Unraveling the Environmental Impact: Sustainable Viscose Production and Deforestation Risks in Fashion Supply Chains

“200 million trees are felled annually for cellulose-based fabric production in the fashion industry.”
In the ever-evolving world of fashion, we find ourselves at a critical juncture where sustainable viscose production and deforestation in fashion supply chains have become pressing concerns. As we delve into this complex issue, we’ll explore the environmental impact of cellulose-based fabrics and the urgent need for transformative action in the industry.
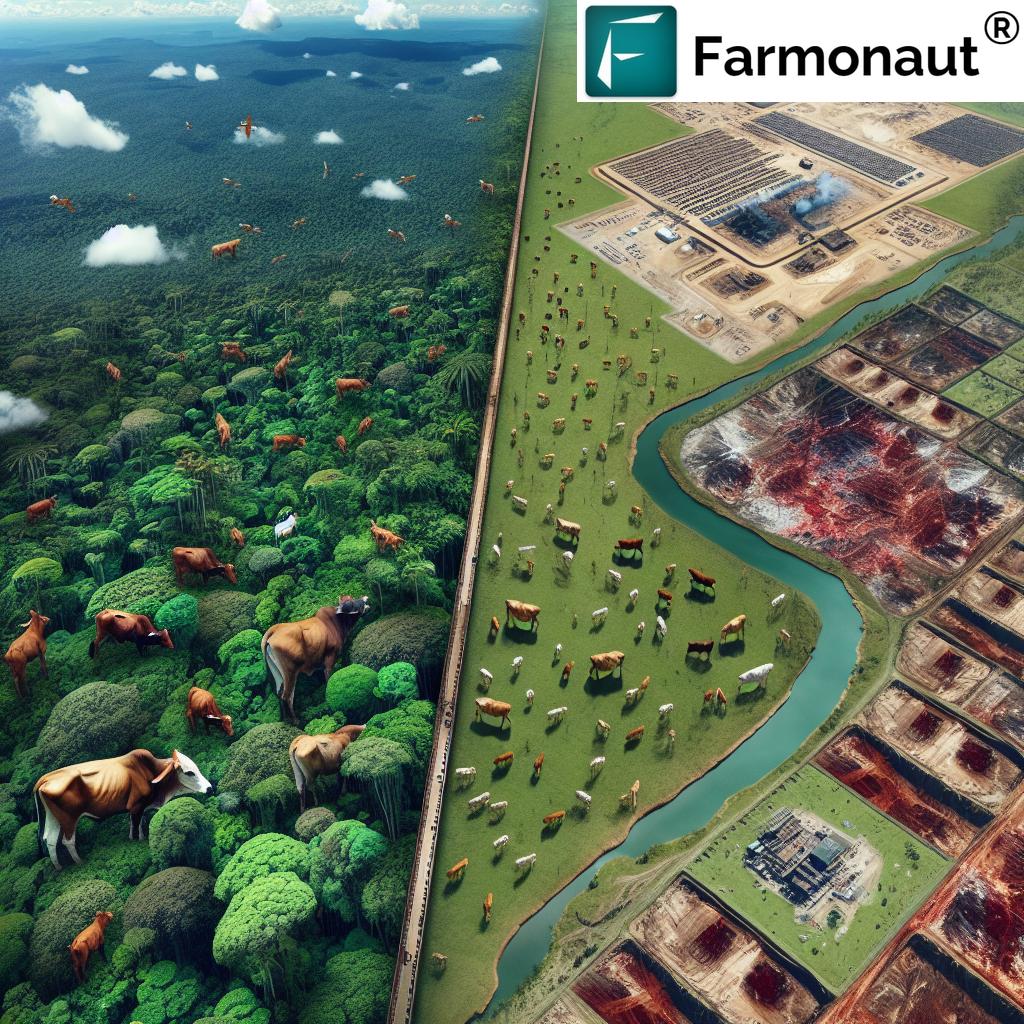
The fashion industry’s reliance on viscose, a popular cellulose-based fabric, has led to significant environmental challenges. We’ll uncover the stark reality that an astounding 200 million trees are felled annually to meet the demand for these materials. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for sustainable alternatives and responsible sourcing practices.
The Environmental Cost of Viscose Production
Viscose, also known as rayon, is derived from cellulose fibers extracted from trees. While it offers a soft and versatile fabric option, its production process comes at a hefty environmental price. Let’s break down the key issues:
- Deforestation: The demand for wood pulp leads to extensive logging, often in ancient and endangered forests.
- Biodiversity Loss: Clearing forests for plantations disrupts ecosystems and threatens wildlife habitats.
- Chemical Pollution: The viscose production process involves harsh chemicals that can contaminate water sources if not properly managed.
- Carbon Emissions: Deforestation and the energy-intensive production process contribute significantly to CO2 emissions.
As we confront these challenges, it’s crucial to explore sustainable alternatives and promote transparency in textile sourcing. Fashion brands and retailers must take responsibility for their supply chains and commit to zero deforestation practices.
Peatland Conservation: A Critical Factor in Climate Change Mitigation
“Peatland degradation is a significant source of CO2 emissions, impacting climate change more than deforestation.”
When discussing the environmental impact of viscose production, we cannot overlook the critical role of peatland conservation in combating climate change. Peatlands are unique ecosystems that store vast amounts of carbon, and their degradation releases significant CO2 emissions into the atmosphere.
- Carbon Storage: Peatlands cover only 3% of the Earth’s land surface but store twice as much carbon as all forests combined.
- Emissions Impact: When drained or burned for agriculture or forestry, peatlands release massive amounts of greenhouse gases.
- Indonesia’s Peatlands: A significant portion of the world’s tropical peatlands are found in Indonesia, a major producer of viscose.
The fashion industry must recognize the importance of peatland conservation and take steps to ensure that their viscose supply chains do not contribute to the degradation of these vital ecosystems.
Zero Deforestation Commitments: Progress and Challenges
In recent years, we’ve seen a growing number of fashion brands and retailers making zero deforestation commitments. These pledges aim to eliminate deforestation from their supply chains and promote sustainable forest management practices. However, the implementation and monitoring of these commitments remain challenging.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Fashion supply chains are often long and complex, making it difficult to trace the origin of materials.
- Lack of Transparency: Many brands struggle to provide full transparency on their viscose sourcing practices.
- Verification Challenges: Independently verifying zero deforestation claims can be resource-intensive and complex.
To address these challenges, we need increased collaboration between brands, suppliers, and third-party verification organizations. Technologies like blockchain and satellite monitoring can play a crucial role in improving supply chain transparency and accountability.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Viscose Production
Innovative technologies are emerging as powerful tools in the fight against deforestation and the promotion of sustainable viscose production. Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this technological revolution, offering solutions that can significantly impact the fashion industry’s sustainability efforts.
- Satellite Monitoring: Advanced satellite imagery can track forest cover changes and identify potential deforestation hotspots in real-time.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Blockchain technology enables transparent and tamper-proof tracking of materials throughout the supply chain.
- AI-Powered Risk Assessment: Artificial intelligence can analyze vast amounts of data to identify and mitigate deforestation risks in supply chains.
These technologies not only help brands monitor their supply chains more effectively but also provide valuable data for making informed decisions about sourcing and production practices.
Sustainable Alternatives to Viscose
As the fashion industry seeks to reduce its environmental footprint, several sustainable alternatives to traditional viscose are gaining traction. These eco-friendly fabrics offer similar properties to viscose while minimizing the impact on forests and ecosystems:
- Lyocell: Made from eucalyptus trees grown on sustainably managed plantations, Lyocell requires less water and chemicals in its production process.
- Recycled Cellulose: This innovative material is created from pre-consumer textile waste, reducing the need for virgin wood pulp.
- Bamboo Viscose: While still requiring careful sourcing, bamboo grows quickly and can be a more sustainable option when properly managed.
- Hemp and Organic Cotton: These natural fibers offer biodegradable alternatives with lower environmental impacts.
By incorporating these sustainable alternatives into their collections, fashion brands can significantly reduce their reliance on traditional viscose and mitigate deforestation risks.
The EU Deforestation Regulation: A Game-Changer for the Fashion Industry
The upcoming EU Deforestation Regulation is set to reshape industry practices and have a profound impact on fashion supply chains. This landmark legislation aims to ensure that products sold in the EU market do not contribute to deforestation or forest degradation. Key aspects of the regulation include:
- Due Diligence Requirements: Companies will need to conduct thorough risk assessments and implement measures to ensure their products are deforestation-free.
- Traceability Obligations: Brands must be able to trace their products back to the point of origin and provide evidence of compliance.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Significant fines and potential market exclusion for companies failing to meet the regulation’s requirements.
This regulation will likely accelerate the adoption of sustainable sourcing practices and drive innovation in the development of eco-friendly materials.
Transparency in Textile Sourcing: A Key to Sustainable Fashion
Transparency in textile sourcing has become a critical factor in the pursuit of sustainable fashion. Consumers are increasingly demanding to know where their clothes come from and how they’re made. This shift in consumer behavior is driving brands to be more open about their supply chains and sourcing practices.
- Supply Chain Mapping: Brands are investing in detailed mapping of their supply chains to identify potential risks and areas for improvement.
- Public Disclosure: Many companies are now publishing lists of their suppliers and providing regular updates on their sustainability progress.
- Third-Party Certifications: Independent certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) provide assurance of responsible forest management.
Improved transparency not only builds trust with consumers but also helps brands identify and address environmental and social issues in their supply chains more effectively.
The Role of Financial Institutions in Promoting Sustainable Practices
Financial institutions play a crucial role in driving sustainability in the fashion industry. By incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into their lending and investment decisions, banks and investors can incentivize brands to adopt more sustainable practices:
- Green Financing: Offering preferential rates for projects that promote sustainable viscose production and forest conservation.
- ESG Risk Assessment: Evaluating the environmental risks associated with fashion brands’ supply chains before making investment decisions.
- Sustainability-Linked Loans: Providing financial incentives for brands that meet specific sustainability targets, including deforestation-free supply chains.
As financial institutions increasingly prioritize sustainability, fashion brands will face growing pressure to address environmental risks in their supply chains.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for cutting-edge satellite monitoring solutions.
Comparative Analysis of Viscose Production and Sustainable Alternatives
| Fabric Type | Estimated Annual Tree Consumption | Estimated CO2 Emissions | Peatland Impact | Water Usage | Chemical Usage | Biodegradability | Sustainability Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Viscose | High (200 million trees) | High | High | High | High | Moderate | 3 |
| Lyocell | Low (sustainably managed) | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | 8 |
| Recycled Cellulose | Very Low (recycled materials) | Low | Very Low | Moderate | Moderate | High | 9 |
| Bamboo Viscose | Moderate (fast-growing) | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | High | 6 |
This table clearly illustrates the significant environmental advantages of sustainable alternatives over traditional viscose production. As we can see, options like Lyocell and recycled cellulose offer substantial improvements in terms of tree consumption, CO2 emissions, and overall sustainability.
Consumer Demand and the Future of Sustainable Fashion
The shift towards environmentally responsible materials is largely driven by changing consumer preferences. Today’s consumers are more informed and conscious about the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions. This growing awareness is reshaping the fashion industry:
- Eco-Conscious Buying: Consumers are actively seeking out brands that prioritize sustainability and transparency.
- Circular Fashion: There’s increasing interest in recyclable and biodegradable materials that support a circular economy.
- Brand Accountability: Consumers are holding brands accountable for their environmental claims and demanding real action.
As consumer demand for sustainable fashion continues to grow, brands that fail to adapt risk losing market share to more environmentally responsible competitors.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
As we look to the future of sustainable viscose production and deforestation-free fashion supply chains, we face both challenges and opportunities:
- Scaling Sustainable Production: Increasing the production of eco-friendly alternatives to meet growing demand while maintaining quality and affordability.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI, blockchain, and satellite monitoring to enhance supply chain transparency and traceability.
- Collaboration and Innovation: Fostering partnerships between brands, suppliers, researchers, and technology providers to drive innovation in sustainable materials and production processes.
- Policy and Regulation: Navigating the evolving landscape of environmental regulations and ensuring compliance across global supply chains.
By addressing these challenges head-on and embracing the opportunities for innovation, the fashion industry can make significant strides towards a more sustainable and responsible future.
Discover Farmonaut’s innovative solutions in our API Developer Docs.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Sustainable Fashion
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the environmental impact of viscose production and the risks of deforestation in fashion supply chains are significant challenges that require urgent attention. However, we’ve also seen that there are viable solutions and alternatives that can pave the way for a more sustainable fashion industry.
The transition to sustainable viscose production and deforestation-free supply chains is not just an environmental imperative; it’s also a business opportunity. Brands that take the lead in adopting sustainable practices and transparently communicating their efforts stand to gain consumer trust and loyalty in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
We must remember that every stakeholder in the fashion industry has a role to play in this transformation:
- Brands and Retailers: Commit to sourcing sustainable materials and implementing transparent supply chain practices.
- Consumers: Make informed choices and support brands that prioritize sustainability.
- Policymakers: Develop and enforce regulations that promote responsible forest management and sustainable production practices.
- Innovators and Technologists: Continue to develop sustainable alternatives and technologies that support transparency and traceability.
By working together and leveraging the power of innovation, transparency, and consumer demand, we can create a fashion industry that not only looks good but does good for our planet. The time for action is now – let’s embrace the challenge and opportunity of sustainable fashion for a better, greener future.
FAQ Section
Q: What is viscose, and why is it problematic for the environment?
A: Viscose, also known as rayon, is a cellulose-based fabric derived from wood pulp. It’s problematic because its production often leads to deforestation, contributes to CO2 emissions, and involves the use of harmful chemicals that can pollute water sources if not properly managed.
Q: How can fashion brands ensure their viscose is sustainably sourced?
A: Brands can ensure sustainable sourcing by partnering with certified suppliers, implementing robust traceability systems, and opting for alternatives like Lyocell or recycled cellulose. Regular audits and transparency in reporting are also crucial.
Q: What role do consumers play in promoting sustainable viscose production?
A: Consumers play a vital role by choosing products made from sustainable materials, supporting brands with transparent supply chains, and demanding information about the environmental impact of their clothing purchases.
Q: How does the upcoming EU Deforestation Regulation affect the fashion industry?
A: The EU Deforestation Regulation will require fashion brands to conduct due diligence on their supply chains, ensure products are deforestation-free, and provide traceability information. Non-compliance could result in significant penalties and market exclusion.
Q: What are some eco-friendly alternatives to traditional viscose?
A: Eco-friendly alternatives include Lyocell (made from sustainably managed eucalyptus plantations), recycled cellulose (created from textile waste), bamboo viscose (when sourced responsibly), and natural fibers like organic cotton and hemp.