Exploring the World of Beekeeping: Challenges, Sustainability, and the Sweet Rewards
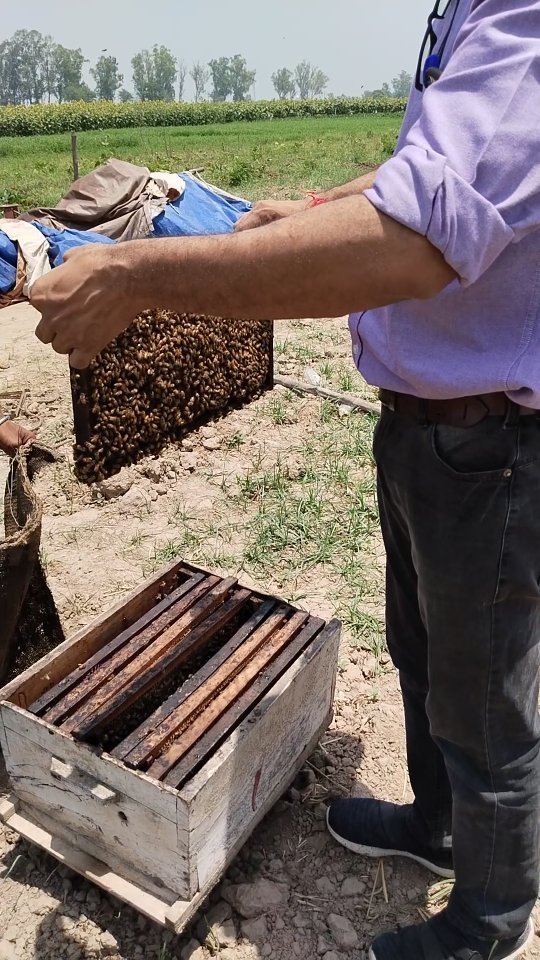

As we embarked on our journey to explore the fascinating world of beekeeping, we were immediately struck by the dedication and passion of the beekeepers we encountered. The first day of our exploration unveiled diligent individuals laboring amidst the picturesque scenery of blossoming flowers. Their meticulous work facilitates the miraculous transformation of floral nectar into the golden honey that we so cherish.
However, the idyllic image of bee farming masks a series of challenges. Beekeepers grapple with maintaining hive health, adjusting to inconsistent weather patterns, and managing complex logistics and market access. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve deep into the world of beekeeping, exploring its challenges, the push for sustainable beekeeping, and the sweet rewards that come from this ancient practice.
The Art and Science of Beekeeping
Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is both an art and a science. It requires a deep understanding of bee biology, behavior, and the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Beekeepers must possess a unique blend of skills, combining traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches to ensure the health and productivity of their hives.
The Importance of Bees
Before we dive into the intricacies of beekeeping, it’s crucial to understand the vital role that bees play in our ecosystem and food production:
- Pollination: Bees are responsible for pollinating approximately 70% of the world’s crops.
- Biodiversity: They contribute to the maintenance of biodiversity by pollinating wild plants.
- Economic Impact: The global economic value of bee pollination is estimated to be over $150 billion annually.
- Honey Production: Bees produce honey, which has been used for centuries for its nutritional and medicinal properties.
Challenges Faced by Beekeepers
While beekeeping can be a rewarding endeavor, it comes with its fair share of challenges. Let’s explore some of the major hurdles that beekeepers face in their day-to-day operations:
1. Maintaining Hive Health
One of the most critical aspects of beekeeping is ensuring the health of the hive. Beekeepers must constantly monitor their colonies for signs of disease, parasites, and other threats. Some common issues include:
- Varroa Mites: These parasitic mites can devastate bee colonies if left unchecked.
- American Foulbrood: A highly contagious bacterial disease that can quickly spread through a hive.
- Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD): A phenomenon where worker bees abandon the hive, leaving behind the queen and young bees.
Maintaining hive health requires constant vigilance, regular inspections, and sometimes the use of treatments or interventions to protect the bees.
2. Adapting to Weather Patterns
Bees are highly sensitive to weather patterns, and climate changes can significantly impact their behavior and productivity. Beekeepers must be adept at adapting their practices to account for:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme heat or cold can stress bee colonies and affect honey production.
- Rainfall Patterns: Too much rain can prevent bees from foraging, while drought can lead to a lack of nectar sources.
- Seasonal Changes: Shifting seasons can alter the timing of flower blooms, affecting the bees’ food sources.
Understanding and adapting to these weather patterns is crucial for successful beekeeping.
3. Managing Logistics and Market Access
Beyond the care of bees, beekeepers must also navigate the complexities of running a business. This includes:
- Equipment Management: Maintaining and upgrading hives, protective gear, and honey extraction equipment.
- Transportation: Moving hives for pollination services or to follow nectar flows.
- Marketing and Sales: Finding markets for honey and other bee products, often competing with imported products.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to food safety regulations and beekeeping standards.
The Push for Sustainable Beekeeping
In light of these challenges, there’s a growing movement towards sustainable beekeeping practices. This approach aims to balance the needs of bees, beekeepers, and the environment. Here are some key aspects of sustainable beekeeping:
1. Natural Beekeeping Methods
Many beekeepers are adopting more natural approaches to hive management, including:
- Top-Bar Hives: These allow bees to build comb naturally, potentially reducing stress on the colony.
- Minimal Intervention: Reducing the frequency of hive inspections to minimize disturbance to the bees.
- Chemical-Free Pest Management: Using natural methods to control pests and diseases, such as essential oils or mechanical mite removal.
2. Habitat Conservation
Sustainable beekeeping also involves protecting and enhancing the bees’ natural habitat:
- Planting Bee-Friendly Flora: Creating diverse, pesticide-free flower gardens to support bee populations.
- Preserving Wild Areas: Maintaining natural landscapes that provide forage and nesting sites for wild bees.
- Educating Communities: Raising awareness about the importance of bees and how to support them.
3. Genetic Diversity
Maintaining genetic diversity in bee populations is crucial for their long-term survival:
- Local Breeding Programs: Focusing on breeding bees adapted to local conditions.
- Avoiding Artificial Insemination: Allowing natural mating to preserve genetic diversity.
- Supporting Native Bee Species: Encouraging the conservation of local bee populations alongside managed honeybees.
The Role of Technology in Modern Beekeeping
While traditional beekeeping practices remain important, technology is playing an increasingly significant role in supporting beekeepers and promoting sustainable beekeeping. At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of this technological revolution in agriculture, and our solutions can be adapted to support beekeeping operations as well.
Satellite-Based Monitoring for Beekeeping
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can be utilized to support beekeeping operations in several ways:
- Vegetation Health Monitoring: By tracking the NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), beekeepers can identify areas with healthy flowering plants, potentially indicating good foraging grounds for bees.
- Weather Forecasting: Our system provides accurate weather forecasts, helping beekeepers prepare for changing weather patterns that might affect their hives.
- Land Use Analysis: Satellite imagery can help identify changes in land use that might impact bee habitats, allowing beekeepers to adapt their strategies accordingly.
To learn more about our satellite-based solutions, visit Farmonaut’s Satellite Monitoring System.
AI-Powered Advisory Systems
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System can be adapted to provide personalized advice for beekeepers:
- Hive Health Predictions: By analyzing weather data and historical patterns, the AI system could predict potential threats to hive health.
- Optimal Harvesting Times: The system could suggest the best times for honey harvesting based on weather conditions and flower bloom predictions.
- Resource Management: AI-driven insights could help beekeepers optimize their resource allocation, from feed supplementation to equipment deployment.
Blockchain for Honey Traceability
Our blockchain-based traceability solutions can be particularly valuable for the honey industry:
- Origin Verification: Ensuring the authenticity of honey sources, combating fraud in the industry.
- Quality Assurance: Tracking the journey of honey from hive to shelf, maintaining quality standards throughout the supply chain.
- Consumer Trust: Providing transparent information about honey production, building consumer confidence in the product.
For more information on our API services, including weather data that can be crucial for beekeepers, visit our API documentation.
The Sweet Rewards of Beekeeping
Despite the challenges, beekeeping offers numerous rewards, both tangible and intangible:
1. Honey Production
The most obvious reward of beekeeping is the production of honey. This golden nectar has been prized for millennia for its sweetness and health benefits. Modern beekeepers can produce a variety of honey types, including:
- Monofloral Honey: Derived primarily from one type of flower, such as manuka or acacia honey.
- Raw Honey: Unprocessed honey that retains all its natural enzymes and nutrients.
- Comb Honey: Honey still in its natural beeswax comb, prized by many consumers.
2. Other Bee Products
Beyond honey, bees produce several other valuable substances:
- Beeswax: Used in cosmetics, candles, and food preservation.
- Propolis: A resin-like material with antimicrobial properties, used in natural medicine.
- Royal Jelly: A nutrient-rich substance fed to queen bees, sometimes used as a dietary supplement.
- Bee Pollen: Collected from plants and used as a protein-rich food supplement.
3. Pollination Services
Many beekeepers offer pollination services to farmers, helping to increase crop yields and quality. This service is vital for many agricultural operations and can provide a significant income stream for beekeepers.
4. Environmental Stewardship
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in environmental conservation. By maintaining healthy bee populations, beekeepers contribute to:
- Biodiversity preservation
- Ecosystem balance
- Food security through pollination
5. Personal Satisfaction
Many beekeepers find immense personal satisfaction in their work. The connection with nature, the fascinating world of bees, and the production of wholesome food products can be deeply rewarding on a personal level.
The Future of Beekeeping: Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future, beekeeping faces both challenges and opportunities:
Challenges:
- Climate Change: Shifting weather patterns and extreme weather events pose significant threats to bee populations.
- Pesticide Use: The widespread use of neonicotinoids and other pesticides continues to harm bee populations.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization and intensive agriculture are reducing natural habitats for bees.
- Disease and Parasites: Evolving threats to hive health require constant vigilance and research.
Opportunities:
- Technological Advancements: New technologies, like those offered by Farmonaut, can help beekeepers manage their operations more efficiently.
- Growing Demand for Natural Products: Increasing consumer interest in natural and organic products creates new markets for honey and other bee products.
- Sustainable Agriculture Movement: The push for more sustainable farming practices aligns well with the needs of bees and beekeepers.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing research into bee health and behavior can lead to improved beekeeping practices.
How Farmonaut Supports Sustainable Agriculture and Beekeeping
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting sustainable agricultural practices, including beekeeping. Our satellite-based farm management solutions offer several advantages over traditional monitoring methods:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (regional to global) | Limited (local) | Limited (site-specific) |
| Frequency of Data | Regular (every 3-5 days) | As needed (manual flights) | Continuous |
| Cost | Low (subscription-based) | High (equipment + operator) | High (sensors + infrastructure) |
| Ease of Use | High (cloud-based platform) | Medium (requires skilled operator) | Medium (requires setup and maintenance) |
| Weather Independence | High (can penetrate clouds) | Low (affected by wind and rain) | Medium (some sensors affected by weather) |
Our system can help beekeepers by providing valuable insights into vegetation health, weather patterns, and land use changes that can impact bee populations. To learn more about how our technology can support your agricultural or beekeeping operation, visit our Android app or iOS app.
Conclusion: The Buzz about Sustainable Beekeeping
As we conclude our exploration of the world of beekeeping, we’re left with a profound appreciation for the work of beekeepers and the critical role they play in our ecosystem and food production. The challenges they face are significant, from maintaining hive health to adapting to changing weather patterns. However, the push towards sustainable beekeeping practices, supported by technological advancements, offers hope for the future of this ancient craft.
The sweet reward of honey is just one of the many benefits that come from beekeeping. As consumers, we can support sustainable beekeeping by choosing local, ethically produced honey and bee products, and by advocating for bee-friendly policies in our communities.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting sustainable agriculture in all its forms, including beekeeping. Our advanced satellite-based solutions and AI-powered advisory systems can help beekeepers make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and contribute to the broader goal of environmental stewardship.
As we face the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, the importance of bees and beekeeping cannot be overstated. By supporting sustainable beekeeping practices and embracing innovative technologies, we can help ensure a sweet future for bees, beekeepers, and our planet.
FAQ: Beekeeping and Sustainable Agriculture
Q1: What is sustainable beekeeping?
A: Sustainable beekeeping is an approach that balances the needs of bees, beekeepers, and the environment. It involves using natural beekeeping methods, preserving bee habitats, maintaining genetic diversity, and minimizing the use of chemicals and antibiotics.
Q2: How does weather affect beekeeping?
A: Weather patterns significantly impact beekeeping. Temperature fluctuations, rainfall, and seasonal changes can affect bee behavior, foraging patterns, and honey production. Extreme weather events can also damage hives and disrupt bee colonies.
Q3: What are the main challenges in maintaining hive health?
A: The main challenges in maintaining hive health include managing pests and diseases (such as varroa mites and foulbrood), ensuring adequate nutrition, protecting against pesticide exposure, and adapting to climate changes.
Q4: How can technology help in beekeeping?
A: Technology can assist beekeeping in various ways, including satellite-based monitoring of vegetation health and weather patterns, AI-powered advisory systems for hive management, and blockchain solutions for honey traceability and quality assurance.
Q5: What are the benefits of local honey?
A: Local honey offers several benefits, including supporting local beekeepers, potentially helping with seasonal allergies, ensuring freshness, and reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation. It also often has a unique flavor profile reflecting the local flora.
Q6: How can individuals support bee conservation?
A: Individuals can support bee conservation by planting bee-friendly flowers, avoiding pesticide use, supporting local beekeepers by buying their products, providing water sources for bees, and raising awareness about the importance of bees in their communities.
Q7: What is Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD)?
A: Colony Collapse Disorder is a phenomenon where the majority of worker bees in a colony disappear, leaving behind the queen, plenty of food, and a few nurse bees to care for the remaining immature bees. The exact cause is not fully understood but is thought to be a combination of factors including pesticides, parasites, and environmental stressors.
Q8: How does Farmonaut’s technology apply to beekeeping?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring can help beekeepers by providing insights into vegetation health, which can indicate good foraging areas for bees. Our weather forecasting can help in planning hive management activities, and our AI advisory system can be adapted to provide personalized beekeeping advice based on local conditions.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support sustainable agriculture and beekeeping, please visit our API documentation.
Join us in revolutionizing agriculture and supporting sustainable practices across the globe!