Arizona’s Water Crisis: Balancing Groundwater Management and Sustainable Development in Phoenix
“Arizona’s new regulations require proof of a 100-year water supply for development, impacting future urban growth.”
In the heart of the American Southwest, Arizona faces a critical juncture in its water management journey. As we delve into the complexities of Arizona water rights and the ongoing legal disputes surrounding groundwater management in Arizona, we find ourselves at the forefront of a crucial debate that will shape the future of the state’s urban development and environmental sustainability.
The arid landscape of Arizona has long been a testament to human ingenuity in the face of water scarcity. However, recent events have brought the state’s water crisis into sharp focus, highlighting the delicate balance between growth and conservation. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll explore the multifaceted issues surrounding water conservation in Phoenix, the implications of new Arizona housing development regulations, and the quest for a sustainable water supply in Arizona.
The Epicenter of Controversy: Phoenix’s Water Dilemma
Phoenix, the bustling metropolis at the heart of Arizona’s Sonoran Desert, stands as a symbol of both progress and environmental challenge. The city’s rapid expansion has put unprecedented pressure on its water resources, leading to a contentious legal battle that underscores the broader issues of water rights and urban development across the state.
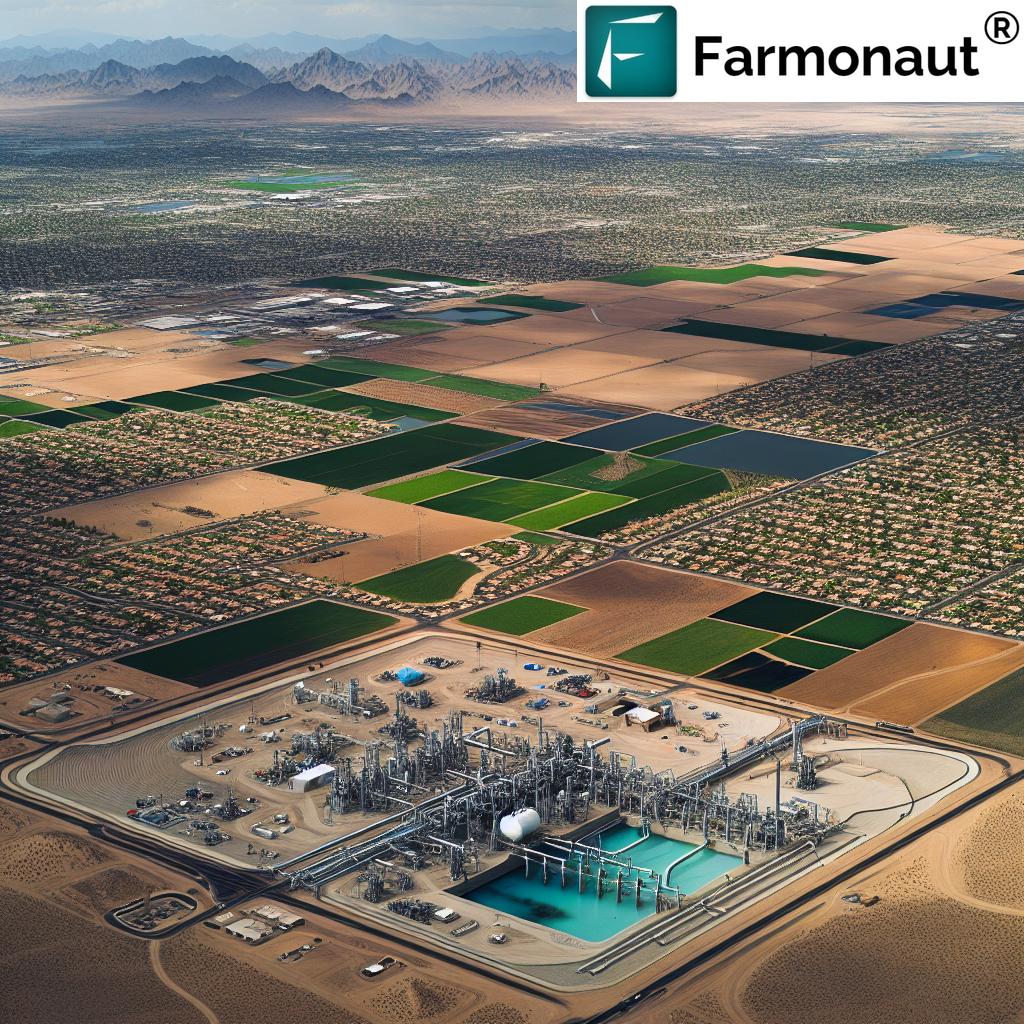

At the center of this dispute is a lawsuit filed by the Goldwater Institute on behalf of the Home Builders Association of Central Arizona. This legal action challenges the enforcement of what they claim are illegal rules regarding groundwater management that are hindering new construction projects due to insufficient groundwater availability.
The Legal Landscape: Unraveling the Water Rights Dispute
The lawsuit, unfolding in Maricopa County, accuses the Arizona Department of Water Resources (ADWR) of overstepping its authority. The crux of the matter lies in the department’s denial of certificates necessary for development based on newly imposed requirements, most notably the need for evidence of a sustainable 100-year water supply.
These changes, implemented in November 2023, are at the heart of the legal challenge. The Goldwater Institute argues that these alterations violate state law regarding regulatory processes. Jon Riches, Vice President for Litigation at the Goldwater Institute, emphasizes the need for a transparent and comprehensive approach to decisions surrounding water availability and housing, rather than what they perceive as executive mandates.
The Policy of “Unmet Demand”: A New Approach to Water Management
Central to the ongoing legal dispute is a new policy addressing “unmet demand.” This concept reflects the discrepancy between the groundwater allocated for development and the actual available supply. Kathleen Ferris, a former director of the ADWR, has pointed out a chronic issue in Arizona’s water management: the consistent over-allocation of groundwater resources.
This over-allocation has led to a persistent water deficit, complicating plans for future development and raising serious questions about the long-term viability of current growth patterns in water-scarce regions like Phoenix and its surrounding areas.
The Alarming Findings: Phoenix’s Water Future in Jeopardy
“Phoenix, Arizona’s largest city, could face potential water shortages within the next century due to rapid expansion.”
Approximately 18 months ago, Governor Katie Hobbs made a startling announcement based on updated water models. These models indicated that groundwater supplies in the Phoenix area could become insufficient within a century, with fast-growing regions like Buckeye and Queen Creek particularly at risk.
This revelation has effectively put the brakes on new development and triggered the current lawsuit. Critics within the industry argue that the scope of these regulations is unnecessarily broad and could exacerbate Arizona’s already challenging housing affordability crisis.
Historical Context: A Pattern of Water Conservation Measures
It’s crucial to note that the requirements for demonstrating an assured water supply are not new to Arizona’s regulatory landscape. During former Governor Doug Ducey’s administration, similar findings regarding unmet water demands resulted in halted construction in Pinal County. Interestingly, this situation did not provoke the same level of legal action from the Goldwater Institute, raising questions about the political dimensions of the current dispute.
Governor Hobbs has retained Tom Buschatzke, the former ADWR director, who has reaffirmed the department’s commitment to the existing methodology for evaluating water supply applications. In response to the lawsuit, Hobbs’ administration has firmly defended its position, suggesting that the Goldwater Institute’s motives may be politically driven, given its connections to past Republican governance.
The Stakes: Water Sustainability vs. Economic Growth
The outcome of this lawsuit carries significant implications for Arizona’s water sustainability efforts. If the court rules against the ADWR, it could impede the state’s ability to take necessary actions based on hydrological data, potentially jeopardizing Arizona’s long-term water security.
Moreover, this legal battle highlights the existing tensions as Governor Hobbs moves to prioritize the preservation of public water supplies against the backdrop of growth pressures from developers eager to capitalize on Arizona’s increasing population.
Balancing Act: Conservation, Development, and Political Realities
As Governor Hobbs contemplates a potential re-election bid in 2026, she faces the challenging task of balancing the urgent need for conservation against economic growth pressures. This delicate balancing act is further complicated by a complex political landscape that includes both support and resistance from various stakeholders in Arizona’s development community.

The Role of Technology in Water Management
In addressing these complex water management challenges, advanced technologies play a crucial role. Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, offers innovative solutions that can assist in monitoring and managing water resources effectively. Through its satellite-based farm management solutions, Farmonaut provides valuable tools for precision agriculture and resource management.
For more information on Farmonaut’s advanced solutions, visit their web application or explore their API for developers.
Arizona Water Resource Management Comparison
| Region | Current Water Supply (acre-feet/year) | Projected Water Demand in 2050 (acre-feet/year) | Groundwater Depletion Rate (inches/year) | Water Conservation Measures Implemented | Sustainable Development Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maricopa County (Phoenix) | 1,000,000 | 1,500,000 | 2.5 | Xeriscaping, water recycling, low-flow fixtures | Rapid urban expansion, high water demand |
| Pima County (Tucson) | 350,000 | 450,000 | 1.8 | Rainwater harvesting, greywater reuse | Limited surface water sources, reliance on groundwater |
| Pinal County | 200,000 | 300,000 | 3.2 | Drought-resistant crops, efficient irrigation systems | Agricultural water needs, growing urban areas |
| Yavapai County | 100,000 | 150,000 | 1.5 | Water-smart landscaping, conservation education | Limited watershed, increasing population |
The Path Forward: Innovative Solutions and Collaborative Efforts
As Arizona grapples with its water crisis, innovative solutions and collaborative efforts are crucial. We’re seeing an increasing emphasis on:
- Water Conservation Technologies: Implementation of advanced irrigation systems and water-saving fixtures in both urban and agricultural settings.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Developing cities with water conservation at the forefront, including green infrastructure and water-efficient landscaping.
- Agricultural Innovations: Adoption of drought-resistant crops and precision farming techniques to reduce water usage in the agricultural sector.
- Policy Reform: Ongoing discussions about updating water rights laws to reflect current environmental realities and future projections.
- Public Education: Increasing awareness about water conservation and its importance in desert environments.
Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can play a significant role in these efforts. Their satellite-based crop health monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems can help farmers optimize water usage and improve overall resource management. For more information on how Farmonaut’s technology can assist in water conservation efforts, check out their Android app or iOS app.
The Economic Impact of Water Scarcity
The ongoing water crisis in Arizona has far-reaching economic implications. The state’s economy, heavily reliant on sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and real estate development, faces significant challenges due to water scarcity. Some key economic considerations include:
- Agricultural Productivity: As water becomes scarcer, farmers may need to shift to less water-intensive crops or reduce cultivated areas, potentially impacting Arizona’s agricultural output and economy.
- Real Estate Development: The new regulations requiring proof of a 100-year water supply could slow down housing development, affecting the construction industry and potentially driving up housing costs.
- Tourism: Water-based recreational activities and the overall appeal of Arizona’s landscapes could be affected by prolonged drought conditions, potentially impacting the tourism sector.
- Industrial Growth: Industries requiring significant water usage may face challenges in expanding or establishing new operations in Arizona, potentially limiting job creation and economic diversification.
These economic challenges underscore the need for innovative solutions that balance water conservation with economic growth. Technologies like those provided by Farmonaut can help businesses and farmers optimize their water usage, potentially mitigating some of these economic impacts.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Water Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool in addressing water management challenges. AI can help in various aspects of water resource management, including:
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze historical data and current conditions to predict future water availability and demand, helping in long-term planning.
- Leak Detection: AI-powered systems can detect leaks in water distribution networks more efficiently, reducing water loss.
- Irrigation Optimization: AI can help farmers determine the optimal amount of water needed for crops based on real-time soil and weather conditions.
- Water Quality Monitoring: AI systems can continuously monitor water quality parameters, alerting authorities to potential issues before they become critical.
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System is an excellent example of how AI can be applied in agriculture to optimize water usage. This system provides real-time insights and expert crop management strategies, helping farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and resource allocation.
Public Engagement and Water Conservation
Public engagement plays a crucial role in addressing Arizona’s water crisis. Effective water conservation strategies require the participation of all stakeholders, from individual households to large corporations. Some key aspects of public engagement include:
- Education Programs: Implementing comprehensive education programs to raise awareness about water scarcity and conservation methods.
- Community Initiatives: Encouraging community-led water conservation projects and initiatives.
- Incentive Programs: Offering incentives for water-efficient appliances and xeriscaping in residential and commercial properties.
- Transparency: Ensuring transparent communication about water usage, availability, and conservation efforts to build public trust and encourage participation.
By fostering a culture of water conservation and responsible usage, Arizona can work towards a more sustainable water future. Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can support these efforts by providing data-driven insights into water usage and conservation opportunities.
Looking to the Future: Sustainable Water Management in Arizona
As we look to the future, it’s clear that sustainable water management will be crucial for Arizona’s continued growth and prosperity. This will require a multifaceted approach, including:
- Policy Reform: Updating water rights laws and regulations to reflect current environmental realities and future projections.
- Technological Innovation: Investing in and adopting new technologies for water conservation, treatment, and distribution.
- Collaborative Governance: Fostering cooperation between different levels of government, private sector entities, and communities to manage water resources effectively.
- Ecosystem Preservation: Recognizing the importance of natural ecosystems in water management and working to preserve and restore these systems.
- Adaptive Planning: Developing flexible, adaptive plans that can respond to changing climatic conditions and water availability.
By embracing these strategies and leveraging advanced technologies like those provided by Farmonaut, Arizona can work towards a more sustainable and water-secure future.
Conclusion: A Watershed Moment for Arizona
The current water crisis and legal disputes in Arizona represent a watershed moment for the state. The decisions made now will have far-reaching implications for future generations, shaping the landscape of urban development, agriculture, and environmental conservation in the region.
As we navigate these complex issues, it’s clear that innovative solutions, collaborative efforts, and a commitment to sustainability will be key. By leveraging advanced technologies, implementing thoughtful policies, and fostering public engagement, Arizona can work towards a future where water resources are managed sustainably, supporting both economic growth and environmental preservation.
The path forward will undoubtedly be challenging, but with concerted effort and innovative approaches, Arizona can set a precedent for responsible water management in arid regions around the world.
FAQ Section
- Q: What is the main issue in Arizona’s current water crisis?
A: The main issue is the balance between groundwater management and sustainable development, particularly in rapidly growing areas like Phoenix. New regulations requiring proof of a 100-year water supply for development have sparked legal disputes and raised concerns about future urban growth. - Q: How is the Arizona Department of Water Resources (ADWR) involved in this issue?
A: The ADWR is at the center of the controversy due to its enforcement of new regulations regarding groundwater management. They are responsible for evaluating water supply applications and have implemented stricter requirements for development approvals. - Q: What is the “unmet demand” policy, and why is it important?
A: The “unmet demand” policy addresses the discrepancy between allocated groundwater for development and actual available supply. It’s important because it highlights the chronic over-allocation of groundwater resources in Arizona, which complicates future development planning. - Q: How might the current legal dispute impact Arizona’s future development?
A: If the court rules against the ADWR, it could limit the state’s ability to regulate water usage based on hydrological data, potentially jeopardizing long-term water security. This could also affect future urban development patterns and housing affordability. - Q: What role can technology play in addressing Arizona’s water management challenges?
A: Advanced technologies, such as those offered by Farmonaut, can assist in monitoring and managing water resources effectively. These include satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and precision agriculture techniques that optimize water usage.
Earn With Farmonaut
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Farmonaut Subscriptions
As we continue to navigate the complexities of water management in Arizona, it’s clear that innovative solutions and collaborative efforts will be crucial. Technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can play a significant role in optimizing water usage and improving overall resource management. By leveraging these advanced tools and implementing thoughtful policies, Arizona can work towards a more sustainable water future.
For more information on how Farmonaut’s technology can assist in water conservation efforts, explore their web application, Android app, or iOS app. Developers interested in integrating Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data into their own systems can check out the API and API Developer Docs.