’s top leadership selection process influences over $150 billion in annual US agricultural exports.”
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, the interplay between government leadership, market trends, and technological advancements is shaping the future of farming in unprecedented ways. As we delve into the agricultural landscape of Georgia and beyond, we’ll explore how the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) leadership and US agriculture market trends are influencing the grain and fertilizer business, crop production, and the adoption of precision farming technology.
The Pivotal Role of USDA Leadership in Agricultural Policy
The USDA plays a crucial role in shaping agricultural policy and guiding the nation’s farming sector. The selection process for the USDA’s top position is a critical factor that influences the direction of American agriculture. Let’s examine how political experience and industry background impact these key government appointments.
Selection Process for USDA Leadership
- Political considerations
- Industry expertise
- Regional representation
- Agricultural advisory committee input
The USDA Secretary, appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate, must navigate complex political landscapes while possessing a deep understanding of agricultural issues. This balance is crucial for effective leadership in an industry that spans from small family farms to large-scale agribusinesses.

Impact of USDA Leadership on Agricultural Policy
USDA leadership significantly influences policy decisions that affect farmers, ranchers, and consumers nationwide. These policies shape:
- Crop subsidy programs
- Trade agreements
- Conservation efforts
- Rural development initiatives
For instance, recent USDA policies have focused on promoting sustainable agriculture practices, addressing climate change, and expanding market opportunities for American agricultural products.
US Agriculture Market Trends: A Dynamic Landscape
The US agricultural market is constantly evolving, influenced by various factors including global demand, weather patterns, and technological advancements. Let’s explore some key trends shaping the industry:
Crop Price Fluctuations
Grain and oilseed markets, including corn, wheat, and soybeans, have experienced significant price volatility in recent years. Factors contributing to these fluctuations include:
- Global supply and demand imbalances
- Weather-related crop yield variations
- Changes in biofuel policies
- International trade disputes
Farmers in Georgia and across the US must navigate these price uncertainties while making critical decisions about crop selection and resource allocation.
Global Trading in Agriculture
International trade plays a vital role in the US agricultural sector. Key aspects include:
- Export markets for US grains, soybeans, and livestock
- Import competition in certain commodities
- Trade agreements and their impact on market access
- Currency exchange rate fluctuations
Agricultural export consulting has become increasingly important as farmers and agribusinesses seek to navigate complex international markets and regulations.
Fertilizer Market Dynamics
The fertilizer business is a critical component of modern agriculture. Recent trends include:
- Volatility in nitrogen, phosphate, and potash prices
- Increased focus on sustainable and organic fertilizers
- Impact of energy prices on fertilizer production costs
- Adoption of precision fertilizer application techniques
These trends directly impact farm input costs and influence decisions about crop nutrition management.
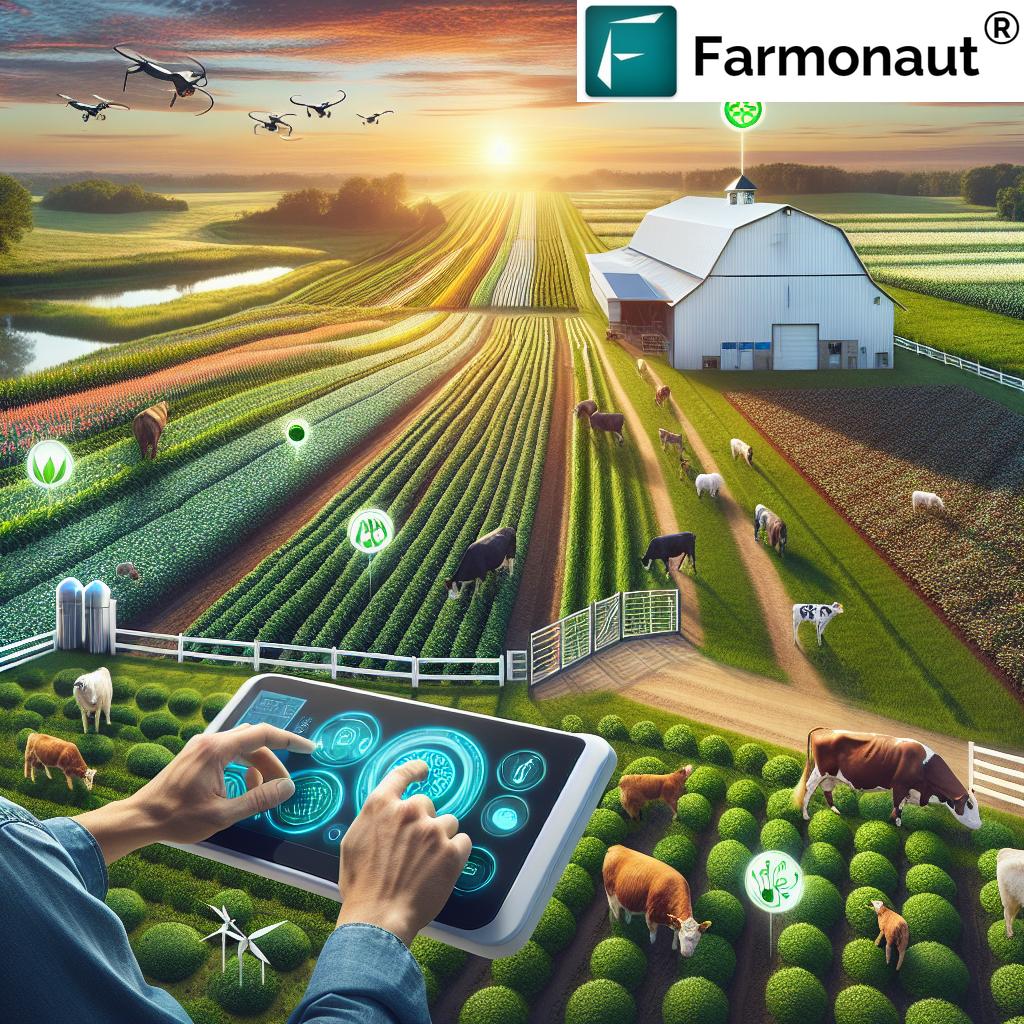
Precision Farming Technology: Revolutionizing Agriculture
“Precision farming technology has increased crop yields by up to 30% while reducing water usage by 20-50%.”
The adoption of precision farming technology is transforming the agricultural landscape in Georgia and beyond. This innovative approach leverages data, technology, and management practices to optimize crop production and resource use.
Key Components of Precision Farming
- GPS-guided machinery
- Remote sensing and satellite imagery
- Variable rate technology for input application
- Soil and crop health monitoring systems
These technologies enable farmers to make data-driven decisions, leading to improved efficiency and sustainability in their operations.
For those interested in leveraging precision farming technology, Farmonaut offers innovative solutions through its  and mobile applications for
and mobile applications for  and
and  .
.
Benefits of Precision Agriculture
The adoption of precision farming technologies offers numerous advantages:
- Increased crop yields
- Reduced input costs
- Improved environmental stewardship
- Enhanced farm management capabilities
These benefits are particularly relevant for Georgia’s diverse agricultural landscape, which includes crops such as cotton, peanuts, and peaches.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices: A Growing Priority
As environmental concerns become increasingly prominent, sustainable agriculture practices are gaining traction among farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike. This shift is influencing both USDA policy and market trends.
Key Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- Conservation tillage
- Crop rotation and diversification
- Integrated pest management
- Water conservation techniques
These practices not only benefit the environment but can also improve long-term farm productivity and resilience.
USDA Initiatives Supporting Sustainability
The USDA has implemented various programs to promote sustainable agriculture, including:
- Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP)
- Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP)
- Organic certification cost-share programs
- Research funding for sustainable farming practices
These initiatives provide financial and technical assistance to farmers adopting sustainable practices, aligning agricultural production with environmental stewardship goals.
The Future of Cereals, Soybeans, and Other Crucial Crops
The outlook for major crops like cereals and soybeans is shaped by a combination of market forces, technological advancements, and policy decisions. Let’s explore some key trends:
Cereal Crops: Wheat, Corn, and Rye
- Increasing global demand for food and feed
- Climate change impacts on growing regions
- Advancements in drought-resistant varieties
- Shift towards value-added and specialty grains
In Georgia, corn is a significant crop, and farmers are adapting to changing market conditions and environmental challenges.
Soybeans and Other Oilseeds
- Growing demand for plant-based proteins
- Expansion of biofuel markets
- Development of high-oleic soybean varieties
- Increasing competition from international producers
While not a major soybean producer, Georgia farmers are affected by national and global trends in oilseed markets.
Specialty Crops: Focus on Georgia
Georgia’s agricultural landscape includes several important specialty crops:
- Peanuts: A key crop with unique market dynamics
- Peaches: An iconic Georgia product facing climate challenges
- Vidalia onions: A high-value crop with protected designation
- Cotton: An important fiber crop with evolving market demands
These crops require specialized management practices and are influenced by both local and global market trends.
The Role of Agricultural Advisory Committees
Agricultural advisory committees play a crucial role in shaping policy decisions and market dynamics. These committees provide valuable insights and recommendations to the USDA and other government agencies.
Types of Agricultural Advisory Committees
- Commodity-specific committees (e.g., Cotton Board, Peanut Standards Board)
- Research and promotion boards
- State and local Farm Service Agency committees
- National Agricultural Research, Extension, Education, and Economics Advisory Board
These committees ensure that diverse perspectives from across the agricultural sector are considered in policy formulation and implementation.
Impact on Policy and Market Dynamics
Agricultural advisory committees influence various aspects of the industry:
- Shaping research priorities
- Informing trade policy decisions
- Guiding conservation and sustainability initiatives
- Advising on crop insurance and risk management programs
By providing on-the-ground insights, these committees help ensure that policies and programs are responsive to the needs of farmers and the broader agricultural community.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Agricultural Landscape
As we look to the future of farming in Georgia and across the United States, several challenges and opportunities emerge:
Challenges Facing Agriculture
- Climate change and extreme weather events
- Water scarcity and management issues
- Labor shortages and workforce development
- Consolidation in the agricultural industry
- Evolving consumer preferences and market demands
Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions and collaborative efforts across the industry.
Opportunities for Growth and Innovation
- Adoption of advanced technologies like AI and robotics in farming
- Development of climate-resilient crop varieties
- Expansion of value-added and specialty product markets
- Integration of sustainable practices for premium market access
- Leveraging data analytics for improved farm management
These opportunities present exciting possibilities for farmers and agribusinesses to enhance productivity, sustainability, and profitability.
The Impact of Farm Machinery and Seed Treatment Advancements
Innovations in farm machinery and seed treatment technologies are revolutionizing agricultural practices:
Farm Machinery Trends
- Autonomous and semi-autonomous tractors and harvesters
- Precision planting and harvesting equipment
- Drones for crop monitoring and spraying
- Smart irrigation systems
These advancements are improving efficiency and reducing labor requirements on farms of all sizes.
Seed Treatment Innovations
- Biological seed treatments for pest and disease control
- Seed coatings for improved germination and early growth
- Nutrient-enhanced seed treatments
- Gene editing technologies for crop improvement
Advanced seed treatments are helping farmers protect their crops and improve yields while reducing the need for chemical inputs.
The Role of Technology in Agricultural Export Consulting
As global trade in agriculture becomes increasingly complex, technology is playing a crucial role in agricultural export consulting:
- Market intelligence platforms for real-time trade data
- Blockchain solutions for supply chain traceability
- AI-powered analytics for market trend predictions
- Digital documentation systems for streamlined export processes
These technological advancements are helping US farmers and exporters navigate international markets more effectively.
For those interested in leveraging technology for agricultural insights, Farmonaut offers comprehensive solutions through its API and API Developer Docs.
USDA Leadership and Agricultural Market Trends Comparison
| Year | USDA Secretary | Political Background | Industry Experience | Major Policy Initiatives | Grain Prices (estimated) | Fertilizer Prices (estimated) | Precision Farming Adoption Rate (estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Sonny Perdue | Former Governor of Georgia | Agribusiness owner | Trade mitigation programs | Moderate | Low | 25% |
| 2021 | Tom Vilsack | Former Governor of Iowa | Previous USDA Secretary | Climate-smart agriculture | High | High | 35% |
| 2023 | Tom Vilsack | Former Governor of Iowa | Previous USDA Secretary | Sustainable agriculture, equity in farming | Fluctuating | Moderate | 45% |
Farmonaut: Empowering Precision Agriculture
As we navigate the complex landscape of modern agriculture, tools like Farmonaut are becoming increasingly valuable. Farmonaut offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions that align perfectly with the industry trends we’ve discussed:
- Real-time crop health monitoring using satellite imagery
- AI-driven advisory systems for personalized farm management
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions for supply chain transparency
- Resource management tools for optimized farming operations
These technologies empower farmers to make data-driven decisions, improve productivity, and adopt sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Embracing Change in Agriculture
The agricultural landscape in Georgia and across the United States is undergoing significant transformation. From the influence of USDA leadership and evolving market trends to the adoption of precision farming technologies and sustainable practices, the industry is adapting to meet new challenges and opportunities.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that success in agriculture will depend on embracing innovation, staying informed about policy changes, and leveraging data-driven insights. By doing so, farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers can work together to ensure a resilient, productive, and sustainable agricultural sector for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- How does USDA leadership impact agricultural policy?
USDA leadership plays a crucial role in shaping agricultural policies, including subsidy programs, trade agreements, and conservation initiatives. The Secretary’s background and priorities can significantly influence the direction of these policies. - What are the main factors affecting crop price fluctuations?
Crop prices are influenced by global supply and demand, weather conditions, trade policies, biofuel mandates, and currency exchange rates. - How is precision farming technology changing agriculture?
Precision farming uses technologies like GPS, satellite imagery, and IoT sensors to optimize crop production, reduce input costs, and improve sustainability. - What role do agricultural advisory committees play?
These committees provide expert advice to the USDA and other agencies, helping to shape policies and programs that address the needs of farmers and the agricultural sector. - How is climate change affecting US agriculture?
Climate change is impacting agriculture through altered growing seasons, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and shifts in pest and disease patterns. - What are the main challenges facing Georgia’s agriculture?
Key challenges include water management, labor shortages, market competition, and adapting to changing climate conditions. - How are advancements in seed treatment benefiting farmers?
Modern seed treatments improve crop resilience, enhance germination rates, and reduce the need for chemical inputs during the growing season. - What opportunities does sustainable agriculture present?
Sustainable agriculture offers opportunities for reduced input costs, premium market access, improved soil health, and long-term farm viability. - How is technology impacting agricultural export consulting?
Technology is enhancing export consulting through improved market intelligence, supply chain traceability, and streamlined documentation processes. - What role does Farmonaut play in modern agriculture?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based farm management solutions that enable precision agriculture, helping farmers optimize their operations and improve productivity.













