Protect Washington’s Crops: 4 Sustainable Strategies to Combat Invasive Pests and Boost Agricultural Productivity
“The USDA’s Invasive Plant Pest and Disease Awareness Month in April promotes 4 key strategies for agricultural biosecurity.”
As we enter April 2025, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has once again launched its annual Invasive Plant Pest and Disease Awareness Month campaign. This year, the focus is on empowering citizens with cost-efficient strategies to protect one of our nation’s most valuable assets: healthy, abundant crops. In Washington state, where agriculture plays a crucial role in the economy, this initiative takes on particular significance.
We, as residents of Washington and stewards of our agricultural heritage, have a responsibility to understand and implement sustainable practices that safeguard our crops from invasive pests. These unwanted visitors can hitch a ride on everyday items, from outdoor gear to vehicles, and even on agricultural products purchased online from overseas sources. Their rapid spread not only disrupts local ecosystems but also threatens crop productivity and the economic strength of our farming communities.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore four sustainable strategies to combat invasive pests and boost agricultural productivity in Washington. We’ll delve into the importance of invasive plant pest awareness, discuss effective crop protection strategies, and highlight the role of agricultural pest prevention in maintaining the health of our state’s diverse agricultural landscape.
Understanding the Threat: Invasive Pests in Washington
Before we dive into the strategies, it’s crucial to understand the scope of the problem. Invasive pests pose a significant threat to Washington’s agricultural sector, which contributes billions of dollars to the state’s economy annually. These pests can cause extensive damage to crops, reduce yields, and increase production costs for farmers.
Some of the most concerning invasive pests in Washington include:
- Asian Giant Hornet (Vespa mandarinia)
- Spotted Lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula)
- European Grapevine Moth (Lobesia botrana)
- Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys)
These pests not only affect crops directly but can also introduce plant diseases, further complicating pest management efforts. The challenge lies in developing and implementing sustainable farming practices that protect crops while minimizing environmental impact.

The Role of Technology in Modern Agriculture
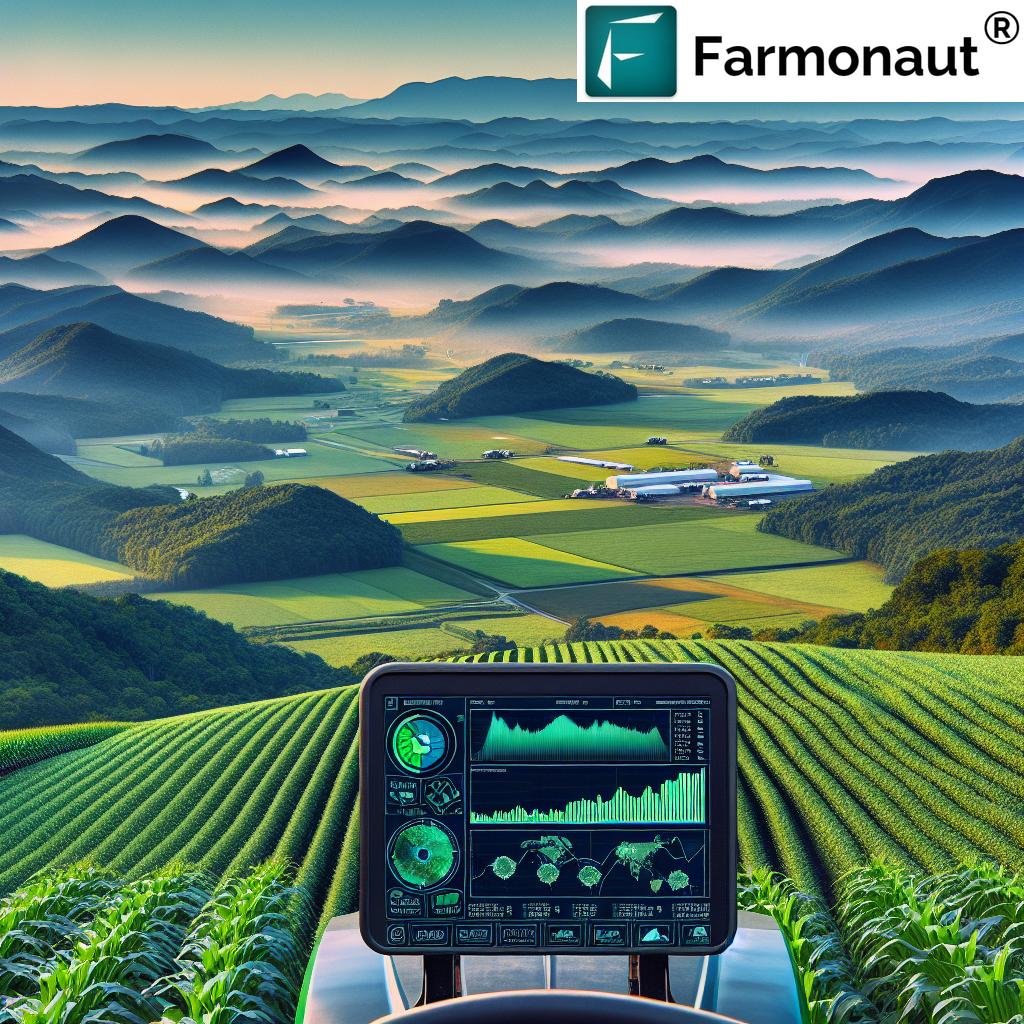
Before we delve into our sustainable strategies, it’s important to acknowledge the pivotal role that technology plays in modern agriculture. Innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut are revolutionizing the way we approach crop management and pest control.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions provide real-time crop health monitoring, which is crucial for early detection of pest infestations. By leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, farmers can make data-driven decisions to protect their crops more effectively.
For instance, Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services offer valuable insights that can help farmers implement targeted pest control measures, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticides and promoting more sustainable farming practices.
Strategy 1: Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture and a key component of effective invasive pest management. This holistic approach combines various pest control methods to minimize economic, health, and environmental risks.
Key Components of IPM:
- Prevention: Implementing practices that stop pests from becoming a problem.
- Monitoring: Regular field inspections to identify pest populations and their potential impact.
- Decision-making: Determining when action is necessary based on established economic thresholds.
- Intervention: Using a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical control methods.
IPM aligns perfectly with the USDA’s emphasis on invasive plant pest awareness and agricultural pest prevention. By adopting IPM practices, Washington farmers can significantly reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides, leading to more sustainable farming practices and improved long-term crop productivity.
Implementing IPM in Washington:
To effectively implement IPM in Washington, farmers can take advantage of technological solutions like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring. This technology enables early detection of pest infestations, allowing for timely and targeted interventions.
Additionally, Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management tools can help agricultural enterprises coordinate their IPM efforts across vast areas, ensuring consistent and effective pest control strategies.
Strategy 2: Promoting Biodiversity
Biodiversity is a powerful tool in the fight against invasive pests. By cultivating a diverse range of plants and encouraging beneficial insects, we can create resilient ecosystems that naturally resist pest invasions.
Benefits of Biodiversity in Agriculture:
- Creates natural barriers to pest movement
- Supports populations of natural predators
- Reduces the risk of pest resistance to control methods
- Improves overall soil and plant health
Implementing biodiversity in farming practices is an excellent example of sustainable farming practices that contribute to long-term crop protection strategies.
Practical Steps for Promoting Biodiversity:
- Crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles
- Intercropping or companion planting
- Maintaining hedgerows and natural habitats around fields
- Using cover crops to improve soil health and attract beneficial insects
Farmonaut’s technology can assist in planning and monitoring these biodiversity initiatives. The platform’s carbon footprinting feature can help farmers track the environmental impact of their biodiversity efforts, ensuring they’re making progress towards more sustainable agricultural practices.
Strategy 3: Early Detection and Rapid Response
Early detection and rapid response (EDRR) is a critical component of invasive species control. This strategy focuses on identifying and eradicating invasive pests before they have a chance to establish and spread.
Key Elements of EDRR:
- Regular monitoring and surveillance of crops and surrounding areas
- Quick and accurate pest identification
- Immediate reporting to relevant authorities
- Swift implementation of control measures
EDRR is essential for effective agricultural pest prevention and plays a crucial role in protecting crop productivity. By catching invasions early, we can minimize damage and reduce the need for more intensive control measures later on.
Implementing EDRR with Technology:
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system is an invaluable tool for implementing EDRR. The platform’s real-time data and AI-driven insights can help farmers detect unusual patterns or changes in crop health that might indicate a pest infestation.
Moreover, Farmonaut’s fleet management solutions can optimize the deployment of pest control teams, ensuring rapid response to potential threats across large agricultural areas.
“Proper cleaning of outdoor gear is one of the citizen-driven, cost-efficient crop protection strategies highlighted by the USDA campaign.”
Strategy 4: Community Engagement and Education
The fight against invasive pests is not just the responsibility of farmers and agricultural professionals. Every citizen has a role to play in protecting Washington’s crops and ecosystems. Community engagement and education are crucial for raising invasive plant pest awareness and encouraging widespread participation in agricultural biosecurity measures.
Key Areas of Focus for Community Education:
- Identifying common invasive pests
- Understanding the economic and environmental impacts of invasive species
- Learning proper cleaning techniques for outdoor gear and vehicles
- Recognizing the importance of not transporting plants or soil from one area to another
- Knowing how to report suspected invasive species sightings
By educating the public about these issues, we can create a network of informed citizens who actively contribute to invasive pest management and crop protection.
Leveraging Technology for Community Engagement:
Digital platforms like Farmonaut can play a significant role in community education efforts. While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on providing farm management solutions, its technology can be adapted to create educational resources and interactive tools for the public.
For instance, Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory system could be used to develop a public-facing app that helps citizens identify potential invasive species and report sightings to the relevant authorities. This kind of innovative approach can significantly enhance community involvement in pest control efforts.
Implementing the Strategies: A Holistic Approach
While each of these strategies is powerful on its own, the most effective approach to combating invasive pests and boosting agricultural productivity in Washington involves integrating all four strategies into a comprehensive pest management plan.
Here’s how these strategies work together:
- Integrated Pest Management forms the foundation of the approach, providing a framework for decision-making and intervention.
- Promoting Biodiversity strengthens the resilience of agricultural ecosystems, making them naturally more resistant to pest invasions.
- Early Detection and Rapid Response ensures that any pest threats that do emerge are quickly identified and addressed before they can cause significant damage.
- Community Engagement and Education creates a wider network of informed individuals who can contribute to pest prevention and detection efforts.
By implementing these strategies in concert, we can create a robust and sustainable system for protecting Washington’s crops from invasive pests.
The Role of Technology in Implementing These Strategies
Advanced agricultural technologies play a crucial role in implementing and optimizing these strategies. Farmonaut’s suite of tools, for instance, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of each strategy:
- For IPM: Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring can help farmers make informed decisions about when and where to intervene with pest control measures.
- For Biodiversity: The platform’s carbon footprinting feature can help track the environmental impact of biodiversity initiatives.
- For EDRR: Satellite imagery and AI-driven insights can detect early signs of pest infestations, enabling rapid response.
- For Community Engagement: While not directly offered by Farmonaut, the company’s technology could potentially be adapted to create educational tools for the public.
Moreover, Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance services can provide financial protection for farmers implementing these strategies, helping to mitigate the risks associated with transitioning to more sustainable farming practices.
The Economic Impact of Sustainable Pest Management
Implementing these sustainable strategies for combating invasive pests can have significant economic benefits for Washington’s agricultural sector:
- Reduced Crop Losses: Effective pest management can significantly reduce crop damage, leading to higher yields and improved farm income.
- Lower Input Costs: By reducing reliance on chemical pesticides, farmers can lower their input costs over time.
- Premium Pricing: Crops grown using sustainable practices may command premium prices in certain markets.
- Long-term Soil Health: Sustainable practices improve soil health over time, potentially leading to increased productivity and reduced need for fertilizers.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversified farming systems are more resilient to pest outbreaks and other environmental stresses.
Farmonaut’s traceability solutions can help farmers demonstrate their sustainable practices to consumers and buyers, potentially opening up new market opportunities and premium pricing options.
Looking to the Future: Emerging Trends in Sustainable Pest Management
As we continue to develop more effective and sustainable ways to manage invasive pests, several emerging trends are worth watching:
- Precision Agriculture: Advanced sensors and data analytics are enabling increasingly targeted pest control measures.
- Biological Control: Research into beneficial insects and microorganisms is opening up new possibilities for natural pest control.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: As climate change affects pest distributions, adaptive management strategies will become increasingly important.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to predict pest outbreaks and optimize control strategies.
- Robotics: Automated systems for pest monitoring and precise application of control measures are being developed.
These trends align well with Farmonaut’s technology-driven approach to farm management. As these technologies evolve, platforms like Farmonaut will likely play an increasingly important role in helping farmers implement cutting-edge pest management strategies.
4 Sustainable Strategies to Combat Invasive Pests in Washington
| Strategy Name | Description | Implementation Difficulty | Estimated Impact on Crop Protection | Environmental Sustainability Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | A holistic approach combining various pest control methods to minimize economic, health, and environmental risks. | Medium | High | ★★★★☆ |
| Promoting Biodiversity | Cultivating a diverse range of plants and encouraging beneficial insects to create resilient ecosystems. | Medium | Medium | ★★★★★ |
| Early Detection and Rapid Response (EDRR) | Identifying and eradicating invasive pests before they have a chance to establish and spread. | Hard | High | ★★★★☆ |
| Community Engagement and Education | Raising awareness and encouraging widespread participation in agricultural biosecurity measures. | Easy | Medium | ★★★★★ |
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Washington’s Agricultural Community
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide, protecting Washington’s crops from invasive pests requires a multifaceted approach that combines sustainable farming practices, advanced technology, and community engagement. By implementing the four key strategies we’ve discussed – Integrated Pest Management, Promoting Biodiversity, Early Detection and Rapid Response, and Community Engagement and Education – we can significantly enhance our state’s agricultural biosecurity and boost crop productivity.
The USDA’s Invasive Plant Pest and Disease Awareness Month serves as a crucial reminder of the ongoing threat posed by invasive species and the importance of remaining vigilant. As citizens of Washington, we all have a role to play in safeguarding our state’s agricultural heritage and ensuring its prosperity for future generations.
We encourage all readers to take action:
- Stay informed about invasive pests in your area
- Practice proper cleaning of outdoor gear and vehicles
- Support local farmers who implement sustainable pest management practices
- Report any suspected invasive species sightings to the relevant authorities
- Consider incorporating technology like Farmonaut’s solutions into your agricultural practices
By working together and leveraging the power of sustainable practices and innovative technologies, we can create a resilient and thriving agricultural sector in Washington that’s well-equipped to face the challenges of invasive pests.
FAQ Section
Q: What are some common invasive pests in Washington?
A: Some common invasive pests in Washington include the Asian Giant Hornet, Spotted Lanternfly, European Grapevine Moth, and Brown Marmorated Stink Bug.
Q: How can technology help in managing invasive pests?
A: Technology like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring can help detect early signs of pest infestations, enabling rapid response. AI and machine learning can also predict pest outbreaks and optimize control strategies.
Q: What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
A: IPM is a holistic approach to pest management that combines various control methods to minimize economic, health, and environmental risks. It includes prevention, monitoring, decision-making, and intervention strategies.
Q: How can individuals contribute to invasive pest management?
A: Individuals can contribute by staying informed about local invasive species, properly cleaning outdoor gear and vehicles, reporting suspected sightings, and supporting sustainable farming practices.
Q: What are the economic benefits of sustainable pest management?
A: Sustainable pest management can lead to reduced crop losses, lower input costs, potential premium pricing for sustainably grown crops, improved long-term soil health, and better risk mitigation.
Explore Farmonaut’s Solutions
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s innovative technologies can support sustainable farming practices and invasive pest management, explore our range of solutions:
For developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s capabilities into their own applications, check out our API and API Developer Docs.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Learn more about our Affiliate Program.
Farmonaut Subscriptions