Organic Alfalfa Mosaic Disease: Symptoms, Control, and Protection for Crops

In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we at Farmonaut understand the importance of staying ahead of potential threats to crop health. One such threat that has been gaining attention in recent years is the Alfalfa Mosaic Disease. This viral disease affects not only alfalfa but also a wide range of other crops, making it a significant concern for farmers and agricultural professionals alike. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of this disease, exploring its symptoms, control methods, and protection strategies for both organic and conventional farming practices.
Understanding Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
Alfalfa Mosaic Disease, caused by the Alfamovirus, is a common and potentially devastating viral infection that affects a wide range of host plants. While its name suggests a primary association with alfalfa, this disease can impact various crops, including pepper, potato, tomato, tobacco, eggplant, and clover, as well as other legumes.
The Causative Agent: Alfamovirus
The Alfamovirus responsible for Alfalfa Mosaic Disease belongs to the family Bromoviridae. This virus is known for its ability to infect a broad spectrum of plant species, making it a significant concern in agricultural settings. The virus can be transmitted through various means, which we’ll explore in detail later in this article.
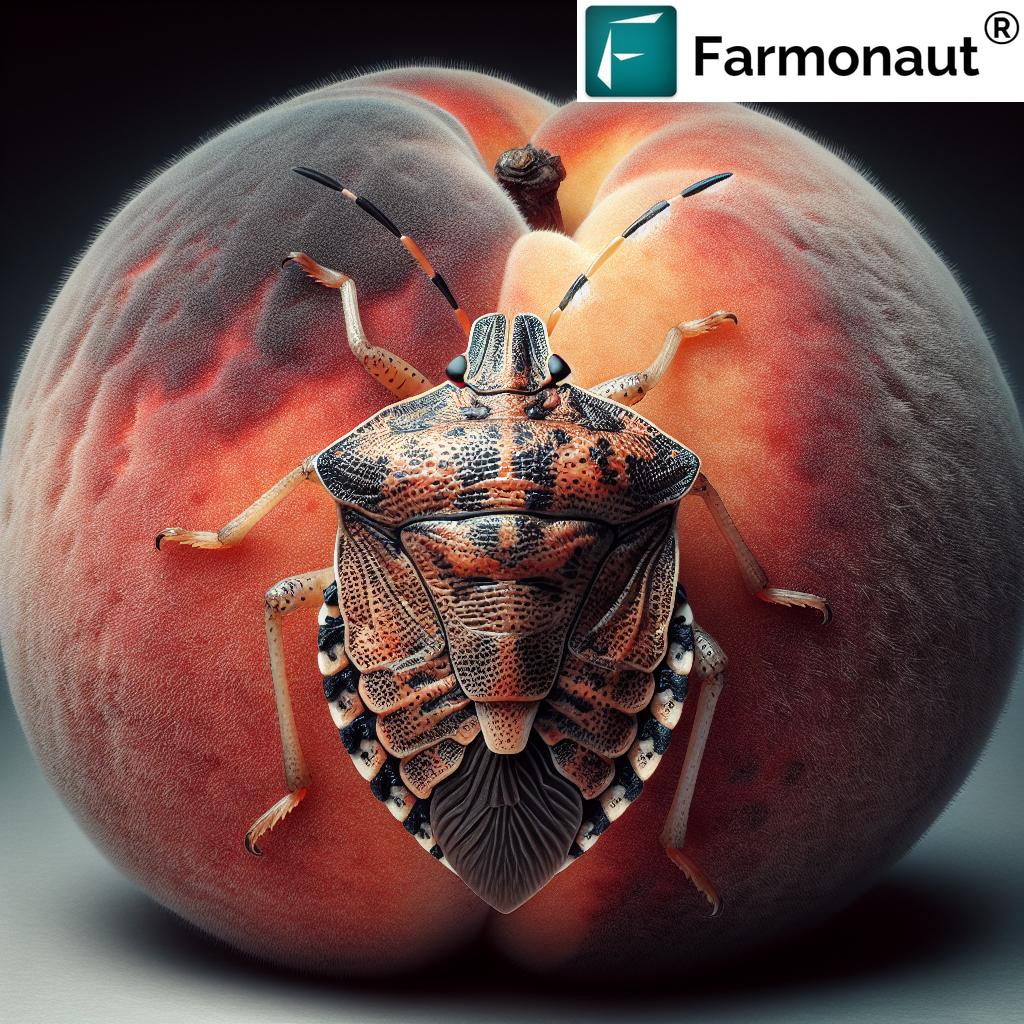
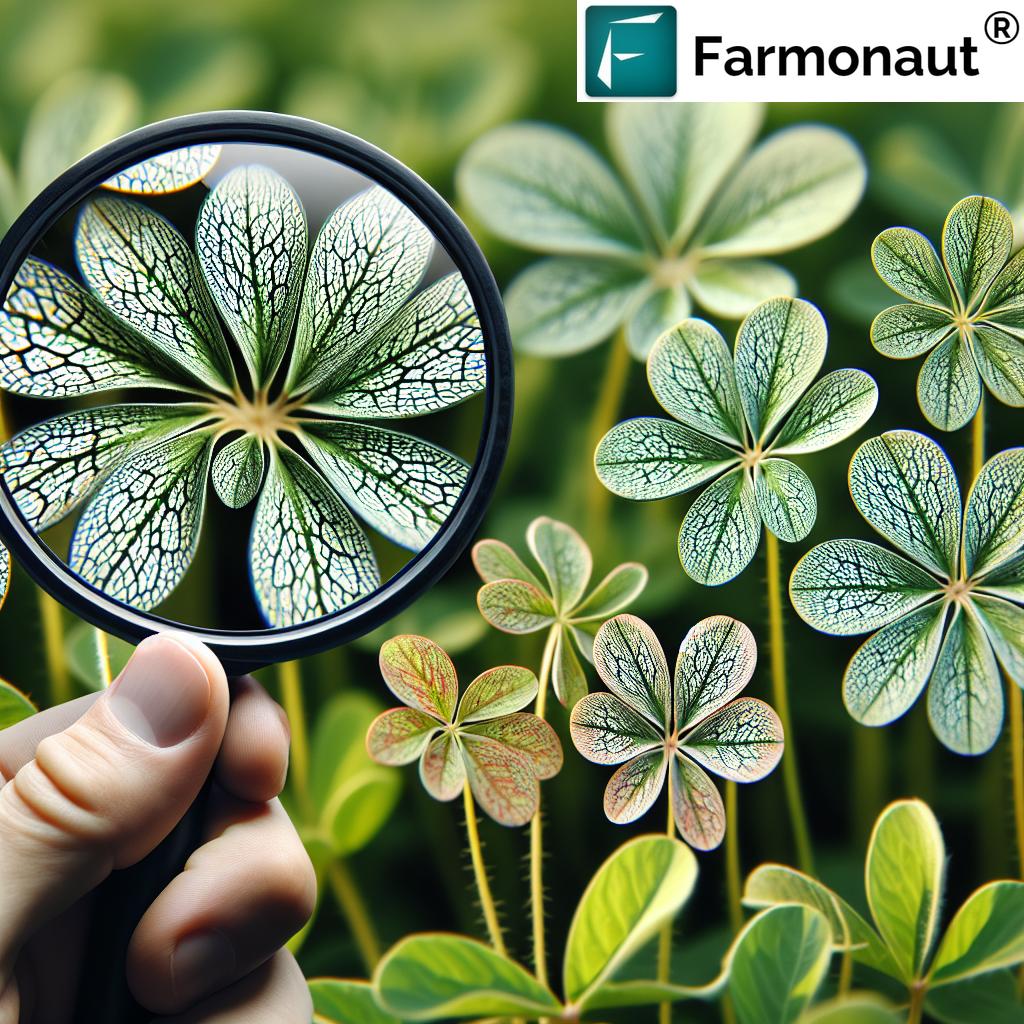
Recognizing the Symptoms of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
Early detection is crucial in managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease effectively. As agricultural experts, we at Farmonaut emphasize the importance of regular crop monitoring to identify symptoms as soon as they appear. Here are the key symptoms to watch out for:
- Mosaic Patterns on Leaves: The most characteristic symptom is the appearance of a mosaic pattern on the leaves of infected plants. This pattern typically manifests as irregular light and dark green areas on the leaf surface.
- Leaf Discoloration: Affected leaves may exhibit yellowing or bleached areas, often accompanied by the mosaic pattern.
- Stunted Growth: Infected plants may show reduced growth rates, resulting in smaller overall plant size compared to healthy specimens.
- Leaf Deformation: In severe cases, leaves may become distorted, curled, or develop an abnormal shape.
- Reduced Yield: As the disease progresses, it can significantly impact crop yield, leading to economic losses for farmers.
It’s important to note that symptom expression can vary depending on factors such as plant species, environmental conditions, and the specific strain of the virus. This variability underscores the need for advanced monitoring techniques, which we’ll discuss later in this article.
Transmission Mechanisms of Alfalfa Mosaic Virus
Understanding how the Alfalfa Mosaic Virus spreads is crucial for developing effective control and protection strategies. The virus can be transmitted through several means:
- Aphid Transmission: Aphids are the primary vectors for spreading Alfalfa Mosaic Virus. These small insects feed on plant sap and can carry the virus from infected plants to healthy ones.
- Seed Transmission: The virus can be passed on through seeds from infected plants, leading to new generations of infected crops.
- Mechanical Transmission: Mechanical means, such as contaminated farming equipment or human hands, can spread the virus during routine agricultural practices.
- Grafting: In horticultural settings, grafting infected plant material onto healthy rootstock can transmit the virus.
The Impact of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease on Agriculture
Alfalfa Mosaic Disease can have significant economic and ecological impacts on agriculture. Here’s an overview of its effects:
- Reduced Crop Yields: Infected plants often produce lower yields, directly affecting farm productivity and profitability.
- Quality Degradation: The disease can negatively impact the quality of harvested crops, potentially reducing their market value.
- Increased Production Costs: Managing the disease often requires additional inputs and labor, increasing overall production costs.
- Ecological Disruption: The spread of the virus can affect wild plant populations, potentially disrupting local ecosystems.
Control and Management Strategies for Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated approach to managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease. This involves combining various strategies to effectively control the disease while minimizing environmental impact. Here are some key management strategies:
1. Cultural Control Methods
- Crop Rotation: Implementing a proper crop rotation system can help break the disease cycle and reduce the risk of infection.
- Weed Management: Many weeds can serve as reservoirs for the virus. Regular weed control can help reduce the presence of alternative hosts.
- Sanitation Practices: Regularly cleaning and disinfecting farm equipment can prevent mechanical transmission of the virus.
2. Biological Control
Encouraging natural predators of aphids, such as ladybugs and lacewings, can help reduce vector populations and limit disease spread. This approach is particularly valuable in organic farming systems.
3. Chemical Control
While not a cure for the virus itself, insecticides can be used to manage aphid populations in conventional farming systems. However, we always recommend judicious use of chemicals to minimize environmental impact.
4. Resistant Varieties
Planting varieties of crops that have been bred for resistance to Alfalfa Mosaic Virus can significantly reduce the risk of infection and crop loss.
5. Advanced Monitoring and Early Detection
This is where Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system comes into play. Our advanced technology allows for early detection of disease symptoms across large areas, enabling prompt intervention.

Farmonaut’s Role in Managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to leveraging cutting-edge technology to support farmers in their fight against crop diseases like Alfalfa Mosaic. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers several advantages:
- Early Detection: Our system can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate the presence of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease before symptoms are visible to the naked eye.
- Large-Scale Monitoring: Unlike traditional scouting methods, our satellite technology can monitor vast areas of farmland quickly and efficiently.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: We provide farmers with actionable insights based on real-time data, enabling them to make informed decisions about disease management.
- Integration with Other Management Practices: Our system can be seamlessly integrated with other agricultural practices, supporting a holistic approach to crop management.
To better understand the advantages of our system, let’s compare traditional methods with Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach:
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | Farmonaut Satellite System |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Slow – Relies on manual scouting | Fast – Real-time satellite imagery analysis |
| Accuracy | Variable – Depends on scout’s expertise | High – Uses advanced algorithms for consistent analysis |
| Cost-effectiveness | Low – Labor-intensive and time-consuming | High – Covers large areas with minimal human input |
| Coverage Area | Limited – Only areas physically scouted | Extensive – Can monitor entire farms or regions |
As you can see, our satellite-based system offers significant advantages in managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease and other crop health issues. To learn more about how Farmonaut can help protect your crops, visit our app page or explore our API services.
Organic vs. Conventional Approaches to Alfalfa Mosaic Disease Management
The management of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease can differ significantly between organic and conventional farming systems. Let’s explore the approaches and considerations for each:
Organic Farming Approaches
In organic farming systems, the focus is on preventive measures and natural control methods:
- Crop Diversity: Increasing plant diversity can help reduce the spread of the disease by creating natural barriers.
- Beneficial Insects: Encouraging populations of natural predators to control aphids without the use of synthetic pesticides.
- Organic Pesticides: Using approved organic pesticides derived from natural sources to manage aphid populations.
- Soil Health: Focusing on building healthy soils to promote strong, resilient plants that can better withstand disease pressure.
Conventional Farming Approaches
Conventional farming systems have a wider range of tools at their disposal:
- Chemical Pesticides: Using synthetic insecticides to control aphid populations more aggressively.
- Genetically Modified Crops: Some conventional systems may use GM crops engineered for resistance to the Alfalfa Mosaic Virus.
- Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR) Inducers: Applying chemicals that trigger the plant’s natural defense mechanisms.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring for targeted disease management.
Regardless of the farming system, Farmonaut’s technology can be invaluable in early detection and monitoring of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease. Our system is adaptable to both organic and conventional farming practices, providing crucial data to inform management decisions.
The Role of Climate and Environmental Factors
Climate and environmental conditions play a significant role in the development and spread of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective disease management:
- Temperature: The virus and its aphid vectors thrive in moderate temperatures. Climate change may be altering the geographical range and severity of the disease.
- Humidity: High humidity can favor the survival and spread of aphids, potentially increasing disease transmission.
- Rainfall Patterns: Excessive rainfall can stress plants, making them more susceptible to infection. Conversely, drought conditions can also weaken plants, increasing their vulnerability.
- Wind Patterns: Wind can play a role in the long-distance dispersal of aphids, potentially introducing the virus to new areas.
Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system takes these environmental factors into account, providing farmers with a comprehensive view of their crop’s health in relation to local climate conditions. This holistic approach allows for more precise and effective disease management strategies.
Economic Impact and Risk Assessment
The economic impact of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease can be substantial, affecting not only individual farmers but entire agricultural sectors. Here’s an overview of the potential economic consequences:
- Direct Yield Losses: Infected crops often produce lower yields, directly impacting farm income.
- Quality Reduction: The disease can affect crop quality, potentially lowering market prices for harvested produce.
- Increased Production Costs: Managing the disease often requires additional inputs, labor, and resources, increasing overall production costs.
- Market Access: In some cases, the presence of the disease can affect access to certain markets, particularly for export crops.
At Farmonaut, we believe in the importance of comprehensive risk assessment to mitigate these economic impacts. Our satellite monitoring system can help farmers:
- Identify high-risk areas within their fields
- Predict potential outbreaks based on historical data and current conditions
- Implement targeted management strategies to minimize economic losses
By providing early warning and precise monitoring, we aim to help farmers make informed decisions that protect their crops and their bottom line.
Future Perspectives and Research Directions
As we look to the future, several promising areas of research and development could significantly impact the management of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease:
- Advanced Genetic Engineering: Developing new crop varieties with enhanced resistance to the virus through techniques like CRISPR gene editing.
- Novel Biological Control Agents: Exploring new natural predators or microorganisms that can help control aphid populations or suppress virus replication.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Developing more sensitive and rapid diagnostic tests for early detection of the virus in both plants and vectors.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing disease prediction models by integrating more data sources and advanced algorithms.
- Sustainable Pest Management: Researching new, environmentally friendly methods for managing aphid populations in both organic and conventional systems.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continuously improving our satellite monitoring and data analysis capabilities to provide farmers with the most advanced tools for managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease and other crop health challenges.
Case Studies: Successful Management of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
While we don’t include specific case studies or success stories, it’s worth noting that many farmers have successfully managed Alfalfa Mosaic Disease through integrated approaches that combine traditional farming wisdom with modern technology. These success stories often involve:
- Early detection through regular monitoring and advanced technologies like satellite imaging
- Prompt implementation of control measures upon disease detection
- Holistic farm management practices that promote overall plant health and ecosystem balance
- Collaboration with agricultural experts and researchers to develop tailored management strategies
These examples highlight the importance of a proactive, integrated approach to disease management, which is at the core of Farmonaut’s philosophy.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
As we’ve explored throughout this article, managing Alfalfa Mosaic Disease requires a comprehensive, integrated approach that combines traditional farming practices with cutting-edge technology. At Farmonaut, we believe that the key to successful disease management lies in:
- Early detection through advanced monitoring systems
- Informed decision-making based on real-time data and expert insights
- Implementation of targeted control measures that respect the environment and farm ecosystem
- Continuous learning and adaptation as new research and technologies emerge
By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring system, farmers can gain a significant advantage in the fight against Alfalfa Mosaic Disease and other crop health challenges. Our technology provides the data and insights needed to make timely, informed decisions that protect crops, optimize yields, and ensure long-term farm sustainability.
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can support your farm’s health and productivity. Visit our website or download our app to learn more:
For developers interested in integrating our technology into their own systems, check out our API documentation.
Together, we can build a more resilient and productive agricultural future, one field at a time.
FAQs about Alfalfa Mosaic Disease
- Q: Can Alfalfa Mosaic Disease affect humans or animals?
A: No, Alfalfa Mosaic Disease is specific to plants and does not pose a direct health risk to humans or animals. - Q: How long can the Alfalfa Mosaic Virus survive outside of a host plant?
A: The virus can survive for short periods outside of a host, but it requires a living plant to replicate and spread. - Q: Are there any natural predators of aphids that can help control the spread of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease?
A: Yes, ladybugs, lacewings, and certain parasitic wasps are natural predators of aphids and can help reduce their populations. - Q: Can crop rotation help prevent Alfalfa Mosaic Disease?
A: While crop rotation can be helpful, it may not be entirely effective due to the wide host range of the virus. However, it can still be a valuable part of an integrated management strategy. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for signs of Alfalfa Mosaic Disease?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, you can receive updates on crop health as frequently as every 3-5 days, depending on your subscription plan.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage Alfalfa Mosaic Disease and other crop health issues, consider subscribing to our services: