Maryland’s Agricultural Crisis: PFAS Contamination and Its Impact on Soil, Water, and Crop Safety
“PFAS, known as ‘forever chemicals,’ can persist in the environment for thousands of years, contaminating soil and water resources.”
We are facing a critical environmental challenge in Maryland that threatens the very foundation of our agricultural sector and public health. The recent lawsuit filed by Maryland against W.L. Gore & Associates has brought to light a severe crisis involving per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), commonly known as “forever chemicals.” This legal action marks a turning point in our state’s fight against environmental contamination and its far-reaching consequences on our soil, water, and crop safety.
Understanding the PFAS Contamination Crisis in Maryland
The lawsuit alleges that W.L. Gore & Associates, renowned for their Gore-Tex products, continued to use harmful PFAS despite being aware of the serious health risks associated with these chemicals for decades. This negligence has led to widespread contamination, particularly in Cecil County, affecting our drinking water, surface waters, groundwater, soils, and various natural resources.
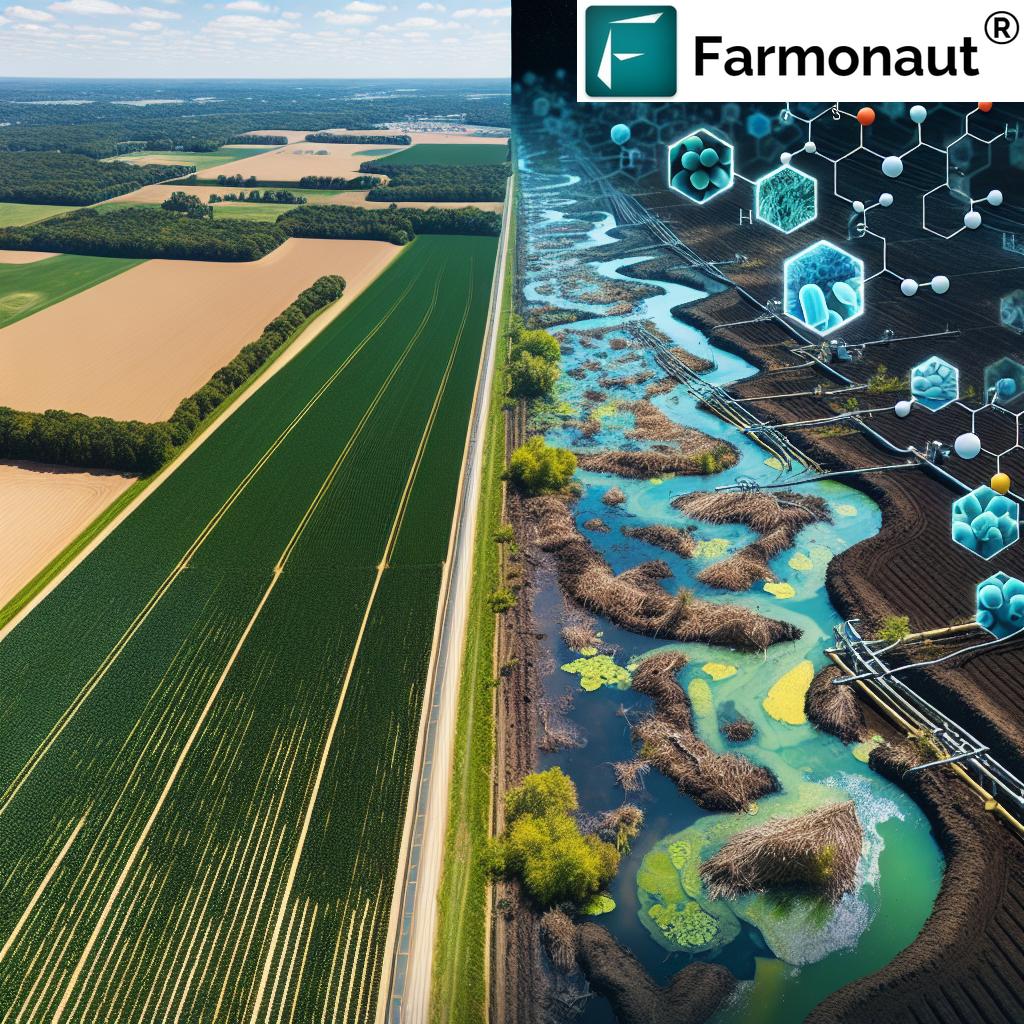
PFAS contamination in agriculture poses significant risks to soil pollution and agricultural water quality, impacting crops and sustainable farming practices. The environmental impact on crops extends beyond immediate yield concerns, potentially affecting long-term soil health and ecosystem balance.
The Scope of PFAS Contamination in Maryland’s Agriculture
The extent of PFAS contamination in Maryland’s agricultural sector is alarming. These chemicals have been detected in various components of our agricultural system:
- Soil Pollution: PFAS have infiltrated our farmlands, potentially altering soil chemistry and fertility.
- Water Resources: Both surface and groundwater have shown traces of these chemicals, raising concerns about irrigation safety.
- Crop Absorption: There’s growing evidence that some crops can absorb PFAS from contaminated soil and water.
- Livestock Exposure: Animals grazing on contaminated land or drinking affected water are at risk of PFAS accumulation.
The persistence of these chemicals in the environment makes them particularly troublesome for sustainable farming practices. As we strive to maintain and improve our agricultural output, the presence of PFAS poses a significant challenge to crop safety and chemical management strategies.
Health Risks and Environmental Impact
The health risks associated with PFAS exposure are severe and wide-ranging. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and our state health officials, potential health effects include:
- Increased risk of certain cancers
- Immune system complications
- Developmental delays in children
- Reproductive issues
- Hormonal imbalances
These health concerns extend beyond the farm, affecting drinking water safety for farms and surrounding communities. The long-term effects of PFAS exposure on public health are still being studied, but the current evidence is alarming enough to warrant immediate action.
The Legal Battle and Its Implications
Maryland’s lawsuit against W.L. Gore & Associates is not just about holding a single company accountable; it represents a broader struggle against environmental pollution and corporate responsibility. The state is seeking to recover costs associated with investigation and cleanup, as well as damages resulting from the pollution.
This legal action highlights the urgent need for stricter environmental regulations in agriculture and industry. It also underscores the importance of transparency and corporate responsibility in handling potentially harmful chemicals.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Mitigation
In the face of this crisis, innovative technologies are emerging as crucial tools in our fight against PFAS contamination. Farmonaut’s advanced remote sensing technology is at the forefront of this battle, offering farmers and environmental agencies powerful means to monitor soil and water quality.
Through satellite-based monitoring and AI-driven analytics, Farmonaut provides:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Soil moisture analysis
- Detection of anomalies that could indicate contamination
These tools are essential for implementing effective agricultural toxin management strategies and ensuring crop safety in the face of environmental challenges.
PFAS Contamination Impact Comparison
| Agricultural Aspect | Contamination Level | Potential Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Quality | High | Reduced fertility, altered soil chemistry | Soil remediation, phytoremediation, remote sensing monitoring |
| Water Resources | High | Contaminated irrigation, livestock exposure | Water filtration systems, alternative water sources, regular testing |
| Crop Safety | Medium | Bioaccumulation in plants, reduced crop quality | Crop rotation, selective planting, advanced crop monitoring |
| Public Health | High | Cancer risks, developmental issues, immune system effects | Public awareness campaigns, health monitoring programs, policy interventions |
The Path Forward: Sustainable Solutions and Policy Changes
Addressing the PFAS contamination crisis requires a multi-faceted approach combining technological innovation, policy reform, and community action. We need to focus on:
- Enhanced Monitoring: Utilizing advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based solutions for comprehensive environmental monitoring.
- Stricter Regulations: Implementing and enforcing more stringent environmental regulations to prevent future contamination.
- Remediation Efforts: Investing in research and implementation of effective soil and water remediation techniques.
- Public Awareness: Educating communities about the risks of PFAS and ways to minimize exposure.
- Support for Affected Farmers: Providing resources and assistance to farmers dealing with contaminated land and water.
“Maryland’s agricultural crisis involves PFAS contamination affecting over 270 farms, impacting thousands of acres of farmland.”
The crisis in Maryland serves as a wake-up call for the entire nation. It highlights the delicate balance between industrial progress and environmental stewardship, and the critical need for sustainable practices in all sectors of our economy.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Research
As we grapple with the PFAS contamination issue, the role of continuous monitoring and research cannot be overstated. This is where technologies like those offered by Farmonaut become invaluable. By providing real-time data on soil and crop health, these tools enable:
- Early detection of potential contamination
- Tracking the effectiveness of remediation efforts
- Informing policy decisions with accurate, up-to-date information
The integration of such technologies into our agricultural practices is not just beneficial; it’s becoming increasingly necessary in the face of environmental challenges like PFAS contamination.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural monitoring
Community Impact and Response
The PFAS contamination crisis in Maryland has had a profound impact on local communities, particularly in areas like Cecil County. Residents are grappling with:
- Concerns over long-term health effects
- Decreased property values
- Loss of trust in local water sources
- Economic impact on farming communities
In response, we’re seeing a rise in community activism and increased demand for transparency from both corporations and government agencies. This grassroots movement is crucial in driving policy changes and ensuring that the voices of affected communities are heard.

The Role of Innovation in Sustainable Agriculture
As we confront the challenges posed by PFAS contamination, the importance of innovation in sustainable agriculture becomes ever more apparent. Advanced technologies are not just tools for monitoring; they’re catalysts for transforming our approach to farming and environmental stewardship.
Farmonaut’s suite of tools exemplifies this innovative approach:
- AI-Driven Crop Management: Utilizing artificial intelligence to optimize crop health and yield while minimizing environmental impact.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Ensuring transparency in the agricultural supply chain, from farm to consumer.
- Precision Resource Management: Enabling farmers to use water, fertilizers, and other resources more efficiently, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
These technologies not only help in managing current crises but also in building a more resilient and sustainable agricultural future.
Check out Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs for integration possibilities
The Broader Environmental Context
While our focus is on Maryland’s agricultural crisis, it’s crucial to understand that PFAS contamination is a global issue. From the arctic to urban centers, these chemicals have been detected in various environments, highlighting the interconnectedness of our ecosystems.
Key global concerns include:
- Oceanic pollution affecting marine life
- Contamination of polar regions through atmospheric transport
- Bioaccumulation in wildlife food chains
- Cross-border water pollution issues
This global perspective underscores the need for international cooperation and standardized approaches to tackling PFAS contamination.
Economic Implications of PFAS Contamination
The economic impact of PFAS contamination extends far beyond the immediate costs of cleanup and litigation. We’re looking at long-term effects on:
- Agricultural productivity and exports
- Property values in affected areas
- Healthcare costs related to PFAS-induced illnesses
- Tourism and recreation in contaminated regions
These economic challenges necessitate innovative solutions and support systems for affected communities and industries.
The Future of Agriculture in a PFAS-Affected World
As we move forward, the agriculture sector must adapt to the realities of a PFAS-affected environment. This adaptation involves:
- Developing PFAS-resistant crop varieties
- Implementing advanced filtration systems for irrigation
- Adopting precision agriculture techniques to minimize chemical use
- Exploring alternative farming methods like vertical farming and hydroponics
These adaptations, coupled with ongoing research and technological advancements, will be crucial in ensuring food security and safety in the face of environmental challenges.
Policy Recommendations and Future Directions
To effectively address the PFAS contamination crisis, we propose the following policy recommendations:
- Comprehensive PFAS Testing: Implement mandatory, regular testing of soil, water, and agricultural products for PFAS contamination.
- Stricter Regulations on PFAS Use: Enact and enforce more stringent regulations on the production, use, and disposal of PFAS-containing products.
- Investment in Remediation Technologies: Allocate significant resources to research and develop effective PFAS remediation technologies.
- Support for Affected Farmers: Establish programs to provide financial and technical assistance to farmers dealing with PFAS-contaminated land.
- Public Education Initiatives: Launch comprehensive public awareness campaigns about PFAS risks and mitigation strategies.
These policies, combined with ongoing technological advancements and community engagement, will be crucial in addressing the PFAS crisis and preventing future environmental contamination.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The PFAS contamination crisis in Maryland’s agricultural sector is a wake-up call for all of us. It highlights the delicate balance between industrial progress and environmental stewardship, and the critical need for sustainable practices in all sectors of our economy.
As we move forward, it’s clear that addressing this crisis will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders – government agencies, agricultural communities, technology providers like Farmonaut, and the public at large. By leveraging advanced technologies, implementing stringent regulations, and fostering a culture of environmental responsibility, we can overcome this challenge and build a more sustainable future for Maryland’s agriculture and beyond.
The path ahead is challenging, but with innovation, determination, and collective action, we can turn this crisis into an opportunity for positive change, ensuring the safety of our soil, water, and crops for generations to come.
FAQ Section
- What are PFAS and why are they harmful?
PFAS (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a group of man-made chemicals that persist in the environment and can accumulate in living organisms, leading to various health issues including cancer and developmental problems. - How does PFAS contamination affect agriculture?
PFAS contamination can affect soil quality, water resources, and crop safety. It may lead to reduced soil fertility, contaminated irrigation water, and potential bioaccumulation of PFAS in crops. - What steps can farmers take to mitigate PFAS contamination?
Farmers can implement soil testing, use alternative water sources, adopt crop rotation strategies, and utilize advanced monitoring technologies like those offered by Farmonaut to detect and manage contamination. - How can technology help in addressing the PFAS crisis?
Technologies like satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven analytics, and blockchain-based traceability can help in early detection of contamination, efficient resource management, and ensuring transparency in the agricultural supply chain. - What are the long-term implications of PFAS contamination for public health?
Long-term exposure to PFAS has been linked to various health issues including cancer, immune system disorders, and developmental problems in children. The full extent of long-term effects is still being studied.