Minnesota Farmers’ Guide: Navigating Unusual Weather Patterns for a Successful Growing Season
“Minnesota’s below-average snowfall has allowed frost to penetrate deeper into the soil, affecting up to 90% of farmland.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how Minnesota farmers can navigate the challenges posed by unusual weather patterns to ensure a successful growing season. As we delve into this crucial topic, we’ll explore the intricate relationship between climate, soil conditions, and crop resilience. Our goal is to provide you with valuable insights and practical strategies to adapt to these changing conditions.
Understanding the Current Climate Situation in Minnesota
Minnesota’s agricultural landscape is experiencing significant shifts due to atypical weather patterns. These changes are having profound impacts on farming conditions, particularly affecting soil moisture and frost depth. As we prepare for the upcoming growing season, it’s essential to understand these challenges and their potential effects on our crops.

Below-Average Snowfall and Its Implications
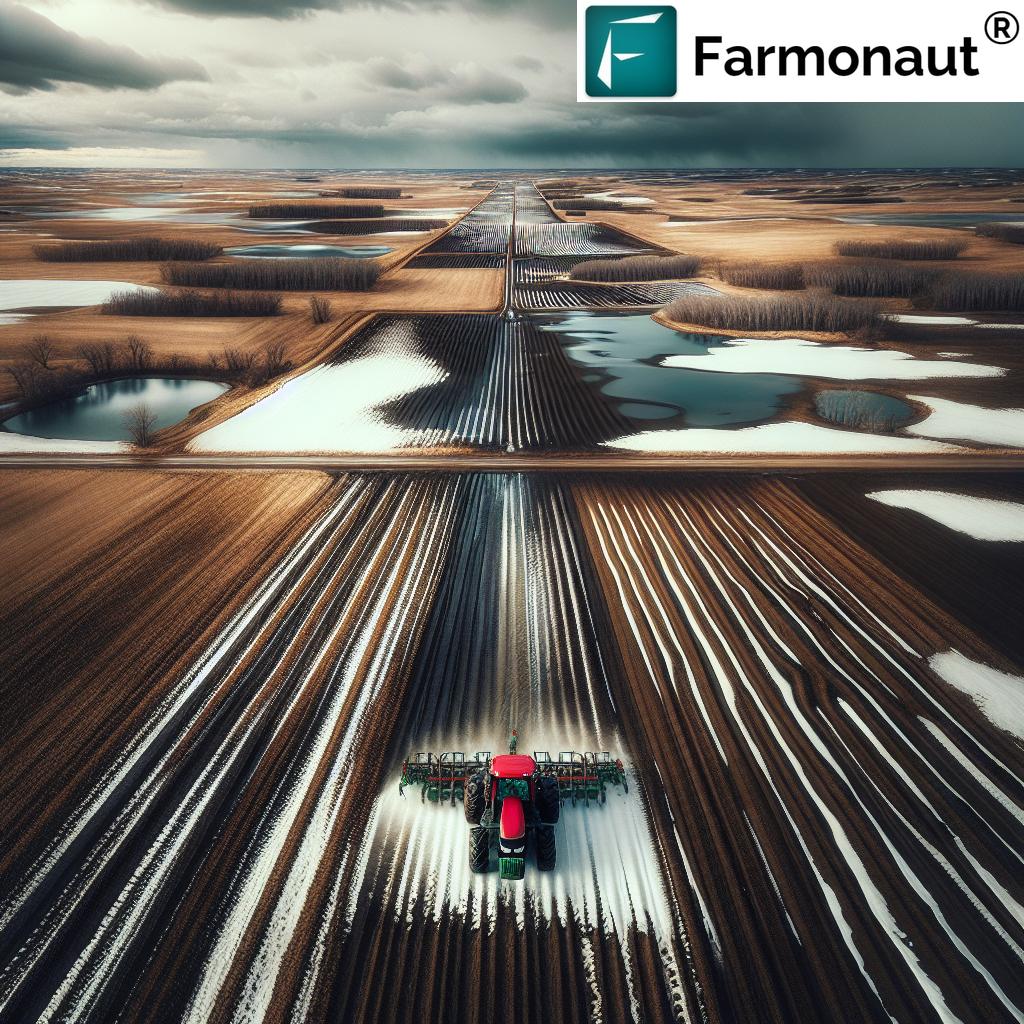
One of the most notable changes we’re observing is the below-average snowfall across the state. Typically, Minnesota experiences lighter, fluffier snow from December to February, followed by heavier, wetter snow from March to May. However, current snowfall totals are significantly lower than the 30-year average. This reduction in snow cover has far-reaching consequences for our agricultural practices.
- Reduced insulation for the soil
- Increased vulnerability to temperature fluctuations
- Potential changes in soil moisture retention
Arctic Blasts and Frost Penetration
The combination of reduced snowfall and arctic blasts with sub-zero temperatures has led to deeper frost penetration in many areas. Without the insulating layer of snow, the ground is more exposed to these extreme cold conditions. This deeper frost can complicate soil conditions and pose challenges for spring planting.
To better understand how these unusual weather patterns are affecting Minnesota’s agricultural landscape, let’s take a look at this comparative table:
| Weather Factor | Normal Conditions | Current Unusual Patterns | Potential Crop Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snowfall | Average 55 inches annually | Below-average, 30-40 inches | Reduced soil insulation, potential moisture deficit |
| Frost Depth | Typically 3-5 feet | Deeper, potentially 5-7 feet | Delayed soil warming, possible planting delays |
| Soil Moisture | Adequate spring moisture | Variable, potentially lower | Challenges for seed germination, especially for corn and soybeans |
| Temperature Fluctuations | Gradual spring warm-up | More extreme swings | Stress on emerging crops, potential frost damage |
As we can see from this table, the unusual weather patterns are creating a complex set of challenges for Minnesota farmers. However, with proper understanding and adaptation, we can navigate these changes successfully.
Soil Moisture and Crop Planning
One of the most critical factors in our crop planning process is soil moisture. Despite the below-average snowfall, it’s important to note that the total precipitation remains near the norm due to moisture-rich snowfall events. However, the availability of this moisture for our crops is a more complex issue.
The Moisture Availability Conundrum
Jeffrey Strock, a soil scientist from the University of Minnesota Southwest Research & Outreach Center, emphasizes a crucial point: while moisture is present in the soil, it may not be readily available for plants. This is particularly true in areas with insufficient snow cover to insulate the ground.
The lack of insulating snow cover allows for deeper frost penetration, which can lead to several challenges:
- Delayed soil thawing in spring
- Potential water runoff as the frost layer melts
- Complications in soil preparation for planting
Crop Resilience in Dry Conditions
In Minnesota, our major crops – corn, soybeans, and wheat – are generally resilient to dry soil conditions. However, the situation becomes more complex when we consider the potential for rapid temperature increases. Such temperature spikes could hinder the plants’ access to necessary moisture for seed germination.
This delicate balance between soil moisture, temperature, and crop needs underscores the importance of careful planning and monitoring as we approach the growing season.
Adapting to Climate Effects: Strategies for Minnesota Farmers
“Rapid temperature increases in spring can reduce seed germination rates by up to 30% for major crops like corn and soybeans.”
As we face these unusual weather patterns, it’s crucial that we adapt our agricultural practices to ensure a successful growing season. Here are some strategies that Minnesota farmers can consider:
1. Soil Moisture Monitoring
Regular monitoring of soil moisture levels is more important than ever. Consider investing in soil moisture sensors or utilizing services that provide detailed soil moisture data. This information can help you make informed decisions about irrigation and planting times.
Farmonaut’s API offers real-time satellite data on soil moisture, which can be invaluable for precise decision-making.
2. Adjusting Planting Schedules
Given the potential for deeper frost and variable soil conditions, be prepared to adjust your planting schedules. This might mean delaying planting in some areas or using different varieties of crops that are better suited to the current conditions.
3. Conservation Tillage Practices
Implementing conservation tillage practices can help retain soil moisture and improve soil health. These practices can be particularly beneficial in years with unusual weather patterns.
- No-till or reduced tillage systems
- Cover cropping to improve soil structure and moisture retention
- Crop residue management to protect soil surface
4. Diversifying Crop Selection
Consider diversifying your crop selection to spread risk. Some crops may be more resilient to the current conditions than others. Researching and possibly incorporating drought-resistant varieties could be a wise strategy.
5. Efficient Irrigation Systems
If irrigation is part of your farming practice, now is the time to ensure your systems are as efficient as possible. Consider technologies like drip irrigation or precision sprinklers that can maximize water use efficiency.
Leveraging Technology for Precision Agriculture
In these challenging times, technology can be a farmer’s best friend. Precision agriculture tools can help you make data-driven decisions to optimize your farming practices.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
Satellite imagery can provide valuable insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. These tools allow you to monitor your fields remotely and identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
AI-Powered Advisory Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems can analyze vast amounts of data to provide personalized recommendations for your farm. These systems can take into account factors like weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop characteristics to offer tailored advice.
The Impact of Weather on Specific Crops
Let’s take a closer look at how these unusual weather patterns might affect some of Minnesota’s major crops:
Corn
Corn is particularly sensitive to soil temperature and moisture at planting time. The deeper frost penetration could delay soil warming, potentially pushing back planting dates. Additionally, if rapid temperature increases occur, it could lead to moisture stress during the critical germination period.
Soybeans
Soybeans are generally more tolerant of varying soil conditions than corn. However, they still require adequate soil moisture for successful germination and early growth. The variable moisture conditions we’re experiencing could lead to uneven emergence in soybean fields.
Wheat
Winter wheat, which is planted in the fall, may face challenges due to the lack of insulating snow cover. This could lead to winter kill in some areas. Spring wheat, on the other hand, might benefit from the earlier soil warming if precipitation levels remain adequate.

Long-Term Considerations for Minnesota Agriculture
While we’re focusing on navigating the immediate challenges of this growing season, it’s also important to consider the long-term implications of these changing weather patterns.
Climate Resilience Planning
Developing a climate resilience plan for your farm can help you prepare for future variability. This might include:
- Investing in water management infrastructure
- Exploring new crop varieties that are better suited to changing conditions
- Implementing soil health practices to improve overall farm resilience
Collaborative Research and Knowledge Sharing
Staying connected with agricultural research institutions and participating in farmer networks can provide valuable insights and support. The University of Minnesota’s agricultural research programs, for example, are continually working on solutions to help farmers adapt to changing conditions.
Leveraging Farmonaut for Successful Farming
As we navigate these challenging weather conditions, tools like Farmonaut can be invaluable for Minnesota farmers. Farmonaut offers advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions that can help you make informed decisions throughout the growing season.
Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring
Farmonaut’s platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing insights into vegetation health (NDVI) and soil moisture levels. This real-time data can help you identify potential issues early and take corrective action.
AI-Driven Advisory System
The Jeevn AI Advisory System delivers personalized farm advice based on satellite data and other inputs. This can be particularly helpful in adapting to unusual weather patterns, as it provides customized strategies for your specific farm conditions.
Resource Management Tools
Farmonaut’s resource management tools can help you optimize your use of water, fertilizers, and other inputs. In a year with variable moisture conditions, this level of precision can be crucial for maximizing crop yields while minimizing waste.
Earn With Farmonaut: Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Conclusion: Embracing Adaptability for a Successful Growing Season
As we face these unusual weather patterns in Minnesota, adaptability and informed decision-making are key to ensuring a successful growing season. By leveraging technology, implementing sustainable practices, and staying informed about changing conditions, we can navigate these challenges effectively.
Remember, while the weather may be unpredictable, our response to it doesn’t have to be. By staying proactive and utilizing the tools and knowledge available to us, we can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation in our farming practices.
FAQs
Q: How can I best prepare my farm for the upcoming growing season given the unusual weather patterns?
A: Focus on soil moisture monitoring, be flexible with planting schedules, implement conservation tillage practices, consider crop diversification, and leverage technology like Farmonaut for precision agriculture.
Q: What impact does reduced snowfall have on soil conditions?
A: Reduced snowfall can lead to deeper frost penetration, potentially delaying soil warming in spring and affecting moisture availability for crops.
Q: How can satellite-based crop monitoring help my farm?
A: Satellite-based monitoring provides real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical factors, allowing for more informed decision-making and early problem detection.
Q: Are there any long-term strategies I should consider for adapting to changing weather patterns?
A: Yes, developing a climate resilience plan, investing in water management infrastructure, exploring new crop varieties, and implementing soil health practices are all valuable long-term strategies.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s tools help me navigate these unusual weather conditions?
A: Farmonaut offers real-time crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and resource management tools that can help you make data-driven decisions and optimize your farming practices in response to changing conditions.
By staying informed, adaptable, and leveraging the right tools and technologies, Minnesota farmers can successfully navigate these unusual weather patterns and ensure a productive growing season. Remember, in agriculture, challenges often lead to innovation and improved practices. Let’s embrace this opportunity to grow not just our crops, but also our knowledge and resilience as farmers.