Revolutionizing Ethiopian Agriculture: How Modern Farming Techniques Boost Crop Yields and Food Security
“Ethiopia cultivates 20.5 million hectares, with 11.8 million using advanced farming methods, revolutionizing its agricultural sector.”
Welcome to an exciting journey through Ethiopia’s agricultural revolution! In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll explore how modern farming techniques are transforming the landscape of Ethiopian agriculture, boosting crop yields, and enhancing food security across the nation. As we delve into this fascinating topic, we’ll uncover the innovative approaches and technologies that are driving this remarkable change.
The Dawn of a New Agricultural Era in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, a country with a rich agricultural heritage, is experiencing a profound transformation in its farming sector. The Ethiopian government has implemented extensive reforms aimed at revitalizing and modernizing agriculture, recognizing its pivotal role in the nation’s economy and food security. These efforts have culminated in what is expected to be the highest agricultural yield in Ethiopia’s history.
Let’s explore the key factors contributing to this agricultural renaissance:
- Implementation of modern farming practices
- Adoption of mechanized techniques
- Efficient water resource management
- Timely distribution of agricultural inputs
- Favorable weather conditions
As we journey through this blog, we’ll examine each of these elements in detail, showcasing how they intertwine to create a robust and productive agricultural sector.
The Scale of Ethiopia’s Agricultural Transformation
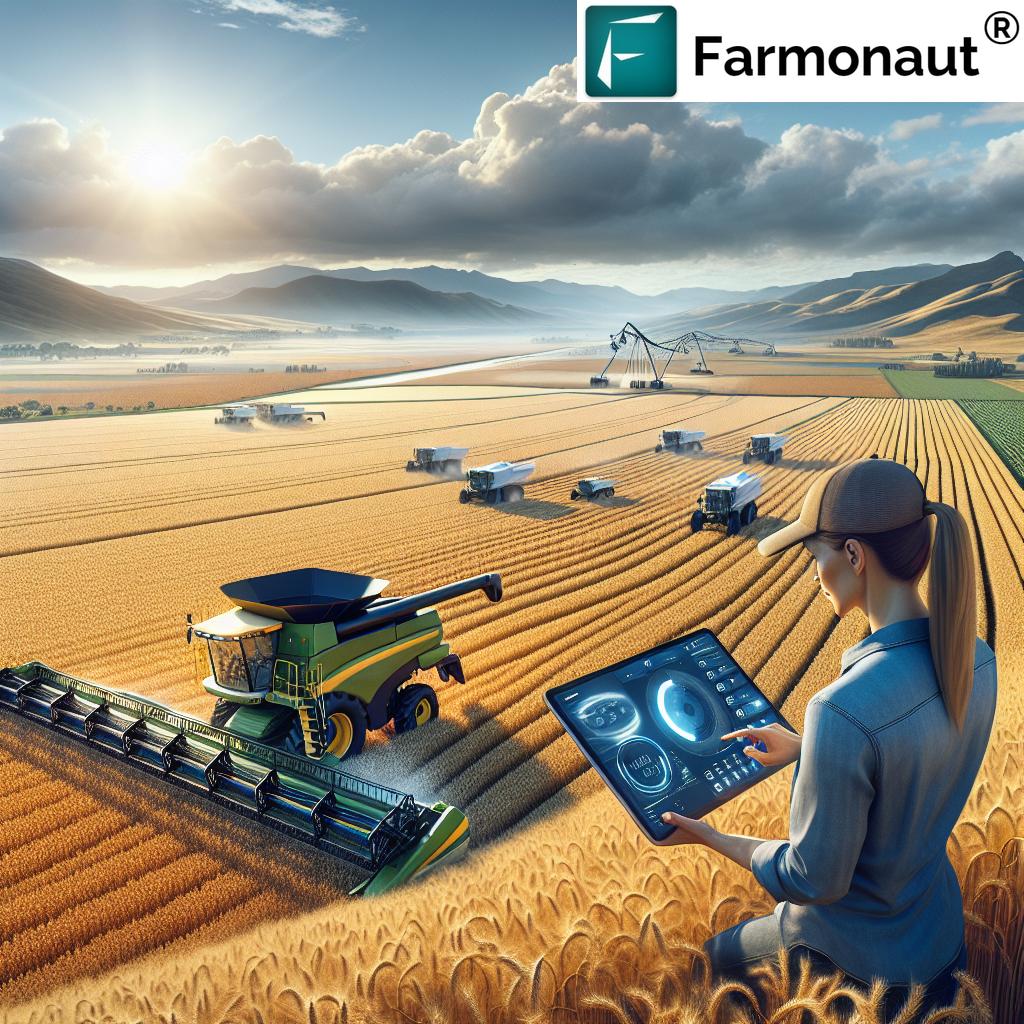
The sheer scale of Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation is truly impressive. Recent statistics reveal that the country has cultivated an unprecedented 20.5 million hectares of land with crops. Even more remarkable is that 11.8 million hectares of this land are being cultivated using modern, mechanized farming methods. This shift from traditional practices to advanced techniques underscores a substantial transformation in the agricultural landscape.

This modernization is particularly evident in arid and bordering areas, where mechanized farming is becoming increasingly prevalent. The adoption of these advanced techniques is not just a quantitative achievement but also a qualitative one, showcasing the effectiveness of modern agricultural approaches being adopted throughout the nation.
Modern Farming Practices: The Cornerstone of Ethiopia’s Agricultural Success
At the heart of Ethiopia’s agricultural revolution lies the widespread adoption of modern farming practices. These innovative techniques have dramatically improved crop productivity and resource efficiency. Let’s explore some of the key modern farming practices that are making a difference:
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is revolutionizing farming in Ethiopia by allowing farmers to optimize their resources and maximize yields. This approach uses technology to make farming more accurate and controlled. Key aspects of precision agriculture include:
- GPS-guided tractors for precise planting and harvesting
- Variable rate technology for optimized fertilizer and pesticide application
- Soil mapping for targeted nutrient management
These technologies enable farmers to treat their fields with extraordinary precision, leading to improved crop yields and reduced resource waste.
Conservation Agriculture
Conservation agriculture is another modern practice gaining traction in Ethiopia. This approach focuses on preserving soil health and biodiversity while maintaining high productivity. Key principles include:
- Minimal soil disturbance (no-till or reduced tillage)
- Permanent soil cover (use of cover crops)
- Crop rotation to enhance soil fertility
By adopting these practices, Ethiopian farmers are not only increasing their yields but also ensuring the long-term sustainability of their land.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that minimizes the use of chemical pesticides. This modern farming technique involves:
- Regular monitoring of crops for pests and diseases
- Use of biological control methods (e.g., beneficial insects)
- Targeted application of pesticides only when necessary
IPM has helped Ethiopian farmers reduce crop losses while minimizing environmental impact and production costs.
Mechanization: Powering Ethiopia’s Agricultural Growth
Mechanization has been a game-changer for Ethiopian agriculture. The introduction of modern farm machinery has significantly increased efficiency and productivity across various farming operations. Let’s look at how mechanization is transforming different aspects of farming:
Land Preparation
Modern tractors and tillage equipment have revolutionized land preparation in Ethiopia. These machines can prepare large areas of land quickly and efficiently, allowing farmers to:
- Cultivate more land in less time
- Achieve better soil structure for planting
- Reduce labor requirements and physical strain on farmers
Planting and Seeding
Mechanized planters and seeders have greatly improved the precision and speed of planting operations. Benefits include:
- Uniform seed spacing and depth for optimal plant growth
- Reduced seed waste
- Faster planting, allowing farmers to take advantage of optimal planting windows
Harvesting
The introduction of combine harvesters and other harvesting machinery has transformed the harvesting process. These machines offer:
- Faster harvesting, reducing crop losses due to weather or pests
- Improved grain quality through timely harvesting
- Reduced post-harvest losses
The impact of mechanization is particularly evident in Ethiopia’s wheat production. The country has emerged as Africa’s leading wheat producer, a historic development that signifies a new chapter in the nation’s agricultural journey.
Water Resource Management: Sustaining Ethiopia’s Agricultural Revolution
Efficient water resource management is crucial for maintaining high agricultural productivity, especially in a country like Ethiopia with diverse climatic conditions. The government and farmers are implementing various strategies to optimize water use:
Irrigation Systems
Modern irrigation systems are being deployed across Ethiopia to ensure reliable water supply for crops. These include:
- Drip irrigation for water-efficient crop watering
- Sprinkler systems for even water distribution
- Canal networks for large-scale water distribution
Water Harvesting Techniques
To make the most of available water resources, Ethiopia is implementing various water harvesting techniques:
- Construction of small dams and reservoirs
- Rainwater harvesting systems
- Contour bunding to capture and retain rainwater
Soil Moisture Conservation
Techniques to conserve soil moisture are being widely adopted, including:
- Mulching to reduce evaporation
- Terracing on sloped land to prevent water runoff
- Use of drought-resistant crop varieties
These water management strategies are crucial as Ethiopia prepares for future rainy seasons, ensuring that the country can maintain its agricultural productivity even in the face of climate variability.
Agricultural Input Distribution: Fueling Growth
The efficient distribution of agricultural inputs has played a significant role in Ethiopia’s agricultural success. The government and private sector have worked together to ensure farmers have timely access to essential inputs:
Improved Seeds
Access to high-quality, improved seeds has been crucial for increasing crop yields. Efforts in this area include:
- Development and distribution of high-yielding crop varieties
- Establishment of seed multiplication centers
- Promotion of drought-resistant and disease-tolerant varieties
Fertilizers
Efficient fertilizer distribution has helped farmers optimize their crop nutrition. Key initiatives include:
- Subsidies to make fertilizers more affordable
- Establishment of distribution networks to reach remote areas
- Training on proper fertilizer application techniques
Crop Protection Products
Timely access to pesticides and herbicides has helped farmers protect their crops from pests and diseases. Efforts in this area include:
- Regulation of crop protection products to ensure safety and efficacy
- Training on integrated pest management techniques
- Establishment of early warning systems for pest outbreaks
“Ethiopia’s agricultural modernization has propelled it to become Africa’s leading wheat producer, boosting food security across the region.”
The Role of Technology in Ethiopian Agriculture
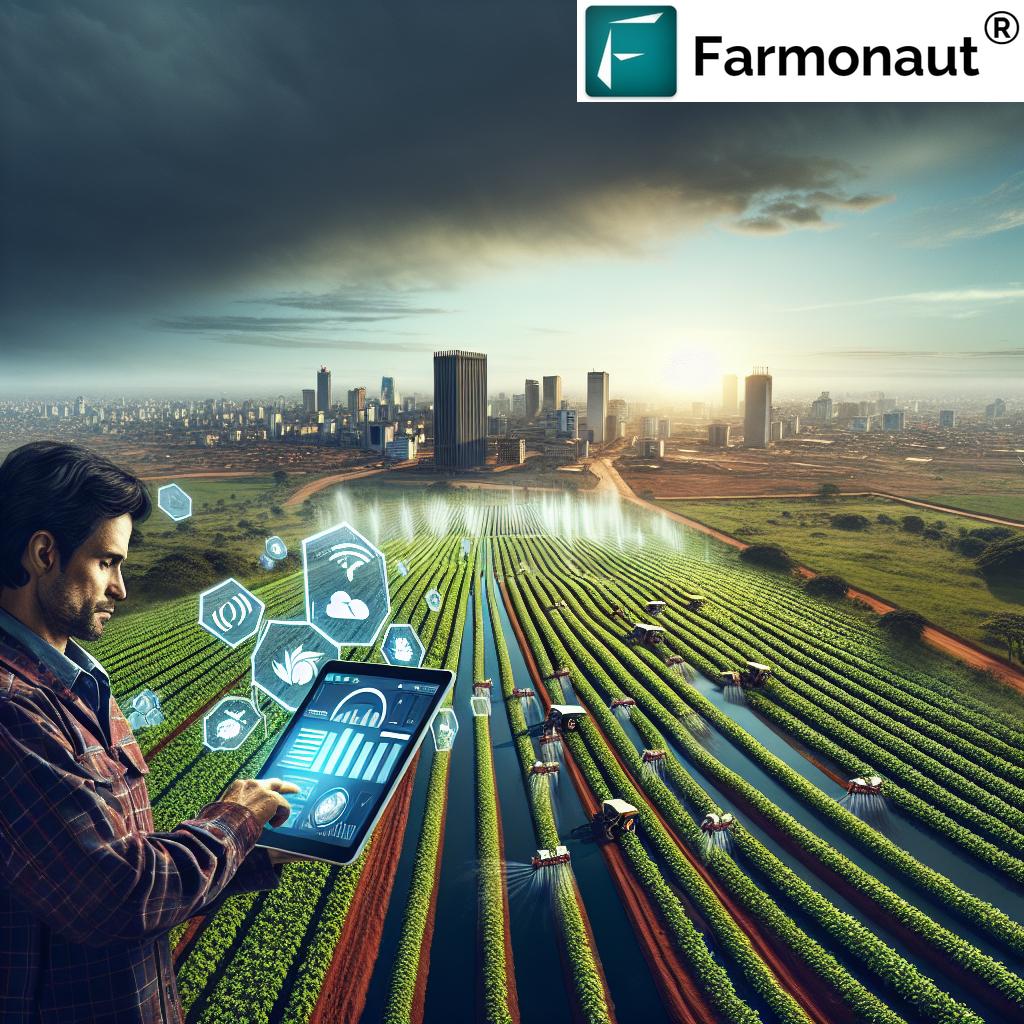
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation. From satellite-based monitoring to mobile apps, various technological solutions are helping farmers make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring
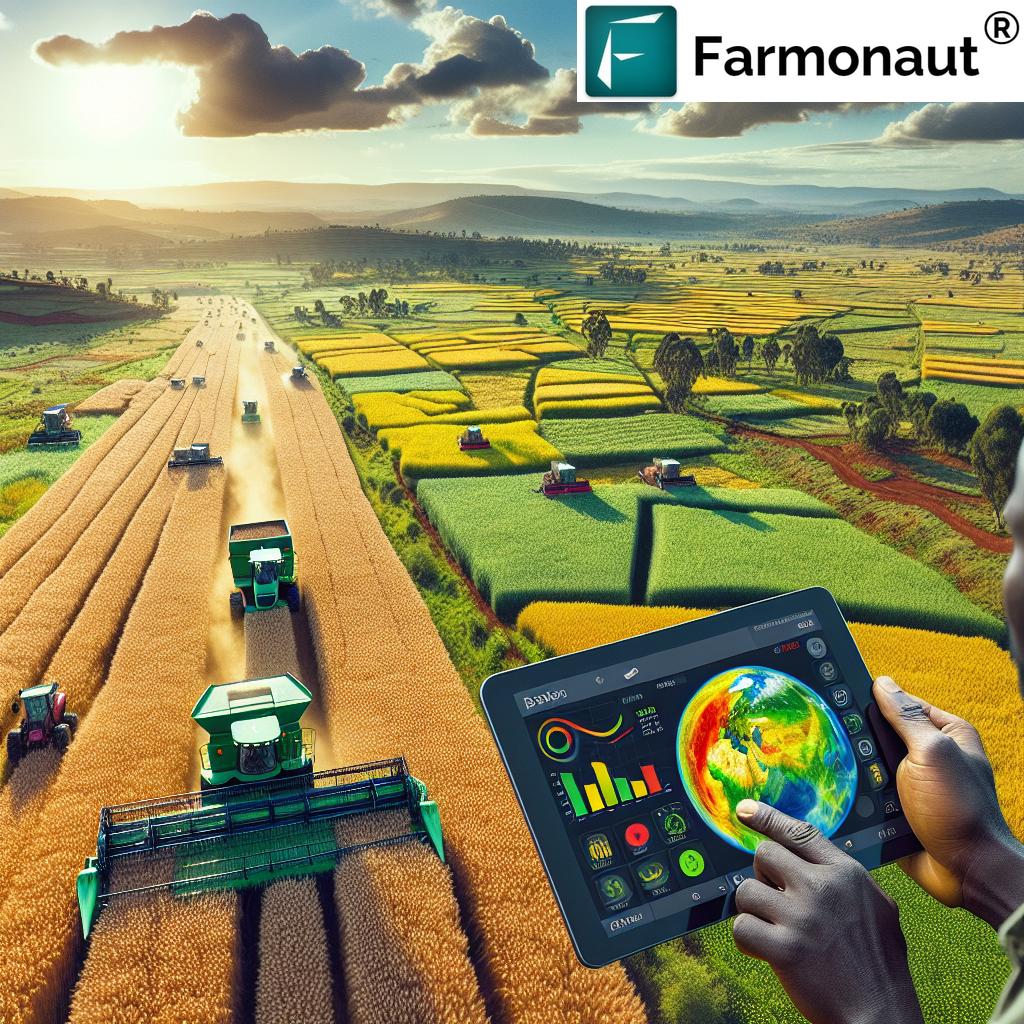
Satellite technology is revolutionizing crop monitoring in Ethiopia. Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this innovation, offering advanced satellite-based farm management solutions. These technologies provide:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- Early detection of crop stress and diseases
- Yield prediction and optimization
Farmers can access this valuable information through user-friendly mobile and web applications, enabling them to make data-driven decisions about their crops.

Weather Forecasting and Climate Information Services
Access to accurate weather forecasts and climate information is crucial for farmers. Technology is enabling:
- Localized weather forecasts
- Seasonal climate outlooks
- Early warning systems for extreme weather events
This information helps farmers plan their activities, from planting to harvesting, more effectively.
Mobile Agriculture Services
Mobile technology is bringing agricultural information and services directly to farmers’ fingertips. These services include:
- Market price information
- Agricultural advisory services
- Mobile banking and insurance services
By leveraging mobile technology, even smallholder farmers in remote areas can access crucial information and services.
Download Farmonaut’s Android App


The Impact of Modern Farming Techniques on Crop Yields
The adoption of modern farming techniques has had a profound impact on crop yields in Ethiopia. Let’s look at some of the key improvements:
Wheat Production
Ethiopia’s emergence as Africa’s leading wheat producer is a testament to the success of its agricultural modernization efforts. Factors contributing to increased wheat yields include:
- Introduction of high-yielding wheat varieties
- Improved crop management practices
- Expansion of irrigated wheat production
Maize and Teff
Significant yield improvements have also been observed in other staple crops like maize and teff. Modern techniques have helped:
- Increase resistance to pests and diseases
- Improve drought tolerance
- Enhance nutrient use efficiency
Horticulture
The horticulture sector has also benefited from modern farming techniques, with increased production of fruits and vegetables. Key improvements include:
- Greenhouse technology for year-round production
- Improved post-harvest handling and storage
- Adoption of organic farming practices for high-value crops
Enhancing Food Security Through Agricultural Modernization
The modernization of Ethiopian agriculture has significantly contributed to enhancing food security in the country and the region. Here’s how:
Increased Domestic Food Production
By boosting crop yields and expanding cultivated areas, Ethiopia has greatly increased its domestic food production. This has resulted in:
- Reduced dependence on food imports
- Improved availability of staple foods
- Stabilization of food prices
Diversification of Food Sources
Modern farming techniques have enabled the diversification of food sources, contributing to better nutrition. This includes:
- Increased production of nutrient-rich fruits and vegetables
- Introduction of new crop varieties
- Promotion of integrated farming systems (crops and livestock)
Improved Resilience to Climate Shocks
The adoption of modern farming practices has improved the resilience of Ethiopia’s agricultural sector to climate shocks. This is achieved through:
- Use of drought-tolerant crop varieties
- Implementation of soil and water conservation practices
- Diversification of farming systems
The Role of Farmonaut in Ethiopia’s Agricultural Transformation
As Ethiopia continues its journey of agricultural modernization, technology companies like Farmonaut are playing a crucial role. Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring technology complements the country’s efforts by offering farmers real-time insights for improved decision-making.
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Farmonaut’s platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing Ethiopian farmers with valuable insights into:
- Vegetation health (NDVI)
- Soil moisture levels
- Early detection of crop stress and diseases
This data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, ultimately optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
AI-Powered Advisory System
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI advisory system delivers personalized farm advice to Ethiopian farmers. This system:
- Provides real-time insights and weather forecasts
- Offers expert crop management strategies
- Helps improve farm productivity and efficiency
Resource Management Tools
For larger agricultural operations in Ethiopia, Farmonaut offers tools for efficient resource management, including:
- Fleet management for agricultural machinery
- Carbon footprint tracking for sustainable farming
- Blockchain-based traceability for supply chain transparency
These tools can help Ethiopian agribusinesses optimize their operations and contribute to more sustainable farming practices.
Comparison of Traditional vs. Modern Agricultural Practices in Ethiopia
| Agricultural Aspect | Traditional Methods | Modern Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Land Cultivation | Manual labor, ox-drawn plows | Mechanized farming (tractors, advanced implements) |
| Crop Yield | Lower yields due to limited inputs and techniques | Higher yields through improved varieties and practices |
| Water Management | Reliance on rainfall, basic irrigation | Advanced irrigation systems, water harvesting techniques |
| Input Distribution | Limited access to quality seeds and fertilizers | Efficient distribution of improved seeds and fertilizers |
| Technology Adoption | Minimal use of technology | Satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory systems, mobile apps |
Challenges and Future Prospects
While Ethiopia has made significant strides in modernizing its agriculture sector, challenges remain. Addressing these will be crucial for sustaining and expanding the gains made so far.
Challenges
- Ensuring equitable access to modern farming technologies for smallholder farmers
- Balancing mechanization with employment in the agricultural sector
- Adapting to climate change and increasing frequency of extreme weather events
- Maintaining soil health and biodiversity in the face of intensified agriculture
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, Ethiopia’s agricultural sector has promising prospects:
- Further integration of digital technologies in farming
- Expansion of sustainable and climate-smart agricultural practices
- Development of value-added agricultural products for export markets
- Continued research and development of improved crop varieties
Conclusion
Ethiopia’s journey in revolutionizing its agricultural sector through modern farming techniques is a testament to the power of innovation and strategic planning. From the adoption of mechanized farming to the implementation of advanced water management techniques, the country has made remarkable progress in boosting crop yields and enhancing food security.
The integration of technologies like satellite-based crop monitoring, offered by companies like Farmonaut, further exemplifies Ethiopia’s commitment to embracing cutting-edge solutions in agriculture. As the country continues to build on these successes, it not only secures its own food future but also sets an inspiring example for agricultural development across Africa.
The transformation of Ethiopian agriculture demonstrates that with the right mix of policy support, technological adoption, and farmer engagement, significant improvements in agricultural productivity and sustainability are achievable. As Ethiopia looks to the future, the continued focus on modernizing agriculture promises to yield even greater benefits for farmers, the economy, and food security in the years to come.
FAQs
- How has mechanization improved Ethiopian agriculture?
Mechanization has significantly increased efficiency in land preparation, planting, and harvesting, allowing farmers to cultivate larger areas and improve crop yields. - What role does satellite technology play in Ethiopian farming?
Satellite technology, such as that provided by Farmonaut, offers real-time crop health monitoring, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest management. - How has Ethiopia become Africa’s leading wheat producer?
Through the adoption of high-yielding wheat varieties, improved crop management practices, and expansion of irrigated wheat production. - What are some challenges facing Ethiopia’s agricultural modernization?
Key challenges include ensuring equitable access to modern farming technologies for smallholder farmers, balancing mechanization with employment, and adapting to climate change. - How is Ethiopia addressing water management in agriculture?
Ethiopia is implementing modern irrigation systems, water harvesting techniques, and soil moisture conservation practices to optimize water use in agriculture.