Identifying and Controlling Black Bugs on Citrus Trees: A Comprehensive Guide for Growers

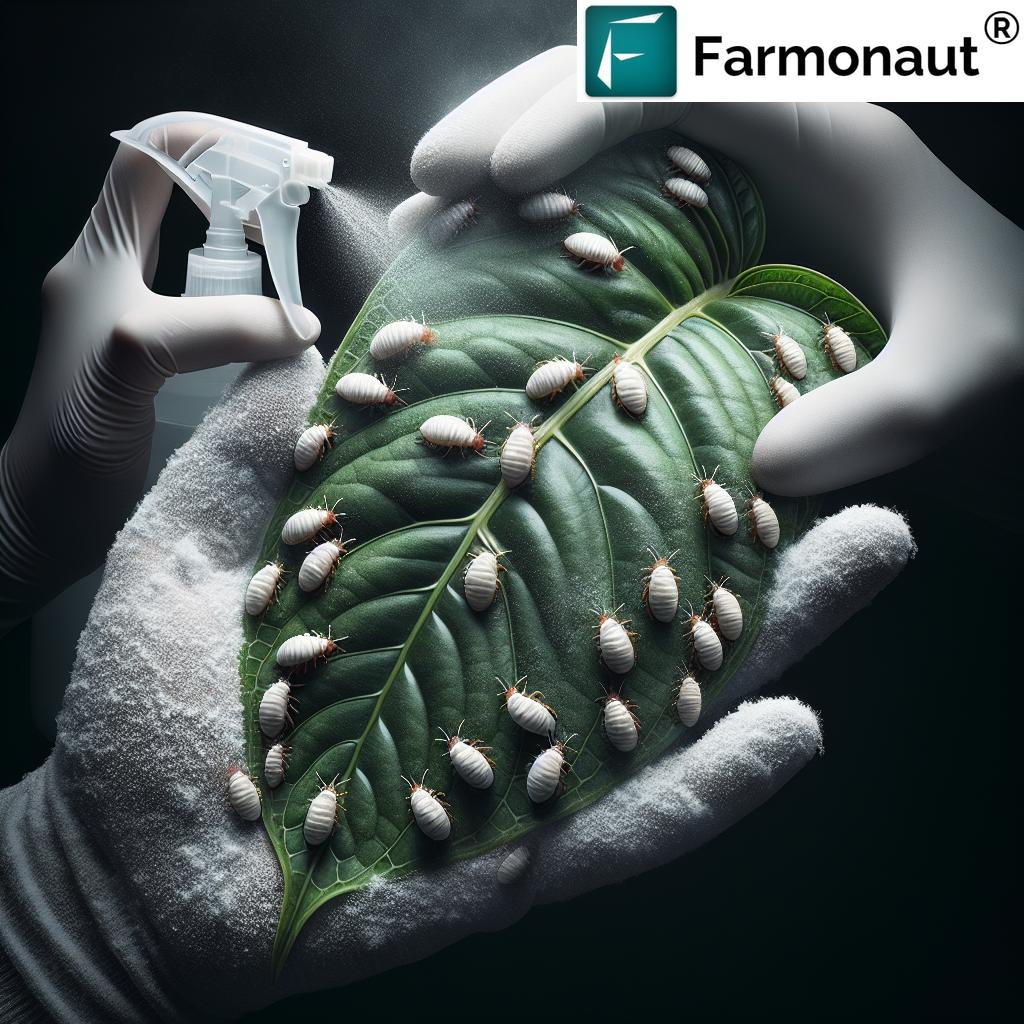
As citrus growers, we understand the challenges that come with maintaining healthy orchards. One of the most persistent issues we face is the presence of bugs on citrus plants, particularly the notorious big black bugs on citrus trees. These pests can wreak havoc on our crops, affecting both yield and quality. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of citrus pests, focusing on identification, prevention, and control methods for these troublesome insects.
Understanding the Threat: Black Bugs on Citrus Trees
When we talk about black stink bugs on citrus trees, we’re referring to a variety of pest species that can infest our orchards. These insects not only damage the fruit but can also harm the overall health of the tree. Let’s delve into the most common types of black bugs you might encounter in your citrus groves:
- Citrus Black Fly
- Asian Citrus Psyllid
- Citrus Leafminer
- Black Citrus Aphid
- Citrus Root Weevil
Each of these pests presents unique challenges and requires specific management strategies. As we progress through this guide, we’ll provide detailed information on identifying and controlling these bugs on citrus leaves and fruit.
The Impact of Black Bugs on Citrus Production
Before we dive into identification and control methods, it’s crucial to understand the significant impact these pests can have on our citrus production:
- Reduced Yield: Severe infestations can lead to premature fruit drop and decreased overall yield.
- Quality Deterioration: Bugs feeding on fruit can cause scarring, deformities, and color changes, reducing marketability.
- Tree Health: Continuous pest pressure can weaken trees, making them more susceptible to diseases and environmental stress.
- Economic Losses: The combination of reduced yield and quality can result in significant financial losses for growers.
Given these potential consequences, it’s clear why effective pest management is crucial for maintaining a thriving citrus orchard.
Identifying Black Bugs on Citrus Plants
Accurate identification is the first step in developing an effective pest management strategy. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common black bugs on citrus plants you might encounter:
1. Citrus Black Fly (Aleurocanthus woglumi)
Appearance: Adult black flies are small (about 1.5mm long) with dark wings held tent-like over their bodies. Nymphs are oval-shaped and black.
Damage: They feed on plant sap, causing leaf yellowing and potentially transmitting plant viruses.
2. Asian Citrus Psyllid (Diaphorina citri)
Appearance: Adults are small (3-4mm long) with mottled brown wings. Nymphs are yellowish-orange and produce waxy tubules.
Damage: Besides direct feeding damage, they are vectors for the devastating citrus greening disease (Huanglongbing).
3. Citrus Leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella)
Appearance: Adults are tiny moths (2-3mm long). Larvae are translucent green and create distinctive serpentine mines in leaves.
Damage: Their feeding creates tunnels in leaves, reducing photosynthetic capacity and potentially providing entry points for pathogens.
4. Black Citrus Aphid (Toxoptera aurantii)
Appearance: These aphids are shiny black and about 2mm long. They often cluster on new growth.
Damage: They suck sap from leaves and shoots, causing distortion and potentially spreading viruses.
5. Citrus Root Weevil (Diaprepes abbreviatus)
Appearance: Adults are large beetles (10-20mm long) with distinctive ridged wing covers. Larvae are white, legless grubs that feed on roots.
Damage: Adult feeding causes notched leaves, while larval feeding can severely damage roots, leading to tree decline.
By familiarizing ourselves with these pests, we can more quickly identify and address infestations in our citrus orchards.
Prevention: The First Line of Defense
As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure. This is particularly true when it comes to managing bugs on citrus. Here are some preventive measures we can implement to reduce the risk of infestations:
- Maintain Tree Health: Healthy trees are more resistant to pest attacks. Ensure proper nutrition, irrigation, and pruning practices.
- Implement Quarantine Measures: When introducing new plants to your orchard, isolate them for a period to prevent potential pest introduction.
- Use Resistant Varieties: Some citrus varieties are more resistant to certain pests. Consider these when planting new trees.
- Practice Good Sanitation: Remove fallen fruit and leaves, which can harbor pests and diseases.
- Encourage Natural Predators: Create a habitat that supports beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which prey on many citrus pests.
Monitoring: The Key to Early Detection
Regular monitoring is crucial for catching pest problems early before they become severe. Here are some effective monitoring techniques:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly examine leaves, stems, and fruit for signs of pest activity or damage.
- Sticky Traps: Use yellow sticky traps to monitor flying insects like citrus blackfly and psyllids.
- Pheromone Traps: These can be effective for monitoring specific pest populations, such as citrus leafminers.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of pest observations, treatments, and their effectiveness to inform future management decisions.
At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of early detection in pest management. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system can help detect potential pest hotspots by identifying areas of stress in your orchard. To learn more about how our technology can enhance your pest management strategy, visit Farmonaut’s App.

Control Methods: Integrated Pest Management for Citrus Orchards
When it comes to controlling bugs on citrus leaves and fruit, an integrated pest management (IPM) approach is often the most effective. This strategy combines various control methods to manage pest populations while minimizing environmental impact. Let’s explore the different components of an effective IPM program for citrus:
1. Cultural Control
Cultural control methods focus on creating an environment that is less favorable for pest development:
- Proper irrigation management to avoid water stress
- Balanced fertilization to promote tree health
- Regular pruning to improve air circulation and reduce hiding spots for pests
- Removal of weeds that may harbor pests
2. Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural enemies to manage pest populations:
- Release of predatory insects like ladybugs and green lacewings
- Use of parasitic wasps that target specific pests
- Application of entomopathogenic fungi or nematodes
3. Chemical Control
While we aim to minimize chemical use, sometimes pesticides are necessary for effective control:
- Selective insecticides that target specific pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects
- Horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps for soft-bodied insects
- Systemic insecticides for persistent infestations
Note: Always follow label instructions and local regulations when applying any pesticides.
4. Physical Control
Physical methods can be effective for smaller orchards or when dealing with localized infestations:
- Handpicking and destroying visible pests
- Using reflective mulches to repel certain flying insects
- Installing physical barriers like tree bands to prevent pest movement
5. Biotechnological Control
Emerging biotechnologies offer new possibilities for pest management:
- Pheromone disruption techniques to interfere with pest mating
- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with built-in pest resistance (where legally allowed)
- RNA interference (RNAi) technologies targeting specific pest species
Spotlight: Managing Black Stink Bugs on Citrus Trees
Black stink bugs on citrus trees deserve special attention due to their potential for significant damage. These pests, which include species like the southern green stink bug (Nezara viridula) and the brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys), can cause fruit drop and quality issues.
Here are some specific strategies for managing stink bugs in citrus orchards:
- Monitoring: Use beat sheets or sweep nets to sample for stink bugs, especially during fruit development stages.
- Trap Crops: Plant attractive crops like sunflowers or soybeans around the orchard perimeter to draw stink bugs away from citrus trees.
- Biological Control: Encourage natural predators like birds, spiders, and parasitic wasps.
- Chemical Control: If necessary, use targeted insecticides approved for stink bug control in citrus. Always follow integrated pest management principles and local regulations.
Leveraging Technology: Farmonaut’s Role in Modern Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to helping citrus growers tackle pest challenges through innovative technology. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers several advantages in pest management:
- Early Detection: Our system can identify areas of stress in your orchard, which may indicate pest activity before it becomes visible to the naked eye.
- Precision Application: By pinpointing problem areas, we help you target your pest control efforts more efficiently, reducing overall pesticide use.
- Historical Analysis: Our platform allows you to track pest pressure over time, helping you identify patterns and predict future outbreaks.
- Integration with Weather Data: By correlating pest activity with weather patterns, we can help you make more informed decisions about timing your control measures.
To explore how Farmonaut can enhance your pest management strategy, visit our Satellite API page or download our app for Android or iOS.
Farmonaut Satellite System vs. Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (thousands of acres) | Medium scale (hundreds of acres) | Small to medium scale |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (every few days) | On-demand | Continuous |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium to High |
| Operational Complexity | Low (cloud-based) | High (requires trained operators) | Medium (requires maintenance) |
| Weather Dependency | Moderate | High | Low |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI-driven analytics | Varies by provider | Real-time but often limited in scope |
Best Practices for Sustainable Pest Management in Citrus Orchards
As we strive for more sustainable farming practices, it’s essential to adopt an approach that balances effective pest control with environmental stewardship. Here are some best practices we recommend:
- Rotate Control Methods: Avoid relying on a single pest control method to prevent resistance development.
- Preserve Beneficial Insects: Choose selective pesticides and application methods that minimize impact on beneficial insects.
- Practice Good Orchard Hygiene: Regularly remove fallen fruit and prune dead or diseased branches to reduce pest habitats.
- Implement Buffer Zones: Maintain diverse plant species around your orchard to support natural predators and create barriers against pest migration.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and recommendations from local agricultural extension services.
- Train Your Team: Ensure all staff members are trained in pest identification and proper management techniques.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your pest management strategies and be prepared to adjust as needed.
The Future of Pest Management in Citrus Production
As we look to the future, several emerging technologies and approaches show promise for more effective and sustainable pest management in citrus orchards:
- Gene Editing: CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies may lead to citrus varieties with enhanced pest resistance.
- Artificial Intelligence: Advanced AI algorithms could improve pest detection and prediction capabilities.
- Precision Agriculture: Integration of sensors, drones, and satellite data for more targeted pest management.
- Biopesticides: Development of new, environmentally friendly pest control agents derived from natural materials.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adapting pest management strategies to changing climate conditions.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these advancements. Our team continually updates our satellite-based monitoring system to incorporate the latest technologies and insights. For more information on our cutting-edge solutions, visit our API documentation.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Managing Bugs on Citrus
Effectively managing bugs on citrus, particularly the troublesome big black bugs on citrus trees, requires a comprehensive and adaptive approach. By combining traditional pest management techniques with modern technology and sustainable practices, we can protect our citrus orchards while minimizing environmental impact.
Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, knowledge, and the right tools. By staying informed, implementing integrated pest management strategies, and leveraging advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, we can ensure the health and productivity of our citrus orchards for years to come.
FAQs: Managing Black Bugs on Citrus Trees
- Q: How often should I inspect my citrus trees for pests?
A: We recommend conducting visual inspections at least once a week during the growing season, and more frequently during periods of high pest pressure. - Q: Are organic control methods effective against black bugs on citrus?
A: Yes, many organic methods can be effective, especially when used as part of an integrated pest management approach. These include biological controls, horticultural oils, and certain botanical insecticides. - Q: How can I encourage natural predators in my citrus orchard?
A: Planting diverse flora around your orchard, providing water sources, and minimizing broad-spectrum pesticide use can help attract and sustain beneficial insects. - Q: Is it possible to completely eradicate black bugs from my citrus trees?
A: Complete eradication is often unrealistic and unnecessary. The goal should be to manage pest populations below economically damaging levels. - Q: How does climate change affect pest populations in citrus orchards?
A: Climate change can alter pest life cycles, expand their geographical range, and potentially increase the number of generations per season. It’s important to stay informed about changing pest dynamics in your region. - Q: Can Farmonaut’s system detect specific pest species?
A: While our system doesn’t identify specific pest species, it can detect areas of plant stress that may indicate pest activity, allowing for targeted ground-level inspections. - Q: How do I balance pest control with protecting pollinators in my citrus orchard?
A: Time pesticide applications to avoid bloom periods, choose selective pesticides when possible, and maintain pollinator-friendly habitats around your orchard. - Q: What should I do if I suspect a new or unusual pest in my citrus trees?
A: Contact your local agricultural extension office immediately. They can help with identification and provide guidance on appropriate management strategies.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your pest management efforts, consider subscribing to our services:
By staying informed, implementing integrated strategies, and leveraging advanced technologies, we can effectively manage bugs on citrus plants and ensure the health and productivity of our orchards. Remember, successful pest management is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, adaptability, and the right tools. Together, we can overcome the challenges posed by citrus pests and cultivate thriving, productive orchards.