Preserving Illinois’ Heritage: How Climate Change Threatens Historic Sites Along the Fox River
“Over 50% of Illinois’ historic sites along the Fox River are at risk due to climate change-induced flooding.”
As we delve into the rich tapestry of Illinois’ cultural heritage, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where the past and future collide along the banks of the Fox River. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll uncover the challenges faced by historic sites in the face of climate change and the efforts being made to preserve these invaluable treasures for generations to come.
The Fox River Valley: A Confluence of History and Nature
The Fox River Valley in Illinois is not just a picturesque landscape; it’s a living museum of human history spanning thousands of years. From ancient Native American settlements to architectural marvels of the modern era, this region tells the story of our collective past. However, the increasing threat of historic flooding in Illinois poses a significant risk to these cultural landmarks.
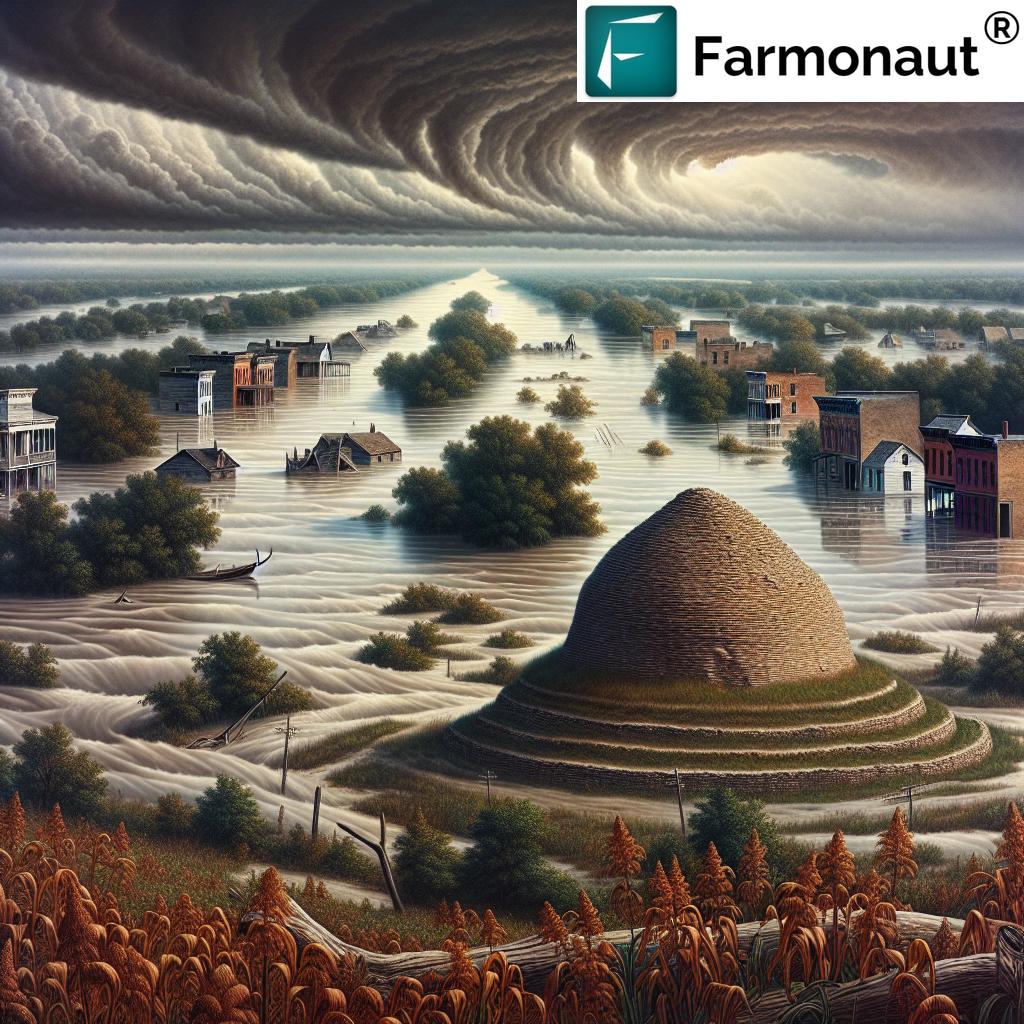

As we witness the climate change impact on cultural landmarks, it becomes clear that our heritage is intrinsically linked to the health of our environment. The Fox River, once a lifeline for indigenous peoples and early settlers, now threatens to erase the very history it helped create.
Climate Change: The Silent Destroyer of History
The effects of climate change on the Fox River Valley are multifaceted and far-reaching. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events are conspiring to reshape the landscape in ways that our ancestors could never have imagined.
- Flooding: Increased rainfall and snowmelt are leading to more frequent and severe flooding events along the Fox River.
- Erosion: Higher water levels and stronger currents are accelerating bank erosion, threatening sites close to the water’s edge.
- Invasive Species: Warmer temperatures are allowing non-native plants and animals to thrive, altering the ecosystem and potentially damaging historic structures.
These environmental pressures are not just abstract concepts; they have real and devastating consequences for our cultural heritage. The Fox River Valley heritage sites are facing an unprecedented challenge, and the race is on to protect them before it’s too late.
At-Risk Heritage: A Table of Treasures in Peril
| Site Name | Type | Historical Significance | Primary Climate Threats | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farnsworth House | Architectural Structure | Modernist masterpiece by Mies van der Rohe | Flooding, Invasive Species | Active preservation efforts |
| Plano Mounds | Native American Landmark | Ancient Mississippian culture site | Erosion, Flooding | At high risk, limited protection |
| Aurora Masonic Temple | Architectural Structure | Early 20th-century Neoclassical design | Foundation Damage, Moisture Intrusion | Ongoing restoration |
| Fabyan Villa Museum | Architectural/Landscape | Frank Lloyd Wright remodeled estate | Flooding, Landscape Alterations | Protected, but facing challenges |
| Red Oak Nature Center | Natural/Cultural Landscape | Indigenous habitat and educational site | Erosion, Invasive Species | Active conservation programs |
This table illustrates the diversity of heritage sites at risk and the complex challenges they face. From architectural wonders to ancient earthworks, each site represents a unique chapter in Illinois’ story that we cannot afford to lose.
The Farnsworth House: A Case Study in Resilience
One of the most iconic structures along the Fox River is the Farnsworth House, designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. This modernist retreat stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our desire to commune with nature. However, it also serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of our built heritage to environmental forces.
The Farnsworth House has faced numerous floods since its construction, with water levels rising dramatically in recent years. Conservationists have implemented various flood mitigation for historic buildings strategies, including:
- Temporary flood barriers
- Improved drainage systems
- Ongoing monitoring and rapid response protocols
These efforts showcase the innovative approaches being developed to protect our heritage in the face of climate change. However, they also highlight the ongoing struggle to balance preservation with the realities of a changing environment.
Ancient Echoes: Preserving Native American Heritage
“The Fox River Valley contains more than 1,000 years of Native American archaeological history threatened by erosion.”
The Fox River Valley is not just home to modern architectural marvels; it also contains a wealth of Illinois Native American history. Ancient mounds, village sites, and artifacts tell the story of the indigenous peoples who called this land home for millennia.
Archaeological sites are particularly vulnerable to climate change impacts. Erosion can quickly destroy delicate stratigraphic layers, washing away centuries of history in a single flood event. The challenge of preserving archaeological sites requires a multifaceted approach:
- Detailed mapping and documentation of known sites
- Proactive excavation of at-risk areas
- Collaboration with tribal nations to ensure respectful preservation
- Public education to foster stewardship of these irreplaceable resources
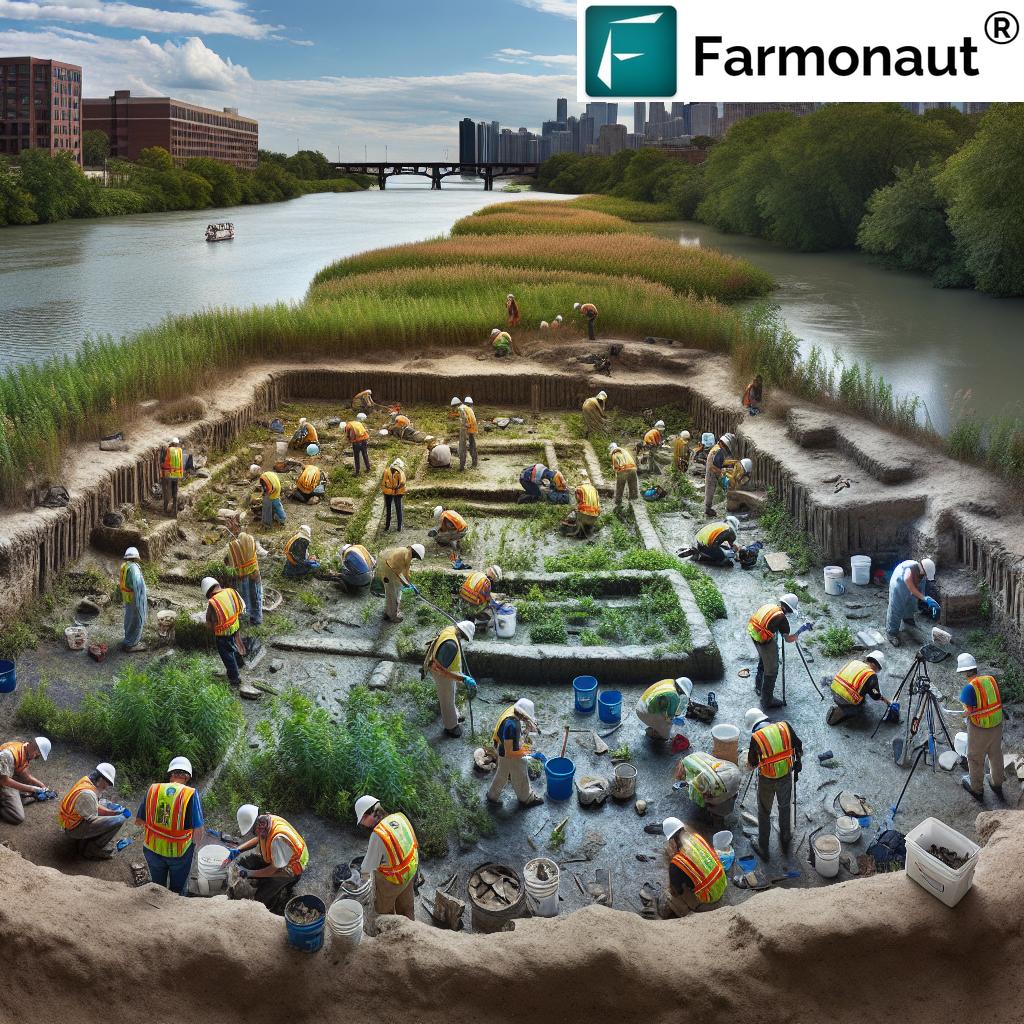

By preserving these ancient sites, we not only protect valuable scientific data but also honor the cultural legacy of the first inhabitants of the Fox River Valley.
The Role of Technology in Heritage Preservation
As we face the challenges of climate change, technology is emerging as a powerful ally in our efforts to preserve cultural heritage. Advanced monitoring systems, digital documentation techniques, and predictive modeling are revolutionizing the field of conservation.
One such technological innovation comes from Farmonaut, a company that specializes in satellite-based monitoring solutions. While primarily focused on agricultural applications, their technology has potential implications for heritage preservation as well.
Farmonaut’s satellite imagery and AI-driven analysis could be adapted to monitor changes in landscapes surrounding historic sites, providing early warnings of erosion or other environmental threats. This kind of proactive monitoring could be invaluable for sites along the Fox River.
By leveraging cutting-edge technology, conservationists can stay one step ahead of climate change impacts, allowing for more targeted and effective preservation efforts.
Community Engagement: The Heart of Heritage Protection
Preserving our cultural heritage is not just the responsibility of archaeologists and conservationists; it requires the engagement and support of the entire community. Local residents, schools, and businesses all have a role to play in protecting the Fox River Valley’s historic sites.
- Educational programs that teach the value of local history
- Volunteer opportunities for site maintenance and monitoring
- Community-led fundraising initiatives for preservation projects
- Partnerships between heritage sites and local schools for hands-on learning experiences
By fostering a sense of ownership and pride in local heritage, we can create a network of citizen conservationists who will be the first line of defense against the impacts of climate change.
The Economic Impact of Heritage Preservation
While the cultural value of preserving historic sites is clear, it’s also important to consider the economic benefits. Heritage tourism is a significant driver of local economies, bringing visitors and their spending to communities along the Fox River.
Investing in the preservation and promotion of historic sites can lead to:
- Increased tourism revenue
- Job creation in the heritage and hospitality sectors
- Revitalization of historic downtowns and main streets
- Enhanced property values in areas with well-preserved historic character
By framing heritage preservation as an economic development strategy, we can build broader support for conservation efforts and create a sustainable model for protecting our cultural assets.
Policy and Planning: A Framework for Preservation
Effective heritage preservation requires a strong policy framework and comprehensive planning at all levels of government. Local, state, and federal agencies must work together to create and implement strategies that address the unique challenges posed by climate change to historic sites.
Key elements of a robust preservation policy include:
- Integration of heritage considerations into climate action plans
- Funding mechanisms for preservation and adaptation projects
- Zoning and land-use regulations that protect historic areas
- Incentives for private property owners to maintain historic structures
By creating a supportive policy environment, we can ensure that preservation efforts have the resources and legal backing needed to succeed in the face of climate change.
The Future of Fox River Valley Heritage
As we look to the future, the preservation of Fox River Valley heritage sites faces both challenges and opportunities. Climate change will continue to pose threats, but with proactive planning, community engagement, and innovative technologies, we can work to ensure that these irreplaceable cultural resources endure for future generations.
Key strategies for the future include:
- Continued research into climate resilience for historic structures
- Expansion of digital documentation and virtual access to heritage sites
- Development of green infrastructure solutions that protect both natural and cultural resources
- Increased collaboration between heritage professionals, climate scientists, and technology experts
By embracing these strategies and remaining committed to the value of our shared heritage, we can write a new chapter in the story of the Fox River Valley—one of resilience, innovation, and respect for the legacy of those who came before us.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The preservation of Illinois’ heritage along the Fox River is not just a task for experts—it’s a calling for all who value the rich tapestry of our past. As climate change continues to threaten these irreplaceable cultural landmarks, we must act with urgency and purpose.
We invite you to join us in this vital mission:
- Educate yourself about the historic sites in your area and the challenges they face
- Support local preservation organizations through volunteerism or donations
- Advocate for policies that protect cultural heritage and address climate change
- Visit and appreciate these historic sites, creating new memories while honoring the old
Together, we can ensure that the stories etched in the landscape of the Fox River Valley continue to inspire and inform for generations to come. The time to act is now—let us be the stewards our heritage deserves.
FAQ: Preserving Illinois’ Heritage in the Face of Climate Change
Q: Why is climate change such a significant threat to historic sites?
A: Climate change leads to more frequent and severe flooding, increased erosion, and changes in temperature and humidity that can damage historic structures and archaeological sites. These impacts can accelerate decay and even lead to the complete loss of irreplaceable cultural resources.
Q: What can individual citizens do to help preserve historic sites?
A: Individuals can get involved by volunteering at local heritage sites, supporting preservation organizations, advocating for protective policies, and educating others about the importance of cultural heritage. Even small actions like reporting signs of damage or participating in community clean-up events can make a difference.
Q: How are Native American sites being protected along the Fox River?
A: Efforts to protect Native American sites include collaborative partnerships with tribal nations, increased archaeological surveys and documentation, and the implementation of erosion control measures. Public education programs also play a crucial role in fostering respect and stewardship for these ancient sites.
Q: What role does technology play in heritage preservation?
A: Technology is increasingly important in preservation efforts. Tools like 3D scanning, drone surveys, and satellite monitoring help document sites and track changes over time. Advanced modeling can predict future impacts, allowing for proactive conservation measures.
Q: How does preserving historic sites benefit local communities economically?
A: Historic preservation can boost local economies through heritage tourism, job creation in restoration and maintenance, increased property values, and revitalization of historic districts. Well-preserved historic areas often become focal points for community identity and pride, attracting both visitors and new residents.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For more information on Farmonaut’s innovative agricultural solutions, visit our API page or check out our API Developer Docs.