American Bollworm: Identification, Damage, and Symptoms in Tomatoes and Other Crops

As agricultural experts and representatives of Farmonaut, we understand the critical importance of pest management in ensuring optimal crop yields and maintaining the health of your fields. One of the most significant pests that farmers and horticulturists face is the American bollworm, scientifically known as Helicoverpa armigera. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of the American bollworm, exploring its identification, the damage it causes, and the symptoms it presents in various crops, with a special focus on tomatoes.
Understanding the American Bollworm
The American bollworm, despite its name, is a pest that affects crops worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. It’s known for its voracious appetite and ability to damage a wide variety of crops, making it a significant concern for farmers across the globe.
Taxonomy and Distribution
- Scientific Name: Helicoverpa armigera
- Common Names: American bollworm, cotton bollworm, corn earworm
- Distribution: Found in Africa, Asia, Europe, and Oceania
The American bollworm is part of the Noctuidae family, which includes many other destructive moth species. Its widespread distribution and ability to adapt to various climates make it a formidable pest for farmers worldwide.
American Bollworm Identification
Proper American bollworm identification is crucial for effective pest management. The pest goes through several life stages, each with distinct characteristics:
Egg Stage
- Small, spherical eggs (about 0.5mm in diameter)
- Initially white, turning brown before hatching
- Usually laid singly on leaves or flowers
Larval Stage
- Newly hatched larvae are 1-1.5mm long
- Color varies from green to brown, with distinctive light and dark stripes
- Fully grown larvae can reach 30-40mm in length
- Characterized by tiny black spots on the body segments
Pupal Stage
- Brown, smooth-surfaced pupae
- Usually found in the soil
- 14-18mm in length
Adult Stage
- Moths with a wingspan of 30-45mm
- Forewings are yellowish-brown with dark spots
- Hindwings are pale with a dark border
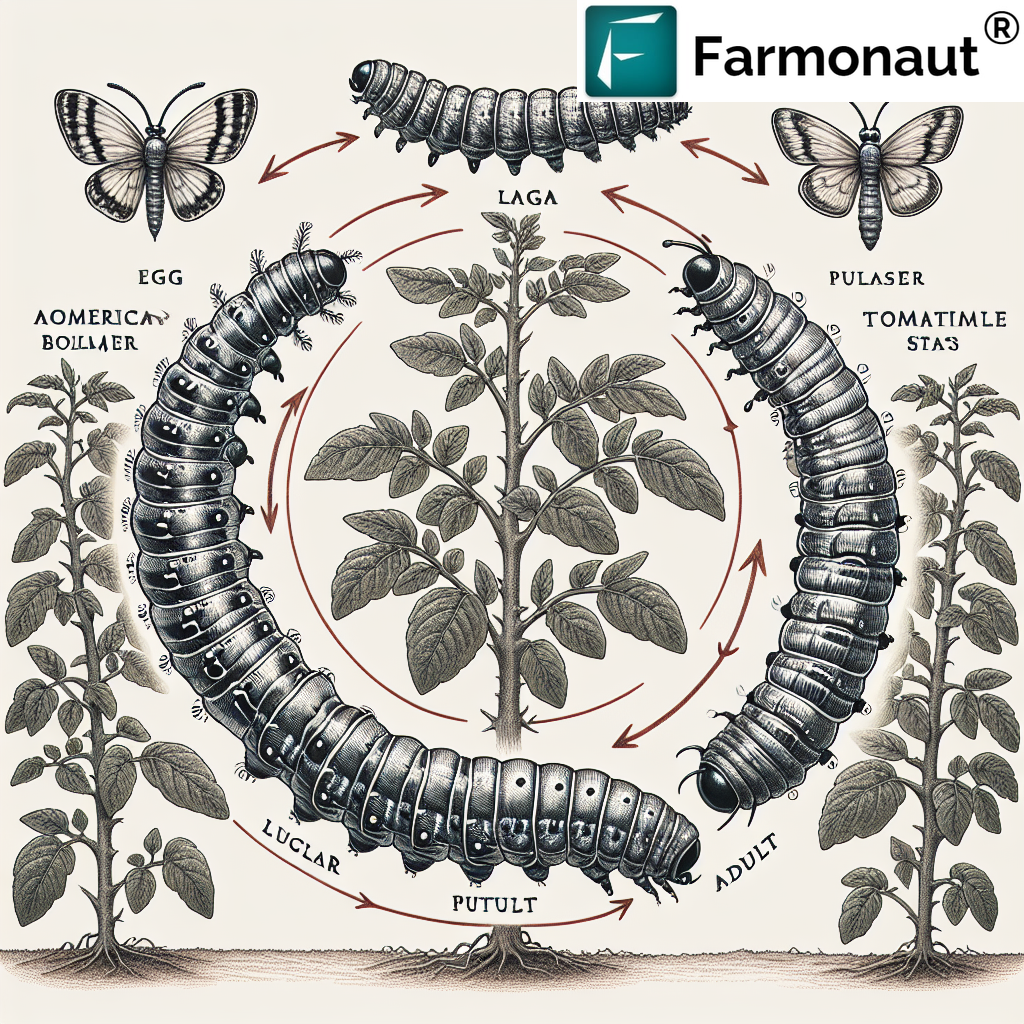
This American bollworm diagram illustrates the different life stages of the pest, aiding in accurate identification.
American Bollworm Damage
The American bollworm damage can be extensive and devastating to crops. Understanding the nature of this damage is crucial for early detection and effective management.
General Damage Characteristics
- Larvae feed on leaves, flowers, and fruits
- Circular holes in leaves and fruits
- Wilting of young shoots
- Premature fruit drop
- Secondary fungal and bacterial infections at damage sites
Crop-Specific Damage
The American bollworm is a polyphagous pest, meaning it can feed on various plant species. Here’s how it affects different crops:
Cotton
- Feeding on squares (flower buds) and bolls
- Circular holes in bolls, often leading to rot
- Significant yield reduction and quality degradation
Corn
- Damage to silk and developing kernels
- Entry holes at the tip of the ear
- Increased susceptibility to fungal infections
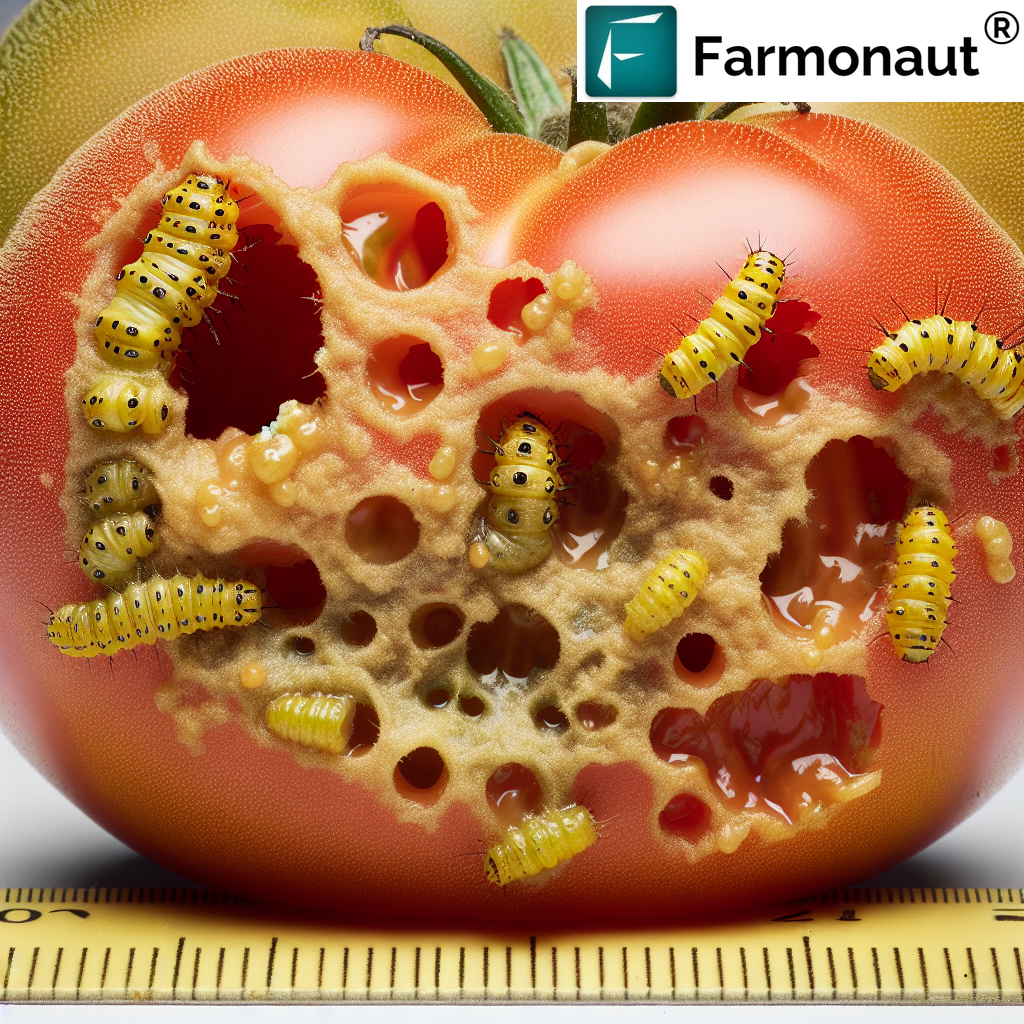
Tomatoes
- Feeding on leaves, flowers, and fruits
- Circular holes in fruits, often near the calyx
- Internal fruit damage, making them unmarketable
Chickpeas and Pigeon Peas
- Damage to pods and developing seeds
- Significant yield losses in severe infestations
American Bollworm in Tomatoes
The presence of American bollworm in tomatoes is particularly concerning due to the high value of the crop and the visible damage caused by the pest. Let’s explore this in more detail:
Why Tomatoes are Susceptible
- Soft fruit structure makes it easy for larvae to penetrate
- Rich nutrient content attracts the pest
- Long fruiting period provides continuous food source
Specific Damage to Tomatoes
- Circular entry holes, often near the calyx
- Internal fruit damage, making them unmarketable
- Premature fruit drop
- Secondary infections leading to fruit rot
Economic Impact
The economic impact of American bollworm on tomato crops can be severe:
- Yield losses of up to 50% in severe infestations
- Reduced market value due to fruit damage
- Increased production costs for pest management
American Bollworm Symptoms
Recognizing American bollworm symptoms early is key to effective management. Here are the primary symptoms to look out for:
Foliar Symptoms
- Irregular holes in leaves
- Skeletonized leaves in severe infestations
- Wilting of young shoots
Fruit Symptoms
- Circular entry holes on fruits
- Presence of frass (insect excrement) near entry points
- Internal rotting of fruits
- Premature fruit drop
Plant Growth Symptoms
- Stunted growth in heavily infested plants
- Reduced flowering and fruit set
- Overall decline in plant vigor
Management Strategies for American Bollworm
Effective management of American bollworm requires an integrated approach. Here are some strategies that we at Farmonaut recommend:
Cultural Control
- Crop rotation with non-host plants
- Early planting to avoid peak pest populations
- Removal and destruction of infested plant parts
- Proper field sanitation to reduce overwintering populations
Biological Control
- Use of natural predators like ladybirds and lacewings
- Application of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) formulations
- Release of parasitic wasps like Trichogramma species
Chemical Control
- Use of selective insecticides to preserve beneficial insects
- Rotation of insecticide classes to prevent resistance
- Timing applications to target the most vulnerable life stages
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
At Farmonaut, we strongly advocate for an Integrated Pest Management approach, which combines various control methods for sustainable and effective pest control. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help in early detection of pest infestations, allowing for timely interventions.
The Role of Technology in Pest Management
Modern technology plays a crucial role in effective pest management, particularly in the early detection and monitoring of pests like the American bollworm. At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced satellite technology to provide farmers with real-time insights into their crop health.
Satellite-Based Monitoring vs. Traditional Methods
Here’s how Farmonaut’s Satellite System compares to traditional monitoring methods:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large (Entire farm at once) | Medium | Limited (Point-based) |
| Frequency of Data | Every 3-5 days | On-demand (Weather dependent) | Continuous |
| Cost-effectiveness | High | Medium | Low (High initial investment) |
| Ease of Use | High (No on-field equipment needed) | Medium (Requires skilled operator) | Medium (Requires installation and maintenance) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI-powered analytics | Requires separate analysis tools | Often limited to basic metrics |
Our satellite-based system offers comprehensive coverage, frequent updates, and advanced analytics, making it an ideal choice for modern farmers looking to stay ahead of pest problems.
Farmonaut’s Solutions for Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we offer a range of solutions to help farmers combat pests like the American bollworm effectively:
- Real-time Crop Health Monitoring: Our satellite imagery provides up-to-date information on crop health, helping detect potential pest infestations early. Learn more about our app.
- AI-powered Advisory System: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized recommendations for pest management based on your specific crop and location.
- Weather Forecasting: Accurate weather predictions help you time your pest control measures for maximum effectiveness. Check out our Weather API documentation.
- Data Integration: Our system can integrate with your existing farm management tools. Explore our API options.
Download our app for Android or iOS to get started with smart pest management today.
Conclusion
The American bollworm remains a significant threat to various crops, particularly tomatoes. By understanding its lifecycle, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing a comprehensive management strategy, farmers can minimize the damage caused by this pest. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing cutting-edge technology solutions to support farmers in their pest management efforts.
Remember, early detection and prompt action are key to controlling American bollworm infestations. By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring system, you can stay one step ahead of pest problems, ensuring healthier crops and better yields.
FAQs
- Q: How can I distinguish American bollworm damage from other pest damage?
A: American bollworm damage is characterized by circular holes in fruits and leaves, often accompanied by frass near the entry points. The presence of the distinctive caterpillars with light and dark stripes is also a key identifier. - Q: Are there any resistant varieties of tomatoes against American bollworm?
A: While there are no completely resistant varieties, some tomato cultivars show higher tolerance to American bollworm. Consult with local agricultural extension services for recommendations suitable for your region. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for American bollworm?
A: Regular monitoring, at least twice a week during the growing season, is recommended. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can get updates every 3-5 days without manual field inspections. - Q: Can American bollworm develop resistance to pesticides?
A: Yes, American bollworm can develop resistance to pesticides if the same class of chemicals is used repeatedly. It’s important to rotate pesticides and integrate other control methods. - Q: How does climate change affect American bollworm populations?
A: Climate change can potentially expand the geographical range of American bollworm and increase the number of generations per year in some regions, making monitoring and management even more crucial.
For more information on how Farmonaut can help you manage pests like the American bollworm, check out our subscription options below:
By staying informed and utilizing advanced technologies, we can work together to minimize the impact of pests like the American bollworm and ensure sustainable, productive agriculture.





