Maximizing Soybean Yields: Illinois Study Reveals Surprising Link Between Soil Fertility and Planting Dates
“Illinois study finds early-planted soybeans in low-fertility fields yield 5-10% more than late-planted crops.”
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we’re constantly seeking innovative ways to maximize crop yields while optimizing resource use. A recent groundbreaking study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has shed new light on the complex relationship between soil fertility, planting dates, and soybean yields. This research challenges long-held assumptions and provides valuable insights that could revolutionize soybean production practices.
As we delve into the details of this study, we’ll explore how early soybean planting and soil fertility impact crop yields, and discuss the implications for farmers and agricultural practices. We’ll also examine how modern technologies, such as those offered by Farmonaut, can help implement these findings to optimize soybean production.
The Surprising Link Between Soil Fertility and Planting Dates
The study, conducted by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has revealed an unexpected connection between soil fertility levels and optimal planting dates for soybeans. Contrary to traditional beliefs, the research suggests that unfertilized soybean fields with lower soil fertility should be planted earlier than those with higher fertility levels.

This finding challenges the prevailing assumption that high soil fertility would lead to better yields if soybeans are planted early. Fred Below, a professor in the Department of Crop Sciences at the University of Illinois, explains that while increasing the planting date generally enhances yield potential through a longer growing season, it also heightens the demand for soil nutrients.
The Role of Soil Testing in Soybean Production
Soil testing plays a crucial role in soybean production, as farmers often rely on these tests to determine whether to utilize residual nutrients from previous crops. However, the study highlights a significant issue: the soil sufficiency values used to determine fertilizer needs have not been updated since the 1960s.
This outdated information poses a challenge for modern soybean growers, as production practices have significantly evolved over the past six decades. The research team sought to re-establish the correlation between modern soil testing values and yield, recognizing the need for updated information in the face of changing agricultural practices.
The Study: Methodology and Findings
Between 2014 and 2021, the research team conducted an extensive study involving 133 unfertilized soybean trials across Illinois. They collected soil samples and correlated the results with yield data based on various planting dates, categorized as very early, early, late, or very late.
The analysis revealed a notable correlation:
- High fertility fields generally yielded better when soybeans were planted late.
- When planted early, the yield did not significantly depend on soil test values.
- Earlier planting allows crops more time to absorb and utilize nutrients effectively.
Connor Sible, a co-author of the study, elaborated on these findings. He explained that while a higher soil test indicates more fertility, it holds less importance for early-planted soybeans. This is possibly due to the crops having a longer time frame to gather the required nutrients and the ability to mobilize stored nutrients effectively for seed development.
Implications for Soybean Growers
These findings have significant implications for soybean growers and their management strategies. Here are some key takeaways:
- Early planting benefits: For fields with lower soil fertility, early soybean planting can lead to better yields by allowing plants more time to absorb available nutrients.
- Late planting considerations: High-fertility fields may benefit from later planting dates, as the increased nutrient availability can support rapid growth during a shorter growing season.
- Nutrient management: The study emphasizes the importance of tailored nutrient management strategies based on soil fertility levels and planting dates.
- Soil testing updates: There’s a clear need for updated soil sufficiency values that reflect modern agricultural practices and soybean varieties.
“Research reveals current soybean soil testing values rely on outdated data from over 60 years ago.”
Optimizing Soybean Planting Dates
The study’s findings highlight the importance of optimizing soybean planting dates based on soil fertility levels. Here are some strategies farmers can consider:
- For low-fertility fields, prioritize early planting to maximize nutrient uptake over a longer growing season.
- In high-fertility fields, consider later planting dates to take advantage of the abundant nutrients during peak growth periods.
- Use soil testing results to inform planting date decisions, but be aware of the limitations of current sufficiency values.
- Monitor crop performance and yield data across different planting dates and soil fertility levels to fine-tune strategies for specific fields.

Soybean Nutrient Management Strategies
Effective nutrient management is crucial for maximizing soybean yields. Based on the study’s findings, we can recommend the following strategies:
- Soil testing: Regularly conduct soil tests to assess fertility levels, but interpret results cautiously given the outdated sufficiency values.
- Targeted fertilization: Consider applying fertilizers based on both soil test results and planned planting dates.
- Cover crops: Implement cover crops to improve soil health and nutrient availability, especially in low-fertility fields.
- Residual nutrient utilization: Take advantage of residual nutrients from previous crops, particularly when planning early planting in low-fertility fields.
- Precision agriculture: Utilize precision agriculture tools, such as those offered by Farmonaut, to optimize nutrient application and monitor crop health throughout the growing season.
Maximizing Soybean Crop Yield: A Comprehensive Approach
To maximize soybean crop yield, farmers should adopt a comprehensive approach that considers various factors beyond soil fertility and planting dates. Here are some additional strategies to consider:
- Variety selection: Choose soybean varieties that are well-suited to your local climate and soil conditions.
- Pest and disease management: Implement integrated pest management practices to protect crops from yield-reducing threats.
- Irrigation management: Optimize irrigation practices to ensure adequate water availability throughout the growing season.
- Crop rotation: Implement effective crop rotation strategies to improve soil health and break pest and disease cycles.
- Technology adoption: Embrace precision agriculture technologies for data-driven decision-making and resource optimization.
By combining these strategies with the insights from the Illinois study, soybean growers can work towards achieving optimal yields while managing resources efficiently.
The Role of Modern Agricultural Technologies
As we strive to implement the findings of this groundbreaking study, modern agricultural technologies play a crucial role in optimizing soybean production. Farmonaut, a leading provider of satellite-based farm management solutions, offers tools that can help farmers apply these insights effectively:
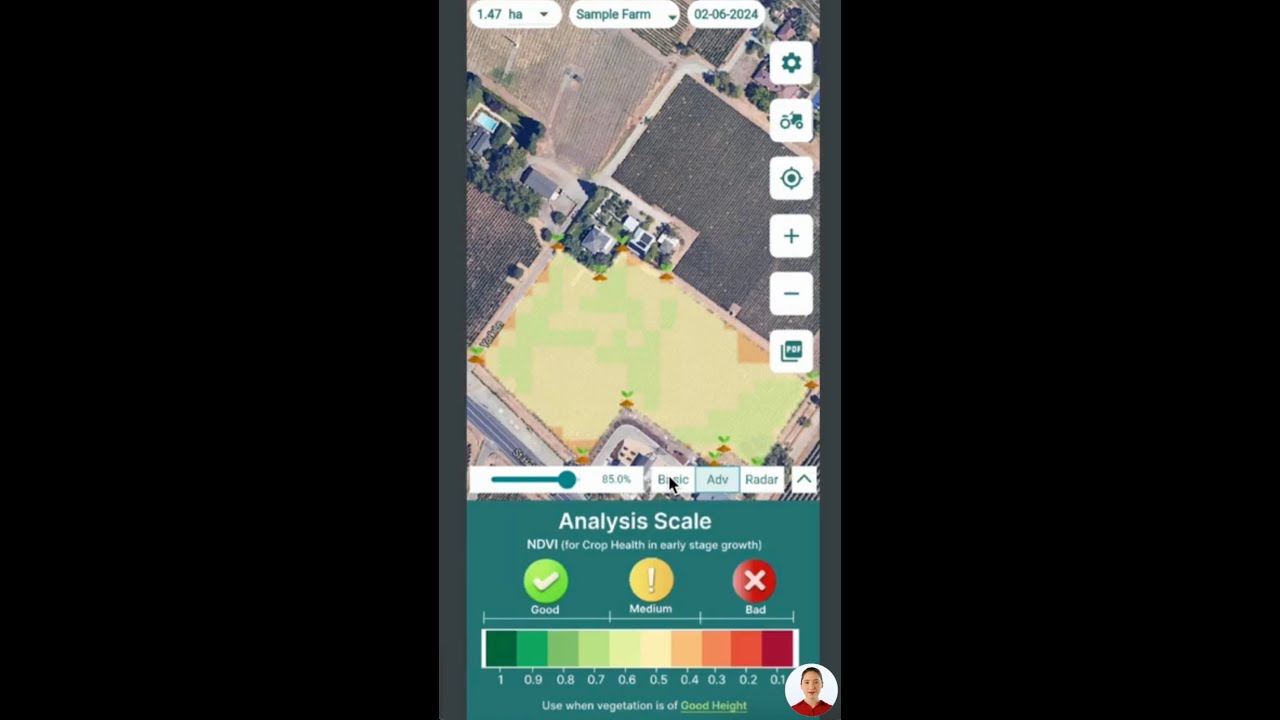
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut’s platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing valuable insights into vegetation health (NDVI) and soil moisture levels. This data can help farmers make informed decisions about planting dates and nutrient management.
- AI-Driven Advisory System: The Jeevn AI advisory system delivers real-time insights and expert crop management strategies, helping farmers optimize their soybean production based on field-specific conditions.
- Resource Management Tools: Farmonaut’s fleet and resource management features can help agribusinesses optimize their operations, ensuring efficient use of machinery and resources during critical planting and harvesting periods.
To learn more about how Farmonaut’s technologies can support your soybean production efforts, visit their web application or explore their mobile apps:
Soybean Yield Comparison by Planting Date and Soil Fertility
| Soil Fertility Level | Early April | Late April | Early May | Late May |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 65 bu/acre | 62 bu/acre | 58 bu/acre | 52 bu/acre |
| Medium | 70 bu/acre | 72 bu/acre | 70 bu/acre | 65 bu/acre |
| High | 72 bu/acre | 75 bu/acre | 78 bu/acre | 76 bu/acre |
Note: The values in this table are estimates based on the study’s findings and may vary depending on specific field conditions and management practices.
Adapting to Environmental Factors
While the Illinois study provides valuable insights into the relationship between soil fertility and planting dates, it’s important to consider how environmental factors can influence soybean growing seasons. Climate change and varying weather patterns can significantly impact optimal planting times and crop development.
Farmers should consider the following environmental factors when planning their soybean production:
- Temperature trends: Monitor long-term temperature trends in your region, as warmer springs may allow for earlier planting dates.
- Precipitation patterns: Consider historical and predicted rainfall patterns when determining planting dates and irrigation strategies.
- Frost risk: Assess the risk of late spring frosts in your area, which could affect early-planted soybeans.
- Growing degree days: Track growing degree days to predict crop development stages and optimize management practices.
By taking these environmental factors into account, farmers can adapt their planting strategies to maximize soybean yields in the face of changing climate conditions.
Economic Implications for Soybean Growers
The findings of the Illinois study have significant economic implications for soybean growers. By optimizing planting dates based on soil fertility levels, farmers can potentially improve their yields and, consequently, their economic outcomes. Here are some key economic considerations:
- Input costs: Early planting in low-fertility fields may reduce the need for additional fertilizer inputs, potentially lowering production costs.
- Yield potential: Maximizing yields through optimized planting dates can lead to increased revenue per acre.
- Risk management: Adapting planting strategies based on soil fertility can help mitigate risks associated with environmental factors and market fluctuations.
- Long-term soil health: Implementing these findings as part of a comprehensive soil management strategy can contribute to long-term soil health and sustained productivity.
To fully capitalize on these economic benefits, farmers may need to invest in soil testing, precision agriculture technologies, and potentially adjust their equipment and labor schedules to accommodate different planting dates across their fields.
The Future of Soybean Production Practices
As we look to the future of soybean production, it’s clear that the insights from this Illinois study will play a crucial role in shaping farming practices. Here are some potential developments we may see in the coming years:
- Updated soil testing standards: The agricultural community may push for updated soil sufficiency values that reflect modern soybean varieties and production practices.
- Precision planting technologies: We may see the development of advanced planting equipment that can adjust seeding rates and depths based on real-time soil fertility data.
- AI-driven planting date recommendations: Artificial intelligence systems, like those offered by Farmonaut, may evolve to provide highly accurate, field-specific planting date recommendations based on multiple data points.
- Climate-adaptive soybean varieties: Plant breeders may focus on developing soybean varieties that are better suited to specific soil fertility levels and planting date ranges.
- Integrated farm management systems: We may see the rise of comprehensive farm management platforms that integrate soil fertility data, weather predictions, and market information to optimize planting decisions.
As these developments unfold, it will be crucial for soybean growers to stay informed and adapt their practices accordingly.
Conclusion: Embracing Innovation in Soybean Production
The groundbreaking study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has provided valuable insights into the complex relationship between soil fertility, planting dates, and soybean yields. By challenging traditional assumptions, this research opens up new possibilities for optimizing soybean production practices.
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the key findings suggest that:
- Early planting can benefit low-fertility fields by allowing crops more time to absorb available nutrients.
- High-fertility fields may yield better with later planting dates.
- Current soil testing values may need updating to reflect modern agricultural practices.
- A comprehensive approach to soybean production, considering factors beyond soil fertility and planting dates, is crucial for maximizing yields.
To implement these findings effectively, soybean growers can leverage modern agricultural technologies, such as those offered by Farmonaut. These tools can provide valuable insights into crop health, soil conditions, and optimal management strategies.
As we look to the future of soybean production, it’s clear that embracing innovation and adapting to new research findings will be key to success. By combining the insights from this study with precision agriculture technologies and sustainable farming practices, soybean growers can work towards maximizing their yields while optimizing resource use.
We encourage farmers to consider these findings in their planning processes, conduct their own field trials, and stay informed about ongoing research in this area. By doing so, they can continue to improve their soybean production practices and contribute to a more sustainable and productive agricultural future.
FAQ Section
Q: How does early planting benefit low-fertility soybean fields?
A: Early planting in low-fertility fields allows soybean plants more time to absorb available nutrients throughout the growing season, potentially leading to higher yields.
Q: Why might high-fertility fields perform better with late planting?
A: High-fertility fields have abundant nutrients available, which can support rapid growth during a shorter growing season, making late planting a viable option.
Q: How often should I conduct soil tests for my soybean fields?
A: It’s generally recommended to conduct soil tests every 2-3 years, but annual testing can provide more accurate data for precision management.
Q: Can I apply the findings of this study to other crops?
A: While the study focused on soybeans, the principles of optimizing planting dates based on soil fertility may apply to other crops. However, specific research for each crop would be necessary to confirm this.
Q: How can precision agriculture tools help me implement these findings?
A: Precision agriculture tools, like those offered by Farmonaut, can provide detailed soil fertility maps, monitor crop health, and offer data-driven insights to help optimize planting dates and nutrient management strategies.
For more information on Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions, visit their web application or explore their API Developer Docs.