Agricultural Biologicals: 7 Game-Changers for Farmers
Introduction: The Rise of Agricultural Biologicals
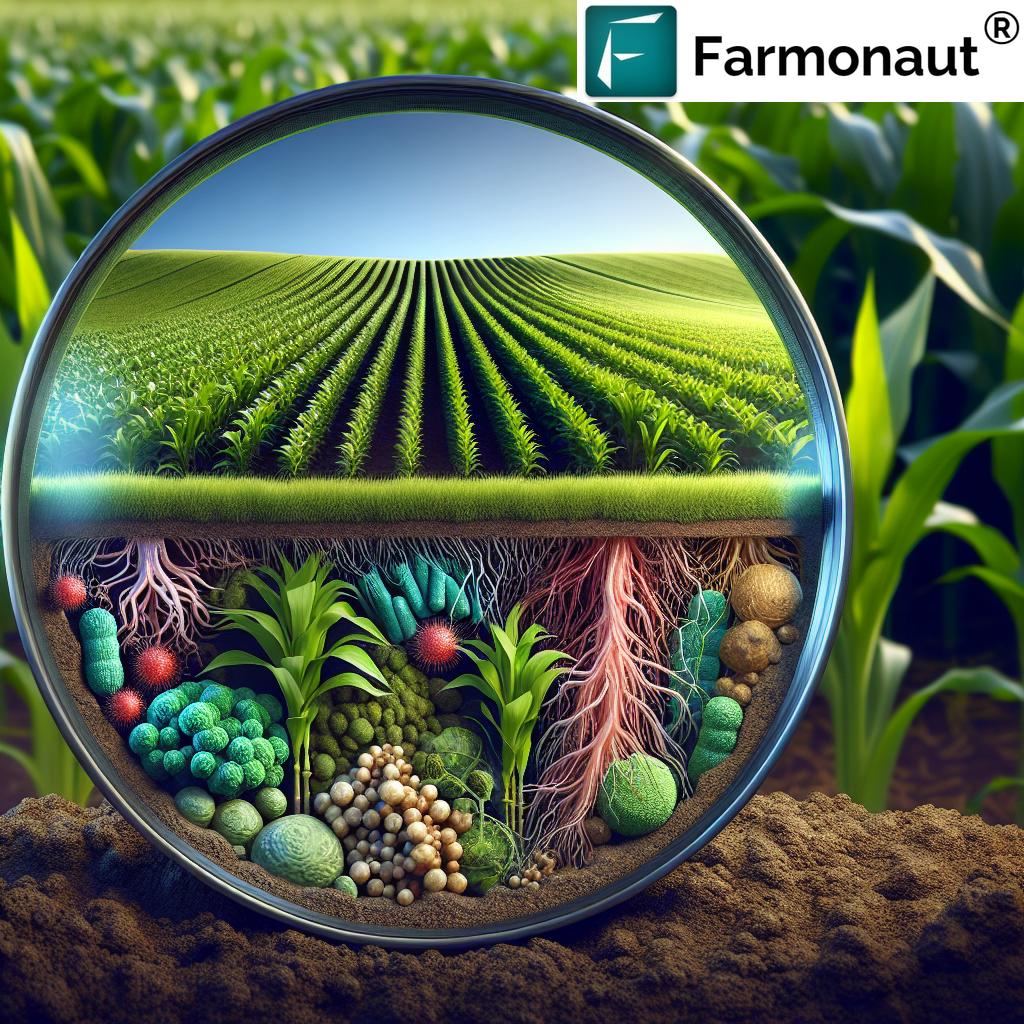
In every corner of modern agriculture, farmers and agricultural professionals like us face mounting pressure to deliver higher crop productivity while minimizing harm to the environment. Agricultural biologicals have emerged as powerful, natural alternatives to conventional chemical inputs. Derived mainly from microorganisms, plants, and other naturally occurring substances, they are instrumental in improving plant growth, boosting soil health, and enabling farmers to manage pests and diseases more sustainably. This aligns perfectly with the global shift toward sustainable farming practices—and especially with the principles of regenerative agriculture solutions.
Our goal is to explore the wide-ranging impact of agricultural biologicals—focusing on the major categories: biopesticides, biofertilizers, and plant biostimulants. We’ll delve into their development, application, game-changing benefits, and regulatory landscape—painting a comprehensive picture of their role in modern agriculture. Plus, we’ll share how Farmonaut’s tech-driven, satellite-based solutions integrate seamlessly into these biological approaches, maximizing sustainability and crop productivity for farmers worldwide.
Categories of Agricultural Biologicals:
Understanding Biopesticides, Biofertilizers, and Biostimulants
Agricultural biologicals are primarily classified into three categories. Each category aligns closely with our objectives of regenerative agriculture and improving soil and plant health for lasting farm productivity.
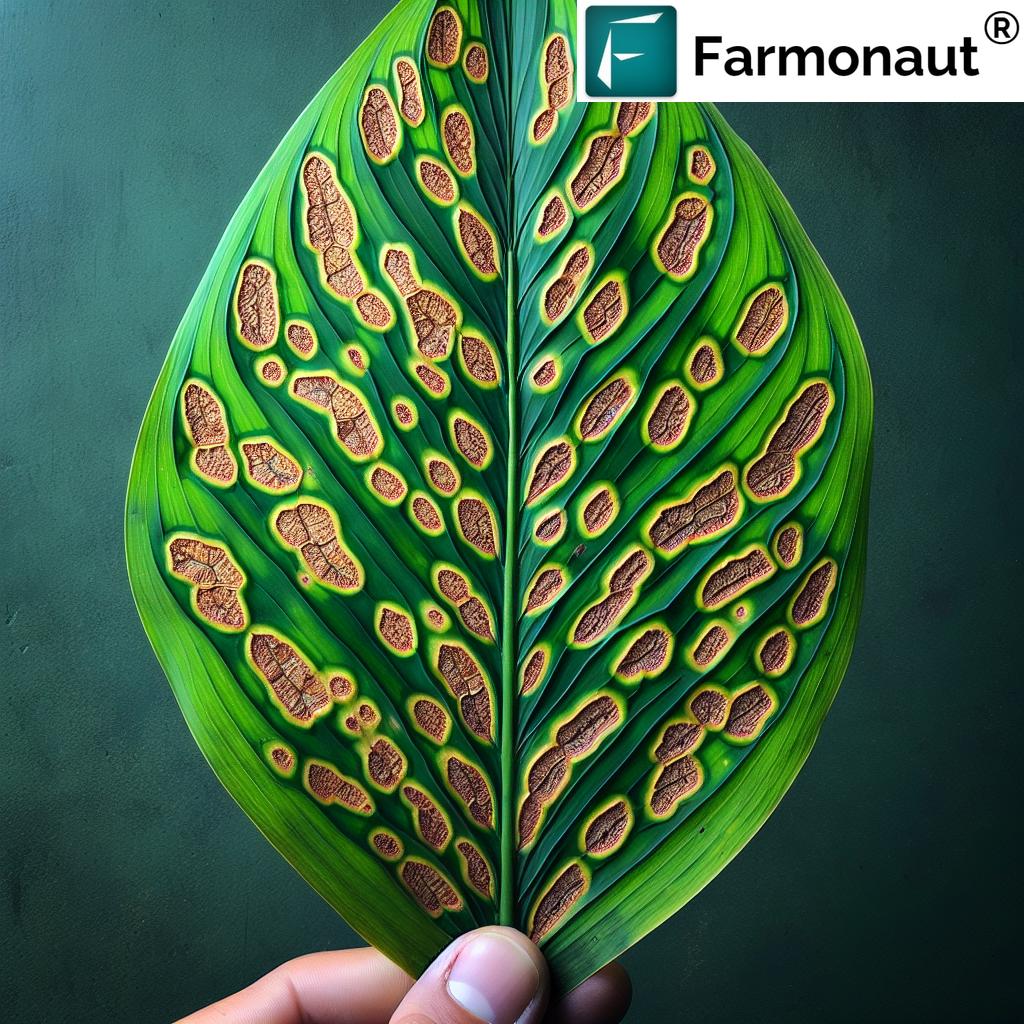
1. Biopesticides for Pest Management
Biopesticides are natural substances, extracts, or beneficial microorganisms utilized to control pests and diseases. Let us break down the major types:
- Microbial Pesticides: Used against specific pest or disease targets. These originate from beneficial bacteria (like Bacillus thuringiensis), fungi, or viruses that infect and manage harmful organisms with precision, lessening collateral damage to beneficial insects or microbes.
- Biochemical Pesticides: Naturally occurring substances (like plant extracts or pheromones) that influence pest behavior. Pheromones can disrupt mating cycles, reducing infestation without toxic chemicals.
- Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs): These are genetically modified plants that produce substances toxic only to specific pests, reducing the need for chemical sprays.
By embracing biopesticides for pest management, we can manage resistance and limit environmental harm—integral to sustainable farming practices.
2. Biofertilizers for Soil Health
Biofertilizers are formulations containing living microorganisms that—when applied to seed, soil, or plants—enhance the nutrient availability for crop growth. Their main types:
- Nitrogen Fixers (e.g., Rhizobium): Convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for plants—ensuring a natural increase in soil fertility and minimizing synthetic fertilizer use.
- Phosphate Solubilizers: Make otherwise inaccessible phosphorus compounds available for plant uptake, supporting strong root growth and development.
- Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): Use diverse mechanisms to stimulate growth, defend against diseases, and promote overall plant resilience.
With biofertilizers for soil health, we embrace natural alternatives to chemical fertilizers, restoring soil vitality and aligning with regenerative agriculture solutions.
3. Plant Biostimulants
Biostimulants are substances or living microbes that, when applied to plants or soils, stimulate natural processes—enabling enhanced nutrient uptake, stress tolerance, and growth. These include:
- Microbial Biostimulants: Beneficial microbes that improve root structure, soil structure, and resilience against environmental stress like drought or salinity.
- Natural Product Biostimulants: Derived from seaweed extracts, humic substances, and other organic materials to promote plant health naturally.
Using plant biostimulants, we can actively improve crop productivity naturally—a foundation of environmental stewardship in farming.
Maximize the Impact of Biologicals with Farmonaut
-
Carbon Footprinting Tool:
Want to ensure that adopting agricultural biologicals also slashes your carbon emissions? Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool tracks emissions and guides you on strategies for environmental sustainability. -
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability:
Guarantee transparency and trace your biological applications through the supply chain with Farmonaut’s secure, blockchain-integrated traceability solutions—especially vital for proving the regenerative impact of your practices. -
Fleet and Resource Management:
Applying biologicals over large or fragmented fields? Farmonaut’s fleet management system optimizes logistics and ensures timely applications for best results. -
Satellite-Based Crop Loan & Insurance:
Secure finance easily as you transition to biologicals—Farmonaut enables smooth verification for crop loans and insurance using satellite data.
7 Game-Changers for Farmers: The Most Impactful Agricultural Biologicals
Let’s highlight seven of the most impactful biologicals revolutionizing modern agriculture, enabling us to enhance crop productivity, manage pests sustainably, improve soil health, and support regenerative agriculture solutions on every farm.
-
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) – The Precise Biopesticide
Type: Microbial biopesticide
Main Benefit: Effective, targeted pest control against caterpillar larvae without harming beneficial insects or leaving toxic residues.
Mode of Action: Bt bacteria produce proteins toxic only to specific insect pests; safe for humans, animals, and most beneficial species.
Impact: Drastically reduces reliance on chemical pesticides while helping manage pest resistance. -
Azospirillum – Nitrogen-Fixing Biofertilizer
Type: Biofertilizer
Main Benefit: Converts atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants, especially vital for cereals and legumes.
Mode of Action: Colonizes plant roots and establishes a symbiotic relationship, providing continual nitrogen enrichment.
Impact: Decreases need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers—leading to improved soil health and fertility in regenerative systems. -
Trichoderma harzianum – Biocontrol Fungus
Type: Microbial biopesticide/biostimulant
Main Benefit: Controls soil-borne pathogens (like Fusarium, Pythium, and Rhizoctonia) and enhances root development.
Mode of Action: Outcompetes, attacks, or produces substances that inhibit plant pathogens; boosts plant growth indirectly.
Impact: Dual action: protects against diseases and stimulates resilient plant growth. -
Pseudomonas fluorescens – Disease-Suppressing Bacteria
Type: PGPR biofertilizer/biocontrol
Main Benefit: Suppresses fungal diseases and stimulates plant immunity.
Mode of Action: Produces antibiotics and enzymes that inhibit pathogens; colonizes roots to stimulate robust plant health.
Impact: Useful in integrated pest management for disease-prone crops. -
Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria – Boosting Phosphorus Uptake
Type: Biofertilizer
Main Benefit: Mobilizes phosphorus for plant use; reduces dependence on mined phosphate fertilizers.
Mode of Action: Secretes organic acids and enzymes to break down insoluble phosphorus compounds.
Impact: Strengthens root development and crop resilience. -
Seaweed Extracts – Nature’s Biostimulant
Type: Natural product biostimulant
Main Benefit: Promotes plant growth, increases stress tolerance, and enhances yield and quality.
Mode of Action: Rich in phytohormones, micronutrients, and stress-mitigating compounds.
Impact: A sustainable input that supports overall farm resilience. -
Pheromones for Mating Disruption
Type: Biochemical biopesticide
Main Benefit: Disrupts pest mating cycles, reducing pest outbreaks without harming beneficial insects or pollinators.
Mode of Action: Synthetic copies of natural pheromones are released to confuse male insects.
Impact: Reduces pest populations effectively and safely—ideal for environmental sustainability in crop management.
Development & Application of Agricultural Biologicals
The development of biologicals is a carefully orchestrated, science-driven process, involving these key steps:
- Isolation & Cultivation: Scientists identify desirable microorganisms or natural materials from soil, plants, or other sources, then multiply them under controlled conditions.
- Fermentation: Production is scaled up using fermentation tanks, ensuring sufficient, high-quality biological actives for broad agricultural application.
- Formulation: Biologicals are processed into stable products (liquids, powders, granules) for easy on-farm use.
- Stabilization: Preservation techniques maintain activity during storage and shipping, maximizing shelf life and effectiveness—even under tough field conditions.
Application methods vary by biological type and crop target:
- Seed Treatments: Early inoculation delivers protective and growth-boosting microbes straight to the emerging plant—excellent for defense and early vigor.
- Soil Applications: Direct soil incorporation (as in compost teas or granular products) enhances microbial cycling and nutrient availability.
- Foliar Sprays: Application to plant leaves with biopesticides, biostimulants, or disease-suppressing microbes for immediate protective or growth-stimulating effects.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Tools, we can plan and monitor biological applications across hundreds to thousands of hectares—optimizing results and driving sustainable farming practices at scale.
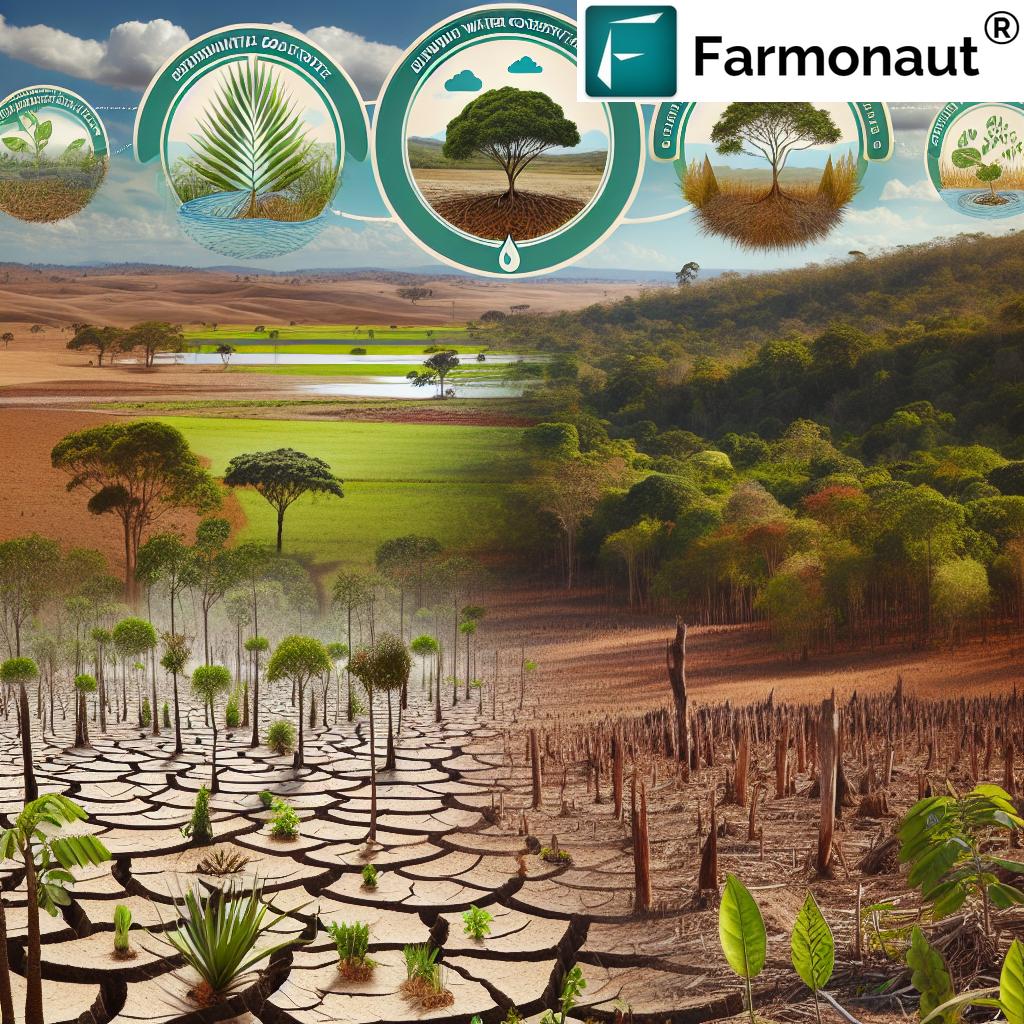
Benefits of Agricultural Biologicals in Regenerative Agriculture
The adoption of agricultural biologicals unlocks a wide array of environmental, agronomic, and economic benefits for every farmer committed to sustainability:
- Environmental Sustainability: Natural alternatives to chemical pesticides and fertilizers dramatically lower pollution, enhance biodiversity, and restore the ecological balance of our farm ecosystems.
- Soil Health & Fertility: Biofertilizers and biostimulants rejuvenate soil with living microbes, improving organic matter, nutrient cycles, and soil structure.
- Pest and Disease Resistance Management: Biopesticides for pest management utilize diverse, specific modes of action—helping us manage resistance and reducing outbreaks caused by “superbugs.”
- Increased Crop Productivity: Biologicals stimulate plant growth, enhance nutrient uptake, and improve stress tolerance—leading to higher quality and quantity yields, naturally.
- Resilience to Stress: With the help of biostimulants and PGPRs, plants become more resilient to drought, heat, and other environmental stresses—key in a changing climate.
By integrating advanced satellite-based Farmonaut API solutions, data-driven biological adoption can be planned, monitored, and optimized—guaranteeing the maximum environmental and yield benefits.
Market Trends and Economic Impact of Agricultural Biologicals
The demand for agricultural biologicals is soaring worldwide—fueled by consumers, governments, and the farming community seeking increased sustainability and resilience in food production. According to MarketsandMarkets, the market is expected to jump from USD 16.67 billion in 2024 to USD 31.84 billion by 2029, with a CAGR of 13.8% ([marketsandmarkets.com](https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/agricultural-biological-market-100393324.html?utm_source=openai)).
Major crop protection companies are expanding their biological portfolios, and governments are offering incentives for regenerative farming. The move toward sustainable farming practices is no longer a trend—it’s a necessity shaping the future of agriculture.
Comparative Table: The 7 Agricultural Biologicals
| Biological Product Name | Type | Main Benefit | Mode of Action | Estimated Soil Health Improvement (%) | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) | Microbial Biopesticide | Targeted insect pest control | Produces insect-specific toxins | +15% | +8-15% | Reduces synthetic pesticide use by 40-60% |
| Azospirillum | Nitrogen-fixing Biofertilizer | Atmospheric nitrogen fixation | Symbiotic root colonization | +25% | +10-22% | Minimizes need for chemical N fertilizers |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Microbial Biopesticide/Biostimulant | Disease suppression & root stimulation | Parasitizes plant pathogens | +20% | +10-18% | Decreases soil disease load naturally |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | PGPR Biofertilizer/Biocontrol | Fungal disease suppression, plant immune boost | Produces antibiotics, root colonization | +18% | +9-14% | Enhances resilience with microbial solutions in agriculture |
| Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria | Biofertilizer | Boosts phosphorus uptake | Dissolves soil P compounds | +22% | +12-19% | Reduces phosphate fertilizer dependency |
| Seaweed Extracts | Biostimulant | Improves growth & stress tolerance | Contains growth hormones/minerals | +17% | +10-20% | Bio-based, supports organic farming |
| Pheromones | Biochemical Biopesticide | Disrupts pest mating cycles | Mimics insect communication signals | +10% | +6-10% | Eco-friendly, no residue or non-target effects |
Regulatory Landscape: Ensuring Responsible Use of Biologicals
The regulation of agricultural biologicals is critical for ensuring their safety and efficacy:
-
United States: Biopesticides are regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). Biofertilizers and biostimulants are generally subject to state-level registration and oversight.
(Read more) -
European Union: Biopesticides fall under Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 for Plant Protection Products, while biofertilizers and biostimulants are subject to the Fertilizers Regulation (EU) 2019/1009, ensuring distinct compliance pathways for each category.
(Read more)
These regulatory frameworks are essential for facilitating the adoption of biologicals without compromising safety, transparency, or efficacy.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While agricultural biologicals are transforming how we grow food, several challenges remain as we scale up their use:
- Performance Variability: Effectiveness often depends on environmental conditions—from temperature and moisture to microbial community interactions.
- Shelf Life Constraints: Many biological products have modest shelf lives, requiring precise storage and logistics planning, especially in remote or hot climates.
- Higher Initial Costs: Upfront expenses are sometimes higher than conventional inputs, although long-term gains in productivity and sustainability far outweigh these costs.
Looking ahead, integrating biologicals with advanced farm management, AI, and satellite-based monitoring platforms—like those offered by Farmonaut—will be crucial for:
- Customized, site-specific application of biologicals
- Maximizing return on investment for regenerative transitions
- Adapting integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to dynamic pest and disease pressures globally
The future of agriculture is data-driven, sustainable, and deeply connected to natural biological processes that enhance both productivity and environmental health.
Empowering Sustainable Farming with Farmonaut’s Technology
At Farmonaut, our vision is to create the future of sustainable agriculture by integrating the latest biological solutions with next-generation technology. Our platform offers:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Use AI-powered apps to monitor plant health, spot early pest and disease outbreaks, and tailor biological applications for maximum benefit—right from your smartphone or desktop.
- AI-Driven Farm Advisory (Jeevn): Get real-time, customized guidance for your farm—making it simple to plan targeted uses of biopesticides, biofertilizers, and biostimulants.
- Blockchain Traceability: Guarantee authenticity and transparency in your biological applications with Farmonaut’s traceability solution.
- Carbon Footprinting & Sustainability: Measure and minimize your farm’s carbon footprint as you transition to biological-based, regenerative systems. Learn more about our carbon footprinting tools.
-
Resource Management APIs: Integrate satellite, weather, and advisory insights into your own agriculture tools using our flexible
Farmonaut API.
Get Started with Farmonaut: Subscription Options
Ready to boost your biologicals adoption and farm sustainability? Farmonaut operates on a flexible subscription-based model, accessible for individual farmers, agribusinesses, NGOs, and more. Choose the package that fits your acreage and data needs—without high upfront cost.
FAQ: Agricultural Biologicals & Their Role in Sustainability
1. What are agricultural biologicals, and why should we use them?
Agricultural biologicals are natural solutions derived from microorganisms, plants, and animals. They enhance plant growth, manage pests, and improve soil health—offering sustainable alternatives to synthetic chemicals and fertilizers, especially in regenerative farming systems.
2. How do biopesticides for pest management differ from conventional pesticides?
Biopesticides are usually target-specific and naturally derived, leaving minimal residues and protecting beneficial species. They have a lower risk of resistance buildup and do not harm pollinators or soil life, making them central to sustainable farming practices.
3. What is the main benefit of biofertilizers for soil health?
Biofertilizers contain living microorganisms like nitrogen fixers and phosphate solubilizers. They naturally increase nutrient availability, restore soil fertility, and reduce dependency on synthetic inputs—crucial for improving long-term soil health.
4. How are plant biostimulants used in regenerative agriculture?
Plant biostimulants enhance natural plant processes, improving nutrient uptake and making crops more resilient to stress. They support higher yield and quality, playing a pivotal role in regenerative agriculture solutions and sustainable food production.
5. How does Farmonaut help us optimize the impact of agricultural biologicals?
Farmonaut delivers real-time crop and soil insights using satellite imagery, AI advisories, and traceability tools—helping us plan, monitor, and measure the effectiveness of biological applications for maximum sustainability impact.
6. Are there limitations or risks associated with adopting biologicals?
While highly beneficial, biologicals can sometimes show variability depending on storage, handling, and field conditions. Selecting the right products, proper application timing, and close monitoring (using platforms like Farmonaut) help maximize success.
7. Where can we learn more about tech-driven solutions for biological and regenerative agriculture?
Explore Farmonaut’s web and mobile platforms for advanced crop monitoring, traceability, resource management, and more. Start here.
Conclusion: Agricultural Biologicals—The Key to Regenerative, Sustainable Farming
The adoption of agricultural biologicals—including biopesticides, biofertilizers, and biostimulants—offers a revolutionary path to improving farm productivity, soil health, and environmental sustainability. By leveraging these natural alternatives, we can manage pests and diseases, enhance nutrient cycling, support biodiversity, and boost resilience against climatic and resource pressures. Powered by precise, data-driven management via Farmonaut’s affordable, accessible technologies, every farmer and enterprise can confidently join the movement toward a regenerative agricultural future.
Build a healthier farm and a better world—embrace agricultural biologicals and Farmonaut innovation today!