Breakthrough in Sydney: First Patient Discharged with Total Artificial Heart – A Cardiac Innovation Milestone
“A patient in Sydney survived over 100 days with a titanium artificial heart before receiving a successful transplant.”
In a groundbreaking development that has sent ripples through the medical community, Sydney, Australia, has become the epicenter of a cardiac innovation milestone. We are thrilled to report on this extraordinary advancement in artificial heart technology that has transformed cardiac care and offers new hope to patients suffering from severe heart failure.
The Landmark Procedure: A Glimpse into the Future of Cardiac Care
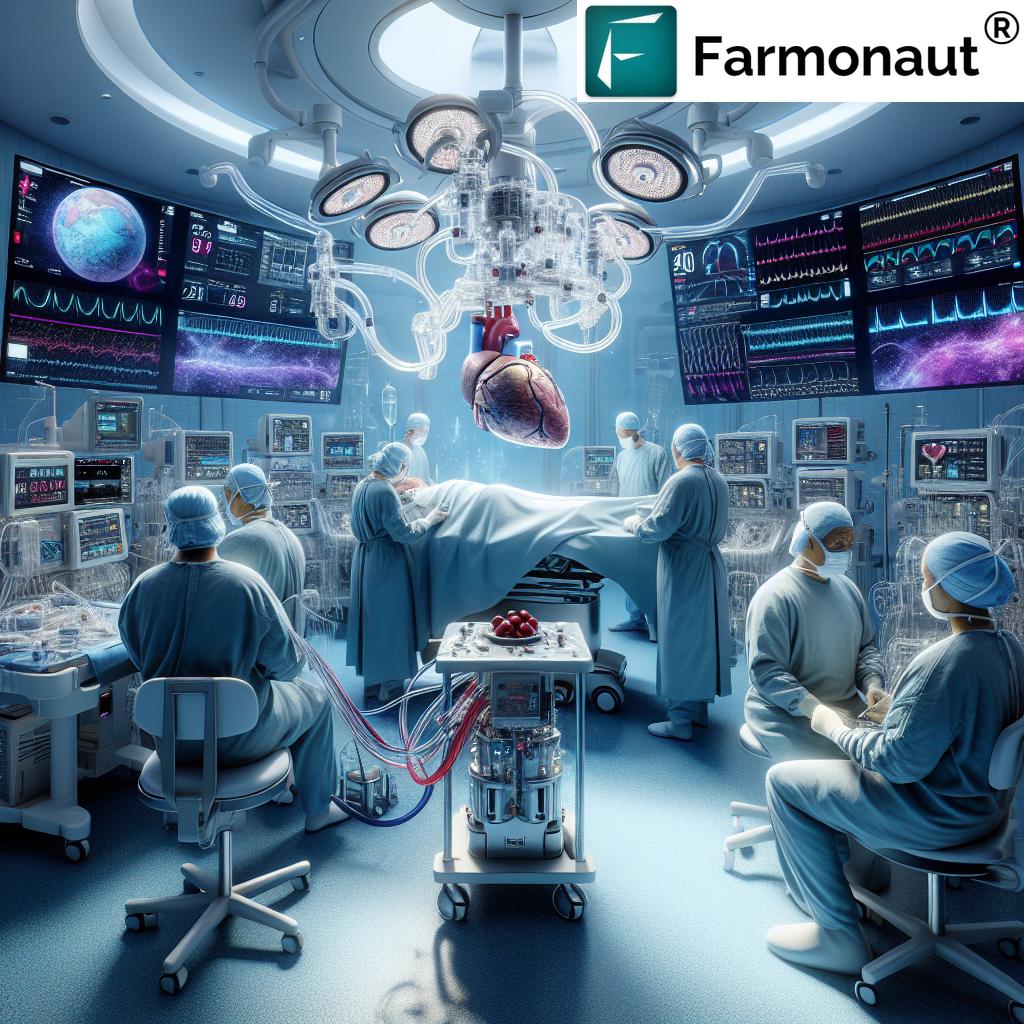
At the heart of this medical breakthrough is a remarkable story of innovation, perseverance, and human triumph. A man in his forties, battling severe heart failure, has become the first patient to be discharged from a hospital with a fully functional total artificial heart. This groundbreaking achievement took place at Sydney’s St Vincent’s Hospital, marking a significant leap forward in the treatment of heart failure and the development of mechanical heart devices.
The patient was fitted with the BiVACOR Total Artificial Heart (TAH), an innovative blood pump implant made of titanium. This artificial heart transplant not only sustained the patient’s life for over 100 days but also paved the way for a successful heart transplant in March. The implications of this cardiac innovation are far-reaching, potentially revolutionizing the field of cardiothoracic surgery and offering new hope to countless individuals suffering from end-stage heart failure.
The BiVACOR Total Artificial Heart: A Marvel of Modern Engineering
The BiVACOR TAH represents a quantum leap in artificial heart technology. This mechanical heart device utilizes magnetic levitation technology, the same principle employed in high-speed trains, to pump blood through both pulmonary and systemic circulations. This innovative approach allows for a more efficient and durable artificial heart, capable of providing sufficient cardiac output even during exercise.
“The innovative artificial heart implant uses magnetic levitation technology, similar to high-speed trains, for blood circulation.”
Key features of the BiVACOR TAH include:
- Titanium construction for durability and biocompatibility
- Magnetic levitation technology for reduced wear and tear
- Ability to adjust blood flow based on the patient’s activity level
- Compact design suitable for most men and women
- Potential for long-term use, possibly eliminating the need for transplants in some cases
This cardiac assist device represents a significant advancement over previous artificial heart designs, offering improved reliability and the potential for a better quality of life for patients awaiting heart transplants.
The Sydney Operation: A Milestone in Artificial Heart Surgery
The groundbreaking operation in Sydney marks a pivotal moment in the history of artificial heart surgery. Dr. Paul Jansz, the cardiothoracic and transplant surgeon who implanted the mechanical heart, described the device as a “complete game-changer.” The successful implantation and subsequent discharge of the patient with the BiVACOR TAH highlight the potential of this technology to transform the landscape of heart failure treatment.
The operation involved:
- Careful patient selection and preparation
- Precision implantation of the BiVACOR TAH
- Comprehensive post-operative care and monitoring
- Gradual rehabilitation and preparation for discharge
- Ongoing support and monitoring after discharge
This successful procedure in Sydney builds upon earlier trials conducted in the United States. Between July and November 2024, five patients received the BiVACOR device as part of an FDA Early Feasibility Study. However, the Sydney case marks the first time a patient was discharged from the hospital with the implant, representing a significant milestone in the device’s development and clinical application.
The Impact on Heart Failure Treatment
This breakthrough in artificial heart technology has profound implications for the treatment of heart failure. Heart failure affects millions of people worldwide, and for many, heart transplantation has been the only viable long-term solution. However, the scarcity of donor hearts and the complexities of transplant surgery have limited this option for many patients.
The development of a reliable, long-term artificial heart offers new hope for these patients. The BiVACOR TAH and similar devices could potentially:
- Serve as a bridge to transplantation, sustaining patients for longer periods while awaiting a donor heart
- Function as a destination therapy, providing a permanent solution for patients who are not candidates for transplantation
- Improve quality of life for patients with end-stage heart failure
- Reduce the burden on transplant waiting lists
- Advance our understanding of artificial organ technology
As we continue to refine and improve this technology, we may be moving closer to a future where artificial hearts can fully replace failing natural hearts, eliminating the need for transplants altogether.
The Role of Technology in Cardiac Innovation
The success of the BiVACOR TAH underscores the crucial role that technology plays in advancing medical care. This cardiac innovation leverages cutting-edge engineering principles to create a device that mimics the function of the human heart with unprecedented accuracy and reliability.
Key technological advancements that have made this breakthrough possible include:
- Magnetic levitation technology for blood pumping
- Advanced materials science for biocompatible components
- Miniaturization of power systems and control units
- Sophisticated software for real-time adjustment of blood flow
- Integration with external monitoring systems for continuous patient care
These technological innovations not only improve the function of the artificial heart but also enhance its durability and reduce the risk of complications, making it a more viable long-term solution for patients with heart failure.

The Journey from Hospital to Home: A New Chapter in Cardiac Care
The discharge of the Sydney patient with the BiVACOR TAH marks a significant milestone in cardiac care. It demonstrates that patients with artificial hearts can potentially lead relatively normal lives outside of the hospital setting. This achievement opens up new possibilities for long-term management of heart failure and could significantly improve the quality of life for patients awaiting heart transplants.
The journey from hospital to home for a patient with a total artificial heart involves:
- Extensive patient education on device management
- Training for family members or caregivers
- Regular follow-up appointments and remote monitoring
- Lifestyle adjustments to accommodate the device
- Ongoing psychological support and counseling
This successful discharge demonstrates the potential for artificial heart technology to provide a bridge to transplantation that extends beyond the confines of the hospital, allowing patients to maintain a semblance of normal life while awaiting a donor heart.
The Future of Artificial Heart Technology
The success of the BiVACOR TAH in Sydney is just the beginning of what promises to be an exciting new chapter in cardiac care. As we continue to refine and improve artificial heart technology, we can anticipate several developments on the horizon:
- Further miniaturization of devices for broader patient compatibility
- Enhanced battery life and wireless charging capabilities
- Integration with smart technology for real-time monitoring and adjustment
- Development of biocompatible materials that reduce the risk of complications
- Potential for 3D-printed custom artificial hearts tailored to individual patients
These advancements could lead to artificial hearts that not only sustain life but also provide a quality of life comparable to that of a healthy natural heart. The long-term goal is for patients to live with these devices indefinitely, potentially eliminating the need for heart transplants in many cases.
Milestones in Artificial Heart Technology
| Year | Milestone | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1957 | First artificial heart prototype | Dr. Willem Kolff and Dr. Tetsuzo Akutsu create the first artificial heart implanted in a dog |
| 1982 | First permanent artificial heart implant in a human | Barney Clark receives the Jarvik-7 artificial heart, surviving for 112 days |
| 2001 | First self-contained artificial heart | AbioCor artificial heart implanted, operating without external wires or tubes |
| 2025 | First discharge of a patient with a total artificial heart (Sydney case) | Patient with BiVACOR TAH discharged, marking a significant leap in artificial heart technology |
| 2030 (Projected) | Long-term artificial heart solution | Development of artificial hearts capable of sustaining patients for years without transplantation |
The Role of Clinical Trials and Research
The success of the BiVACOR TAH in Sydney is the result of years of rigorous research and clinical trials. The FDA Early Feasibility Study conducted in the United States played a crucial role in paving the way for this breakthrough. As we move forward, continued research and clinical trials will be essential to further refine and improve artificial heart technology.
Key areas of ongoing research include:
- Long-term outcomes of patients with total artificial hearts
- Optimization of device settings for different patient populations
- Development of novel materials to improve biocompatibility
- Integration of artificial intelligence for adaptive device function
- Exploration of regenerative medicine approaches to complement artificial heart technology
These research efforts will be crucial in addressing current limitations and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in artificial heart technology.
The Global Impact of the Sydney Breakthrough
The successful implantation and discharge of a patient with the BiVACOR TAH in Sydney has implications that extend far beyond Australia’s borders. This breakthrough has the potential to impact cardiac care worldwide, offering new hope to patients with heart failure across the globe.
The global impact of this innovation includes:
- Inspiring further research and development in artificial heart technology
- Encouraging international collaboration in cardiac care
- Potentially reducing healthcare costs associated with long-term hospitalization for heart failure patients
- Improving access to advanced cardiac care in regions with limited organ donation programs
- Advancing the field of bioengineering and medical technology as a whole
As news of this breakthrough spreads, we can anticipate increased investment in artificial heart research and a renewed focus on developing innovative solutions for heart failure treatment worldwide.
The Patient Experience: Living with an Artificial Heart
While the technical aspects of the BiVACOR TAH are impressive, it’s important to consider the human element of this breakthrough. For patients living with an artificial heart, the experience can be both challenging and liberating. The ability to return home and engage in daily activities represents a significant improvement in quality of life compared to long-term hospitalization.
Patients with artificial hearts may experience:
- Increased mobility and independence
- Improved energy levels and capacity for physical activity
- The psychological benefit of being in a home environment
- Challenges in adapting to the device and its maintenance requirements
- The need for ongoing medical support and monitoring
As we continue to refine artificial heart technology, addressing these patient experiences and improving overall quality of life will be crucial objectives.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Teams in Cardiac Innovation
The success of the BiVACOR TAH implantation in Sydney underscores the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration in advancing medical technology. This breakthrough is the result of cooperation between various specialists, including:
- Cardiothoracic surgeons
- Biomedical engineers
- Cardiologists
- Intensive care specialists
- Rehabilitation experts
- Psychologists and social workers
This collaborative approach ensures that all aspects of patient care are considered, from the technical details of the device to the psychological well-being of the patient. As we continue to push the boundaries of cardiac care, fostering these multidisciplinary partnerships will be crucial for future innovations.
Ethical Considerations in Artificial Heart Technology
As with any major medical advancement, the development and implementation of artificial heart technology raise important ethical considerations. Some of the key ethical issues include:
- Equitable access to this potentially life-saving technology
- The balance between extending life and ensuring quality of life
- Informed consent and decision-making for patients and families
- Resource allocation in healthcare systems
- Long-term psychological impacts on patients living with artificial hearts
Addressing these ethical considerations will be crucial as we continue to advance artificial heart technology and integrate it into mainstream cardiac care.
The Economic Impact of Artificial Heart Technology
The development and implementation of advanced artificial heart technology like the BiVACOR TAH have significant economic implications for healthcare systems worldwide. While the initial costs of these devices and the associated care can be substantial, they have the potential to reduce long-term healthcare costs by:
- Decreasing the length of hospital stays for heart failure patients
- Reducing the need for frequent hospitalizations
- Potentially lowering the demand for heart transplants
- Improving patient productivity and quality of life
- Stimulating innovation and job creation in the medical technology sector
As this technology becomes more widespread, it will be important to conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to understand its full economic impact on healthcare systems and society as a whole.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cardiac Care
The successful implantation and discharge of a patient with the BiVACOR TAH in Sydney represents a significant milestone in cardiac care, but it is just the beginning of a new era in heart failure treatment. As we look to the future, we can anticipate continued advancements in artificial heart technology, including:
- Further miniaturization and improved energy efficiency of devices
- Integration with regenerative medicine techniques
- Development of hybrid biological-mechanical heart solutions
- Improved remote monitoring and telemedicine capabilities
- Personalized artificial hearts tailored to individual patient needs
These advancements have the potential to transform the landscape of cardiac care, offering new hope to millions of people suffering from heart failure worldwide.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Cardiac Innovation
The breakthrough achieved in Sydney with the successful discharge of a patient fitted with the BiVACOR Total Artificial Heart marks a pivotal moment in the history of cardiac care. This achievement represents the culmination of years of research, innovation, and dedication from countless scientists, engineers, and medical professionals.
As we celebrate this milestone, we must also recognize that it is just the beginning of a new chapter in cardiac innovation. The potential of artificial heart technology to transform lives, reduce the burden of heart failure, and push the boundaries of what’s possible in medical science is truly exciting.
While challenges remain, including refining the technology, ensuring equitable access, and addressing ethical considerations, the future of cardiac care looks brighter than ever. The success in Sydney serves as an inspiration and a call to action for continued research, collaboration, and innovation in the field of artificial heart technology.
As we move forward, we can look forward to a future where advanced cardiac assist devices like the BiVACOR TAH offer new hope and improved quality of life for patients with heart failure around the world. This breakthrough is not just a triumph of technology, but a testament to the human spirit of innovation and the unwavering commitment to improving and saving lives.
FAQs
- What is a total artificial heart?
A total artificial heart is a device designed to replace the function of both ventricles of the natural heart. It pumps blood to both the lungs and the body, mimicking the action of a healthy heart. - How does the BiVACOR Total Artificial Heart work?
The BiVACOR TAH uses magnetic levitation technology to pump blood. This technology allows for a more efficient and durable device compared to earlier artificial heart designs. - Can patients with artificial hearts live normal lives?
While patients with artificial hearts face some limitations, many can return home and engage in daily activities. The quality of life can be significantly improved compared to end-stage heart failure. - How long can a patient live with an artificial heart?
The duration varies depending on the device and individual circumstances. Some patients have lived for several years with artificial hearts while awaiting transplants. - Will artificial hearts eventually replace the need for heart transplants?
While this is a long-term goal, currently artificial hearts primarily serve as a bridge to transplantation. However, ongoing research aims to develop devices that could potentially eliminate the need for transplants in some cases.
Explore Farmonaut’s API: Farmonaut API
API Developer Documentation: Farmonaut API Developer Docs