Organic Aphid Control: 7 Powerful Methods for Healthy Crops
“Over 200 species of natural predators can help control aphid populations organically in sustainable farming systems.”
Aphids are among the most notorious agricultural pests, causing far-reaching damage to crops and plants across the globe. Their rapid reproduction and sap-sucking ways threaten our vegetables, fruits, and even ornamental plants, leading to stunted growth, distorted leaves, and the relentless transmission of plant diseases. The challenge? Managing aphid infestations sustainably, without harming our ecological balance or relying on synthetic pesticides.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unlock 7 powerful organic aphid control methods for healthy crops. We’ll dive deep into an informative exploration of natural predators, neem oil, IPM, and intelligent techniques—so you can effectively manage aphid infestations while fostering a sustainable environment for future harvests.
Contents
- Understanding Aphid Behavior and Impact
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The Foundation of Aphid Control
- Organic Aphid Control: 7 Powerful Methods for Healthy Crops
- Organic Aphid Control Methods: Quick Comparison Table
- Monitoring, Early Detection, and Ongoing Evaluation
- Farmonaut: Intelligent Crop Health and Aphid Management
- FAQs: Organic Aphid Control & Aphid Management
- Conclusion: Sowing the Seeds of Healthy, Sustainable Crops
Understanding Aphid Behavior and Impact
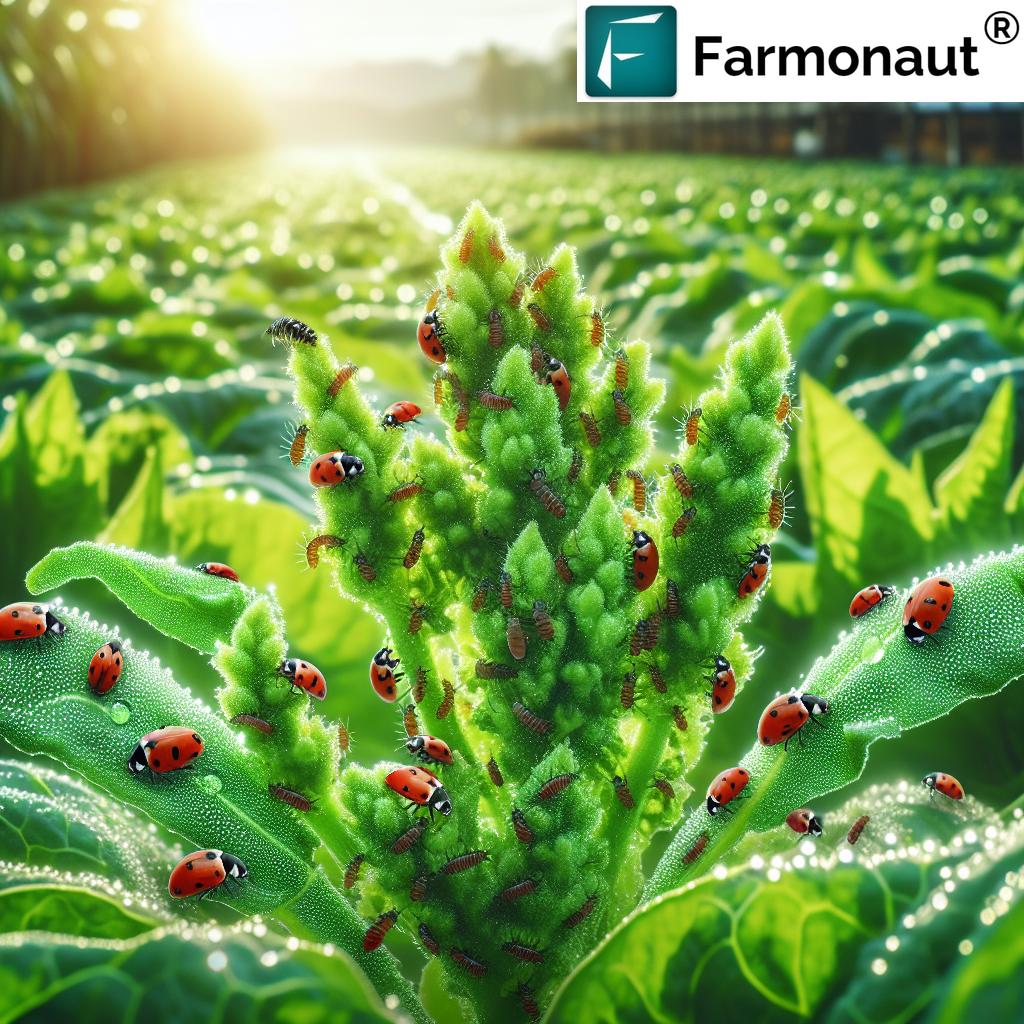
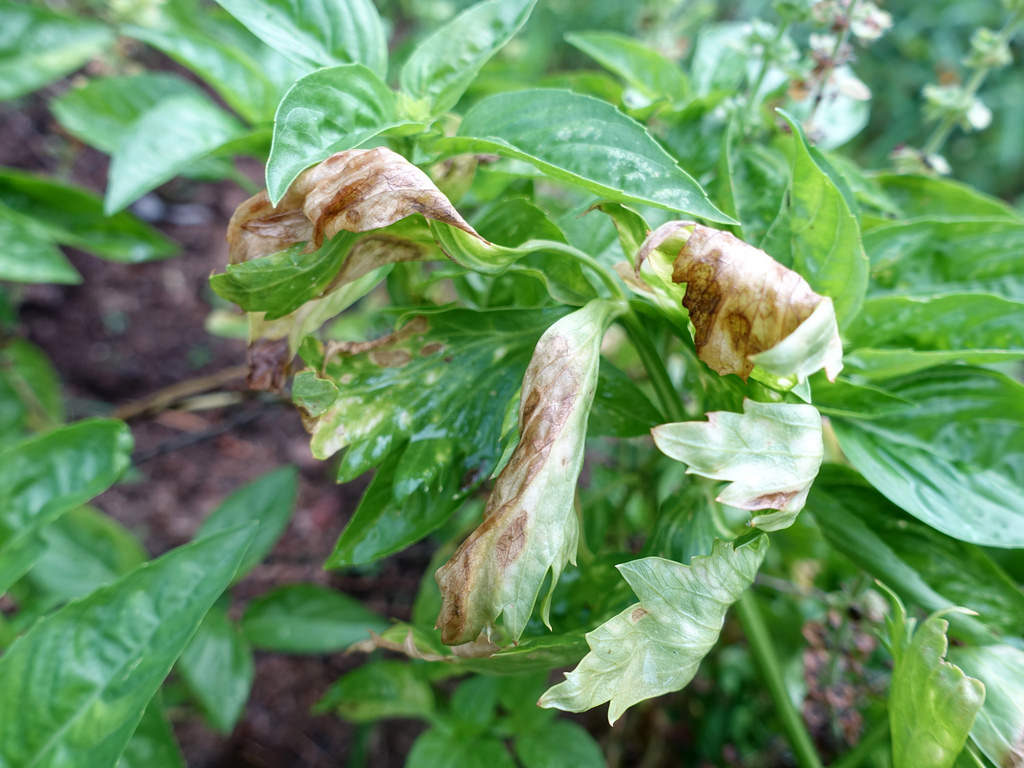
Aphids are tiny, soft-bodied insects known for their alarming reproduction rates and ability to form dense colonies on plant tissues. Their preference is to feed on the phloem sap of plants, draining vital nutrients and in turn weakening plants’ vigor rapidly.
But the story doesn’t end with direct feeding damage. As they extract sap, aphids excrete a sticky, sugary by-product called honeydew. This substance coats leaves and stems, serving as an ideal medium for sooty mold fungi. The resulting black mold further impairs photosynthesis, reducing crop yields and diminishing plant health.
- Direct effects: Stunted growth, curled and distorted leaves, loss of vigor
- Indirect effects: Sooty mold outbreaks, reduced photosynthesis, attraction of other pests, and increased risk of disease transmission
To successfully manage aphid infestations, it’s essential to understand their behavior and life cycle—and then select targeted, sustainable organic aphid control methods.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): The Foundation of Aphid Control
The best approach to sustainable aphid control is through Integrated Pest Management (IPM). A comprehensive IPM strategy recognizes the importance of ecological balance and combines multiple tactics to manage aphid populations sustainably.
- Cultural Practices: Shaping farming approaches to reduce aphid attraction and reproduction
- Biological Controls: Utilizing natural predators and parasitoids for organic protection
- Mechanical Methods: Physically removing and deterring aphids for immediate reduction
- Organic Insecticides: When needed, applying botanically-based sprays such as neem or soap
- Regular Monitoring: Early identification and evaluation enable quick action
By implementing multiple aphid control methods, we create redundancies in our pest management strategy, increase effectiveness, and help preserve beneficial insects vital for a thriving agro-ecosystem.
Organic Aphid Control: 7 Powerful Methods for Healthy Crops
Let’s explore the seven essential, research-backed organic aphid control methods. Each approach offers distinct advantages and can be tailored for specific crops and agro-climatic conditions. Our aim is to sustainably manage aphid populations while supporting plant health, productivity, and environmental stewardship.
“Neem oil reduces aphid infestations by up to 80% when applied regularly as part of an integrated pest management plan.”
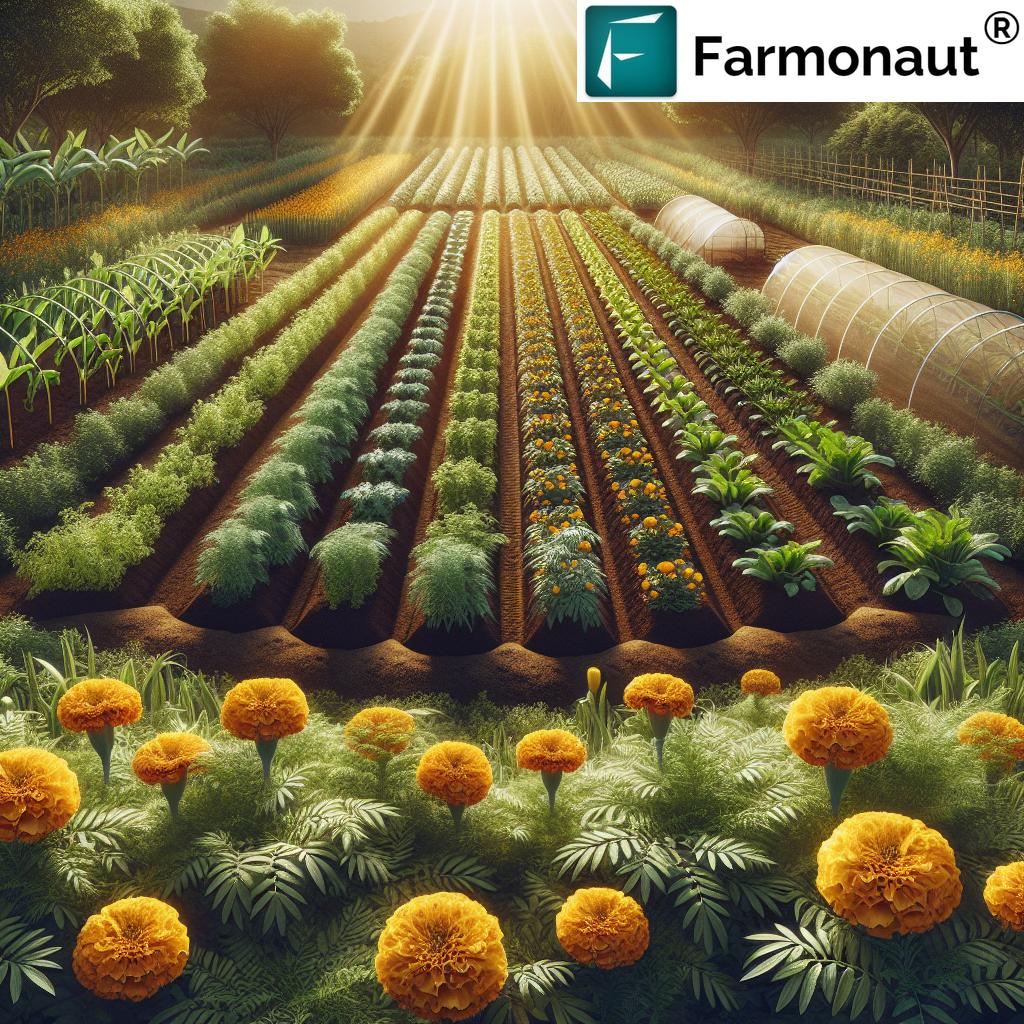
1. Cultural Practices to Reduce Aphid Infestations
Cultural controls focus on modifying our agricultural practices and planting schemes to make the environment less favorable for aphids. Simple changes can greatly reduce aphid attraction and reproduction. Here’s how:
- Companion Planting: Add aphid-repelling plants — for example, mint (Mentha microphylla), garlic, onion, chives, and marigolds. These deter aphids and benefit neighboring crops (see source).
- Trap Cropping: Strategically plant trap crops such as nasturtiums or sunflowers at field edges. Aphids are drawn to these instead of main vegetables or fruits, allowing easy removal (see more).
- Healthy Plant Maintenance: Vigorous plants resist aphids better. Ensure proper watering, balanced nutrients, and avoid overusing nitrogen fertilizers (which triggers soft, lush growth—an aphid favorite) (read how).
By implementing these methods on our farms and gardens, we can proactively deter aphids and support crop health with minimal ecological disruption.
2. Beneficial Insects for Aphid Control – The Power of Biological Control
The presence and encouragement of natural predators represent the most sustainable way for the biological control of aphids. These beneficial insects naturally keep aphid populations in check without the need for synthetic inputs:
- Ladybugs (Coccinellidae): Adults and larvae eat hundreds of aphids daily. Release ladybug populations or encourage them with flowering borders (details).
- Lacewing Larvae (Chrysoperla spp.): Known as “aphid lions”, their larvae voraciously feed on aphids.
- Hoverfly Larvae (Syrphidae): Prefer aphids on plants as a food source.
- Parasitic Wasps (Aphidius colemani): Lay eggs inside aphids; larvae consume the aphid from within, causing certain death (source).
To attract and sustain natural predators, plant native flowers like daisy, yarrow, dill, and marigold, and minimize broad-spectrum pesticides that disrupt beneficial insect populations.
3. Mechanical Methods: Physical Removal and Containment
Mechanical control offers immediate reduction of aphid numbers by removing insects directly:
- Water Spray: For mild to moderate infestations, use a jet of water from a hose (learn more). This dislodges and weakens aphid colonies. Spray early before sunrise or late in the evening to prevent sunscald on wet leaves.
- Manual Removal: Hand-pick or brush aphids off leaves onto the ground (where they become prey for ground beetles).
These mechanical aphid infestation solutions work best as a first response or for smaller outbreaks. Regular inspection is key!
4. Organic Insecticidal Soap for Aphid Control
When natural and mechanical options need reinforcement, consider insecticidal soaps for organic aphid control. These are made from potassium salts of fatty acids; they:
- Disrupt aphid cell membranes, causing dehydration and death
- Must be applied directly to affected plants and can be repeated as needed (more here)
- Leave no toxic residue when used properly
Caution: Test on a few leaves before widespread application to ensure no phytotoxicity. Insecticidal soaps are highly useful for vegetables and delicate fruits.
5. Neem Oil for Aphids – Nature’s Insecticide & Repellent
Neem oil (from the neem tree, Azadirachta indica) is among the most effective organic insecticides for aphid control:
- Disrupts aphid hormonal systems, affecting feeding, growth, and reproduction
- Functions as a repellent and growth inhibitor when applied to plants
- Mix 1-2 teaspoons neem oil in a liter of water, plus a drop of mild liquid soap (for emulsification), and spray directly over aphid colonies
- Regular use dramatically reduces aphid populations (in-depth guide)
Neem oil is gentle on beneficial insects when used as directed and is suitable for vegetables, fruits, and ornamentals.
6. Horticultural Oil & Diatomaceous Earth – Alternative Organic Aphid Remedies
Horticultural Oils:
- Suffocate aphids and eggs by coating their bodies and disrupting respiration
- Best for dormant spraying or on ornamentals; be careful on thin-leaved crops as excess can smother
- Apply as a diluted spray over affected areas (details)
Diatomaceous Earth (DE):
- Natural, fine powder from fossilized diatoms with microscopic sharp edges
- Damages aphid exoskeletons, causing dehydration and death
- Dust undersides of leaves and around plant stems for best effect (how it works)
Both methods offer non-toxic alternatives for organic systems. Avoid DE on flowers during bloom to protect bees.
7. Integrated Pest Management for Aphids: The Holistic Approach
While each above method has unique strengths, IPM leverages the synergy of multiple tactics. An IPM-based aphid infestation solution integrates:
- Routine monitoring of crop health and aphid numbers
- Early application of natural ways to control aphids — i.e., trap cropping, beneficial predators, and companion planting
- Targeted use of neem oil or insecticidal soap sprays when action thresholds are crossed
This approach ensures aphids stay below damaging levels, keeps pesticide use to a minimum, and helps us maintain ecological balance season after season.
Organic Aphid Control Methods: Quick Comparison Table
For fast decision-making, here’s a detailed comparison of key aphid control methods, their benefits, limitations, and suitability for different crops. This table will help you select the right solution for your farm or garden!
| Method Name | How it Works | Estimated Effectiveness (%) | Environmental Impact | Pros | Cons | Suitable Crops |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Predators | Encourage insects (e.g., ladybugs, lacewings) that eat aphids | 60% | Low | Self-sustaining, minimal input required, preserves balance | Needs habitat and time to establish, less effective for severe outbreaks | Vegetables, fruit trees, ornamentals |
| Neem Oil | Natural oil disrupts feeding, growth, and reproduction of aphids | 70-80% | Low | Broad-spectrum, repels and kills, safe for most beneficials | Requires frequent application in rain, possible phytotoxicity on tender leaves | Vegetables, fruits, flowers, berries |
| Insecticidal Soap | Destroys aphid cell membranes leading to dehydration and death | 65% | Low | Fast knockdown, safe if used correctly, no residue | Needs direct contact, may harm some soft-leaved plants if overapplied | Leafy crops, soft vegetables, ornamentals |
| Companion Planting | Use of aphid-repelling/floral trap plants | 50% | Very Low | Supports beneficials, fits any scale, enhances biodiversity | Takes planning, effectiveness varies by region and crop | All vegetables, flower gardens, orchards |
| Diatomaceous Earth | Physical abrasion damages aphid exoskeletons, leading to death by dehydration | 60% | Low | No chemical residue, easy to apply, safe if kept dry | Less effective when wet, can also harm non-pest insects on contact | Fruit, veg, ornamental, greenhouse crops |
| Water Spray | Physically dislodges aphids from plant tissues | 40% | Very Low | Immediate effect, uses only water, no toxicity | Labor-intensive, risk of disease from excess moisture, may not reach undersides | Small gardens, intensive beds, greenhouse crops |
| Integrated Pest Management | Combines cultural, mechanical, biological, and selective organic insecticide practices based on monitoring | 85-90% | Very Low | Highly sustainable, customizable, minimizes pesticides, preserves ecosystem | Needs planning, monitoring, farmer commitment | All farm and horticultural systems |
Monitoring, Early Detection, and Ongoing Evaluation
Continuous monitoring is crucial for early detection and fast intervention:
- Conduct routine checks of leaves (especially the undersides), stems, and flower buds for aphid colonies.
- Use yellow sticky traps to monitor aphid flights and judge infestation timing/severity.
- Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of chosen aphid control methods, adjusting strategies if populations rebound.
Modern farms can benefit from advanced monitoring tools, eco-friendly solutions, and scalable management platforms for more effective results.
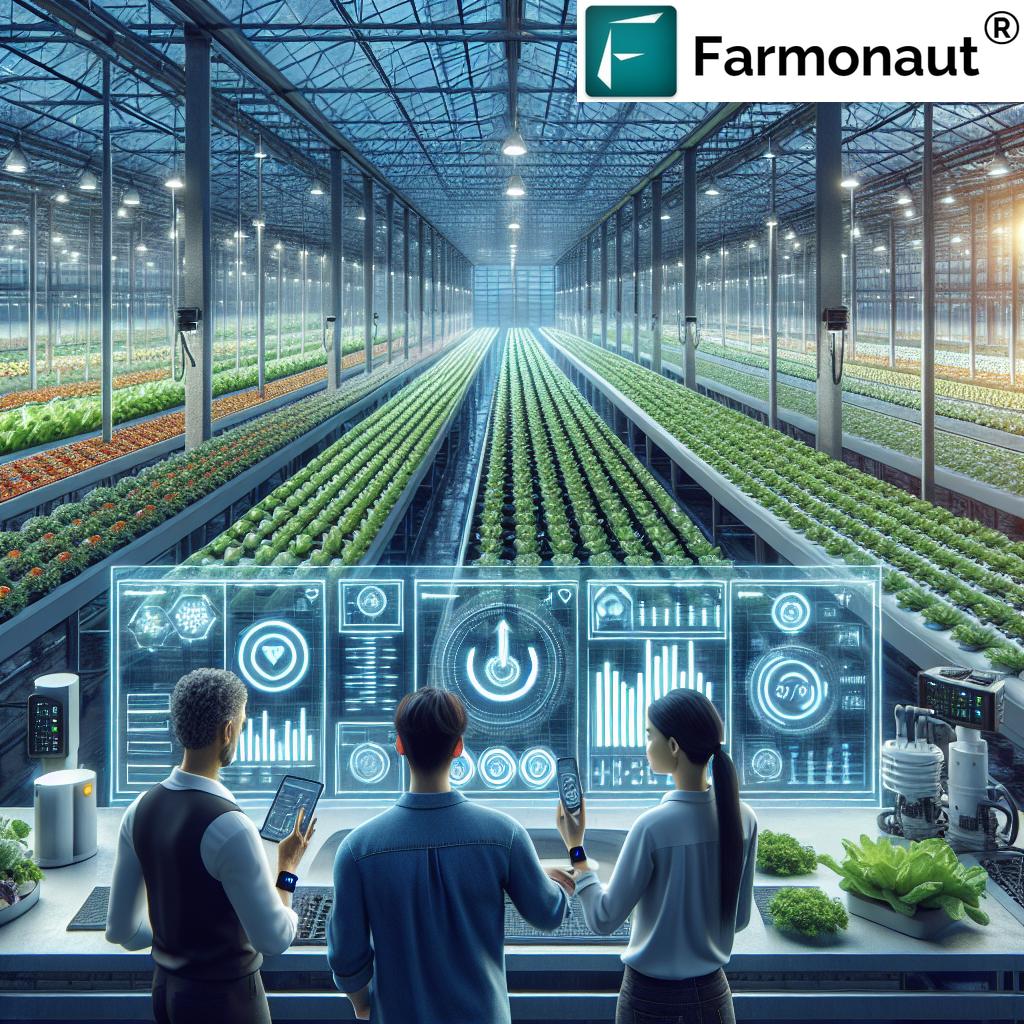
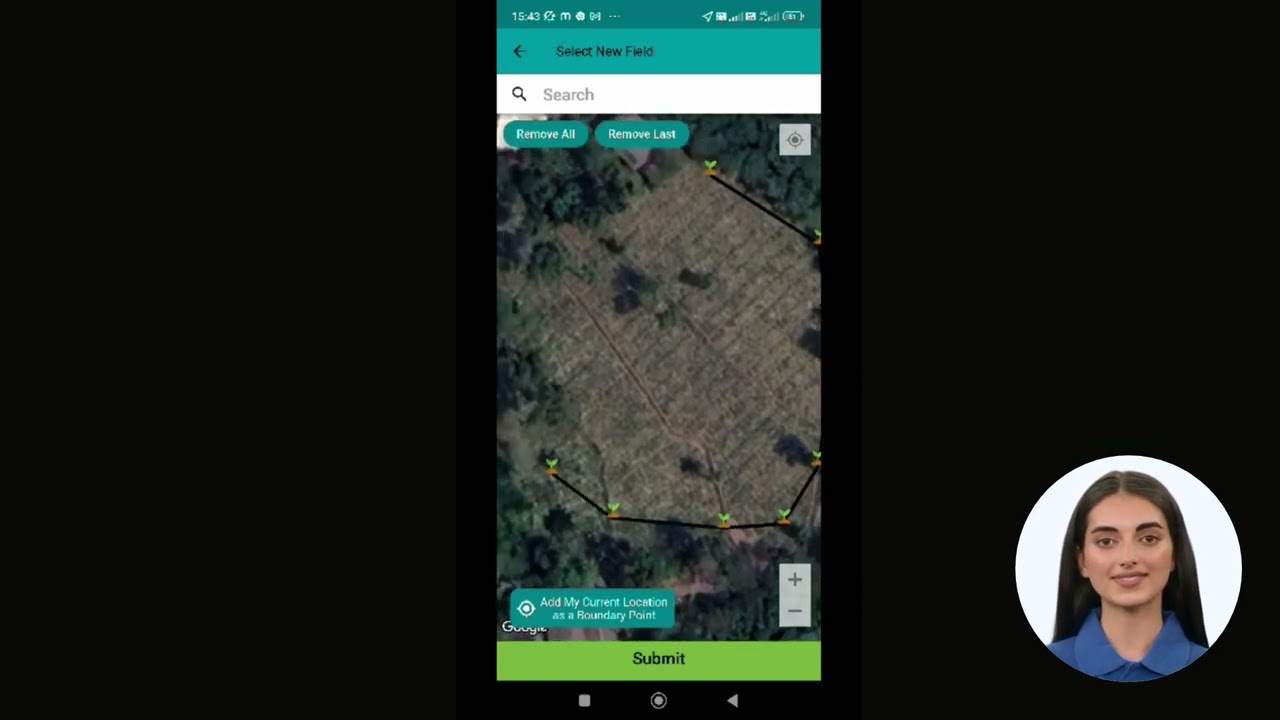
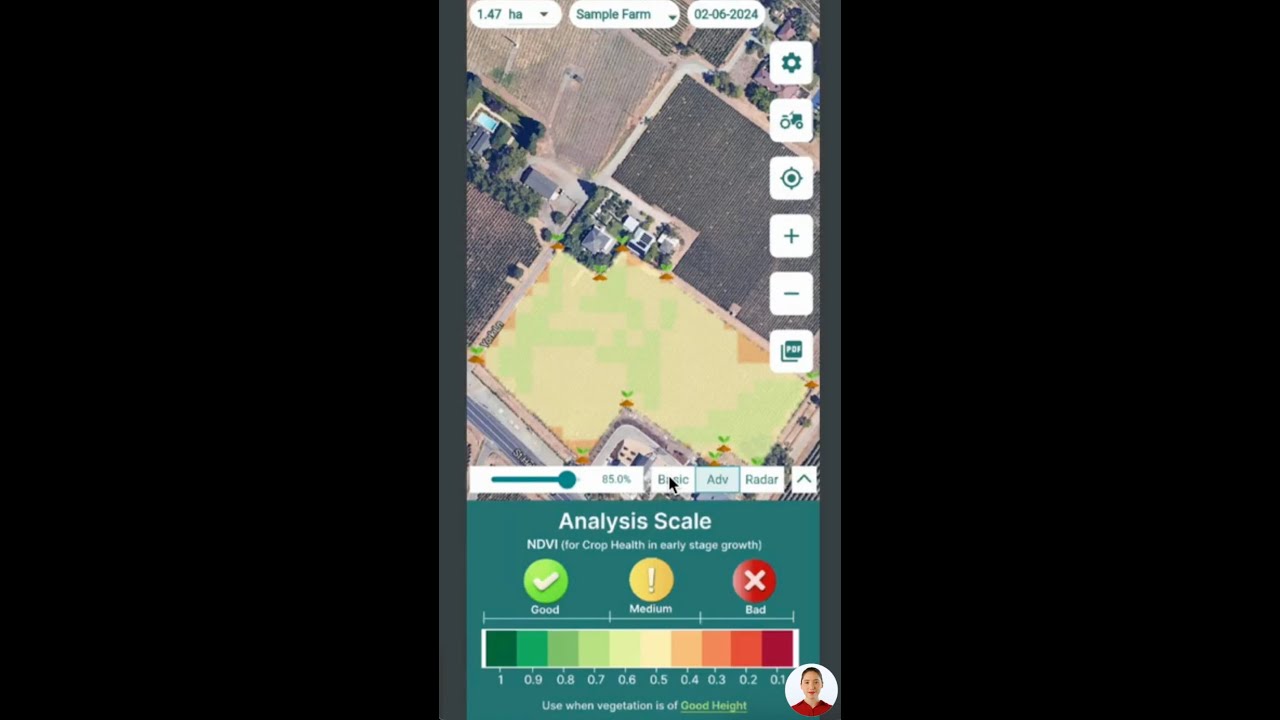
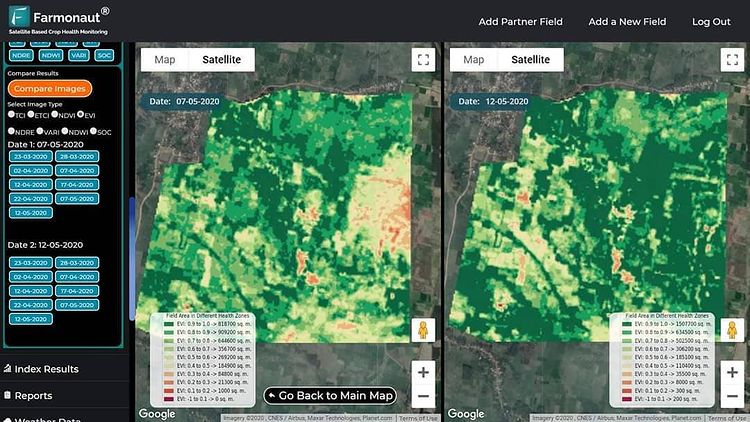
Farmonaut: Intelligent Crop Health and Aphid Management
For those aiming to implement data-driven aphid infestation solutions, Farmonaut offers a pioneering, satellite-powered platform for crop health monitoring, integrated pest management, and more.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: By analyzing multi-spectral imagery (e.g., NDVI), we can track vegetation health, spot early signs of aphid or pest damage, and manage our interventions accordingly.
- AI-Powered Farm Advisory: With Jeevn AI, receive customized recommendations for crop management—be it pest and disease risks, or optimized watering/fertilizer application.
- Blockchain Traceability: Using Farmonaut’s product traceability system, every input and intervention (pest control, fertilizer, irrigation) can be transparently recorded—boosting food safety and trust for the end-consumer.
- Intelligent Resource Management: Fleet management features help optimize equipment use for spraying or mechanical removal, reducing operational waste.
- Sustainability & Carbon Footprinting: Track your carbon footprint in real time and adopt climate-smart pest management methods to achieve long-term agricultural resilience.
- Access via Any Device: Easily manage your farm from anywhere through our web or mobile apps.
- API Access: Integrate satellite and weather data for aphid modeling and smart pest management into your own farm systems using our API. Developers can access our full API documentation here.
With Farmonaut, smallholder farmers, large agribusinesses, and government agencies can optimize aphid control, reduce crop losses, and promote ecologically sustainable agriculture.
FAQs: Organic Aphid Control & Aphid Management
What are the fastest natural ways to control aphids on plants?
For urgent reduction, spraying aphids with a jet of water, hand-removal, and insecticidal soap give immediate results. Encourage ladybugs and lacewings for longer-term management.
How do I use neem oil for aphids?
Mix 1-2 teaspoons neem oil with 1 liter of water plus a drop of liquid soap. Spray this on affected plant areas every 7-10 days or after rain, coating both upper and lower leaf surfaces.
Can I use chemical aphid insecticides in an organic system?
Only certified organic insecticides, such as neem oil and insecticidal soap, should be used in organic production. Synthetic chemical pesticides are not permitted under organic certification standards.
What are the signs of aphid feeding damage?
Look for curling, stunted, or yellowing leaves, sticky honeydew deposits, and the presence of sooty mold. Aphids often cluster on young shoots and the undersides of leaves.
How does Farmonaut help with aphid infestation solutions?
Farmonaut’s technology helps monitor plant health and vegetation stress, which can signal aphid or pest outbreaks before visible damage occurs. This supports timely, targeted intervention using sustainable methods.
Is integrated pest management for aphids suitable for large farms?
Yes. IPM scales easily—from home gardens to large commercial operations—and integrates local monitoring, biological control, and smart resource use to reduce pest impact and environmental harm.
Conclusion: Sowing the Seeds of Healthy, Sustainable Crops
Implementing organic aphid control is more than protecting crops—it’s about embracing resilient agriculture, supporting beneficial insects, minimizing pollution, and leaving a lighter environmental footprint.
By weaving together cultural, biological, mechanical, and natural insecticidal methods—and leveraging integrated crop management solutions like Farmonaut—we give ourselves the tools to tackle aphids and similar pests sustainably. Through continuous monitoring, early action, and ecological wisdom, our fields will thrive for seasons to come.
Ready to defend your crops naturally? Get started with Farmonaut’s precision crop monitoring and management platform now—and harness the power of technology and nature for healthy, productive fields.