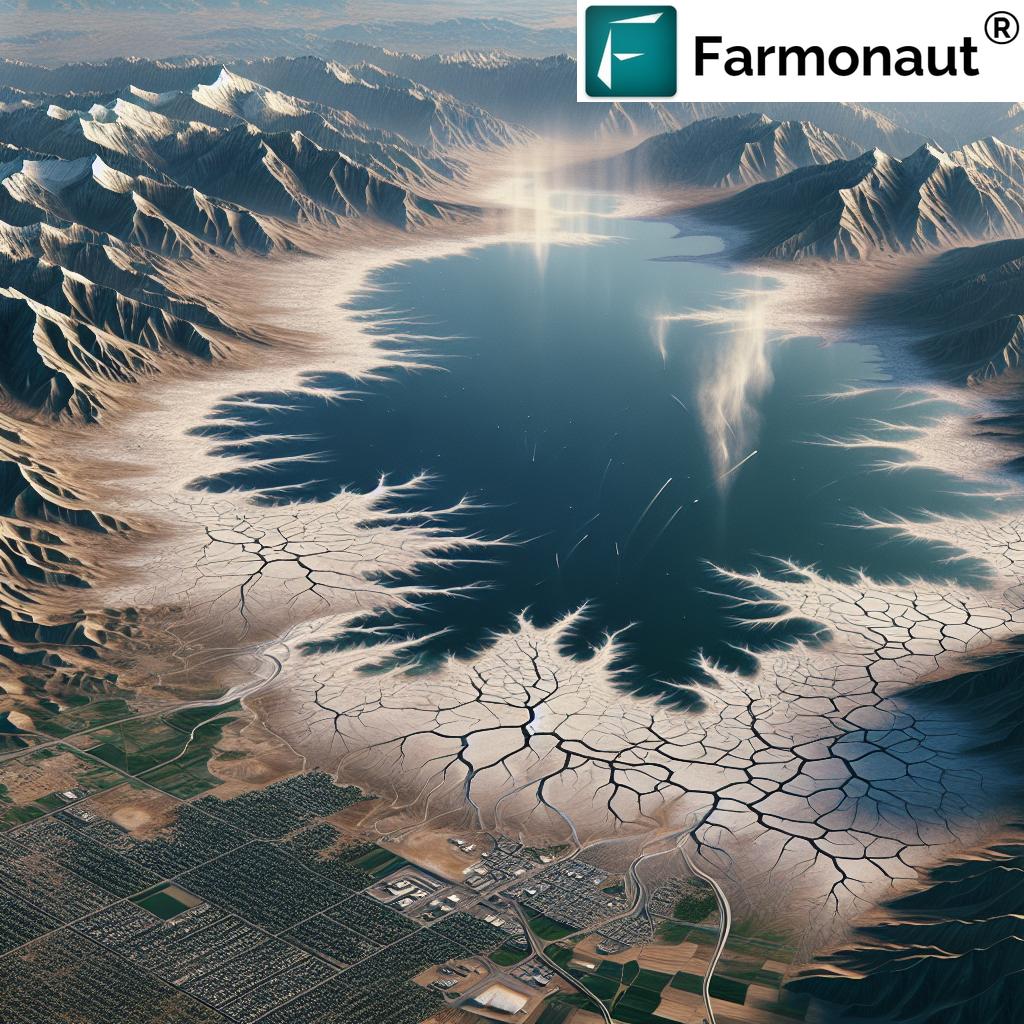
Satellite Reveals Hazardous Dust Storms from Utah’s Shrinking Great Salt Lake: Environmental Monitoring Crucial
“Satellite images reveal dust plumes from Utah’s Great Salt Lake affecting air quality in nearby communities, spanning up to 100 miles.”
As environmental scientists and concerned citizens, we find ourselves at a critical juncture in Utah’s ecological history. The Great Salt Lake, once a vast expanse of saline waters, is now revealing a grim reality that threatens both the environment and public health. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the alarming phenomenon of dust storms originating from the shrinking lake and their far-reaching consequences on Utah’s communities.
The Shrinking Great Salt Lake: A Looming Environmental Crisis
The Great Salt Lake, an iconic feature of Utah’s landscape, has been experiencing a dramatic decline in recent years. This reduction in water levels is not just a matter of changing scenery; it’s a complex environmental issue with severe implications for the region’s ecology, economy, and public health.
Understanding the Decline
- Record Low Water Levels: In 2022, the Great Salt Lake hit a record low water level, exposing vast areas of formerly submerged lake bed.
- Causes of Shrinkage:
- Water Diversions: Increased use of water for agriculture and urban development
- Drought Conditions: Persistent dry periods reducing water inflow
- Climate Change: Altering precipitation patterns and increasing evaporation rates
- Exposed Lake Bed: Over 800 square miles of lakebed have been exposed, creating a new source of potential dust pollution.
The consequences of this shrinkage extend far beyond the lake’s shorelines, affecting everything from local weather patterns to the health of nearby communities.
Dust Storms: A New Environmental Hazard
“The shrinking Great Salt Lake has exposed over 800 square miles of lakebed, increasing the frequency of hazardous dust storms in Utah.”
One of the most alarming consequences of the Great Salt Lake’s recession is the emergence of frequent and potentially hazardous dust storms. These events, captured by weather satellites, are painting a worrying picture of Utah’s changing environment.
The Anatomy of Great Salt Lake Dust Storms
- Origin: Dust primarily originates from exposed areas of Farmington Bay and Bear River Bay.
- Composition: The dust contains a mix of minerals, including potentially toxic elements like arsenic.
- Range: Dust plumes can travel up to 100 miles, affecting communities far from the lake’s shores.
- Frequency: Researchers note an increase in dust events since 2010, correlating with the lake’s decline.
These dust storms are not just a nuisance; they represent a significant threat to air quality and public health in Utah’s most populous areas.

Environmental Monitoring: A Crucial Step
In light of these emerging environmental challenges, the need for comprehensive and advanced monitoring systems has never been more critical. This is where cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions come into play.
The Role of Satellite Technology in Environmental Monitoring
Satellite-based monitoring systems, like those employed by Farmonaut, offer unprecedented insights into environmental changes and their impacts. While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural applications, the principles of satellite-based monitoring are equally valuable for tracking environmental phenomena like dust storms.
- Real-time Data: Satellites provide up-to-date information on dust plume movements and extent.
- Wide Coverage: Ability to monitor large areas, crucial for tracking the spread of dust storms.
- Multispectral Analysis: Advanced sensors can detect various aspects of dust composition and density.
These technologies are not just tools for observation; they are critical in informing policy decisions and public health measures.
Impact on Utah’s Communities
The dust storms originating from the Great Salt Lake are not just an environmental curiosity; they have tangible and significant impacts on the communities of northern Utah.
Health Concerns
- Respiratory Issues: Fine dust particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, exacerbating conditions like asthma and bronchitis.
- Toxic Exposure: Concerns about long-term exposure to potentially toxic minerals in the dust.
- Vulnerable Populations: Children, elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions are at higher risk.
Economic Impact
- Healthcare Costs: Increased respiratory issues lead to higher medical expenses.
- Tourism: Potential reduction in visitors due to poor air quality and environmental concerns.
- Property Values: Areas frequently affected by dust storms may see a decrease in property values.
Quality of Life
- Outdoor Activities: Reduced ability to enjoy outdoor spaces during dust events.
- Community Events: Potential cancellations or modifications of public gatherings due to air quality concerns.
- Mental Health: The stress of living with frequent environmental hazards can impact mental well-being.
These impacts underscore the urgent need for comprehensive monitoring and mitigation strategies.
The Broader Environmental Context
The dust storms from the Great Salt Lake are not an isolated environmental issue. They are part of a broader ecological challenge facing Utah and the American West.
Climate Change and Water Scarcity
- Changing Precipitation Patterns: Alterations in snowfall and rainfall affecting water availability.
- Increased Evaporation: Higher temperatures leading to faster water loss from the lake.
- Snowpack Reduction: Crucial for Utah’s water supply, snowpack is diminishing due to warmer winters.
Ecosystem Disruption
- Wildlife Habitat: The shrinking lake affects migratory birds and local species.
- Salinity Changes: Fluctuations in lake salinity impact unique microbial ecosystems.
- Wetland Loss: Reduction in crucial wetland areas around the lake.
These interconnected environmental challenges require a holistic approach to monitoring and management.
Current Monitoring Efforts and Challenges
As the dust storm issue gains prominence, various efforts are underway to monitor and understand this environmental phenomenon. However, these efforts face significant challenges.
Existing Monitoring Systems
- Air Quality Stations: Fixed monitoring points provide localized data on air quality.
- Satellite Imagery: As demonstrated by the recent NOAA image, satellites offer broad-scale views of dust events.
- Weather Forecasting: Integrating dust predictions into local weather forecasts.
Challenges in Monitoring
- Limited Coverage: Current ground-based monitors may not capture the full extent of dust events.
- Resource Constraints: Funding limitations restrict the deployment of comprehensive monitoring networks.
- Data Integration: Challenges in combining data from various sources for a complete picture.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the impact of dust storms.
The Role of Advanced Technology in Environmental Monitoring
In the face of these environmental challenges, advanced technologies offer promising solutions for more comprehensive and effective monitoring.
Satellite-Based Monitoring Systems
While Farmonaut’s focus is on agricultural applications, the principles of its satellite-based monitoring system are highly relevant to environmental monitoring efforts like those needed for the Great Salt Lake dust storms.
- Real-Time Data: Satellite imagery provides up-to-date information on dust plume movements and extent.
- Wide Coverage: Ability to monitor large areas, crucial for tracking the spread of dust storms.
- Multispectral Analysis: Advanced sensors can detect various aspects of dust composition and density.
These technologies are not just tools for observation; they are critical in informing policy decisions and public health measures.
AI and Machine Learning in Environmental Analysis
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms, similar to those used in Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI system, can be adapted for environmental monitoring:
- Predictive Modeling: Forecasting dust storm events based on historical data and current conditions.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying trends and correlations in environmental data that might not be apparent to human observers.
- Automated Alerts: Generating early warnings for potentially hazardous dust events.
These advanced analytical tools can significantly enhance our understanding and response to environmental challenges.
Policy and Action: Addressing the Great Salt Lake Crisis
The environmental challenges posed by the shrinking Great Salt Lake require a multifaceted approach, combining policy initiatives, community action, and technological solutions.
Legislative Efforts
- Water Conservation Laws: Implementing stricter regulations on water usage and diversions.
- Funding for Monitoring: Allocating resources for enhanced environmental monitoring systems.
- Research Support: Providing grants for studies on dust composition and health impacts.
Community Initiatives
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating residents about water conservation and dust storm safety.
- Citizen Science Programs: Engaging the public in data collection and monitoring efforts.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Fostering cooperation between communities, researchers, and policymakers.
Technological Solutions
Innovative technologies play a crucial role in addressing these environmental challenges. While Farmonaut’s primary focus is on agricultural applications, the principles of its technologies can be adapted for environmental monitoring:
- Satellite-Based Monitoring: Utilizing remote sensing for comprehensive dust plume tracking.
- AI-Driven Analysis: Employing machine learning for predictive modeling of dust events.
- Data Integration Platforms: Creating unified systems for collecting and analyzing environmental data.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for satellite data integration
These technological approaches, when combined with policy initiatives and community action, can form a robust strategy for addressing the Great Salt Lake’s environmental crisis.
The Future of Environmental Monitoring in Utah
As we look to the future, it’s clear that addressing the challenges posed by the Great Salt Lake’s shrinkage and resultant dust storms will require innovative approaches and ongoing commitment.
Emerging Technologies and Approaches
- Advanced Sensor Networks: Deploying more sophisticated ground-based sensors for real-time monitoring.
- Drone Technology: Using unmanned aerial vehicles for targeted, high-resolution dust plume analysis.
- Big Data Analytics: Leveraging vast datasets to uncover long-term trends and patterns in environmental changes.
Collaborative Research Initiatives
- Cross-Disciplinary Studies: Combining expertise from atmospheric sciences, public health, and ecology.
- Regional Cooperation: Sharing data and resources with neighboring states facing similar environmental challenges.
- International Partnerships: Learning from global experiences in managing similar environmental issues.
The future of environmental monitoring in Utah will likely involve a blend of these advanced technologies and collaborative approaches, aimed at providing comprehensive, actionable data for decision-makers and the public.
Comparative Analysis of Great Salt Lake Dust Events
| Year | Estimated Lake Surface Area (sq km) | Number of Recorded Dust Events | Estimated PM2.5 Levels During Events (μg/m³) | Affected Population (estimate) | Economic Impact ($ millions) | Snowpack Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 4,200 | 5 | 35 | 500,000 | 10 | 5 |
| 2016 | 4,100 | 7 | 40 | 600,000 | 15 | 7 |
| 2017 | 4,000 | 10 | 45 | 700,000 | 20 | 8 |
| 2018 | 3,900 | 12 | 50 | 800,000 | 25 | 10 |
| 2019 | 3,800 | 15 | 55 | 900,000 | 30 | 12 |
| 2020 | 3,700 | 18 | 60 | 1,000,000 | 35 | 15 |
| 2021 | 3,600 | 20 | 65 | 1,100,000 | 40 | 18 |
| 2022 | 3,500 | 25 | 70 | 1,200,000 | 50 | 20 |
This table illustrates the alarming trend of increasing dust events and their impacts as the Great Salt Lake continues to shrink. The data underscores the urgent need for comprehensive monitoring and mitigation strategies.
Conclusion: A Call for Comprehensive Environmental Monitoring
The environmental challenges posed by the shrinking Great Salt Lake and the resulting dust storms represent a critical juncture for Utah’s environmental health and public safety. As we’ve explored throughout this article, the implications of these dust events extend far beyond mere inconvenience, touching on public health, economic stability, and long-term ecological balance.
The need for comprehensive, technologically advanced environmental monitoring has never been more apparent. While solutions like those offered by Farmonaut are primarily focused on agricultural applications, the principles of satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven analysis, and data integration are equally vital in addressing environmental challenges like the Great Salt Lake dust storms.
As we move forward, it’s clear that addressing this issue will require a multifaceted approach:
- Continued Investment in Monitoring Technologies: Expanding and upgrading our ability to track and predict dust events.
- Policy Implementation: Enacting and enforcing water conservation measures and environmental protections.
- Public Engagement: Educating and involving communities in both monitoring efforts and conservation practices.
- Collaborative Research: Fostering partnerships between academic institutions, government agencies, and technology providers to develop innovative solutions.
The challenges facing the Great Salt Lake are significant, but they are not insurmountable. With concerted effort, innovative technology, and a commitment to environmental stewardship, we can work towards mitigating the impacts of these dust storms and preserving the unique ecosystem of the Great Salt Lake for future generations.
As we conclude, let us remember that environmental monitoring is not just about collecting data – it’s about using that information to make informed decisions, implement effective policies, and ultimately, safeguard the health and well-being of our communities and the natural world around us.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
FAQs
- What causes the dust storms from the Great Salt Lake?
The dust storms are primarily caused by the exposure of the lake bed due to the shrinking of the Great Salt Lake. Factors contributing to this include water diversions, drought conditions, and climate change. - How do these dust storms affect public health?
The dust storms can have significant health impacts, particularly on respiratory health. Fine dust particles can exacerbate conditions like asthma and bronchitis, and there are concerns about long-term exposure to potentially toxic minerals in the dust. - What role does satellite technology play in monitoring these dust events?
Satellite technology provides real-time data on dust plume movements and extent, offering wide coverage and the ability to track large-scale environmental phenomena. This technology is crucial for early warning systems and comprehensive environmental monitoring. - How can individuals contribute to addressing this environmental challenge?
Individuals can contribute by practicing water conservation, participating in citizen science programs for data collection, and staying informed about local air quality conditions and dust storm safety measures. - What are the long-term solutions being considered for the Great Salt Lake crisis?
Long-term solutions include implementing stricter water conservation laws, investing in advanced monitoring technologies, conducting comprehensive research on dust composition and health impacts, and developing collaborative partnerships between communities, researchers, and policymakers.














Would it kill you to grab a real photo of the lake? this is ridiculous