Devastating Texas Border Floods: Assessing Agricultural Damage and Community Impact in Rio Grande Valley
“The Rio Grande Valley floods resulted in at least four fatalities and left hundreds trapped in flooded homes and vehicles.”
In recent days, we’ve witnessed an unprecedented weather event that has brought widespread devastation to the Texas-Mexico border region, particularly the Rio Grande Valley. The severe flooding has not only claimed lives but also caused significant damage to agriculture, infrastructure, and communities on both sides of the border. As we delve into this critical situation, we’ll explore the extent of the damage, its impact on various sectors, and the ongoing efforts to manage this crisis.
Understanding the Scope of the Disaster
The Rio Grande Valley, known for its rich farmland and vibrant communities, has been hit by record-breaking rainfall, leading to what experts are calling a “historic rainstorm.” The impact of this natural disaster extends far beyond the immediate flooding, affecting agriculture, local economies, and the very fabric of border communities.
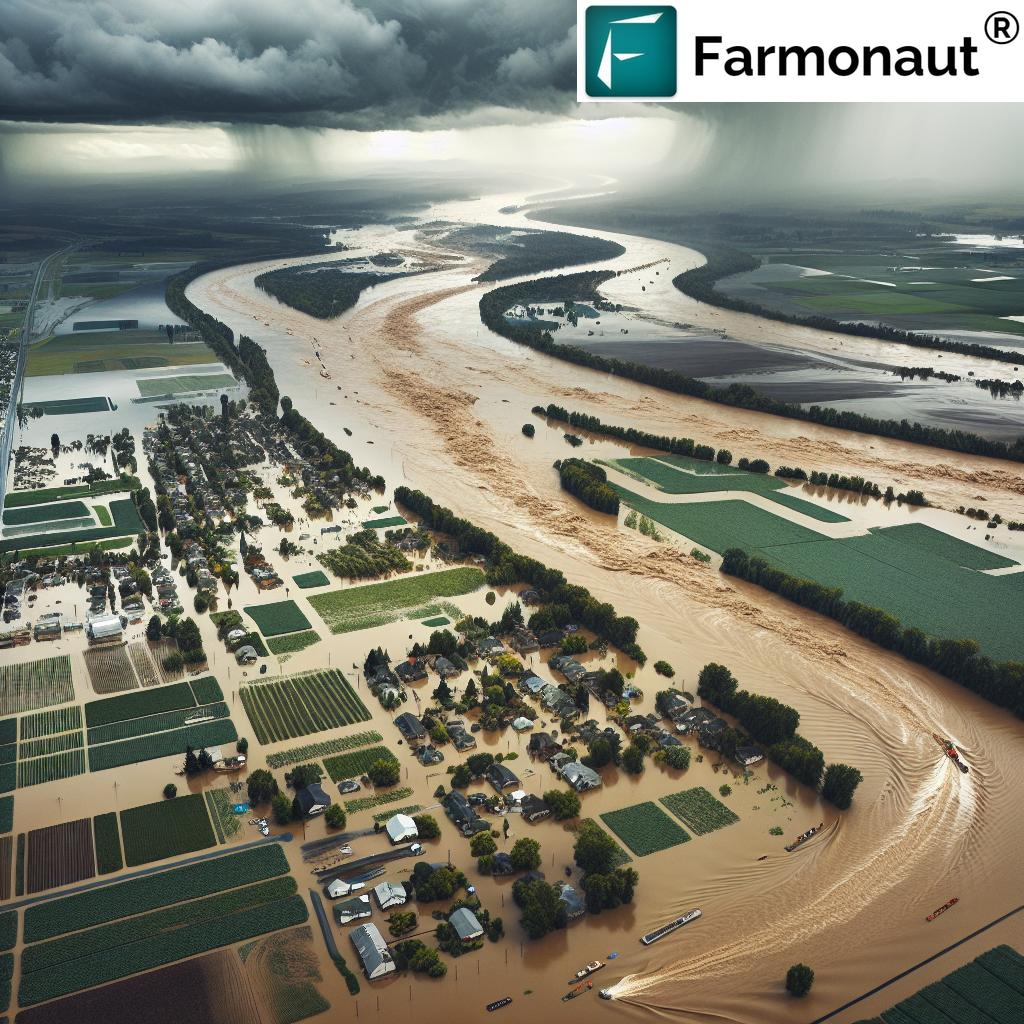

In Hidalgo County alone, officials reported more than 21 inches (53 centimeters) of rain, a staggering amount that overwhelmed local infrastructure and led to widespread flooding. The city of Harlingen, in particular, bore the brunt of this deluge, experiencing some of the most severe flooding in recent memory.
The Human Toll: Rescues, Evacuations, and Fatalities
The immediate impact of the floods on human life has been severe. Emergency services have been working tirelessly, conducting numerous water rescues across the affected areas. In Alamo, a small Texas border city, fire department crews responded to over 100 water rescues, highlighting the scale of the emergency.
Tragically, at least four fatalities have been reported, including drownings, underlining the deadly nature of this disaster. The loss of life serves as a stark reminder of the power of nature and the importance of heeding evacuation warnings and safety measures during such extreme weather events.
Agricultural Devastation: A Blow to the Region’s Economic Backbone
The Rio Grande Valley is renowned for its agricultural productivity, and the flooding has dealt a significant blow to this vital sector. Texas’ agriculture commissioner has reported substantial losses to both crops and livestock, though the full extent of the damage is still being assessed.
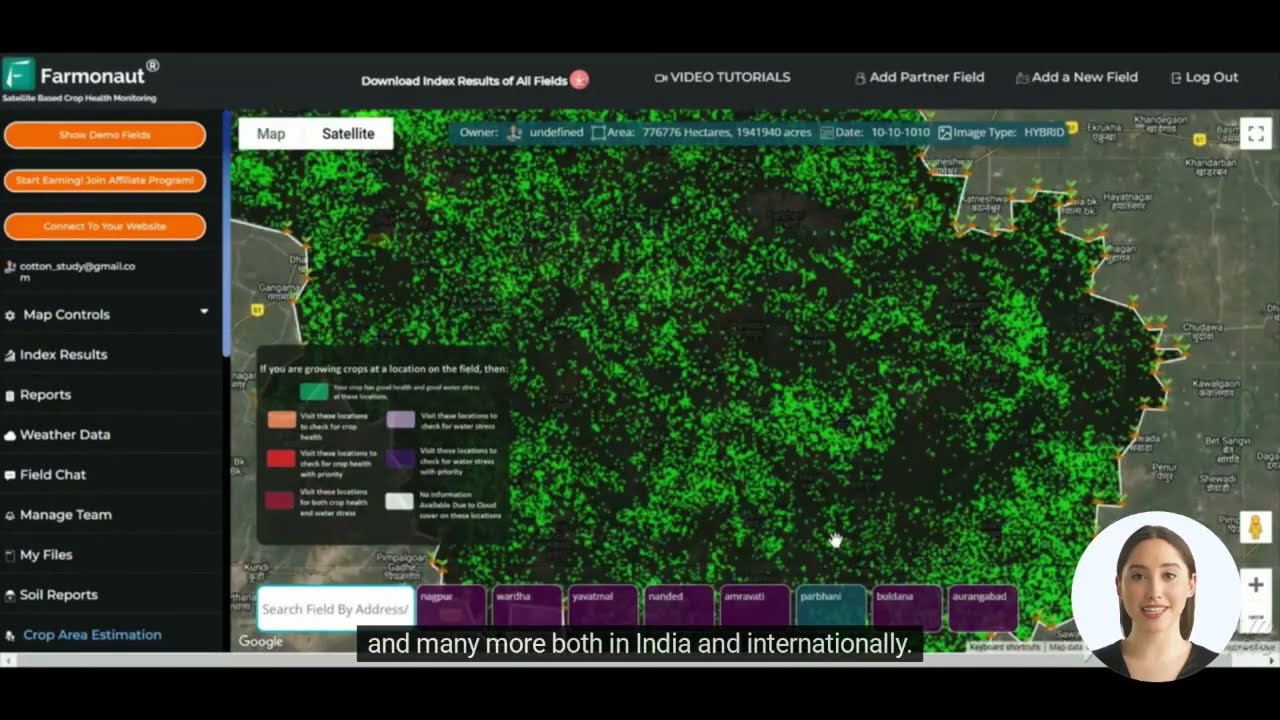
For a more comprehensive understanding of the agricultural impact, tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring can be invaluable. This technology allows for real-time assessment of vegetation health through NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) analysis, providing crucial data on the extent of crop damage across large areas.
The flooding’s impact on agriculture extends beyond immediate crop losses. Soil erosion, contamination of water sources, and damage to agricultural infrastructure will likely have long-term effects on the region’s farming capabilities. This disaster underscores the need for resilient agricultural practices and advanced monitoring systems to mitigate future risks.
Infrastructure Challenges: Power Outages and Transportation Disruptions
“Thousands faced power outages due to the Texas-Mexico border region floods, causing significant agricultural and economic losses.”
The floods have severely strained the region’s infrastructure. Thousands of residents have been left without power, complicating rescue efforts and hampering the recovery process. Major transportation arteries have been rendered impassable, with many roads submerged and bridges damaged.
Valley International Airport in Harlingen was forced to close, canceling all flights and further isolating the affected areas. This disruption to transportation networks not only hampers emergency response but also poses significant challenges for the movement of goods and services, potentially leading to economic repercussions beyond the immediate flood zone.
Cross-Border Impact: A Shared Crisis
The flooding crisis is not confined to the U.S. side of the border. In Mexico’s Tamaulipas state, particularly in cities like Reynosa, Rio Bravo, and parts of Matamoros, severe flooding has also occurred. This cross-border nature of the disaster highlights the interconnectedness of the region and the need for coordinated response efforts.
Mexican authorities have reported that between 7 and 12 inches (20 and 31 centimeters) of rain fell in parts of northeastern Mexico. The deployment of 640 military personnel in the area underscores the severity of the situation and the mobilization of resources to address the crisis.
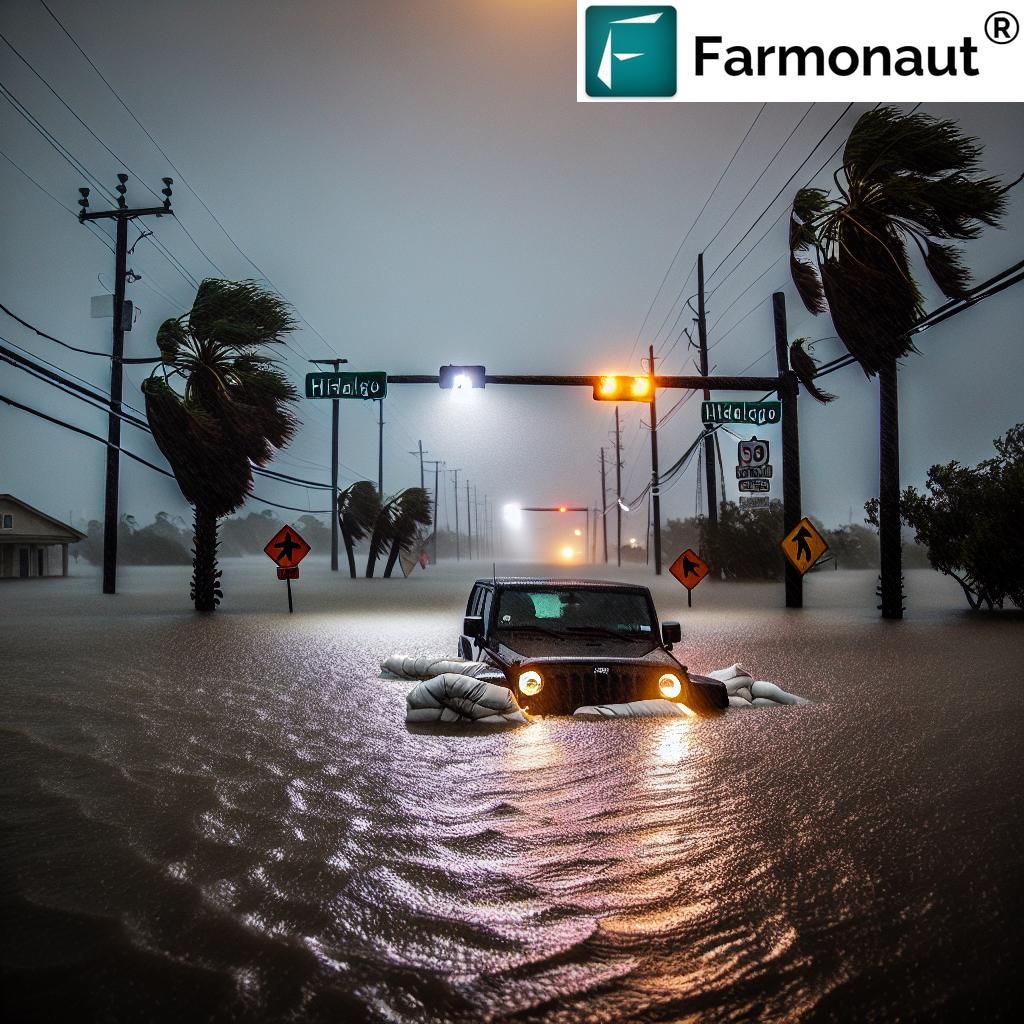

Emergency Response and Community Resilience
In the face of this disaster, we’ve witnessed remarkable efforts from emergency services, local authorities, and community members. Water rescues have been ongoing, with first responders working tirelessly to reach those stranded in flooded homes and vehicles.
The closure of schools and businesses across more than 20 districts demonstrates the widespread impact of the flooding and the prioritization of safety. As the immediate rescue phase transitions into recovery, the focus will shift to assessing damage, providing shelter and support to displaced residents, and beginning the long process of rebuilding.
Assessing the Economic Impact
The economic ramifications of this flooding event are expected to be substantial. Beyond the immediate losses in agriculture and property damage, the long-term effects on local businesses, tourism, and regional trade could be significant.
For a detailed analysis of the economic impact, particularly in agriculture, tools like Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance solutions can play a crucial role. These satellite-based verification systems can help streamline the process of assessing damage for insurance claims and loan applications, potentially speeding up the recovery process for affected farmers.
Environmental Concerns and Future Preparedness
This catastrophic event raises important questions about environmental management and disaster preparedness in the region. The intensity of the rainfall and the extent of the flooding point to the potential impacts of climate change on weather patterns in the area.
Moving forward, there will likely be increased focus on sustainable water management strategies, improved flood control infrastructure, and the development of more robust early warning systems. Technologies like Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools can help agribusinesses and local authorities monitor and reduce their environmental impact, contributing to more sustainable practices in the long term.
Texas Border Floods Impact Assessment
| Affected Area | Rainfall Amount (inches) | Agricultural Damage (est. acres) | Economic Loss (est. USD) | Rescues Conducted | Power Outages | Fatalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hidalgo County | 21+ | 50,000 | $100 million | 200+ | 10,000 | 3 |
| Cameron County (Harlingen) | 14+ | 30,000 | $75 million | 150+ | 5,000 | 1 |
| Tamaulipas State (Mexico) | 7-12 | 25,000 | $50 million | 100+ | 8,000 | 1 |
Note: These figures are estimates based on initial reports and are subject to change as more information becomes available.
The Role of Technology in Disaster Management and Recovery
In the face of such devastating natural disasters, technology plays an increasingly crucial role in both management and recovery efforts. Advanced satellite imagery and data analysis tools, like those provided by Farmonaut, can offer invaluable insights for disaster response teams, agricultural experts, and policymakers.
Farmonaut’s fleet management solutions, for instance, could be instrumental in coordinating rescue efforts and managing the distribution of aid. By optimizing vehicle usage and ensuring safety, these tools can enhance the efficiency of disaster response operations.
Furthermore, the ability to access real-time weather data and forecasts through platforms like Farmonaut can aid in predicting and preparing for future extreme weather events. This proactive approach to disaster management could potentially save lives and mitigate economic losses in the future.
Community Support and Recovery Efforts
As the floodwaters recede, the focus shifts to recovery and rebuilding. Community support networks, both formal and informal, are mobilizing to provide assistance to those affected. Local shelters are accommodating displaced residents, while volunteer organizations are coordinating relief efforts.
The recovery process will be long and challenging, requiring sustained effort and resources. It will involve not only rebuilding physical infrastructure but also supporting the emotional and economic recovery of affected communities. In this context, tools that can expedite the assessment and recovery process, such as satellite-based damage evaluation, will be invaluable.
Looking Ahead: Building Resilience in the Face of Climate Change
The Texas border floods serve as a stark reminder of the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events associated with climate change. As we move forward, it’s crucial to not only address the immediate aftermath of this disaster but also to implement long-term strategies for building resilience in vulnerable regions.
This may involve:
- Upgrading infrastructure to better withstand extreme weather events
- Implementing more robust early warning systems
- Developing comprehensive disaster response plans
- Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices that improve soil health and water retention
- Investing in technologies that provide real-time monitoring and data analysis for better decision-making
Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory services can play a significant role in this context, helping farmers and land managers make informed decisions that enhance resilience to climate-related challenges.
Conclusion: A Call for Unified Action
The devastating floods in the Texas-Mexico border region have brought immense challenges, but they have also highlighted the resilience and solidarity of border communities. As we move forward, it’s clear that addressing the impacts of such extreme weather events requires a coordinated, cross-border approach.
By leveraging advanced technologies, implementing sustainable practices, and fostering community resilience, we can work towards mitigating the impacts of future disasters. The road to recovery will be long, but with concerted effort and innovative solutions, the Rio Grande Valley and its neighboring regions can emerge stronger and more prepared for the challenges ahead.
FAQs
- What caused the severe flooding in the Texas-Mexico border region?
The flooding was caused by record-breaking rainfall, with some areas receiving over 21 inches of rain in a short period. - How many fatalities have been reported due to the floods?
At least four fatalities have been reported, including drownings. - What is the extent of agricultural damage in the Rio Grande Valley?
While exact figures are still being assessed, significant losses to crops and livestock have been reported across the region. - How are emergency services responding to the crisis?
Emergency services have been conducting numerous water rescues and evacuations, with hundreds of people rescued from flooded homes and vehicles. - What is the cross-border impact of this flooding event?
The floods have affected both sides of the border, with Mexico’s Tamaulipas state also experiencing severe flooding and deploying military personnel for assistance.
For more information on how satellite technology can aid in disaster management and agricultural resilience, visit Farmonaut’s web application.
For mobile users:
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!