Eco-Friendly Farming: 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Soil Health
“Cover crops can reduce soil erosion by up to 90%, significantly improving long-term soil health.”
- Introduction to Eco-Friendly Farming and Soil Health
- Core Principles of Eco-Friendly Farming
- 7 Powerful Eco-Friendly Farming Practices for Soil Health Improvement
- Comparative Table: Impact on Soil Health and Sustainability
- Key Benefits of Eco-Friendly Farming
- Unlocking Soil Health & Sustainability with Farmonaut
- Overcoming Challenges in Sustainable Agriculture
- FAQ: Sustainable & Eco-Friendly Farming
- Conclusion
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Farming and Soil Health
As we face increasing environmental and agricultural challenges worldwide, the importance of eco-friendly farming practices has never been more evident. Soil degradation, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity threaten the very foundation of our food systems. To meet these challenges, we must adopt sustainable agriculture that not only enhances food production but conserves natural resources, preserves ecosystems, and promotes the long-term health of our soil.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll discover seven powerful ways to boost soil health using sustainable, eco-friendly farming methods. By embracing these approaches, we can reduce our ecological footprint, improve soil fertility and water conservation, and foster resilient agricultural systems that sustain us for generations to come.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore core principles, practical solutions, key benefits, and even leverage cutting-edge technologies like those offered by Farmonaut—a pioneering agri-tech platform—for sustainable soil and resource management.
Core Principles of Eco-Friendly Farming
Transitioning to eco-friendly farming (or sustainable agriculture) means following principles that seek a balance between productivity, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility. Let’s look at the main guiding ideas behind soil health improvement:
- Conservation of Resources: We use natural resources—including water, soil, and nutrients—efficiently to reduce waste and protect local ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: By encouraging diverse species (plants, insects, and animals), we make our farms more resilient to pests, disease, and climate disruption.
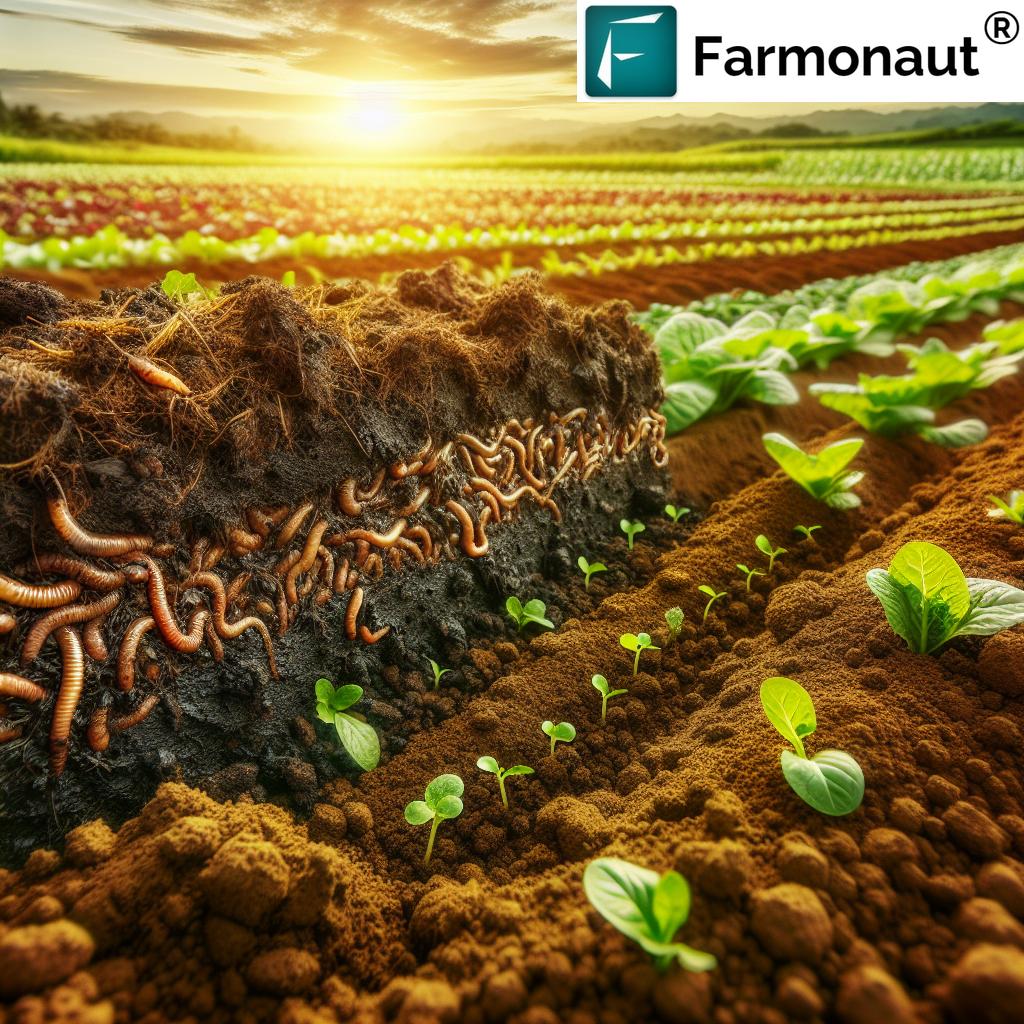
- Soil Health Maintenance: Implementing farming methods that protect and improve soil structure, quality, and fertility.
- Water Conservation: We adopt strategies for water conservation in farming such as rainwater harvesting for irrigation and efficient irrigation systems, reducing water waste and pollution.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combining biological, cultural, and physical controls to reduce dependence on chemical pesticides while safeguarding crops.
By weaving these principles into our everyday agricultural decisions, we improve soil and ecosystem health, enhance yield, and build resilience against climate adaptation challenges.
7 Powerful Eco-Friendly Farming Practices for Soil Health Improvement
Below, we dive into seven field-tested approaches that are transforming the landscape of agricultural sustainability and soil health improvement.
“Organic farming increases soil biodiversity by 30% compared to conventional methods, supporting more resilient ecosystems.”
-
No-Till Farming
No-till farming is a revolutionary sustainable agriculture method where we plant new crops directly into the residue of previous ones without turning (tilling) the soil. This preserves the natural structure and biodiversity of the soil, reduces erosion, and helps the land retain water.
- Reduces soil disturbance, protecting soil organisms and boosting organic matter levels.
- Improves water infiltration and conservation.
- Decreases fuel and labor costs; lowers carbon emissions.
- Keeps crop residue on top, acting as a mulch to reduce weeds and protect against moisture loss.
Want to monitor the transformation of your field’s soil after switching to no-till methods? Farmonaut’s satellite crop health monitoring is the answer. Our platform tracks NDVI, soil moisture, and crop status for powerful data-driven decisions. Explore the service through the Farmonaut App.
-
Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry is the deliberate integration of trees, shrubs, and crops in agricultural landscapes. These systems deliver a suite of ecological and economic benefits:
- Add shade, fix nitrogen, improve soil structure, and increase biodiversity in agriculture.
- Reduce wind and water erosion.
- Yield additional products (fruits, nuts, timber, and fodder) to diversify farm income.
- Support habitat for pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects.
Curious how agroforestry impacts long-term resource use, soil carbon content, or supports carbon footprinting? Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools let you track and optimize your farm’s environmental impact in real time.
-
Cover Cropping
Cover cropping means growing selected plants (like legumes, grasses, or radishes) during off-season periods or between cash crops. These living covers deliver tremendous value:
- Minimize soil erosion and nutrient loss.
- Suppress weeds and disrupt pest cycles.
- Fix atmospheric nitrogen (in the case of legumes), improving future soil fertility.
- Boost organic matter and soil quality.
Real-time insights on soil health gains from cover cropping can be accessed with Farmonaut’s analytics. Use our multispectral imagery to monitor root development, weed cover, and soil moisture.
-
Crop Rotation and Polyculture
Our commitment to crop rotation—systematically changing the types of crops grown in the same field over seasons—offers proven crop rotation benefits:
- Disrupts pest and disease cycles.
- Balances nutrient demands on the soil.
- Improves biodiversity and supports beneficial species.
- Polyculture—growing a mixture of crops—mimics natural systems, bringing ecosystem stability and resilience.
Are you looking to manage complex rotations and polyculture schemes over large areas? Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management App provides everything from crop mapping to yield tracking, so you stay ahead with smart, sustainable decisions.
-
Rainwater Harvesting for Irrigation
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainfall for future use in irrigation. Especially vital in regions struggling with water shortages, this method has multiple benefits:
- Lowers dependence on groundwater and local water supplies.
- Reduces runoff, erosion, and contamination from surface flow.
- Improves drought resilience by ensuring a sustainable water supply.
Curious about how rainwater harvesting can fit into your farm’s workflow and optimize water resource management? Our Farmonaut App tools offer invaluable support for efficient water use and monitoring.
-
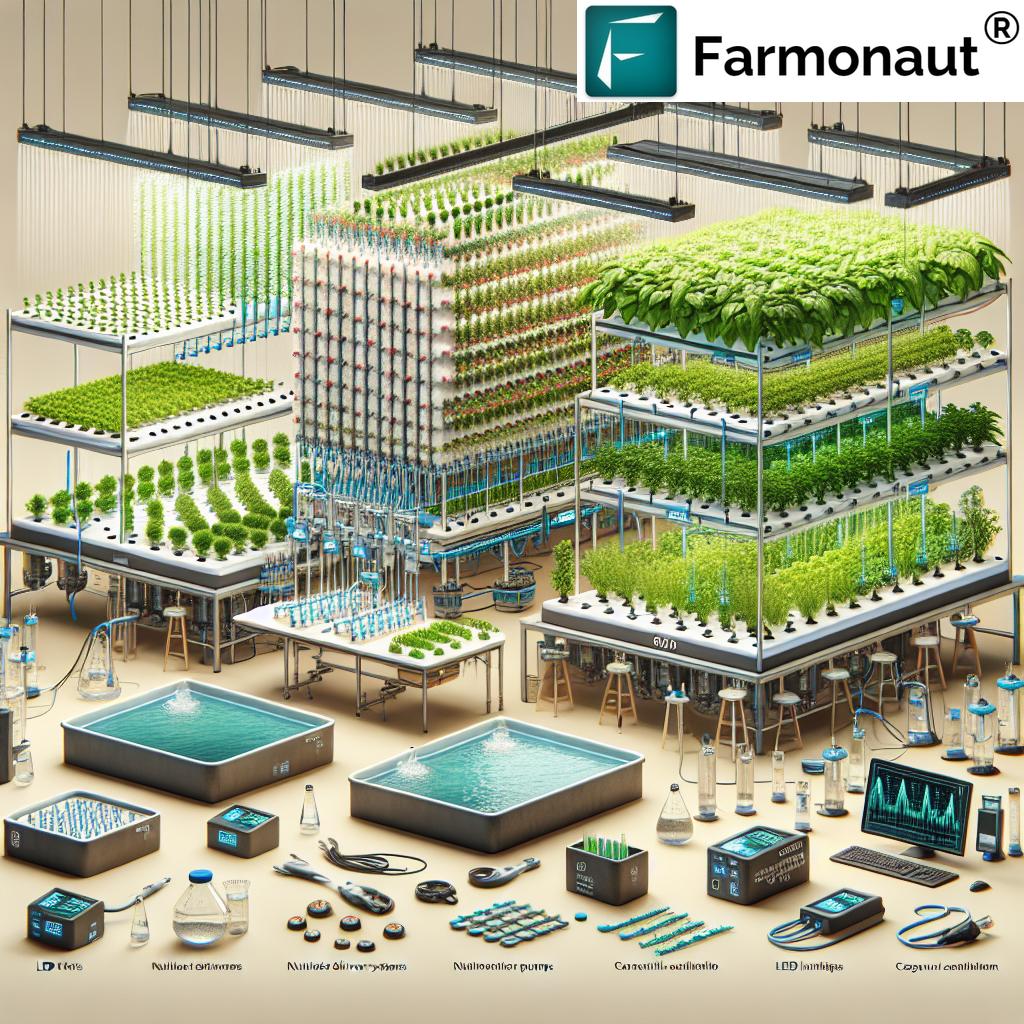
Aquaponics and Hydroponics: Soilless Techniques
Aquaponics and hydroponics are advanced, soilless techniques that allow us to grow crops with minimal water and land requirements, particularly thriving in urban or degraded environments.
- In hydroponics, crops grow in a nutrient-rich water solution; in aquaponics, fish and crops coexist, creating a closed-loop system.
- Use up to 90% less water than conventional farming.
- Produce food year-round, independent of soil quality.
- Limit pest pressures and offer controlled nutrient delivery for optimal growth.
At Farmonaut, we recognize the rise of innovative agriculture: use Farmonaut’s API for tailored integrations and resource monitoring across new-age farming systems.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated pest management uses a combination of biological, physical, and cultural tools to reduce reliance on synthetic pesticides.
- Regular monitoring and targeted interventions minimize chemical use.
- Encourages natural pest predators, preserves soil organisms, and supports biodiversity in agriculture.
- Reduces input costs and lowers chemical residues in food.
Use Farmonaut’s AI-based advisory system for personalized IPM strategies, in-field pest alerts, and resource management—maximize crop quality with less risk!
Eco-Friendly Farming Practices: Impact on Soil Health and Sustainability
| Practice Name | Method Description | Est. Soil Health Improvement (% over 5 yrs) | Biodiversity Impact | Water Conservation Potential | Crop Resilience Benefit | Sustainability Rating (1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Till Farming | Planting crops without disturbing the soil structure | +25–30% | High | Strong | Reduces erosion, stronger against drought | 5 |
| Agroforestry Systems | Integrating trees/shrubs with crops and/or livestock | +30–40% | Very High | Moderate | Supports microclimate, diverse yields | 5 |
| Cover Cropping | Growing cover plants between main crops | +20–25% | High | Good | Improves soil structure and pest resistance | 5 |
| Crop Rotation & Polyculture | Alternating multiple crops together or over seasons | +15–20% | Medium–High | Moderate | Reduces pest buildup, boosts recovery | 4.5 |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Collecting/storing rainwater for on-farm use | +5–10% | Low–Medium | Very High | Critical for drought resilience | 4 |
| Aquaponics & Hydroponics | Soilless growing with water/nutrients or closed-loop fish systems | Variable (up to +30% for degraded soils) |
Medium | Extremely High | Year-round, controlled conditions | 4.5 |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combining biological, physical, & cultural pest controls | +10–15% | High | Depends | Reduced pesticide risk, healthier plants | 5 |
Key Benefits of Eco-Friendly Farming
When we shift toward eco-friendly farming practices, we unlock value for our farms, our communities, and the planet as a whole. The primary outcomes include:
- Environmental Advantages:
- Improved soil quality (structural stability, organic matter, and fertility)
- Significantly higher biodiversity in agriculture
- Stronger water conservation in farming: efficient irrigation, groundwater protection, and drought resilience
- Carbon sequestration, reducing farm-level greenhouse gas emissions (farm carbon footprint tracking)
- Economic Sustainability:
- Reduced input costs and improved yields over time, even if some methods involve higher initial investments
- Opens doors to organic and local markets demanding sustainable products
- Minimizes long-term risks and provides additional income streams (timber, fruits, nuts, fish, etc.)
- Community and Social Well-Being:
- Promotes food security and better nutrition for local communities.
- Preserves local farming heritage and cultural practices.
- Improves overall social equity and farm worker well-being.
Organic food enthusiasts and large-scale cultivators alike benefit from greater transparency and consumer trust. Blockchain-based traceability from Farmonaut ensures origin and journey of harvests are verifiable.
Unlocking Soil Health & Sustainability with Farmonaut
To scale sustainable agriculture and precision resource management, it’s crucial to harness advanced technology. This is where Farmonaut stands apart as a leader in agricultural technology.
Farmonaut’s Key Technologies:
- Satellite-Based Farm Health Monitoring: Track crop health, soil moisture, and vegetation indexes (like NDVI) remotely, helping us reduce waste and target interventions for maximum soil health improvement.
- AI-Based Advisory (Jeevn AI): Receive instant, tailored recommendations for irrigation, fertilization, integrated pest management, and more directly from your phone or web browser.
- Blockchain Traceability: Ensure every harvest reaches the market with full transparency, building trust for organic and local market participants with Farmonaut.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Optimize and track transportation, inputs, vehicles, and machinery for reduced emissions and cost-effective operations. See Fleet Management Solutions
- Farm Carbon Footprinting: Assess and track emissions, take action on sustainability and compliance in line with environmental standards. Explore Carbon Tracking Tools
Whether you’re an individual farmer, an agribusiness, a government body, or seeking to build integrated solutions via APIs, Farmonaut’s modular, scalable platforms support you at every level of your eco-friendly farming journey.
Overcoming Challenges in Sustainable Agriculture & Soil Health Improvement
While the benefits of eco-friendly farming are immense, making the switch can introduce several challenges:
- Learning Curve: New methods—like cover cropping, no-till, and IPM—may require updated knowledge and continuous learning.
- Initial Investments: Practices such as rainwater harvesting systems, hydroponics setups, or transitioning to organic certification may require up-front costs.
- Market Access: Farmers may face barriers in accessing premium markets for sustainable or organic products without proper certification and traceability (Explore Farmonaut Traceability Solutions).
- Local Adaptation: Not every method works the same everywhere; it’s vital to adapt to local climate, soil types, and available resources for optimum results.
Farmonaut’s tech-driven, data-rich platform helps overcome these hurdles by making information actionable, transparent, and easily accessible for farmers and farm managers around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions: Sustainable & Eco-Friendly Farming
What is eco-friendly farming?
Eco-friendly farming, often called sustainable agriculture, refers to production systems that minimize environmental impact, preserve resources, support local biodiversity, and maintain soil health for long-term productivity.
How can we improve soil health on our farms?
Some of the most effective soil health improvement practices include no-till farming, cover cropping, diverse crop rotations, agroforestry, and using integrated pest management to reduce disruptive chemicals. These methods help maintain soil structure, boost organic matter, and foster healthy ecosystems.
How does rainwater harvesting benefit agriculture?
Rainwater harvesting for irrigation conserves water, ensures supply during drought, and helps recharge groundwater, crucial for sustainable farming especially in regions with erratic rainfall.
Are sustainable farming methods suitable for all soils and climates?
While almost every farm benefits from sustainable methods, results and techniques should be adjusted to local soil, climate, and resource conditions for best outcomes.
What technologies can help us manage sustainable farms?
Platforms like Farmonaut provide tools for remote soil health monitoring, crop health analytics, AI-advisory, resource management, carbon footprint reduction, and supply chain traceability.
Conclusion: Building Resilient Farming Futures
By embracing eco-friendly farming practices and leveraging digital innovations like Farmonaut’s agri-tech suite, we dramatically improve soil health, conserve water, and grow more resilient agricultural systems. These methods—no-till, cover cropping, agroforestry, crop rotation, soilless systems, rainwater harvesting, and IPM—transform both the biological and economic fabric of our farms.
Let’s cultivate a future where sustainable agriculture is standard, not exception—producing nutritious food, protecting our planet, and empowering our farmers to prosper.
Ready to start your journey? Download the Farmonaut app on web, Android, or iOS, and unlock tools to shape the next generation of eco-friendly, high-performance agriculture.
Interested in precision farming and real-time resource management for eco-friendly success?
Explore the Farmonaut Satellite API and Developer Docs