Sustainable Agriculture Techniques: 10 Yield Hacks!
“Soil conservation can increase crop yields by up to 50% in degraded lands.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Fundamentals of Sustainable Agriculture
- 10 Sustainable Agriculture Yield Hacks
- Empowering Sustainable Agriculture with Farmonaut
- Comparative Benefits Table
- Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture
- Challenges & Considerations in Adopting Sustainable Practices
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In our rapidly evolving world, sustainable agriculture techniques have become vital for boosting crop productivity, protecting our soil, and enhancing farm biodiversity. Facing ever-growing food demands, it’s clear that farming must adapt—balancing the urgent need for high yields with the responsibility of preserving health, natural resources, and the environment for future generations. Through innovative agricultural practices like soil conservation, organic farming methods, and smart water management, we can ensure a bright, productive, and resilient agricultural future.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover 10 powerful yield hacks that embody the best of sustainable agriculture. These proven techniques not only maximize productivity but also champion the cause of environmental preservation, economic viability, and social equity. We’ll demonstrate how integrating such systems into traditional farming can transform food production worldwide.
The Fundamentals of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture refers to a suite of farming practices that fulfill our current food demands while ensuring the preservation and regeneration of the environment. At its core, it combines scientific ecological principles with practical agronomic techniques to optimize yield, protect natural resources, and support the biodiversity that underpins our future.
- Environmental Health: Preventing erosion, conserving water, and improving soil structure.
- Economic Viability: Cutting dependency on synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides, increasing long-term profitability.
- Social Equity: Fair labor, community support, and healthy food access that sustains all generations.
Let’s now explore the 10 key sustainable agriculture practices that empower farmers to grow resilient, productive, and environmentally-friendly crops!
Sustainable Agriculture Techniques: 10 Yield Hacks!
1. Conservation Tillage (No-Till Farming)
Conserving soil begins with minimizing disturbance. Conservation tillage—especially no-till farming—means seeds are directly planted into undisturbed soil, forgoing traditional plowing and aggressive machinery use. This practice maintains soil structure, allows greater moisture retention, and dramatically reduces erosion.
- Soil Conservation Techniques: No-till allows organic residues—like stems and leaves—to blanket the soil, shielding it from wind and water impact.
- Biological Activity: Fosters nutrients cycling through increased earthworm and microbe activity.
- Water Efficiency: Moisture, preserved near root zones, supports robust crop productivity even in dry seasons.
Conservation tillage is a core sustainable agriculture technique—a win for our environment and for yield!
2. Cover Cropping: Green Blankets for the Soil
Cover cropping is about planting legumes, rye, or clover between main crop seasons. This gives soil a living shield, preventing erosion, boosting fertility, and enriching it with valuable nitrogen—all naturally, with less need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Cover Cropping Benefits:
- Guards against both wind and water-driven erosion.
- Supplies vital nutrients and prevents depletion in successive plantings.
- Increases organic matter for improved soil structure and moisture retention.
By integrating cover cropping into our planting cycle, we support sustainable agriculture and keep our land resilient for generations.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Smarter Pest Control
Traditional farming often relies heavily on chemical pesticides, but this approach can harm beneficial species and contaminate our environment. Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic technique that combines:
- Biological controls: Encouraging natural pest predators like ladybugs or birds, which help manage harmful insect populations.
- Cultural controls: Strategic crop rotation, planting pest-resistant varieties, and modifying habitat layout to deter infestations.
- Minimal intervention: Using targeted pesticides only as a last-resort, reducing risk to human health and local ecosystems.
IPM offers a sustainable, integrated alternative to harsh chemical inputs, authenticating our commitment to safe, healthy, and sustainable agriculture practices.
Monitor crop health, pest risks, and resource efficiency with Farmonaut’s crop monitoring platform—empowering informed, sustainable farm management every season.
4. Agroforestry: Trees in Our Fields, Life Across the Landscape
Agroforestry systems are all about integrating trees and shrubs directly into our agricultural land. These living giants play multiple roles:
- Biodiversity enhancement: Trees provide vital habitat for birds, pollinators, and beneficial species.
- Structural protection: Their roots lock in soil, preventing erosion and fostering a stable environment for crops.
- Resilient systems: Agroforestry buffers farms against wind, weather extremes, and climate volatility.
- Diversified income: Timber, fruit, and tree-sourced products supplement traditional harvests, offering new revenue streams for farmers.
By planting rows or clusters of native species alongside crops, we make our farming systems more resilient and sustainable.
5. Organic Farming: Back to Nature, Forward to Health
Organic farming methods ban synthetic chemicals and focus on natural systems. This practice:
- Promotes biodiversity by avoiding chemical disturbance and cultivating varied species.
- Boosts soil health with composting, crop rotations, and biological pest control.
- Reduces pollution by eliminating synthetic fertilizers and pesticides from runoff.
Obtaining organic certification demonstrates rigorous adherence to sustainable agriculture practices. Beyond environmental benefits, organic farming delivers nutrient-rich food and market confidence.
“Organic farming uses 30% less energy compared to conventional agriculture methods.”
6. System of Rice Intensification (SRI): More Rice with Less
When it comes to rice, a staple food for over half the world, system of rice intensification (SRI) is transforming yields and improving resource efficiency:
- Young seedlings: Planting them at an early stage, sparing roots from shock and loss.
- Wider spacing: Reduces competition, improving crop health.
- Intermittent irrigation: Provides water only when needed, supporting deep rooting and water preservation.
Implementing SRI can increase production by over 40%, with reduced water and chemical inputs. SRI is a robust, sustainable solution for rice-growing regions like India.
7. Conservation Agriculture: Farming That Heals the Land
Conservation agriculture brings together the best practices for preserving the environment and maintaining productivity:
- Minimal soil disturbance: Maintain permanent cover and avoid breaking soil structure.
- Permanent soil cover: Use mulch or plant residues to protect the surface.
- Species diversification: Rotate and intersperse crops to mimic the biodiversity of natural ecosystems.
These practices regenerate degraded soils, control erosion, and create more resilient farming systems. Conservation agriculture is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture techniques.
8. Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems: Nature’s Closed Loop
Instead of separating animal husbandry and crop cultivation, integrated crop-livestock systems unite them for efficiency and sustainability:
- Livestock manure becomes a renewable source of natural fertilizer for crops, nurturing soil health.
- Crop residues serve as rich, cost-effective animal feed, reducing waste.
- Diversification of farm income and improved resource management.
These systems create resilient, circular agricultural models, great for both smallholders and large operations.
9. Water Management in Agriculture: Every Drop Counts
Efficient water management in agriculture is critical. By using precision irrigation and conserving water, we achieve higher yields with reduced resource input.
- Drip irrigation: Delivers water directly to root zones, lowering overall water use by 20-40% and increasing crops by up to 50%!
- Drought-tolerant species: Choosing less-thirsty crops is wise for arid and semi-arid locations.
- Smart scheduling: Align irrigation with weather and soil moisture data to maximize efficiency and avoid waste.
Smart water management supports the sustainability of farms in regions facing drought and climate change.
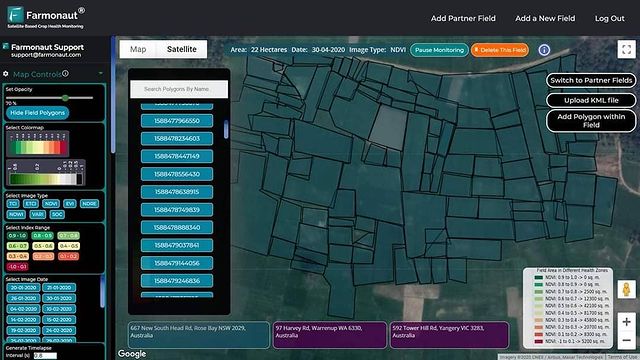
Farmonaut provides accurate satellite-based soil moisture analytics—enabling farmers to optimize irrigation and save water with real-time precision. Learn more and access our agricultural API and developer documentation.
10. Polyculture: Mimicking Nature’s Diversity
Polyculture means growing a mix of crop species within the same field—contrasting the risky one-crop approach of monoculture. Here’s why it matters:
- The mix discourages the spread of pests and diseases—each species plays a defensive role for its neighbors.
- Improved soil health as different species draw on unique nutrients and contribute complementary organic matter.
- Enhanced resilience to weather shifts, improving farm biodiversity and stability.
Adopting polyculture techniques is a proactive way to create balanced, sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
“Organic farming uses 30% less energy compared to conventional agriculture methods.”
Empowering Sustainable Agriculture with Farmonaut
Embracing sustainable agriculture techniques is easier and more effective with data-driven technology. Farmonaut has emerged as a trailblazer—providing affordable, global access to advanced, satellite-based farm management. Our tools empower farmers, agribusinesses, and governments to improve productivity, conserve resources, and protect the environment:
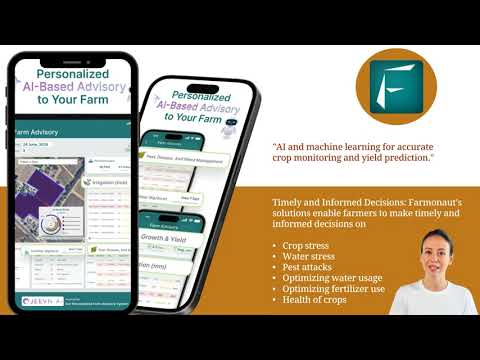
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut offers real-time crop health, soil moisture, and vegetation metrics, enabling precise fertilizer, water, and pest management—all from your smartphone or web browser.
- AI-Powered Jeevn Advisory System: Customized advice on weather, planting, and resource management for better yields using artificial intelligence—helping all farmers thrive.
-
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Transparent, tamper-proof tracking of agricultural products—winning consumer trust and ensuring accountability.
Learn more on our traceability product page. -
Fleet & Resource Management: Real-time monitoring and optimization of your machinery, logistics, and overall farm management—great for scaling up!
Check out our fleet management solution for large-scale farms. -
Carbon Footprinting: Take responsibility for your farm’s environmental impact with real-time carbon footprint analytics, supporting your path to carbon-neutral and sustainable farming.
Discover how on our carbon footprinting page. -
Crop Loan & Insurance Verification: Get verified, satellite-based records to access loans or insurance with confidence.
Find out more at our crop loan and insurance service page.
Our subscription-based platform is accessible via Android, iOS, web, and powerful APIs—making precision, sustainable farming open to all.
Are you a developer or agricultural researcher? Integrate real-time satellite, weather, and soil data with our powerful Farmonaut API and get started today—see the official API docs!
Comparative Benefits Table of Sustainable Agriculture Techniques
| Technique | Description | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Environmental Impact Score (1–5) | Ease of Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservation Tillage | Minimal soil disturbance, no plowing, direct seeding |
10–25 | 5 | Medium |
| Cover Cropping | Planting legumes, rye, or clover between main crops | 10–20 | 5 | Easy |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combining biological, cultural, mechanical, and minimal chemical controls | 8–15 | 4 | Medium |
| Agroforestry | Integrating trees/shrubs into cropland for biodiversity and resilience | 15–35 | 5 | Hard |
| Organic Farming | No synthetic inputs, enhanced biodiversity, soil and crop health | 5–15 | 5 | Medium |
| System of Rice Intensification (SRI) | Early seedlings, wider spacing, smarter irrigation for rice | 30–41 | 5 | Medium |
| Conservation Agriculture | Combining no-till, soil cover, and crop rotations/diversity | 15–27 | 5 | Medium |
| Integrated Crop-Livestock | Manure for soil, crop residues for feed, closed loop fertility | 10–25 | 4 | Medium |
| Water Management (Drip Irrigation) | Efficient, targeted irrigation systems, optimized water use | 20–50 | 5 | Easy |
| Polyculture | Growing multiple crop species per field for resilience | 10–18 | 5 | Medium |
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- Environmental Preservation: Sustainable methods improve soil health, conserve water, reduce pollution, and foster biodiversity—preserving our planet’s future.
- Economic Viability: By lowering reliance on synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides, cost is reduced and profitability increases.
- Social Equity: Resilient agricultural systems support local communities, promote fair labor, and ensure healthy food for all.
- Improved Productivity: Many sustainable agriculture techniques increase yields—especially on degraded or resource-poor land.
- Future-Readiness: As climate changes, sustainable farms are more adaptable, less vulnerable, and better prepared to meet shifting demands.
Challenges & Considerations in Adopting Sustainable Practices
While sustainable agriculture offers clear rewards, it is not without obstacles. Transitioning to new systems—like no-till farming, IPM, or advanced water management—often requires:
- Upfront Investment: Some techniques need specialized equipment or upfront costs before savings emerge.
- Education & Training: Farmers and workers must learn the “why” and “how” of new practices.
- Access to Resources: Seeds for cover cropping, smart irrigation hardware, or biological pest controls are not always widely available.
- Market Support: Organic or sustainably grown food thrives when there’s consumer demand and supportive policy.
Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration, technical guidance, smart subsidies, and informational infrastructure. Solutions like Farmonaut’s technology platforms provide critical technical support and real-time analytics, drastically lowering barriers for farmers worldwide.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Agricultural Future Together
As we’ve explored, sustainable agriculture techniques are not only possible—they’re essential. By practicing conservation tillage, cover cropping, integrated pest management, agroforestry systems, organic farming, and more, we protect soil, conserve water, and build resilient farm systems adapted to the demands of our environment and future generations.
By harnessing the power of technology and ecological principles together—such as those offered by Farmonaut’s advanced satellite and AI-based solutions—farmers and agribusinesses can make informed, sustainable decisions daily. Our shared goal? Ensure abundant, healthy food production for today, while safeguarding the land, resources, and climate for tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Sustainable Agriculture Techniques
1. What is sustainable agriculture, and why is it important?
Sustainable agriculture uses techniques that meet our current food needs while preserving environmental health, ensuring economic viability, and supporting social equity for future generations. It is vital for long-term food security and environmental stewardship.
2. What are the top benefits of conservation tillage?
Conservation tillage improves soil structure, conserves moisture, prevents erosion, increases beneficial biological activity, and reduces labor and fuel input costs over time.
3. How does cover cropping improve farm sustainability?
Cover cropping protects soil from erosion, fixes nitrogen, replenishes nutrients, and enhances water management and biodiversity—making fields more resilient and productive.
4. Is organic farming more profitable than conventional farming?
Over time, many organic farms achieve higher net profitability due to premium market prices and lower reliance on costly inputs. Profitability depends on effective management and market access.
5. How can Farmonaut tools help implement sustainable agriculture techniques?
Farmonaut leverages satellite imagery, AI, and blockchain to assist farmers in monitoring soil health, managing irrigation, detecting pests, tracking carbon footprint, and ensuring transparency in food supply chains—empowering more informed and sustainable farming practices.
6. Where can I explore Farmonaut’s sustainable agriculture solutions?
Explore our advanced tools—including real-time crop health, resource management, carbon tracking, and blockchain traceability—at the Farmonaut platform and sustainability solutions page.