Iowa Study Reveals: Cover Crops Slash Soil Carbon Erosion by 68%, Boosting Sustainable Farming Practices
“Cover crops can reduce annual soil carbon loss through erosion by 68%, significantly enhancing sustainable farming practices.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of sustainable agriculture, a groundbreaking study from Iowa has shed new light on the pivotal role of cover crops in preserving soil health and mitigating climate change. As we delve into the findings of this research, we’ll explore how these innovative farming practices are reshaping the future of agriculture and contributing to global efforts in climate change mitigation.
Understanding Cover Crops and Their Impact
Cover crops, plants grown between cash crop seasons, have long been recognized for their numerous benefits to soil health and farm productivity. However, this recent study from Iowa State University has revealed an even more significant impact: the ability of cover crops to dramatically reduce soil carbon erosion.
The research, led by Wenjuan Huang, an assistant professor of ecology, evolution, and organismal biology, synthesized data from over 150 cover crop field trials. The results were nothing short of remarkable – cover crops reduced the average annual loss of soil carbon through erosion by an impressive 68%.
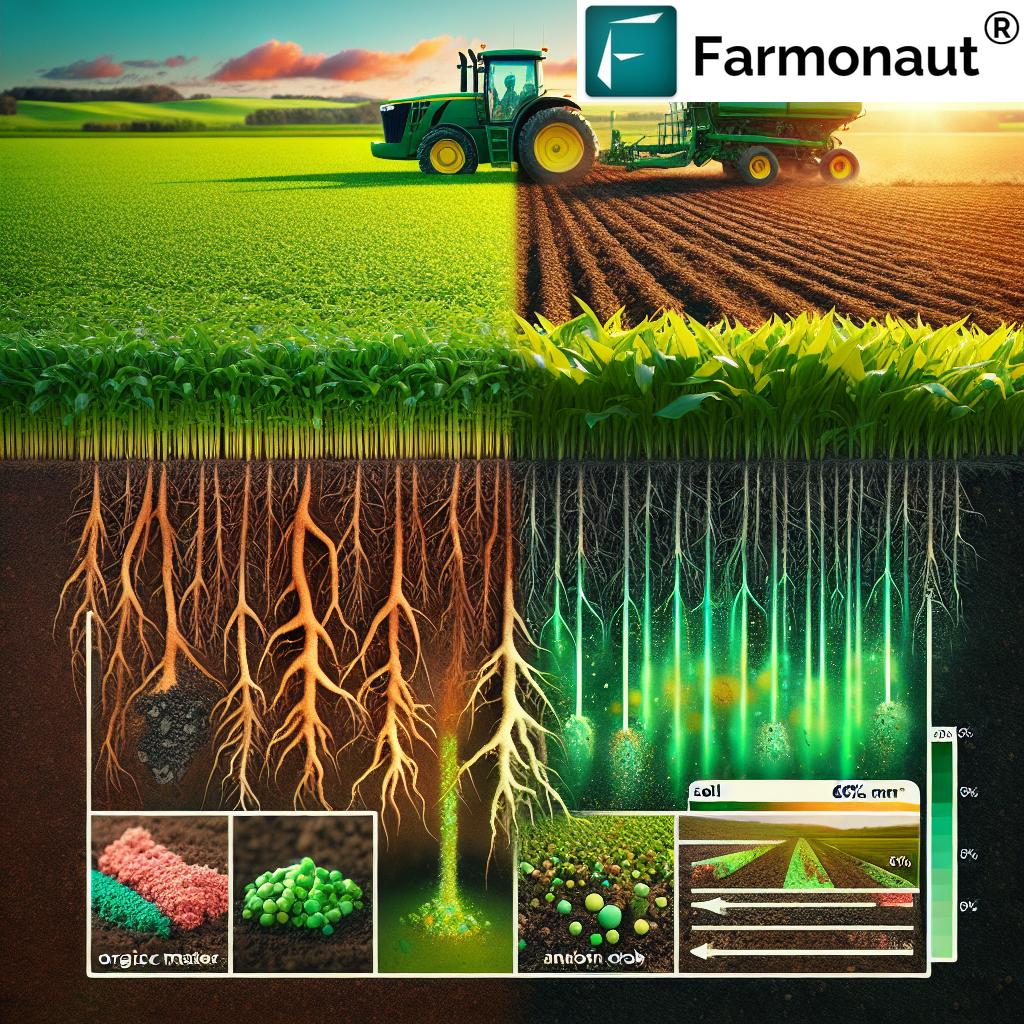

This finding is particularly crucial in the context of soil carbon sequestration and the global fight against climate change. By acting as a carbon sink, cover crops not only prevent soil erosion but also contribute to the reduction of atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
The Science Behind Soil Carbon Erosion
To truly appreciate the significance of this study, we need to understand the process of soil carbon erosion and its implications for agriculture and the environment.
- Soil Carbon Loss: When soil erodes, it carries away organic matter rich in carbon. This process not only depletes the soil of essential nutrients but also releases carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Impact on Soil Health: The loss of carbon through erosion diminishes soil fertility, structure, and water-holding capacity, making it harder for crops to thrive.
- Ecological Consequences: Eroded soil can end up in waterways, leading to water pollution and affecting aquatic ecosystems.
The Iowa study’s findings highlight how cover crops effectively address these issues by providing a protective layer to the soil, reducing erosion, and keeping carbon locked in the ground where it belongs.
Cover Crops: A Multifaceted Solution
While the reduction in soil carbon erosion is impressive, it’s just one of the many benefits that cover crops offer to sustainable farming practices:
- Improved Soil Structure: Cover crops help enhance soil aggregation, leading to better water infiltration and reduced runoff.
- Nutrient Retention: They capture and store nutrients that might otherwise leach out of the soil, making them available for the next cash crop.
- Weed Suppression: By competing for resources, cover crops can help reduce weed pressure in fields.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Cover crops provide habitat and food for beneficial insects and soil microorganisms, fostering a healthier farm ecosystem.
- Water Quality Improvement: By reducing erosion and nutrient runoff, cover crops contribute to cleaner waterways.
These multiple benefits make cover crops a cornerstone of sustainable farming practices, aligning perfectly with the goals of climate change mitigation in agriculture.
The Role of Topography in Soil Carbon Erosion
One of the fascinating aspects of the Iowa study was its analysis of factors influencing soil carbon erosion. Topography emerged as a significant player, with steeper slopes correlating strongly with cover crops’ ability to reduce soil carbon erosion.
This finding has important implications for farmland management, especially in regions with varied terrain. Farmers and agricultural planners can use this information to prioritize cover crop implementation in areas most susceptible to erosion, maximizing the benefits of this sustainable farming practice.
For those interested in leveraging technology to enhance their farming practices, Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services can provide valuable insights into optimal land use and cover crop strategies based on topographical data.
Global Implications of the Study
While the study was conducted in Iowa, its implications reach far beyond the Midwest United States. The research team used machine learning to generate a global farmland map, estimating that planting cover crops could reduce soil carbon erosion by an average of 25% worldwide.
This global perspective underscores the potential of cover crops as a tool for sustainable farming practices across diverse agricultural landscapes. From the rolling hills of Europe to the vast plains of Asia, cover crops can play a crucial role in preserving soil health and combating climate change.
“Iowa study reveals cover crops act as carbon sinks, contributing to atmospheric CO2 reduction while offering multiple benefits to farmers.”
Carbon Market Incentives: A New Frontier
The study’s findings open up exciting possibilities in the realm of carbon market incentives. With the proven ability of cover crops to significantly reduce soil carbon erosion, there’s a strong case for including this benefit in carbon credit calculations.
Currently, many carbon market incentives focus primarily on the carbon sequestered by cover crops through their biomass and root systems. However, the Iowa study suggests that the prevention of carbon loss through erosion should be considered as a separate and valuable benefit.
This could potentially lead to more comprehensive and attractive carbon market incentives for farmers who implement cover crops, further encouraging the adoption of this sustainable farming practice. For farmers looking to optimize their carbon footprint and explore potential market incentives, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting services can provide valuable insights and data-driven recommendations.
Challenges in Cover Crop Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, the adoption of cover crops faces several challenges:
- Initial Costs: Purchasing seeds and managing cover crops can represent an additional expense for farmers.
- Time and Labor: Planting and terminating cover crops requires careful timing and additional field operations.
- Knowledge Gap: Successfully integrating cover crops into existing farming systems requires specific knowledge and expertise.
- Short Growing Seasons: In some regions, the window for establishing cover crops between cash crops can be limited.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for increasing the widespread adoption of cover crops. This is where innovative agricultural technologies can play a significant role.
Technology’s Role in Sustainable Farming Practices
As we navigate the complexities of implementing sustainable farming practices like cover cropping, technology emerges as a powerful ally. Advanced agricultural technologies can help farmers optimize their cover crop strategies, maximize benefits, and overcome adoption challenges.
For instance, satellite-based farm management solutions offered by companies like Farmonaut provide valuable tools for precision agriculture. These technologies can help farmers:
- Monitor crop health in real-time
- Optimize resource allocation
- Make data-driven decisions about cover crop management
By leveraging these technologies, farmers can more effectively implement cover crops and other sustainable farming practices, contributing to soil health improvement and climate change mitigation efforts.
The Future of Sustainable Farming
As we look to the future of agriculture, the integration of cover crops and other sustainable farming practices will undoubtedly play a crucial role. The Iowa study’s findings provide compelling evidence for the environmental and economic benefits of these practices, paving the way for wider adoption and continued research.
To truly realize the potential of cover crops in mitigating climate change and improving soil health, a multifaceted approach is necessary:
- Education and Outreach: Providing farmers with the knowledge and skills needed to successfully implement cover crops.
- Policy Support: Developing policies and incentives that encourage the adoption of sustainable farming practices.
- Technological Innovation: Continuing to develop and refine technologies that support precision agriculture and sustainable farming.
- Research: Ongoing studies to further understand the impacts and optimize the use of cover crops across different regions and farming systems.
By embracing these strategies, we can work towards a future where sustainable farming practices like cover cropping are the norm rather than the exception, benefiting both our agricultural systems and the global environment.
Comparative Analysis: Cover Crop Impact on Farming Practices
| Farming Practice | Annual Soil Carbon Loss (%) | Erosion Prevention (%) | Climate Change Mitigation Impact (scale 1-10) | Soil Health Improvement (scale 1-10) | Potential Carbon Market Incentives ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Cover Crops | 100 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| With Cover Crops | 32 | 68 | 8 | 9 | 50-100 per acre |
This table clearly illustrates the significant benefits of implementing cover crops in farming practices. The dramatic reduction in soil carbon loss, coupled with substantial improvements in erosion prevention and soil health, underscores the potential of cover crops as a key strategy in sustainable agriculture and climate change mitigation.
Integrating Technology for Optimal Cover Crop Management
While the benefits of cover crops are clear, implementing them effectively requires careful planning and management. This is where advanced agricultural technologies can make a significant difference. Farmonaut’s suite of tools, for instance, can provide valuable support in optimizing cover crop strategies:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: By utilizing multispectral satellite imagery, farmers can monitor the health and development of their cover crops in real-time. This information can help in making timely decisions about management practices.
- AI-Driven Advisory Systems: Advanced AI systems can analyze various data points, including soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, to provide personalized recommendations for cover crop selection and management.
- Resource Management Tools: Efficient resource allocation is crucial for successful cover crop implementation. Technology can help farmers optimize their use of water, fertilizers, and other inputs.
For farmers looking to leverage these technologies in their cover crop management strategies, Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management solutions offer comprehensive tools and insights.
The Economic Case for Cover Crops
While the environmental benefits of cover crops are well-established, their economic advantages are equally compelling. By reducing soil erosion, improving soil health, and potentially qualifying for carbon market incentives, cover crops can contribute significantly to a farm’s bottom line.
- Reduced Input Costs: Improved soil health can lead to reduced need for fertilizers and pesticides.
- Increased Yield Stability: Better soil structure and water retention can help crops withstand stress conditions, leading to more consistent yields.
- Potential Additional Income: As carbon markets evolve, cover crops could become a source of additional income through carbon credits.
For farmers interested in exploring the financial implications of implementing cover crops, Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance services can provide valuable insights and support.
FAQs About Cover Crops and Soil Carbon Erosion
- Q: What exactly are cover crops?
A: Cover crops are plants grown between cash crop seasons to protect and improve the soil. They’re not harvested for profit but provide numerous benefits to the soil and environment. - Q: How do cover crops reduce soil carbon erosion?
A: Cover crops protect the soil surface from wind and water erosion, keeping carbon-rich organic matter in place. Their roots also help bind soil particles together, further reducing erosion. - Q: Are all cover crops equally effective at reducing soil carbon erosion?
A: Different cover crops have varying effectiveness. Factors like root structure, biomass production, and growth rate all play a role. It’s best to choose cover crops suited to your specific climate and soil conditions. - Q: Can cover crops actually increase soil carbon levels?
A: Yes, cover crops can increase soil carbon levels by adding organic matter to the soil through their roots and biomass. However, this process is separate from their role in preventing carbon loss through erosion. - Q: How long does it take to see the benefits of cover crops?
A: Some benefits, like erosion control, are immediate. Others, like increased soil organic matter, may take several seasons to become noticeable. Consistent use of cover crops over time yields the best results.
Conclusion: A Path Forward for Sustainable Agriculture
The Iowa study’s revelations about the impact of cover crops on soil carbon erosion mark a significant milestone in our understanding of sustainable farming practices. By reducing annual soil carbon loss through erosion by 68%, cover crops offer a powerful tool in the fight against climate change and soil degradation.
As we move forward, the integration of cover crops with advanced agricultural technologies presents an exciting frontier for sustainable farming. By combining the natural benefits of cover crops with the precision and efficiency of modern agtech solutions, we can create farming systems that are not only more productive but also more resilient and environmentally friendly.
The path to widespread adoption of these practices may have its challenges, but the potential rewards – for farmers, for our food systems, and for the planet – are immense. As we continue to research, innovate, and implement these sustainable farming practices, we move closer to a future where agriculture is not just a necessity for feeding the world, but a key ally in preserving our environment for generations to come.
For farmers looking to take the next step in sustainable agriculture, exploring tools like those offered by Farmonaut can provide valuable support in implementing and optimizing cover crop strategies. Together, we can cultivate a more sustainable and resilient agricultural future.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!