Urea Prices 2025: Powerful Global Market Dynamics Explained
Meta Description: Urea fertilizer prices are shaped by raw material costs, global demand, regulations, and innovation. Uncover the 2025 market dynamics, environmental impact, and sustainable alternatives.
“Global urea prices surged by over 70% in 2022, driven by supply chain disruptions and rising energy costs.”
Introduction: Urea’s Role in Modern Agriculture
As we navigate the evolving landscape of global agriculture, urea stands out as an indispensable ingredient for modern farming. This nitrogen-rich compound is renowned for boosting crop yields and enhancing soil fertility, cementing its position as the world’s most widely used nitrogen fertilizer. The affordability and effectiveness of urea have made it a cornerstone for not just crop production but also food security for billions across continents.
Yet, the seemingly straightforward urea pricing is subject to a web of interdependent factors affecting urea pricing — from raw material costs and energy price fluctuations to global supply chain disruptions, shifting environmental regulations, and rapid technological advancements in fertilizer management. For stakeholders in agriculture, farming, and forestry, understanding these global market dynamics is crucial for staying resilient and sustainable in a volatile landscape.
This comprehensive guide will dissect the urea fertilizer prices for 2025, exploring the environmental, economic, and technological trends driving shifts in the global urea market. Our analysis will uncover powerful market forces, regional variations, impactful innovations like precision agriculture fertilizer application, and the emergence of sustainable fertilizer alternatives—all aimed at empowering decision-makers for the season ahead.
Understanding Urea Prices: Key Global Market Dynamics
The pricing of urea, a global agricultural staple, does not exist in isolation. Rather, it is shaped by a complex interplay of market forces that span energy economics, geo-politics, policy frameworks, and technology adoption. Let’s decode the four principal factors affecting urea pricing as we head toward 2025.
Raw Material Costs and Urea Production Expenses
At the heart of urea manufacturing lies natural gas, which not only serves as a feedstock but also provides the energy for the conversion process. In fact, natural gas prices typically account for 60–80% of the total urea production costs.
- Each $1 per MMBtu rise in natural gas prices can increase urea factory costs by approximately $20–$30 per metric ton.
- During the 2022 energy crisis, European natural gas prices soared to $70/MMBtu, triggering widespread temporary shutdowns at urea plants, curtailing regional output by 18% and compelling increased imports from lower-cost regions.
- The cost structure of urea remains highly sensitive to fluctuations in bulk energy/feedstock markets, with ripple effects for wholesale and retail fertilizer prices globally. (Source)
In practice, this means that shocks in the natural gas market—be it due to geo-political dynamics, supply bottlenecks, or policy interventions—have an outsized impact on urea manufacturing expenses and, by extension, on farmer input costs.
Global Demand, Urea Supply Chain Disruptions, and Regional Markets
Global demand for urea tracks closely with agricultural production cycles, seasonal patterns, and global food commodity markets. In years marked by abundant planting or favorable weather, demand for nitrogen-based inputs like urea surges, leading to elevated fertilizer prices. In lean years, or when adverse weather limits planting, demand slumps, creating downward pressure on prices.
But supply chain disruptions—such as those stemming from geo-political conflicts, sanctions, or logistical bottlenecks—can have an even more abrupt effect:
- The 2022 Russia-Ukraine conflict exemplifies this risk. Russia, a powerhouse in global urea exports, faced trade restrictions and logistical upheaval, cutting off supplies to many markets and sending fertilizer prices higher. (Source)
- Localized events—plant outages, port closures, or extreme weather—can precipitate regional price spikes even without changes in global balances.
- Supply flexibility, storage infrastructure, and local production capacity determine how severely such disruptions hit farmers and end-users.
These dynamics result in marked regional variations in urea pricing—an effect further explored in our regional price comparison table below.
Environmental Regulations and Their Impact on Urea Market
Over the last decade, the environmental impact of urea use has risen to the forefront of policy discussions—most notably due to its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions such as nitrous oxide (N₂O). The agricultural sector is increasingly regulated to account for the carbon footprint of fertilizer application:
- Urea application can lead to significant releases of nitrogen emissions (e.g., N₂O), a greenhouse gas nearly 300 times more potent than CO2.
- Major markets are rolling out carbon accounting policies — the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) directly targets imported fertilizers with high embedded emissions, making urea production costs more sensitive to carbon intensity. (Source)
- Environmental regulation costs feed directly into urea manufacturing and market pricing, influencing everything from capital investments to input use strategies.
- Regions lagging on environmental controls will see regulatory risks rise, particularly as carbon trading systems gain traction globally.
Solutions that help monitor carbon impacts, such as Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tool, are becoming indispensable for both commercial agriculture and policy compliance.
“Precision agriculture can reduce urea fertilizer use by up to 30%, significantly impacting global market demand and pricing.”
Technological Advancements in Urea Fertilizer and Application
The introduction of advanced fertilizer technologies is reshaping the market dynamics for urea, aiming to improve agricultural urea efficiency, minimize environmental loss, and enable smarter cropping decisions.
- Slow-release and coated urea products control nitrogen availability, reducing volatilization and leaching losses, and making urea use more predictable—and acceptable to regulators.
- The adoption of precision agriculture techniques (e.g., GPS-guided tractors, remote sensing, AI-based crop analytics) optimizes fertilizer application, ensuring urea is used precisely where and when it’s needed.
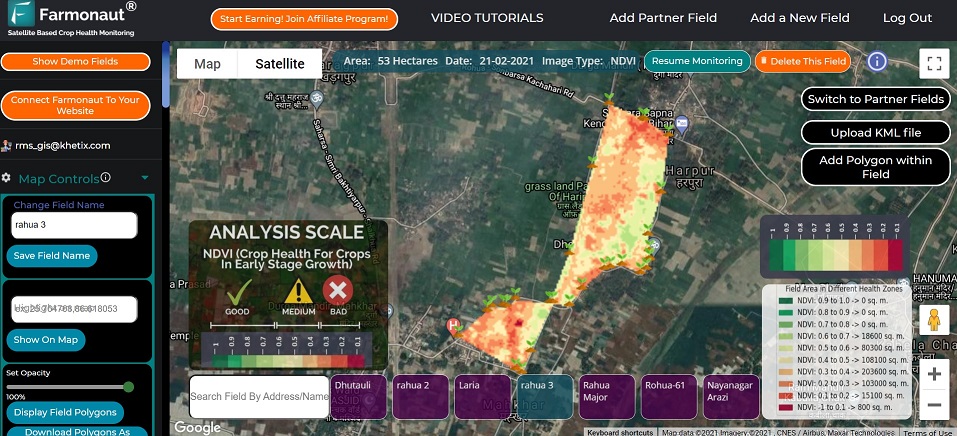
- Technologies like those delivered by Farmonaut’s platform (enabling real-time crop health monitoring, satellite-driven soil analysis, and AI advisory) allow agriculture professionals to make data-driven urea application decisions.
- This precision drives fertilizer cost savings for farmers, reduces urea losses, and lessens environmental impact, making modern farming more resilient and sustainable.
For developers and integrators, Farmonaut’s API and Developer Docs make it easy to embed satellite and weather data directly into third-party agricultural solutions—enabling precision fertilizer management at scale.
Recent Trends in Urea Fertilizer Prices (2024–2025)
The aggregated effect of supply/demand shocks, regulatory changes, and technological evolution is apparent in recent urea fertilizer prices. As we approach February 2025:
- UAN28 (a common nitrogen solution) saw its price rise by 8% month-on-month to an average of $350 per ton.
- Urea prices climbed by 6%, with the average price standing at $546 per ton globally. (Source)
- The upward price movement is attributed to higher energy costs, market demand fluctuations, and persistent supply chain disruptions—notably those stemming from major producers like Russia and the European region.
- Regulatory pressure in regions like the EU and the increasing adoption of advanced application techniques further contribute to market volatility.
These trends reinforce the need for robust precision agriculture systems and data-driven resource management—services that Farmonaut is making accessible, scalable, and affordable for farmers worldwide.
Estimated Urea Prices by Region (2022–2025) with Key Market Drivers
| Year | Region | Estimated Price (USD/tonne) | Key Market Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | North America | $720 | Energy cost spikes; supply chain disruptions; increased demand post-pandemic |
| 2022 | Europe | $840 | Natural gas crisis; regulatory changes (CBAM); plant shutdowns; imports necessity |
| 2022 | Asia-Pacific | $600 | Regional supply stability; exports from lower-cost producers; moderate regulatory pressure |
| 2022 | Latin America | $680 | Import dependency; global shipping delays; volatile demand |
| 2022 | Africa | $790 | Logistical constraints; import reliance; limited local production capacity |
| 2023 | North America | $670 | Stabilizing energy costs; improved logistics; sustained high demand |
| 2023 | Europe | $750 | Continued regulatory costs; partial plant reopening; moderate supply risk |
| 2023 | Asia-Pacific | $570 | Stable production; emerging precision agriculture adoption |
| 2023 | Latin America | $620 | Improved shipping; demand stabilization; technology uptake |
| 2023 | Africa | $740 | Continued logistical barriers; increasing digitization in agriculture |
| 2024 (Est.) | North America | $590 | Enhanced supply chains; lower energy prices; digital transformation |
| 2024 (Est.) | Europe | $670 | Increased CBAM effect; investments in carbon tracking; tech adoption |
| 2024 (Est.) | Asia-Pacific | $540 | Cost competitiveness; scaling precision tools; moderate regulation |
| 2024 (Est.) | Latin America | $565 | Tech-driven demand; alternative fertilizer uptake |
| 2024 (Est.) | Africa | $695 | Supply/demand volatility; pilot projects in farm management |
| 2025 (Proj.) | North America | $540 | Stable energy markets; precision ag mainstream; regulatory compliance |
| 2025 (Proj.) | Europe | $610 | Stringent CBAM enforcement; growth in carbon tracking; demand moderation |
| 2025 (Proj.) | Asia-Pacific | $510 | Rising efficiency; indigenous manufacturing; precision application leading |
| 2025 (Proj.) | Latin America | $530 | Supply chain improvements; sustainable practices; yield focus |
| 2025 (Proj.) | Africa | $670 | Regional supply constraints; adoption of digital ag platforms |
Notes: Prices represent market estimates for granular urea (per tonne). Key drivers include energy/gas price risk, market disruptions, environmental regulations, technology adoption, and logistics capacity.
Environmental and Economic Implications of Urea Use
The extensive use of urea in major agricultural economies, particularly in India and Asia-Pacific regions, has delivered unparalleled increases in crop yields and soil fertility. Urea consumption in India, for example, soared from 6.2 million metric tonnes (MMT) in 1980–81 to 35.7 MMT in 2022–23—more than a fivefold surge in just four decades.
- Correspondingly, the urea subsidy in India ballooned by nearly 340 times, from less than Rs. 5 billion to Rs. 1686.92 billion.
- This over-reliance, while boosting agricultural productivity, has generated environmental challenges—including water eutrophication, air pollution, soil degradation, and the emission of greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide.
- Strikingly, estimates indicate that up to two-thirds of urea applied is lost to the environment through volatilization, leaching, or runoff.
These issues underscore the critical need for more efficient and sustainable fertilizer application. Data-driven platforms like Farmonaut Large Scale Farm Management offer agribusinesses, cooperatives, and governments robust solutions for monitoring, optimizing, and reporting on the environmental footprint of fertilizer inputs.
Sustainable Fertilizer Alternatives and Precision Agriculture Practices
Facing mounting environmental and economic pressures, the global agriculture sector is investing heavily in sustainable fertilizer alternatives and the adoption of precision farming techniques. Here, we outline leading solutions for improving agricultural urea efficiency and reducing total input needs.
-
Protected Urea:
- Protected urea utilizes a urease inhibitor coating that reduces ammonia nitrogen losses by up to 78% and nitrous oxide losses by 71%.
- This technology allows for consistent yield performance while significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, offering flexibility in application from spring to autumn and promoting cost savings.
- (Learn more)
-
Nano Urea:
- Nano urea is a liquid fertilizer comprising nano-sized particles that improve nitrogen uptake efficiency and cut environmental loss rates.
- Adoption challenges remain in the form of higher costs and sometimes mixed field results, underlining the need for further R&D and field trials. Still, it’s a promising direction for sustainable fertilizer use.
- (Read more)
-
Precision Agriculture (PA):
- Through a mix of GPS-guided equipment, remote sensing, and data analytics, PA enables targeted fertilizer application — cutting total urea use by up to 30% and driving down costs.
- Products like Farmonaut’s Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory help farmers leverage AI and satellite data for in-season nutrient management, optimizing yield and minimizing environmental loss.
Supplementing these advancements, digital tools like Farmonaut’s Traceability Solution empower agribusinesses to transparently showcase sustainable practices across the supply chain—building trust and meeting traceability mandates for fertilizer sourcing.
Future Outlook: Nitrogen Fertilizer Market Trends 2025–2030
With world population (and thus food demand) on an upward curve, the global urea market is expected to register a healthy compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% between 2024 and 2030. This expansion is propelled mainly by:
- Growing need for higher crop yield and productivity to ensure food security
- Accelerating adoption of precision agriculture techniques and digital farm management platforms
- Continuous innovations in sustainable fertilizer alternatives and loss-reducing technologies
However, significant challenges loom—namely, increased regulatory scrutiny, competition from newer fertilizer products, and the ever-present specter of global supply chain volatility.
To stay competitive amid these changes, it is imperative for farming businesses, cooperatives, and policymakers to integrate real-time monitoring tools into their operational strategy—enabling adaptable, sustainable, and profitable agriculture for the years ahead.
For institutions needing advanced satellite monitoring, Farmonaut Crop Loan and Insurance Verification provides banks and insurers with satellite-based farm validation—helping ensure resource allocation and insurance claims are both data-driven and secure.
How Farmonaut Supports Efficient Urea Application and Sustainable Farming
As a pioneer in precision agriculture tools, Farmonaut is committed to democratizing access to advanced farm management and crop monitoring solutions —making these invaluable resources accessible and affordable across scales, from smallholder plots to vast corporate estates.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Our core platform leverages multispectral satellite imagery to visualize vegetation health, soil moisture, and nutrient needs at field and regional levels. This empowers optimized fertilizer application, reduced resource wastage, and increased yield.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory tool analyzes satellite, weather, and on-farm data—delivering personalized recommendations on urea and input use to maximize crop health while controlling total expenses.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Our tools enable efficient allocation and tracking of agricultural vehicles, further lowering input delivery costs through fleet optimization.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: For supply chain actors, Farmonaut’s solution ensures that every batch of produce, including those derived from sustainability-focused fertilizer regimes, is verifiably traced from field to end-consumer.
- API Integrations: Farmonaut’s robust API framework and developer documentation support seamless integration of satellite and weather intelligence for any custom farming or research platform.
To make precision agriculture affordable, our services are offered through cost-effective subscription models—available via web, Android, iOS, or direct API integration.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Whether you’re a progressive farmer, a research institution, an agribusiness, or a government agency, Farmonaut has a flexible, affordable plan to help unlock the potential of data-driven agriculture in your operations.
For custom, large-scale farm, plantation, or forest advice, visit our Crop, Plantation & Forest Advisory page.
Need powerful supply chain transparency? See our traceability solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What determines urea fertilizer prices globally?
Urea prices are primarily influenced by natural gas costs, global supply and demand, environmental regulations, and the adoption of advanced production technologies. Regional factors such as logistics, subsidies, and geopolitical disruptions also play significant roles.
Q2: How does precision agriculture help in reducing fertilizer costs?
Precision agriculture uses satellite data, GPS, AI, and analytics to optimize fertilizer use—matching application to exact crop needs. This can lower urea use by ~30%, minimizing waste, reducing costs, and improving yields.
Q3: What is the environmental impact of urea, and how can it be reduced?
Urea use can result in greenhouse gas (nitrous oxide) emissions, soil/water pollution, and nitrogen losses. These impacts can be mitigated through protected urea, nano urea, precision application, and digital monitoring (e.g., with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting).
Q4: What are the major trends expected in the global urea market through 2025?
Key trends are tighter environmental regulations (e.g., EU CBAM), unstable energy prices, rise of data-driven fertilizer management, and an industry-wide movement toward sustainable practices and alternative fertilizers.
Q5: How do I access Farmonaut’s precision agriculture services?
You can use Farmonaut via Web App, Android, or iOS platforms. For large or custom projects, see Agro Admin or contact us for API integration details.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for the Urea Market in 2025
The urea market in 2025 is shaped by powerful, interlocking global forces. Raw material costs, especially natural gas, remain the single largest driver of urea production costs. Supply chain disruptions, regulations around carbon and environmental impact, and technical breakthroughs in fertilizer efficiency add further complexity to the global pricing picture.
As stakeholders in agriculture, forestry, and food production, it’s clear that adaptation requires embracing data-driven, precision practices—not only to stabilize input costs, but to drive sustainable yield growth and meet environmental imperatives. Farmonaut is dedicated to delivering the tools, insights, and platforms that enable such transformation—making innovative precision agriculture cost-effective and accessible worldwide.
Stay ahead in the evolving global urea market by prioritizing efficiency, sustainability, and innovation in every field, for every crop, and at every scale.
For updated market reports, sustainability insights, and advanced farm management solutions,
keep following the Farmonaut blog.