California’s Mudslide Menace: Understanding Risks and Prevention in Drought-Stricken Regions
“California’s coastal and mountainous regions are 40% more susceptible to mudslides due to wildfire-induced vegetation loss.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of California’s mudslide risks and prevention strategies. As we delve into this crucial topic, we’ll uncover the complex interplay of geological, climatic, and human factors that contribute to these dangerous debris flows. Our goal is to provide you with a deep understanding of the challenges faced by communities in vulnerable areas and the innovative solutions being developed to mitigate these risks.
Understanding the Mudslide Menace in California
California, with its diverse landscape and unique climate, faces a particular set of challenges when it comes to mudslides. These dangerous torrents, often referred to by geologists and first responders as debris flows, have proven to be particularly lethal in certain parts of the state. Let’s explore why California is so prone to these devastating events.
The Geological Foundation of California’s Mudslide Risk
From a geological perspective, California’s mountains are relatively young. This means that much of the state’s steep terrain is still in motion and covered in loose rocks and soil. These materials can be easily dislodged, especially when the ground becomes saturated with water. The combination of young, unstable geology and periodic heavy rainfall creates a perfect storm for mudslide occurrence.
The Climate Factor: Drought and Deluge
California’s climate plays a significant role in exacerbating mudslide risks. The state often experiences prolonged periods of drought followed by intense rainfall events. This cycle can be particularly dangerous for several reasons:
- During drought periods, the soil becomes extremely dry and hard-packed.
- When heavy rains finally arrive, the water struggles to penetrate the hardened soil.
- Instead of being absorbed, the water rushes downhill, gaining momentum and energy.
- As it flows, it picks up soil, debris, and rocks, creating a dangerous mudslide.
Understanding this climate-driven risk is crucial for communities in mudslide-prone areas. At Farmonaut, we offer advanced satellite-based monitoring systems that can help track soil moisture levels and vegetation health, providing valuable data for predicting and preparing for potential mudslide events.
The Wildfire Connection
Wildfires, an increasing problem across the Western United States, significantly amplify the risk of mudslides. When a wildfire sweeps through an area, it leaves behind a landscape devoid of vegetation. This loss of plant life has severe consequences:
- Vegetation plays a crucial role in holding soil in place with its root systems.
- Without plants to absorb water, rainfall is more likely to cause erosion and flooding.
- The heat from wildfires can create a water-repellent layer on the soil surface, further increasing runoff.
According to the California Department of Conservation, burning vegetation and soil on a slope more than doubles the rate of water runoff. This dramatic increase in runoff can lead to catastrophic mudslides in the aftermath of wildfires.
Identifying High-Risk Areas in California
While mudslides can occur in many parts of California, certain areas are particularly vulnerable. Understanding these high-risk zones is crucial for both residents and emergency planners.
Recently Burned Areas
The areas most at risk are those on or near hillsides that have burned in recent years. With little to no vegetation left to hold the soil in place, these regions are extremely susceptible to mudslides during heavy rainfall events. Communities located below or near these burn scars must be especially vigilant.
Coastal and Mountainous Regions
California’s coastal areas and mountainous terrains are among the most prone to mudslides. The combination of steep slopes, potentially unstable geology, and exposure to heavy rainfall makes these regions particularly vulnerable. Notable high-risk areas include:
- Santa Barbara County coast
- Sonoma County, including areas near Healdsburg
- Los Angeles County foothills
- San Francisco Bay Area hillsides
At Farmonaut, we provide detailed satellite imagery and analysis that can help identify potential mudslide hot spots in these regions. Our advanced AI systems can analyze terrain, vegetation cover, and soil conditions to assess risk levels.
Urban-Wildland Interface
As urban development continues to expand into previously undeveloped areas, the urban-wildland interface becomes increasingly vulnerable to mudslides. These areas often combine the risk factors of steep terrain, recent wildfire activity, and human alteration of the landscape.
“Early warning systems for mudslides in California have reduced evacuation response times by up to 30% in high-risk areas.”
Historical Mudslide Events in California
To truly understand the impact of mudslides in California, it’s essential to look at some of the most significant events in the state’s history. These past occurrences provide valuable lessons and underscore the importance of prevention and preparedness.
The Montecito Mudslide of 2018
One of the most devastating mudslides in recent California history occurred on January 9, 2018, in Montecito, Santa Barbara County. This tragic event unfolded as follows:
- Intense rain fell on a weeks-old wildfire burn scar in the mountains above Montecito.
- The rainfall triggered massive torrents of mud and debris that tore through the community.
- 23 people lost their lives in the disaster.
- Hundreds of homes were destroyed or damaged.
This event highlighted the deadly combination of recent wildfires and heavy rainfall, serving as a wake-up call for improved mudslide prevention and early warning systems.
The 1934 La Crescenta-Montrose Flood
In 1934, a severe storm over the Southern California mountains unleashed runoff of unprecedented intensity:
- 30 people were killed in the resulting mudslides and floods.
- More than 480 homes were destroyed.
- This event led to significant changes in flood control and debris basin construction in the region.
The 2003 San Bernardino Mountains Mudslide
On Christmas Day in 2003, a tragic mudslide occurred in the San Bernardino Mountains:
- Heavy rain fell over fire-scarred mountains, triggering a massive debris flow.
- 16 people who had gathered at a church facility in Waterman Canyon lost their lives.
- This event underscored the need for better evacuation planning in high-risk areas.
These historical events demonstrate the recurring nature of mudslide risks in California and the critical importance of ongoing research, prevention efforts, and community preparedness.
Prevention Strategies and Protective Measures
In response to the persistent threat of mudslides, California has developed a range of tools and strategies to protect communities and mitigate risks. Let’s explore some of the most effective approaches currently in use.
Debris Basins: A Front-Line Defense
One of the most effective ways to manage landslides is through the use of debris basins. These engineered structures play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of mudslides:
- Debris basins are essentially large pits carved out of the landscape.
- They are strategically placed to catch material flowing downhill.
- According to the U.S. Geological Survey, mudslides can reach speeds exceeding 35 mph (56 kph).
- Debris basins can significantly slow or stop these fast-moving flows.
Often located at the mouths of canyons, debris basins serve a dual purpose:
- They collect debris while allowing water to continue downstream.
- This prevents blockages of the storm drain system, reducing flood risks in developed areas.
However, debris basins require ongoing maintenance:
- Regular removal of sediment is necessary to maintain their effectiveness.
- This process can take days or months, depending on the basin’s size.
- After the 2018 Montecito mudslides, Santa Barbara County invested $20 million in a new debris basin to enhance protection.
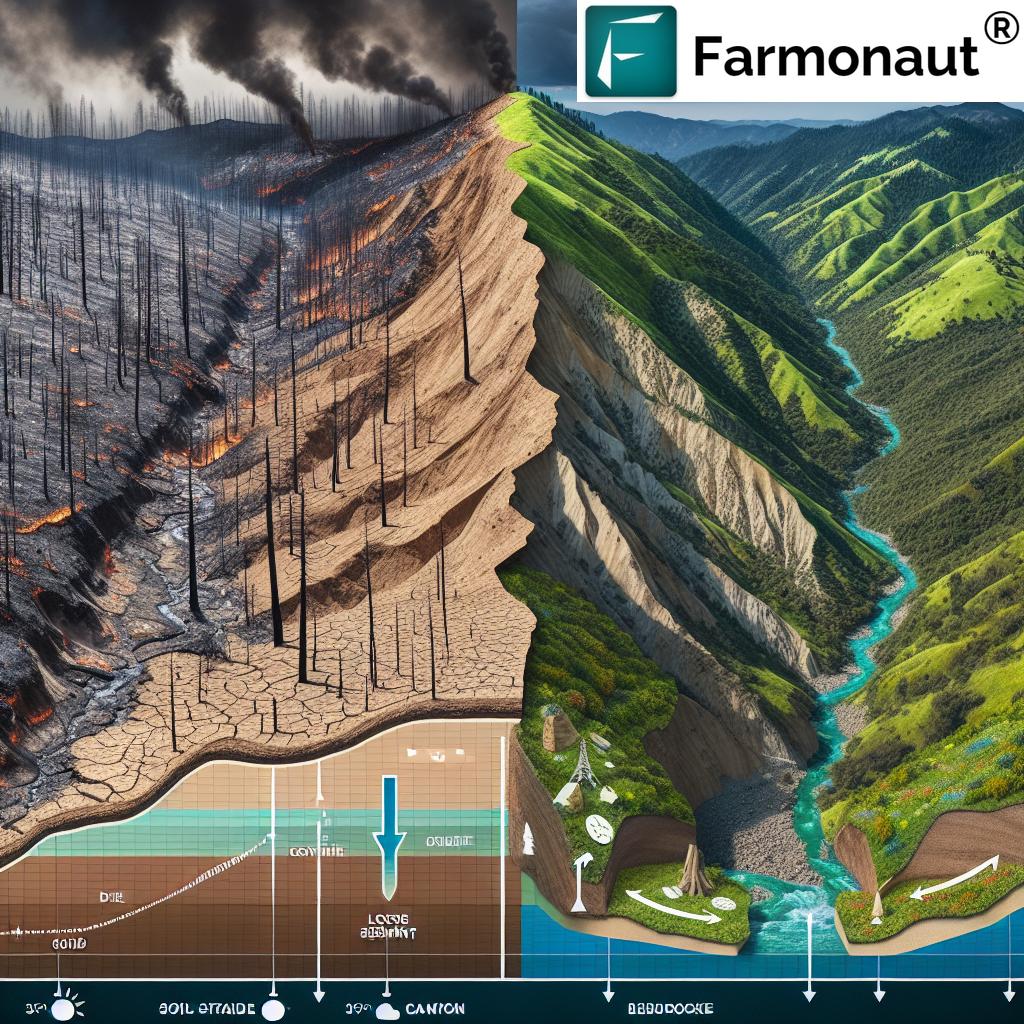
Innovative Debris Flow Prevention Techniques
In addition to traditional debris basins, new and innovative techniques are being employed to prevent and mitigate mudslides:
- Debris Nets: After the 2018 mudslides, Montecito raised millions to install debris nets in key canyons. These nets can catch smaller debris flows before they gain momentum.
- Erosion Control Barriers: These barriers, often made of natural materials, help stabilize slopes and reduce soil erosion.
- Reforestation: Planting trees and vegetation in burn areas can help stabilize soil and reduce runoff.
At Farmonaut, we support these efforts by providing detailed vegetation health analysis through our satellite-based monitoring system. This data can help planners identify areas in need of reforestation or other erosion control measures.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced satellite data analysis
Geological Hazard Mapping and Early Warning Systems
Prevention and preparedness rely heavily on accurate information and timely warnings. California has invested in several key initiatives:
- California Department of Conservation Mapping: The department runs a geological and landslide mapping team that identifies hot spots and continually updates its maps.
- Early Warning Systems: These systems use a variety of tools to gauge the likelihood of landslides in a given area, including:
- Terrain maps
- Lidar technology
- Aerial and satellite photography
- GPS monitoring stations
- Tilt meters and other on-site instrumentation
These advanced systems allow for better evacuation planning and more targeted prevention efforts. Farmonaut’s satellite imagery and AI-powered analysis can contribute valuable data to these early warning systems, helping to identify potential risks before they become critical.
The Role of Climate Change in Mudslide Risk
As we discuss California’s mudslide risks, it’s crucial to consider the impact of climate change on this natural hazard. Climate change is altering weather patterns and increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, which in turn affects mudslide risks in several ways:
Increased Wildfire Activity
Climate change is contributing to more frequent and severe wildfires in California. This increased fire activity has several implications for mudslide risk:
- More areas are left with burned, unstable soil prone to erosion.
- The fire season is extending, potentially overlapping more with the rainy season.
- Larger burn scars create more extensive areas of high mudslide risk.
Changes in Precipitation Patterns
Climate models predict significant changes in California’s precipitation patterns:
- More intense atmospheric river events, bringing heavy rainfall in short periods.
- Longer dry spells between rain events, leading to drier soil conditions.
- These changes can increase the likelihood of flash floods and debris flows when rain does occur.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing up-to-date climate data and analysis to help communities prepare for these changing conditions. Our satellite-based monitoring can track long-term trends in vegetation health, soil moisture, and other key indicators of mudslide risk.
Check out our API Developer Docs for integrating climate data into your applications
Community Preparedness and Response
While prevention strategies are crucial, it’s equally important for communities in high-risk areas to be prepared for potential mudslide events. Here are some key aspects of community preparedness:
Education and Awareness
Informing residents about mudslide risks and warning signs is vital:
- Community workshops and information sessions on mudslide risks and preparedness.
- Distribution of educational materials on recognizing early warning signs of slope instability.
- Regular updates on current risk levels, especially after wildfires or during heavy rain seasons.
Evacuation Planning
Well-planned and practiced evacuation procedures can save lives:
- Clearly marked evacuation routes and assembly points.
- Regular community-wide evacuation drills.
- Special provisions for evacuating vulnerable populations, such as the elderly or disabled.
Emergency Response Training
Training local first responders and community members in mudslide response can improve outcomes:
- Search and rescue techniques specific to mudslide events.
- First aid and triage training for common mudslide-related injuries.
- Training on the use of emergency communication systems.
The Future of Mudslide Prevention in California
As California continues to grapple with mudslide risks, new technologies and approaches are being developed to enhance prevention and response efforts. Here are some promising areas of advancement:
Advanced Monitoring Technologies
Emerging technologies are improving our ability to predict and monitor mudslide risks:
- High-resolution satellite imagery for real-time monitoring of slope stability.
- Machine learning algorithms for analyzing complex geological and weather data.
- IoT sensors for continuous monitoring of soil moisture and movement.
Farmonaut is at the forefront of these technological advancements, offering cutting-edge satellite-based monitoring and AI-powered analysis to support mudslide prevention efforts.
Nature-Based Solutions
There’s growing interest in using natural systems to mitigate mudslide risks:
- Restoration of native plant communities to stabilize slopes.
- Creation of wetlands and bioswales to slow and filter runoff.
- Use of permeable surfaces in urban areas to reduce flash flooding.
Policy and Planning Improvements
Enhanced policies and planning strategies are being developed to address mudslide risks:
- Stricter building codes and zoning regulations in high-risk areas.
- Improved integration of mudslide risk assessment in urban planning.
- Increased funding for research and implementation of prevention strategies.
Conclusion: A Collective Effort for a Safer California
As we’ve explored throughout this article, addressing California’s mudslide risks requires a multifaceted approach combining advanced technology, community preparedness, and innovative prevention strategies. The challenges posed by climate change and ongoing urban development make this effort more crucial than ever.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting these efforts through our advanced satellite-based monitoring and analysis tools. By providing accurate, timely data on vegetation health, soil conditions, and landscape changes, we aim to contribute to more effective mudslide prevention and risk assessment.
Remember, mudslide prevention is a collective responsibility. Whether you’re a resident of a high-risk area, a local official, or a concerned citizen, staying informed and supporting prevention efforts is crucial. Together, we can work towards a safer, more resilient California in the face of this ongoing natural hazard.
| Risk Factor | Impact | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Wildfires | Removes vegetation, destabilizes soil | Reforestation, erosion control barriers |
| Drought | Hardens soil, increases runoff | Soil moisture monitoring, water-efficient landscaping |
| Steep Terrain | Increases flow velocity and erosion | Terracing, retaining walls, slope stabilization |
| Heavy Rainfall | Saturates soil, triggers debris flows | Debris basins, improved drainage systems |
| Coastal Erosion | Undermines cliffs, increases landslide risk | Seawalls, beach nourishment, managed retreat |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main causes of mudslides in California?
A: The main causes include heavy rainfall, especially after periods of drought or wildfires, steep terrain, and unstable soil conditions. Climate change is exacerbating these factors.
Q: How can I tell if my property is at risk for mudslides?
A: Look for signs like cracks in the ground, leaning trees, or suddenly muddy springs. Check local geological hazard maps and consult with experts if you live on or near a steep slope.
Q: What should I do if a mudslide is imminent?
A: Listen to local authorities and be prepared to evacuate immediately. Move to higher ground and stay away from the path of the mudslide.
Q: How can communities prepare for mudslide risks?
A: Communities can implement early warning systems, create and practice evacuation plans, and invest in infrastructure like debris basins and improved drainage systems.
Q: How does Farmonaut contribute to mudslide prevention?
A: Farmonaut provides satellite-based monitoring of vegetation health and soil conditions, which can help identify areas at risk for mudslides and support early warning systems.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!