Here’s a comprehensive blog post based on your requirements:
Exploring Vietnamese Agriculture: Insights from Farmonaut’s Journey
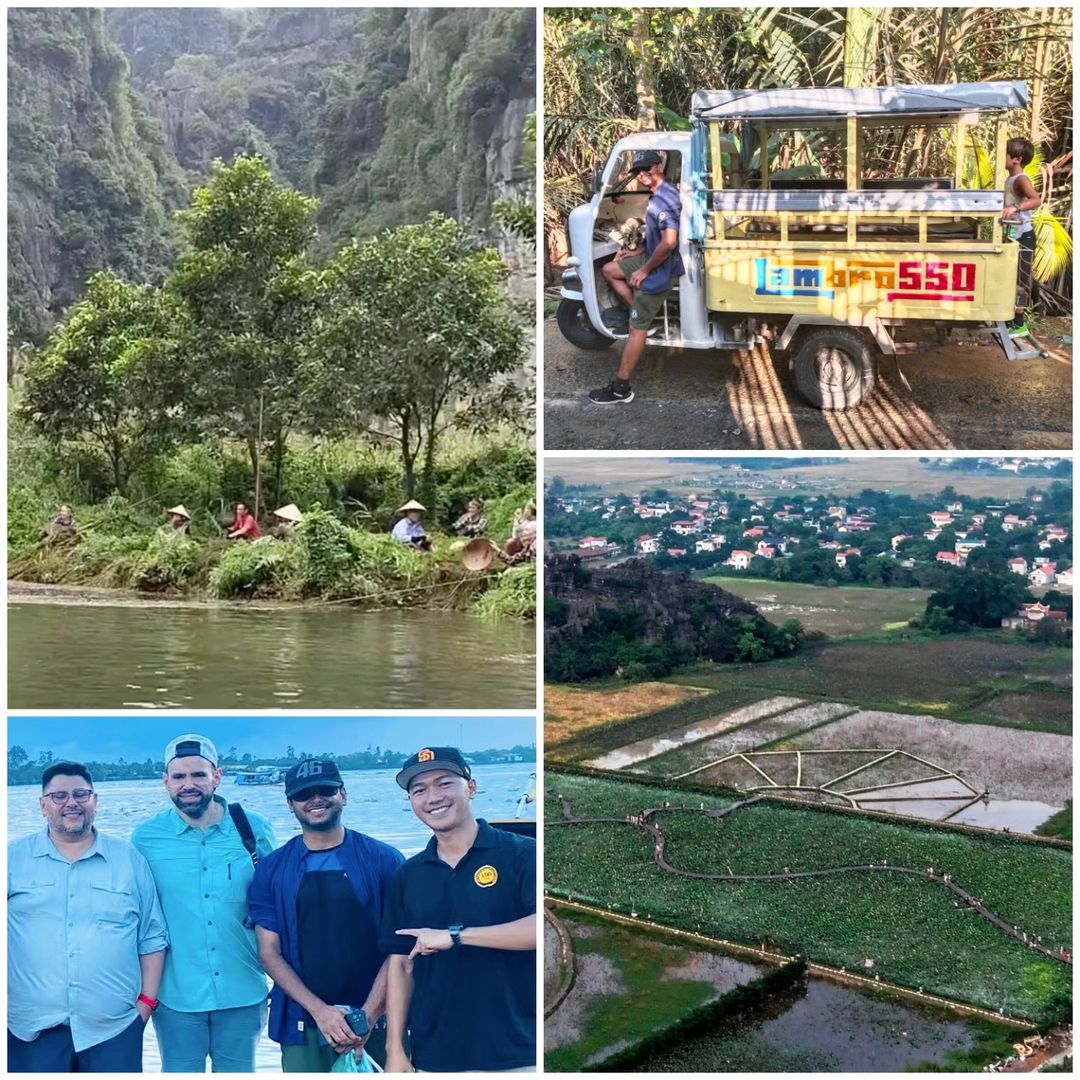

At Farmonaut, we’re always eager to explore and understand agricultural practices around the world. Recently, our journey took us to the vibrant fields of Vietnam, where we had the incredible opportunity to immerse ourselves in the country’s rich agricultural landscape. This experience not only broadened our perspective but also reinforced our commitment to innovating in the field of agricultural technology.
Our Vietnamese Adventure: A Tale of Two Regions
Our expedition in Vietnam was nothing short of enlightening. We had the privilege of traversing both the Northern and Southern parts of the country, each offering unique insights into Vietnamese agriculture. Mr. Ankur Omar, our representative, had the honor of meeting diverse agricultural stakeholders, especially the hardworking farmers who form the backbone of Vietnam’s agricultural sector.
Northern Vietnam: A Tapestry of Tradition and Innovation
In the North, we witnessed a fascinating blend of traditional farming methods and emerging modern practices. The region’s topography, characterized by mountainous terrain and iconic rice terraces, presents unique challenges and opportunities for agriculture.
- Rice Cultivation: The northern regions, particularly around Sapa and Ha Giang, are renowned for their breathtaking rice terraces. These ancient agricultural marvels not only serve as a testament to human ingenuity but also continue to be vital for food production.
- Diverse Crop Portfolio: Beyond rice, we observed a variety of crops including maize, cassava, and various fruits and vegetables adapted to the cooler climate of the north.
- Water Management: The intricate irrigation systems in the northern highlands showcased the farmers’ expertise in water resource management, a critical skill in areas with varying rainfall patterns.
Southern Vietnam: The Rice Bowl of Asia
As we moved to the South, the agricultural landscape transformed dramatically. The Mekong Delta, often referred to as Vietnam’s rice bowl, presented a stark contrast to the northern highlands.
- Extensive Rice Production: The flat, fertile lands of the Mekong Delta are ideal for large-scale rice cultivation. We were amazed by the vast expanse of paddy fields stretching as far as the eye could see.
- Aquaculture: The region’s abundant water resources support a thriving aquaculture industry, with fish and shrimp farming playing a significant role in the local economy.
- Fruit Orchards: The warm tropical climate of the south is perfect for fruit cultivation. We saw numerous orchards producing a variety of tropical fruits like mangoes, dragonfruit, and durian.
Parallels Between Vietnamese and Indian Agriculture
One of the most fascinating aspects of our journey was discovering the striking parallels between Vietnamese and Indian agricultural systems. These similarities provided a familiar context while highlighting the universal challenges faced by farmers globally.
Common Ground: Shared Agricultural Practices
- Rice-Centric Agriculture: Both Vietnam and India have rice as a staple crop, with extensive cultivation practices developed over millennia.
- Small-holder Farming: The prevalence of small-scale farming operations in both countries underscores the importance of family-run farms in the agricultural landscape.
- Monsoon Dependence: The agricultural cycles in both nations are heavily influenced by monsoon patterns, highlighting the critical role of seasonal rains in crop planning and water management.
- Crop Diversification: We observed efforts in both countries to diversify crop portfolios as a strategy to mitigate risks and improve food security.
- Traditional Knowledge: The rich repository of traditional agricultural knowledge passed down through generations forms a crucial part of farming practices in both Vietnam and India.
Shared Challenges: Bridging the Gap with Technology
While the similarities were evident, we also recognized common challenges that both Vietnamese and Indian farmers face:
- Climate Variability: Adapting to changing weather patterns and extreme climate events is a pressing concern for farmers in both countries.
- Water Resource Management: Efficient irrigation and water conservation techniques are crucial in regions facing water scarcity or uneven distribution.
- Market Access: Small-scale farmers in both nations often struggle with access to fair markets and price volatility.
- Technological Adoption: While there’s a growing interest in modern agricultural technologies, adoption rates vary, often limited by factors such as cost and accessibility.
At Farmonaut, we see these shared challenges as opportunities for innovation. Our satellite-based crop monitoring and analytics solutions are designed to address many of these issues, providing farmers with valuable insights regardless of their location.
Unique Challenges in Vietnamese Agriculture
While there were many similarities, our journey also revealed unique challenges faced by Vietnamese agriculture. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing tailored solutions and fostering sustainable growth in the Vietnamese agricultural ecosystem.
1. Climate Change and Sea Level Rise
Vietnam’s extensive coastline and low-lying areas, particularly in the Mekong Delta, make it highly vulnerable to climate change impacts.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Rising sea levels are causing saltwater to intrude further inland, affecting freshwater resources and soil quality in coastal regions.
- Changing Rainfall Patterns: Shifts in monsoon patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events pose significant challenges for crop planning and water management.
2. Land Fragmentation
The historical context of land distribution in Vietnam has led to significant land fragmentation, especially in rural areas.
- Small Plot Sizes: Many farmers work on very small plots of land, which can limit economies of scale and the adoption of certain modern farming techniques.
- Coordination Challenges: Fragmented landholdings can make it difficult to implement large-scale agricultural projects or coordinated pest management strategies.
3. Environmental Concerns
Intensive farming practices have led to environmental challenges that need urgent attention.
- Soil Degradation: Overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides has led to soil degradation in some areas, highlighting the importance of soil in agriculture and the need for sustainable farming practices.
- Water Pollution: Runoff from agricultural lands and aquaculture operations has contributed to water pollution in rivers and coastal areas.
4. Market Volatility and Export Dependence
Vietnam’s position as a major agricultural exporter brings both opportunities and challenges.
- Price Fluctuations: Dependence on global markets exposes farmers to international price volatility, particularly for key exports like rice and coffee.
- Quality Standards: Meeting the stringent quality standards of international markets can be challenging for small-scale farmers.
5. Technological Gap
While Vietnam has made significant strides in agricultural modernization, there’s still a technological gap, especially in rural areas.
- Limited Access to Advanced Tools: Many farmers lack access to modern agricultural technologies that could significantly improve productivity and sustainability.
- Digital Literacy: There’s a need for improved digital literacy among farmers to fully leverage available technological solutions.
The Role of Technology in Addressing Agricultural Challenges
At Farmonaut, we believe that technological advancements hold the key to addressing many of the challenges faced by Vietnamese agriculture. Our journey through Vietnam reinforced our conviction that affordable, accessible technology can transform farming practices and improve livelihoods.
Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: A Game-Changer for Vietnamese Agriculture
Our flagship technology, satellite-based crop monitoring, offers immense potential for Vietnamese farmers. Here’s how it can address some of the specific challenges we observed:
- Climate Adaptation: By providing real-time data on crop health and soil moisture, our ag satellite technology enables farmers to adapt quickly to changing weather patterns and optimize resource use.
- Precision Agriculture: Even for small, fragmented plots, satellite monitoring allows for precise application of inputs, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Early Warning Systems: Our crop monitoring and analytics can detect early signs of crop stress, pest infestations, or disease outbreaks, allowing for timely interventions.
- Water Management: Satellite data on soil moisture and crop water stress can guide irrigation decisions, crucial in areas facing water scarcity or saltwater intrusion.
To illustrate the advantages of our satellite-based system, let’s compare it with other farm monitoring technologies:
| Feature |
Farmonaut Satellite System |
Drone-based Monitoring |
IoT-based Monitoring |
| Coverage Area |
Large (entire farms or regions) |
Medium (limited by flight time) |
Small (limited by sensor placement) |
| Frequency of Data |
Regular (every few days) |
On-demand (requires manual flights) |
Continuous (real-time) |
| Initial Investment |
Low (subscription-based) |
High (equipment costs) |
Medium to High (sensor costs) |
| Operational Complexity |
Low (user-friendly interface) |
High (requires skilled operators) |
Medium (setup and maintenance needed) |
| Weather Dependency |
Low (can penetrate clouds) |
High (affected by wind, rain) |
Low (operates in all weather) |
AI-Powered Advisory Systems: Tailored Solutions for Vietnamese Farmers
Our AI-driven advisory system, Jeevn AI, can be a valuable tool for Vietnamese farmers, offering:
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing satellite data, weather patterns, and local agricultural knowledge, Jeevn AI can provide tailored advice for each farm.
- Market Intelligence: AI-powered insights into market trends can help farmers make informed decisions about crop selection and timing of sales.
- Pest and Disease Management: Our system can function as an automated pest monitoring system market for agriculture sector, alerting farmers to potential threats and suggesting appropriate interventions.
Blockchain for Traceability: Enhancing Vietnam’s Agricultural Exports
Vietnam’s position as a major agricultural exporter can be further strengthened with blockchain-based traceability solutions:
- Quality Assurance: Blockchain can provide an immutable record of a product’s journey from farm to table, assuring international buyers of quality and origin.
- Fair Pricing: Increased transparency can help ensure fair prices for farmers by eliminating intermediaries and reducing information asymmetry.
- Sustainability Certification: Blockchain can verify sustainable farming practices, potentially opening up premium markets for Vietnamese products.
The Path Forward: Collaborative Innovation in Vietnamese Agriculture
Our journey through Vietnam has reinforced our belief in the power of collaborative innovation. As we look to the future, we see immense potential for technological advancements to transform Vietnamese agriculture. Here’s how we envision this transformation:
1. Fostering Technology Adoption
To bridge the technological gap, we propose:
- Educational Initiatives: Partnering with local agricultural organizations to provide training on digital tools and precision farming techniques.
- Demonstrative Pilot Projects: Setting up model farms that showcase the benefits of satellite-based monitoring and AI advisory systems.
- Customized Solutions: Adapting our technologies to meet the specific needs of Vietnamese farmers, considering factors like plot sizes and local crop varieties.
2. Addressing Environmental Concerns
Our technologies can play a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture:
- Precision Input Application: Using satellite data to optimize fertilizer and pesticide use, reducing environmental impact and costs.
- Soil Health Monitoring: Leveraging our expertise in remote sensing to track soil health indicators, promoting sustainable soil management practices.
- Water Conservation: Implementing advanced irrigation scheduling based on satellite-derived soil moisture data.
3. Enhancing Climate Resilience
To help Vietnamese agriculture adapt to climate change:
- Climate-Smart Crop Selection: Using AI to recommend crop varieties and planting schedules based on changing climate patterns.
- Early Warning Systems: Developing sophisticated models to predict and mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events.
- Salinity Monitoring: Utilizing remote sensing techniques to track and manage saltwater intrusion in coastal areas.
4. Improving Market Access and Traceability
Leveraging technology to enhance Vietnam’s position in global agricultural markets:
- Blockchain Implementation: Rolling out our blockchain-based traceability solutions to key export crops, enhancing trust and transparency in international markets.
- Market Intelligence Platform: Developing a data-driven platform to provide farmers with real-time market information and demand forecasts.
- Quality Certification: Using satellite data and blockchain to certify sustainable and organic farming practices, opening up premium market segments.
5. Collaborative Research and Development
To ensure our solutions are tailored to the Vietnamese context:
- Partnerships with Local Institutions: Collaborating with Vietnamese agricultural research institutions to develop locally-relevant AI models and satellite data applications.
- Farmer Feedback Loops: Establishing mechanisms for continuous feedback from Vietnamese farmers to refine and improve our technologies.
- Open Data Initiatives: Contributing to and leveraging open agricultural data platforms to accelerate innovation in the sector.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Vietnamese Agriculture
Our journey through Vietnam has been both inspiring and enlightening. We’ve witnessed the resilience and ingenuity of Vietnamese farmers, who continue to produce bountiful harvests despite numerous challenges. At the same time, we’ve identified significant opportunities for technological innovation to support and enhance Vietnamese agriculture.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to being a part of this exciting journey. By bringing our advanced satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory systems, and blockchain solutions to Vietnam, we aim to contribute to a more productive, sustainable, and resilient agricultural sector.
The parallels we’ve observed between Vietnamese and Indian agriculture reinforce our belief in the power of shared knowledge and collaborative innovation. As we continue to develop and refine our technologies, we look forward to working closely with Vietnamese farmers, agricultural institutions, and policymakers to create tailored solutions that address the unique challenges and opportunities in Vietnamese agriculture.
The future of agriculture in Vietnam is bright, and we at Farmonaut are excited to be a part of this transformative journey. Together, we can build a more sustainable, productive, and prosperous agricultural sector that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
Stay tuned for more updates on our initiatives in Vietnam and beyond. The adventure in agricultural innovation has only just begun!
FAQs
- Q: How can satellite-based crop monitoring benefit small-scale farmers in Vietnam?
A: Satellite-based crop monitoring can provide small-scale farmers with valuable insights into crop health, soil moisture, and potential pest or disease outbreaks, allowing for more precise and efficient farm management even on small plots of land.
- Q: What role does AI play in Farmonaut’s agricultural solutions?
A: AI is crucial in analyzing satellite data and providing personalized recommendations to farmers. Our Jeevn AI system combines satellite imagery, weather data, and agricultural expertise to offer tailored advice on crop management, pest control, and resource optimization.
- Q: How can blockchain technology improve Vietnam’s agricultural exports?
A: Blockchain technology can enhance traceability in the supply chain, providing verifiable information about the origin and journey of agricultural products. This can increase trust in Vietnamese exports, potentially opening up premium markets and ensuring fair prices for farmers.
- Q: Are Farmonaut’s solutions suitable for the diverse agricultural landscape of Vietnam?
A: Yes, our solutions are highly adaptable. We can customize our satellite monitoring and AI advisory systems to suit various crop types, farm sizes, and regional characteristics found across Vietnam’s diverse agricultural landscape.
- Q: How does Farmonaut address the challenge of digital literacy among farmers?
A: We focus on creating user-friendly interfaces and providing comprehensive training and support. We also collaborate with local agricultural organizations to conduct workshops and demonstrations, ensuring farmers can effectively use our technologies.
For more information about our products and services, visit:
Join us in revolutionizing agriculture, one satellite image at a time!
 At Farmonaut, we’re always eager to explore and understand agricultural practices around the world. Recently, our journey took us to the vibrant fields of Vietnam, where we had the incredible opportunity to immerse ourselves in the country’s rich agricultural landscape. This experience not only broadened our perspective but also reinforced our commitment to innovating in the field of agricultural technology.
At Farmonaut, we’re always eager to explore and understand agricultural practices around the world. Recently, our journey took us to the vibrant fields of Vietnam, where we had the incredible opportunity to immerse ourselves in the country’s rich agricultural landscape. This experience not only broadened our perspective but also reinforced our commitment to innovating in the field of agricultural technology.
 At Farmonaut, we’re always eager to explore and understand agricultural practices around the world. Recently, our journey took us to the vibrant fields of Vietnam, where we had the incredible opportunity to immerse ourselves in the country’s rich agricultural landscape. This experience not only broadened our perspective but also reinforced our commitment to innovating in the field of agricultural technology.
At Farmonaut, we’re always eager to explore and understand agricultural practices around the world. Recently, our journey took us to the vibrant fields of Vietnam, where we had the incredible opportunity to immerse ourselves in the country’s rich agricultural landscape. This experience not only broadened our perspective but also reinforced our commitment to innovating in the field of agricultural technology.