Protecting Fruit Trees from Sunscald: Symptoms, Damage Control, and Prevention Tips for Summer Crops

As the summer heat intensifies, fruit trees face a significant threat that many growers often overlook: sunscald. This condition, caused by excessive exposure to intense sunlight, can severely damage trees and impact fruit production. In this comprehensive guide, we at Farmonaut will explore the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods for sunscald in fruit trees, with a particular focus on how our advanced satellite-based monitoring system can help detect and mitigate this issue.
Understanding Sunscald: A Silent Threat to Fruit Trees
Sunscald, also known as southwest injury, is a type of damage that occurs when the bark of a tree is exposed to intense solar radiation, particularly during the hot summer months. This exposure can lead to a range of problems, from cosmetic damage to severe tissue injury that compromises the tree’s health and productivity.
The Science Behind Sunscald
Sunscald typically affects the southwest side of tree trunks and branches in the Northern Hemisphere (and the northwest side in the Southern Hemisphere). This is because these areas receive the most intense afternoon sun. The problem is exacerbated in winter when the sun is lower in the sky and its rays hit the tree bark more directly.
Here’s what happens:
- Temperature Fluctuations: During winter days, the sun can warm the bark to temperatures well above freezing.
- Cellular Activity: This warmth can cause cells in the bark and cambium layer to become active.
- Rapid Cooling: As night falls and temperatures plummet, these active cells can be damaged or killed by the sudden freeze.
- Tissue Damage: Over time, this cycle of warming and freezing leads to damaged or dead tissue beneath the bark.
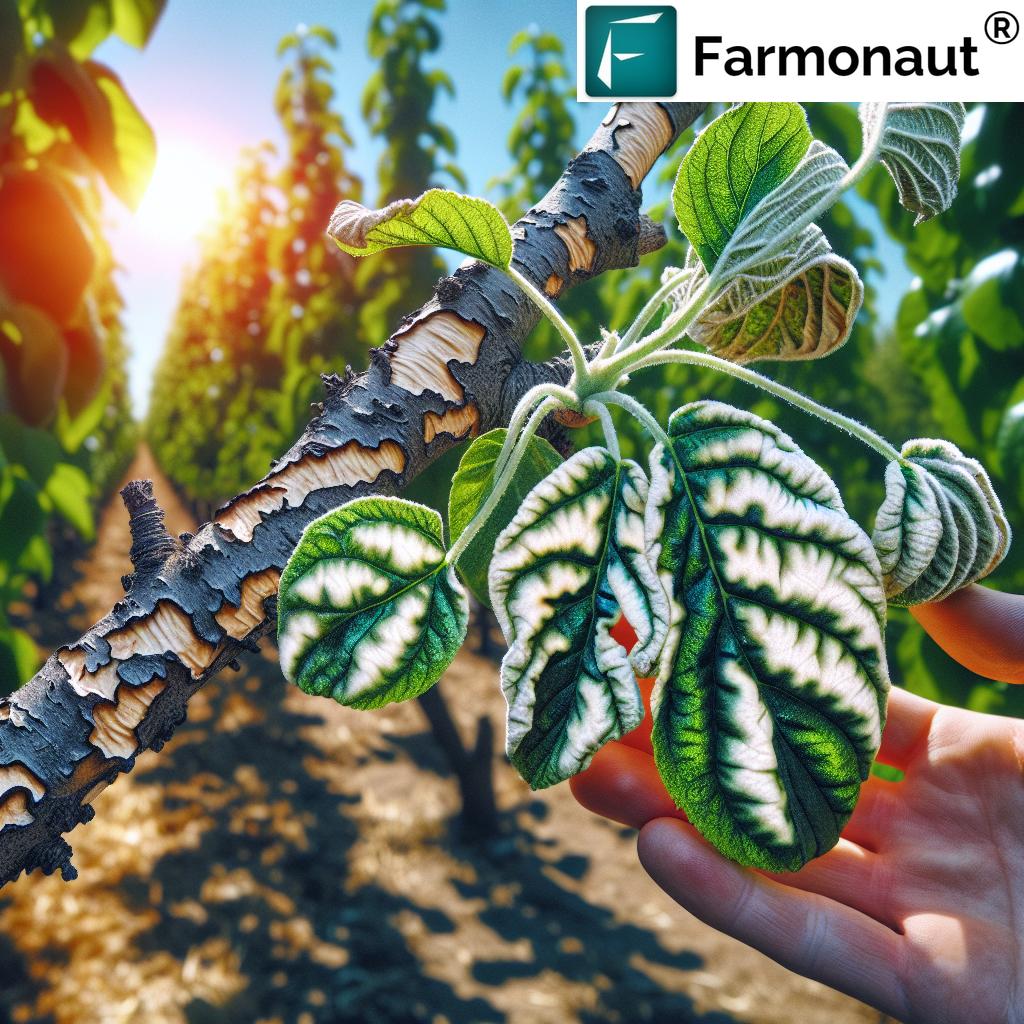
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sunscald
Identifying sunscald early is crucial for effective management. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
- Discolored Bark: The affected area may appear lighter in color, often taking on a whitish or pale brown hue.
- Cracked or Split Bark: As the damage progresses, the bark may crack, split, or peel away from the tree.
- Sunken Areas: The damaged tissue may become depressed, creating sunken areas on the trunk or branches.
- Exposed Wood: In severe cases, the underlying wood may become exposed as the bark falls away.
- Cankers: Open wounds or cankers may develop in the affected areas, providing entry points for pathogens.
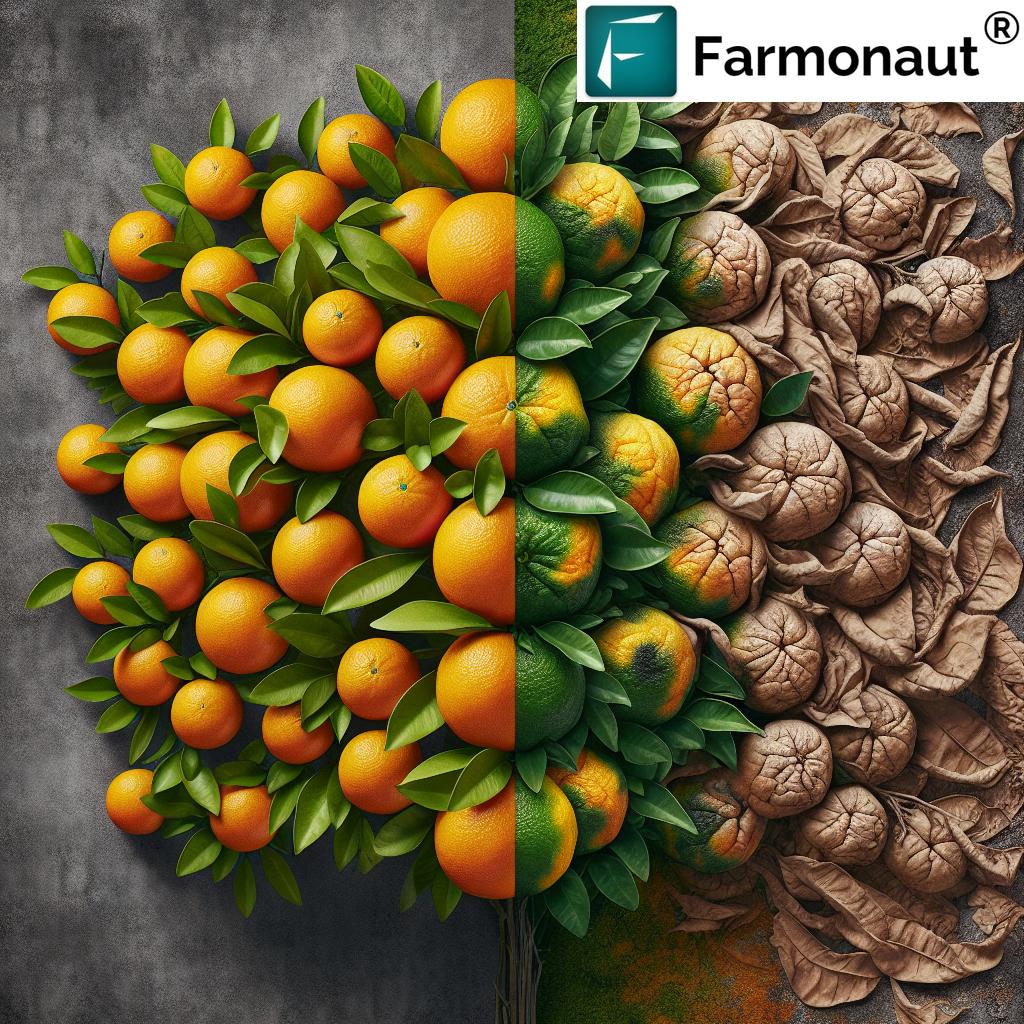

The Impact on Different Fruit Trees
While all fruit trees can be susceptible to sunscald, some species are particularly vulnerable:
- Apple Trees: Young apple trees with thin bark are especially prone to sunscald.
- Citrus Trees: In citrus groves, sunscald can be a significant problem, particularly for newly planted or pruned trees.
- Stone Fruits: Peach, plum, and cherry trees are often affected, especially when grown in regions with hot summers and cold winters.
- Avocado Trees: These trees have sensitive bark and can suffer severe sunscald damage in intense sunlight.
The Role of Farmonaut in Early Sunscald Detection
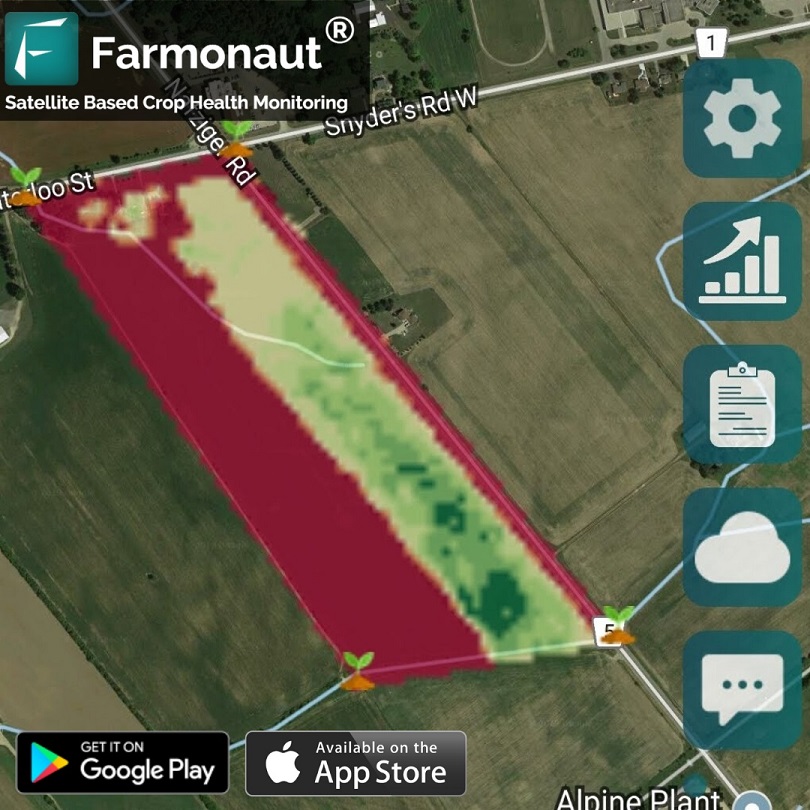
At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of early detection in managing sunscald. Our advanced satellite-based monitoring system offers a unique advantage in identifying potential sunscald issues before they become visible to the naked eye.
How Farmonaut’s Technology Works
- Multispectral Imaging: Our satellites capture multispectral images of orchards and fruit groves.
- Vegetation Health Analysis: We analyze these images using advanced algorithms to assess vegetation health.
- Early Stress Detection: Our system can detect subtle changes in tree health that may indicate the onset of sunscald.
- Real-time Alerts: Growers receive timely notifications about potential issues, allowing for proactive management.
To learn more about our satellite-based monitoring system, visit Farmonaut’s App.
Comparative Advantage of Farmonaut’s Detection Capabilities
| Sunscald Symptoms | Visible to Naked Eye | Detectable by Farmonaut Satellite System | Early Detection Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discolored Bark | Yes, but only after significant damage | Yes, through spectral analysis | Weeks to months before visible symptoms |
| Cracked or Split Bark | Yes, when damage is advanced | Indirectly, through stress indicators | Can detect stress leading to cracking |
| Sunken Areas | Yes, in later stages | Yes, through thermal imaging | Early detection of temperature anomalies |
| Exposed Wood | Yes, in severe cases | Indirectly, through canopy analysis | Can detect canopy changes indicative of severe damage |
| Cankers | Yes, once developed | Yes, through multispectral imaging | Can detect early stages of tissue damage |
This table highlights Farmonaut’s ability to detect sunscald symptoms early, allowing farmers to take preventive measures before visible damage occurs.
Prevention and Management Strategies for Sunscald
While early detection is crucial, prevention remains the best strategy for managing sunscald. Here are some effective methods to protect your fruit trees:
1. Tree Wraps and Guards
One of the most common and effective methods to prevent sunscald is the use of tree wraps or guards. These protective coverings shield the trunk and lower branches from direct sunlight.
- Paper Tree Wrap: Inexpensive and biodegradable, but needs regular replacement.
- Plastic Tree Guards: More durable and can be reused for several seasons.
- Reflective Wraps: These reflect sunlight and help maintain a more consistent bark temperature.
Application Tip: Apply wraps in late fall and remove them in early spring to allow for natural bark growth and air circulation.
2. Paint Application
White latex paint diluted with an equal part of water can be an effective sunscald deterrent:
- The white color reflects sunlight, reducing heat absorption.
- Apply to the trunk and main scaffold branches.
- Reapply annually or as needed.
Caution: Use only latex paint, as oil-based paints can damage the tree.
3. Proper Pruning Practices
Pruning techniques can significantly impact a tree’s susceptibility to sunscald:
- Avoid heavy pruning that suddenly exposes previously shaded bark to sunlight.
- Maintain a balanced canopy to provide natural shade to the trunk and main branches.
- If extensive pruning is necessary, consider doing it gradually over several seasons.
4. Strategic Planting and Orchard Layout
When establishing new orchards or replacing trees, consider:
- Orienting rows north-south to minimize direct afternoon sun exposure.
- Planting trees closer together to provide mutual shading (within agronomic limits).
- Using companion planting or cover crops to reduce reflected heat from the ground.
5. Soil and Water Management
Proper soil and water management can help trees better withstand environmental stresses:
- Maintain adequate soil moisture, especially during hot, dry periods.
- Apply mulch around the base of trees to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
- Ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can weaken trees.
6. Shade Cloth and Netting
For particularly sensitive trees or in extreme climates:
- Use shade cloth or netting to reduce overall sun exposure.
- This can be especially beneficial for young or newly transplanted trees.
- Be cautious not to over-shade, as this can impact fruit production.
Leveraging Farmonaut’s Technology for Sunscald Management
Our satellite-based monitoring system at Farmonaut offers several advantages in managing and preventing sunscald:
1. Early Detection and Intervention
- Our system can detect early signs of tree stress that may indicate the onset of sunscald.
- Growers receive alerts allowing them to intervene before visible damage occurs.
- This early warning system can significantly reduce the impact of sunscald on orchards.
2. Precision Agriculture Techniques
Farmonaut’s platform enables precision agriculture practices that can help mitigate sunscald risks:
- Targeted Irrigation: Our soil moisture analysis helps optimize irrigation, reducing water stress that can exacerbate sunscald.
- Nutrient Management: Proper nutrient balance helps trees withstand environmental stresses better.
- Microclimate Analysis: Identify areas in your orchard more prone to sunscald based on temperature and light exposure data.
3. Historical Data and Trend Analysis
Our system stores historical data, allowing growers to:
- Identify patterns and trends in sunscald occurrence.
- Plan preventive measures based on past experiences.
- Make informed decisions about orchard layout and tree selection for future plantings.
4. Integration with Weather Forecasting
Farmonaut’s platform integrates weather forecasting, enabling growers to:
- Anticipate periods of high sunscald risk.
- Plan protective measures in advance of extreme weather events.
- Adjust management practices based on short-term and seasonal forecasts.
To access these advanced features, consider subscribing to Farmonaut’s services:
Case Studies: Successful Sunscald Management with Farmonaut
While we don’t provide specific case studies, our platform has helped numerous growers across various regions manage sunscald effectively. Here are some general scenarios where our technology has made a significant impact:
Citrus Groves in Mediterranean Climates
Challenge: Intense summer heat and sudden temperature drops in winter.
Farmonaut Solution:
- Early detection of water stress that could exacerbate sunscald.
- Microclimate analysis to identify high-risk areas within groves.
- Targeted interventions based on real-time data.
Apple Orchards in Continental Climates
Challenge: Extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night, especially in late winter.
Farmonaut Solution:
- Predictive alerts for high-risk periods based on weather forecasts.
- Monitoring of tree health to guide pruning and protective measures.
- Historical data analysis to inform long-term orchard management strategies.
Stone Fruit Orchards in Arid Regions
Challenge: Intense solar radiation and low humidity increasing sunscald risk.
Farmonaut Solution:
- Precision irrigation recommendations to maintain optimal tree health.
- Vegetation health analysis to detect early signs of stress.
- Guidance on the strategic use of shade netting based on solar radiation data.
The Economic Impact of Sunscald and the Value of Prevention
Understanding the economic implications of sunscald is crucial for growers. While the direct costs of tree damage and reduced fruit quality are apparent, the long-term impacts can be even more significant:
Direct Costs of Sunscald
- Reduced Fruit Yield: Damaged trees often produce less fruit.
- Lower Fruit Quality: Sunscald can affect the appearance and taste of fruits, reducing their market value.
- Tree Replacement Costs: Severely damaged trees may need to be replaced, incurring significant expenses.
- Treatment and Labor Costs: Managing sunscald damage requires additional labor and materials.
Indirect Costs and Long-term Impacts
- Increased Susceptibility to Pests and Diseases: Sunscald damage can make trees more vulnerable to secondary infections.
- Reduced Orchard Lifespan: Chronic sunscald issues can shorten the productive life of an orchard.
- Market Competitiveness: Consistently lower quality produce can affect a grower’s market position.
The Value of Prevention with Farmonaut
Investing in preventive measures, including advanced monitoring systems like Farmonaut, can offer significant economic benefits:
- Early Intervention: Detecting issues before they become severe can dramatically reduce treatment costs.
- Optimized Resource Use: Precision agriculture techniques enabled by our platform can improve overall orchard efficiency.
- Long-term Orchard Health: Consistent monitoring and preventive actions contribute to the longevity and productivity of fruit trees.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to comprehensive data allows for more informed and cost-effective management strategies.
To explore how Farmonaut can help protect your orchard from sunscald and other environmental stresses, visit our app page or check out our API documentation for integration options.
Future Trends in Sunscald Management
As technology continues to evolve, we at Farmonaut are at the forefront of developing new solutions for sunscald management. Here are some trends and innovations we’re excited about:
1. Advanced Imaging Technologies
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This technology can provide even more detailed information about tree health and stress levels.
- Thermal Imaging Enhancements: Improved thermal sensors can detect subtle temperature variations in tree bark, potentially identifying sunscald risks earlier.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
We’re continuously improving our AI algorithms to:
- Predict sunscald occurrence based on historical data and current conditions.
- Provide more accurate and personalized management recommendations.
- Automate the analysis of complex data sets for easier interpretation by growers.
3. Integration with IoT Devices
The future of sunscald management may involve:
- Smart sensors placed directly on trees to monitor bark temperature and moisture.
- Automated protective systems that deploy shade or misting based on real-time data.
- Integration of ground-based sensors with satellite data for a more comprehensive view of orchard conditions.
4. Climate Change Adaptation Strategies
As global climate patterns shift, we’re focusing on:
- Developing predictive models that account for changing climate patterns.
- Researching and recommending more resilient tree varieties.
- Creating adaptive management strategies for different climate scenarios.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Sunscald Management
Effectively managing sunscald in fruit trees requires a multifaceted approach combining traditional horticultural practices with cutting-edge technology. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing growers with the tools and insights needed to protect their orchards from this pervasive threat.
By leveraging our satellite-based monitoring system, growers can:
- Detect potential sunscald issues early.
- Implement targeted prevention strategies.
- Optimize resource use for better overall orchard health.
- Make data-driven decisions that improve long-term productivity and sustainability.
As we continue to innovate and refine our technology, we remain dedicated to supporting fruit growers in their efforts to produce healthy, high-quality crops. The fight against sunscald is ongoing, but with the right tools and knowledge, it’s a challenge that can be effectively managed.
To start protecting your orchard with Farmonaut’s advanced technology, download our app:
For developers interested in integrating our technology into their own systems, check out our API documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is sunscald in fruit trees?
A1: Sunscald is a type of damage that occurs when the bark of a fruit tree is exposed to intense sunlight, particularly during hot summer months or cold winter days. It can cause tissue damage, bark cracking, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Q2: Which fruit trees are most susceptible to sunscald?
A2: While all fruit trees can be affected, some of the most susceptible include young apple trees, citrus trees, and stone fruits like peaches, plums, and cherries. Trees with thin bark or those recently transplanted are particularly vulnerable.
Q3: How can I identify sunscald on my fruit trees?
A3: Look for symptoms such as discolored or whitish bark, cracking or peeling bark, sunken areas on the trunk or branches, and exposed wood. In severe cases, you may see cankers or open wounds on the affected areas.
Q4: What are the best methods to prevent sunscald?
A4: Effective prevention methods include using tree wraps or guards, applying white latex paint to the trunk and main branches, proper pruning practices, strategic planting to minimize exposure, and maintaining good soil and water management.
Q5: How does Farmonaut help in managing sunscald?
A5: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system provides early detection of tree stress that may indicate sunscald risk. It offers real-time alerts, precision agriculture techniques, historical data analysis, and integration with weather forecasting to help growers implement timely and targeted management strategies.
Q6: Can sunscald occur in winter?
A6: Yes, sunscald can occur in winter, especially on sunny days when the temperature fluctuates significantly. The sun can warm the bark during the day, and when temperatures drop rapidly at night, it can cause tissue damage.
Q7: How long does it take for a tree to recover from sunscald?
A7: Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the damage and the overall health of the tree. Minor damage may heal within a season, while severe cases can take several years and may require ongoing management.
Q8: Can fruit quality be affected by sunscald?
A8: Yes, sunscald can indirectly affect fruit quality. Damaged trees may produce less fruit, and the stress can impact the size, flavor, and overall quality of the fruit.
Q9: Is it necessary to remove the protective wraps or paint every year?
A9: It’s generally recommended to remove tree wraps annually to allow for natural bark growth and air circulation. White paint typically needs to be reapplied annually or as it wears off.
Q10: How can I access Farmonaut’s services for my orchard?
A10: You can start by downloading the Farmonaut app for Android or iOS. For more advanced features and API access, visit our website or contact our support team for tailored solutions.