Revolutionary Artificial Heart Breakthrough: Sydney Hospital Discharges First Patient with Total Implant
“The first patient with a total artificial heart implant in Australia lived over 100 days before receiving a donor transplant.”
In a groundbreaking medical advancement, we are thrilled to report on the revolutionary artificial heart breakthrough that has taken place in Sydney, Australia. This milestone marks a significant leap forward in heart failure treatment and offers new hope to patients awaiting heart transplants worldwide. Today, we’ll delve into the details of this remarkable achievement and explore its implications for the future of cardiac care.
The Landmark Procedure: A New Era in Cardiac Care
At St Vincent’s Hospital in Sydney, a team of skilled medical professionals, led by cardiothoracic surgeon Paul Jansz, successfully implanted the BiVACOR total artificial heart in a patient from New South Wales. This procedure, which took place in November last year, lasted six hours and resulted in the first-ever discharge of a patient with a total artificial heart implant in Australia.
The patient, a man in his 40s, lived with the device for an impressive 100 days before receiving a donor heart transplant in March. This achievement not only showcases the potential of artificial heart technology but also demonstrates the feasibility of using such devices as a bridge to transplantation for patients with end-stage biventricular heart failure.
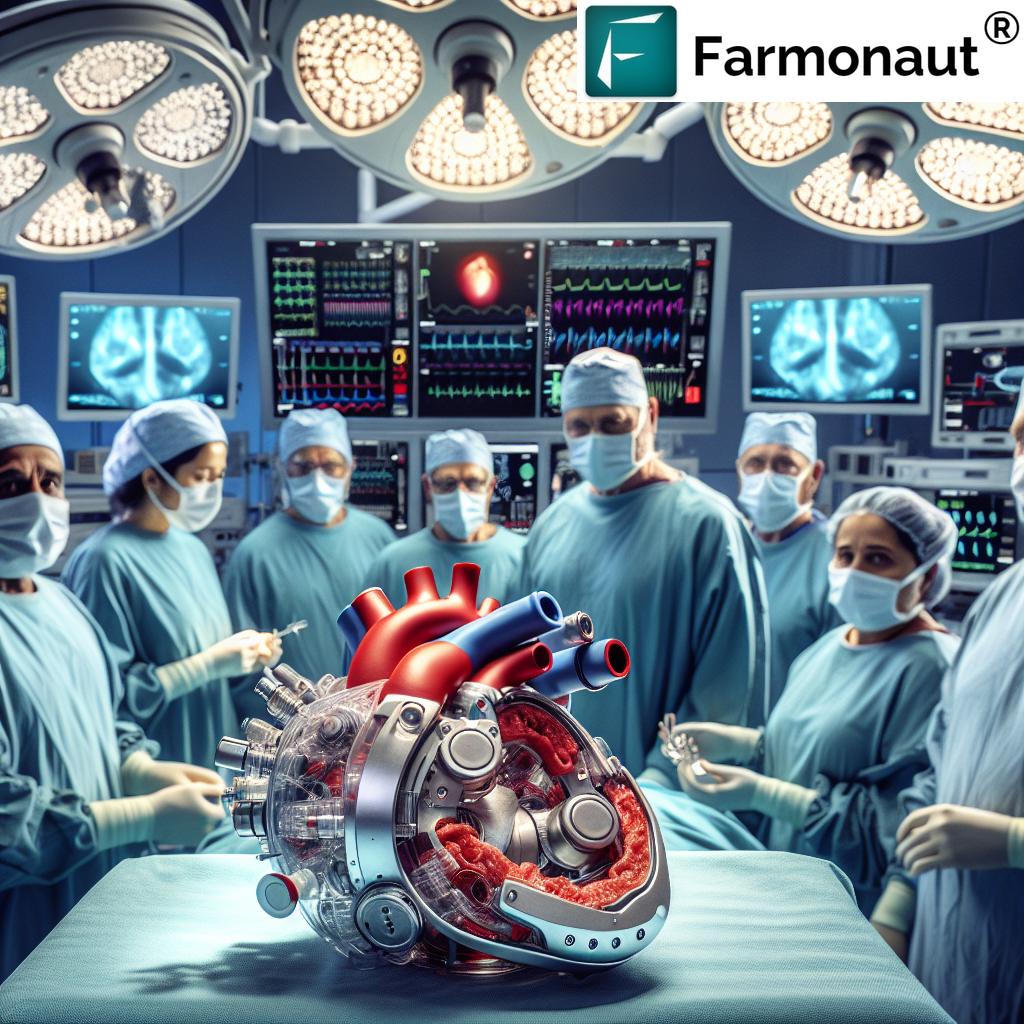
The BiVACOR Artificial Heart: A Technological Marvel
“The revolutionary artificial heart uses magnetic levitation technology to replicate natural blood flow in patients with biventricular heart failure.”
At the heart of this breakthrough lies the BiVACOR artificial heart, a remarkable piece of medical innovation developed by Queensland-born Dr. Daniel Timms. This device represents a significant advancement in artificial heart technology, setting itself apart from previous models in several key ways:
- Magnetic Levitation Technology: The BiVACOR heart utilizes cutting-edge magnetic levitation to replicate natural blood flow, providing a more physiologically accurate circulation system.
- Total Heart Replacement: Unlike some artificial heart devices that assist a failing heart, the BiVACOR is designed to fully replace the human heart, offering a solution for patients with end-stage biventricular heart failure.
- Implantable Rotary Blood Pump: The device functions as the first implantable rotary blood pump specifically designed for total heart replacement, marking a significant milestone in cardiac medical innovation.
This artificial heart breakthrough has the potential to transform heart failure treatment on a global scale. By providing a viable alternative for patients awaiting heart transplants, it could significantly reduce waiting times and improve outcomes for those with severe cardiac conditions.
The Journey to Success: Previous Implants and Australian Innovation
While the Sydney hospital’s success is groundbreaking, it’s important to note that this achievement builds upon previous efforts in artificial heart technology. Five BiVACOR implants had already taken place in the United States, with the longest implant period lasting 27 days. However, the Australian case stands out as the first where a patient was discharged from the hospital with the device, living independently for over three months.
This success story is not just a testament to medical expertise but also highlights Australia’s commitment to advancing medical technology. The Australian government has shown strong support for this initiative, providing US$50 million through its artificial heart frontiers programme to aid in the development and commercialization of the BiVACOR device.
Implications for Heart Failure Treatment
The successful implantation and discharge of a patient with a total artificial heart have far-reaching implications for heart failure treatment worldwide. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Bridge to Transplantation: The BiVACOR heart serves as a crucial bridge for patients awaiting donor hearts, potentially saving lives that might have been lost due to long waiting times.
- Quality of Life Improvement: Patients with end-stage heart failure often experience a severely diminished quality of life. The artificial heart technology could offer them increased mobility and independence while waiting for a transplant.
- Reduced Transplant Wait Times: As more patients can be sustained on artificial hearts, it may help alleviate the pressure on donor heart waiting lists, potentially reducing wait times for all patients.
- Advancement in Cardiac Care: This breakthrough pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in cardiac care, inspiring further research and development in the field of artificial organs.
As we celebrate this artificial heart breakthrough, it’s crucial to recognize its potential impact on the global healthcare landscape. The success in Sydney opens up new possibilities for patients with severe heart conditions, offering hope where previously there may have been limited options.
Comparing Artificial Heart Technology
To better understand the significance of this breakthrough, let’s compare the new artificial heart technology with traditional heart transplants and other artificial heart devices:
| Treatment Type | Estimated Longevity | Blood Flow Mechanism | Patient Mobility | Waiting Time | Rejection Risk | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Artificial Heart (Magnetic Levitation) | Months to years (still under study) | Magnetic levitation technology | High | Potentially shorter | Low (non-biological) | Regular check-ups and battery changes |
| Traditional Heart Transplant | 10-15 years on average | Natural biological mechanism | High (after recovery) | Often long (organ availability) | High (immunosuppression required) | Lifelong immunosuppression and monitoring |
| Other Artificial Heart Devices | Varies (weeks to months) | Mechanical pumps | Moderate | Varies | Low (non-biological) | Regular maintenance and external power source |
This comparison highlights the unique advantages of the new artificial heart technology, particularly in terms of patient mobility and potentially reduced waiting times. However, it’s important to note that traditional heart transplants still offer the longest-term solution, underscoring the need for continued research and development in artificial heart technology.
Challenges and Future Developments
While the success of the BiVACOR artificial heart is undoubtedly a cause for celebration, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that lie ahead and the areas where further development is needed:
- Longevity: As noted by Prof David Colquhoun, artificial hearts currently last far less than donor hearts. Improving the longevity of these devices is a crucial area for future research.
- Long-term Effects: As this is a relatively new technology, the long-term effects of living with a total artificial heart are not yet fully understood and will require ongoing study.
- Cost and Accessibility: Ensuring that this advanced technology becomes accessible to all who need it, regardless of geographical location or economic status, will be a significant challenge.
- Integration with Biological Systems: Further research is needed to optimize the integration of artificial hearts with the human body’s complex biological systems.
Despite these challenges, the potential of this technology to revolutionize heart failure treatment is immense. As research continues and the technology evolves, we may see artificial hearts becoming a viable long-term alternative to traditional heart transplants.
The Role of Technology in Modern Healthcare
The success of the BiVACOR artificial heart underscores the critical role that technology plays in advancing healthcare. From artificial intelligence aiding in diagnostics to robotic surgery and now, fully implantable artificial organs, we are witnessing a technological revolution in medicine.
This breakthrough also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in medical innovation. The development of the BiVACOR heart required expertise not just in medicine, but also in engineering, materials science, and computer technology.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that continued investment in medical technology and research will be crucial in addressing some of the most pressing health challenges of our time. The success of the artificial heart implant in Sydney serves as a powerful reminder of what can be achieved when innovation, dedication, and support come together in the pursuit of better healthcare.
Global Impact and Future Prospects
The implications of this artificial heart breakthrough extend far beyond the borders of Australia. As news of this success spreads, it’s likely to inspire and accelerate similar research and development efforts worldwide. Here are some potential global impacts:
- International Collaboration: This breakthrough may spur increased international collaboration in the field of artificial organ development, leading to faster advancements and more innovative solutions.
- Investment in Medical Technology: Success stories like this often attract increased investment in medical technology, both from governments and private sectors, potentially leading to more breakthroughs in various areas of healthcare.
- Hope for Patients Worldwide: For patients with severe heart conditions around the world, this news offers a new ray of hope, potentially improving mental health outcomes and quality of life even before the technology becomes widely available.
- Ethical Considerations: As artificial organ technology advances, it will likely spark important ethical discussions about the nature of life, death, and the extent to which we can and should replace biological functions with artificial ones.
The success of the BiVACOR heart also opens up exciting possibilities for the future of artificial organs beyond just the heart. We may see similar advancements in artificial lungs, kidneys, and other vital organs, potentially revolutionizing the field of organ transplantation as a whole.
The Patient Experience: A New Lease on Life
While the technical aspects of this breakthrough are fascinating, it’s important not to lose sight of the human impact. For the patient in Sydney, this artificial heart implant literally meant the difference between life and death. It allowed him to live independently for over three months, bridging the gap until a suitable donor heart became available.
This experience raises several important points about the patient perspective:
- Quality of Life: The ability to be discharged from the hospital and live independently with an artificial heart represents a significant improvement in quality of life for patients awaiting transplants.
- Psychological Impact: Knowing that there’s an alternative to waiting indefinitely for a donor heart can have a profound positive impact on patients’ mental health and outlook.
- Family and Social Aspects: The ability to return home and interact with family and friends while waiting for a transplant can greatly improve the social and emotional well-being of patients.
- Future Possibilities: As the technology improves, we may see patients living with artificial hearts for extended periods, potentially even as a permanent solution in some cases.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future of artificial heart technology, we see a landscape filled with both challenges and opportunities. Some key areas to watch include:
- Miniaturization: Future research will likely focus on making artificial hearts smaller and more efficient, potentially leading to less invasive implantation procedures and improved patient comfort.
- Power Sources: Developing more efficient and long-lasting power sources for artificial hearts will be crucial in improving their longevity and reducing the need for frequent interventions.
- Biocompatibility: Enhancing the biocompatibility of artificial heart materials will help reduce the risk of complications and improve long-term outcomes for patients.
- Integration with Biological Systems: Future artificial hearts may incorporate biological elements or be designed to better integrate with the body’s own regulatory systems.
- Personalization: Advances in 3D printing and personalized medicine may lead to artificial hearts tailored to individual patient needs and anatomy.
These advancements will require continued collaboration between medical professionals, engineers, researchers, and policymakers. It will also necessitate ongoing ethical discussions to ensure that as the technology progresses, it does so in a way that prioritizes patient well-being and adheres to the highest standards of medical ethics.
The Role of Government and Industry
The success of the BiVACOR artificial heart implant in Sydney highlights the crucial role that government support and industry collaboration play in advancing medical technology. The Australian government’s investment of US$50 million in the artificial heart frontiers programme was instrumental in bringing this technology from concept to reality.
Moving forward, continued government support and industry partnerships will be essential in:
- Funding Research: Ongoing financial support for research and development in artificial organ technology is crucial for continued progress.
- Regulatory Framework: Developing appropriate regulatory frameworks to ensure the safety and efficacy of new medical technologies while not stifling innovation.
- Clinical Trials: Supporting and facilitating clinical trials to test and refine artificial heart technology in real-world settings.
- Manufacturing and Distribution: Ensuring that once approved, artificial hearts can be manufactured and distributed efficiently to reach patients in need.
- Training and Education: Providing resources for the training of medical professionals in the implantation and management of artificial heart devices.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Cardiac Care
The successful discharge of the first patient with a total artificial heart implant in Sydney marks the beginning of a new chapter in cardiac care. This breakthrough not only demonstrates the viability of artificial heart technology but also offers hope to millions of patients worldwide suffering from end-stage heart failure.
While challenges remain, particularly in terms of longevity and long-term effects, the potential of this technology to transform lives is immense. As research continues and the technology evolves, we may be moving closer to a future where no one dies waiting for a heart transplant.
This achievement is a testament to human ingenuity, perseverance, and the power of collaborative efforts in medical innovation. It reminds us of the incredible progress we can make when science, technology, and compassion come together to solve some of our most pressing health challenges.
As we celebrate this milestone, we look forward with optimism to the future advances that will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in cardiac care and medical technology as a whole.
FAQs about Artificial Heart Technology
- What is a total artificial heart?
A total artificial heart is a device designed to completely replace the function of a failing heart. It pumps blood throughout the body, taking over the role of both ventricles and all four heart valves. - How does the BiVACOR artificial heart work?
The BiVACOR artificial heart uses magnetic levitation technology to create blood flow. This allows for a more natural and efficient circulation compared to older mechanical pump designs. - Who is a candidate for an artificial heart?
Typically, candidates for artificial hearts are patients with end-stage biventricular heart failure who are awaiting a heart transplant. The device serves as a bridge to transplantation. - How long can a person live with an artificial heart?
Currently, artificial hearts are designed as a temporary solution while waiting for a donor heart. In the Sydney case, the patient lived with the device for over 100 days. The longevity of artificial hearts is an area of ongoing research and development. - What are the risks associated with artificial heart implantation?
Risks can include infection, blood clots, device malfunction, and bleeding. However, as technology improves, these risks are being minimized. - Will artificial hearts eventually replace the need for donor hearts?
While this is a long-term goal, currently artificial hearts serve primarily as a bridge to transplantation. Significant advancements are still needed before they can fully replace donor hearts for extended periods. - How does the cost of an artificial heart compare to a traditional heart transplant?
The cost can vary widely depending on the specific device and procedure. Generally, the initial cost of an artificial heart implantation may be comparable to or higher than a traditional transplant, but ongoing costs and long-term comparisons are still being studied. - Are there other artificial organs being developed?
Yes, researchers are working on developing various artificial organs, including lungs, kidneys, and pancreases. The success with artificial hearts is encouraging for the development of other artificial organs.
As we conclude this exploration of the revolutionary artificial heart breakthrough in Sydney, it’s clear that we’re witnessing a pivotal moment in medical history. The successful discharge of a patient with a total artificial heart implant not only represents a triumph of medical science but also opens up new possibilities for treating heart failure and saving lives.
While challenges remain, the potential of this technology to transform cardiac care is immense. As research continues and the technology evolves, we may be moving closer to a future where artificial hearts become a viable long-term solution for patients with severe heart conditions.
This breakthrough serves as a powerful reminder of what can be achieved through innovation, collaboration, and perseverance in the field of medical technology. It offers hope to patients worldwide and inspires further advancements in the realm of artificial organs and cardiac care.
As we look to the future, we can anticipate exciting developments in this field, potentially revolutionizing not just heart failure treatment, but the entire landscape of organ transplantation and replacement. The journey of medical innovation continues, promising a brighter, healthier future for all.
Earn With Farmonaut: Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
For more information on Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data API, visit our API page and check out our API Developer Docs.