Understanding and Managing Leaf Spot Diseases in Cucurbits and Guava: A Comprehensive Guide

As agricultural experts and pioneers in satellite-based farm management solutions, we at Farmonaut understand the critical importance of identifying and managing plant diseases effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into some of the most destructive leaf spot diseases affecting cucurbits and guava, providing valuable insights on identification, prevention, and management strategies. Our focus will be on alternaria leaf spot of cucurbits, angular leaf spot of cucurbits, leaf spot of guava, and xanthomonas leaf spot.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Leaf Spot Diseases
- Alternaria Leaf Spot of Cucurbits
- Angular Leaf Spot of Cucurbits
- Leaf Spot of Guava
- Xanthomonas Leaf Spot
- Prevention and Management Strategies
- The Role of Technology in Disease Management
- Farmonaut’s Approach to Crop Health Monitoring
- FAQs
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Leaf Spot Diseases
Leaf spot diseases are among the most common and destructive plant ailments affecting crops worldwide. These diseases can significantly impact crop yield and quality, leading to substantial economic losses for farmers. Understanding the nature of these diseases, their causes, and effective management techniques is crucial for maintaining healthy and productive crops.
Leaf spot diseases are characterized by the appearance of lesions on the leaves, which can vary in size, shape, and color depending on the specific pathogen involved. These lesions can coalesce and lead to extensive leaf damage, reducing the plant’s photosynthetic capacity and overall health. In severe cases, leaf spot diseases can cause defoliation, fruit damage, and even plant death.
2. Alternaria Leaf Spot of Cucurbits
Alternaria leaf spot of cucurbits is a fungal disease caused by various species of Alternaria, primarily A. cucumerina and A. alternata. This disease affects a wide range of cucurbit crops, including cucumbers, melons, squash, and pumpkins.
Symptoms and Identification
- Small, circular, brown to black spots on leaves, stems, and fruits
- Lesions often have a target-like appearance with concentric rings
- As the disease progresses, spots may enlarge and coalesce, causing leaf yellowing and necrosis
- Severe infections can lead to defoliation and fruit rot
Disease Cycle and Favorable Conditions
Alternaria fungi survive on crop debris and can be spread through wind, rain splash, and contaminated seeds. The disease thrives in warm (68-80°F), humid conditions with frequent rainfall or overhead irrigation.
Impact on Crop Production
Alternaria leaf spot can significantly reduce crop yields by damaging leaves and fruits. Severe infections can lead to premature defoliation, sunscald of fruits, and reduced fruit quality and marketability.
3. Angular Leaf Spot of Cucurbits
Angular leaf spot of cucurbits is a bacterial disease caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans. This disease primarily affects cucumber and melon crops but can also impact other cucurbits.
Symptoms and Identification
- Small, water-soaked lesions on leaves, often angular in shape due to leaf vein boundaries
- Lesions turn tan to brown and may develop a yellow halo
- Infected areas may tear or fall out, giving leaves a ragged appearance
- On fruits, small, circular, water-soaked spots may develop
Disease Cycle and Favorable Conditions
The bacteria can survive on crop debris and infected seeds. It spreads through water splash, wind-driven rain, and contaminated tools. The disease is favored by high humidity and temperatures between 75-82°F.
Impact on Crop Production
Angular leaf spot can cause significant yield losses, especially in cucumber production. Severe infections can lead to defoliation, reduced photosynthesis, and decreased fruit quality and marketability.
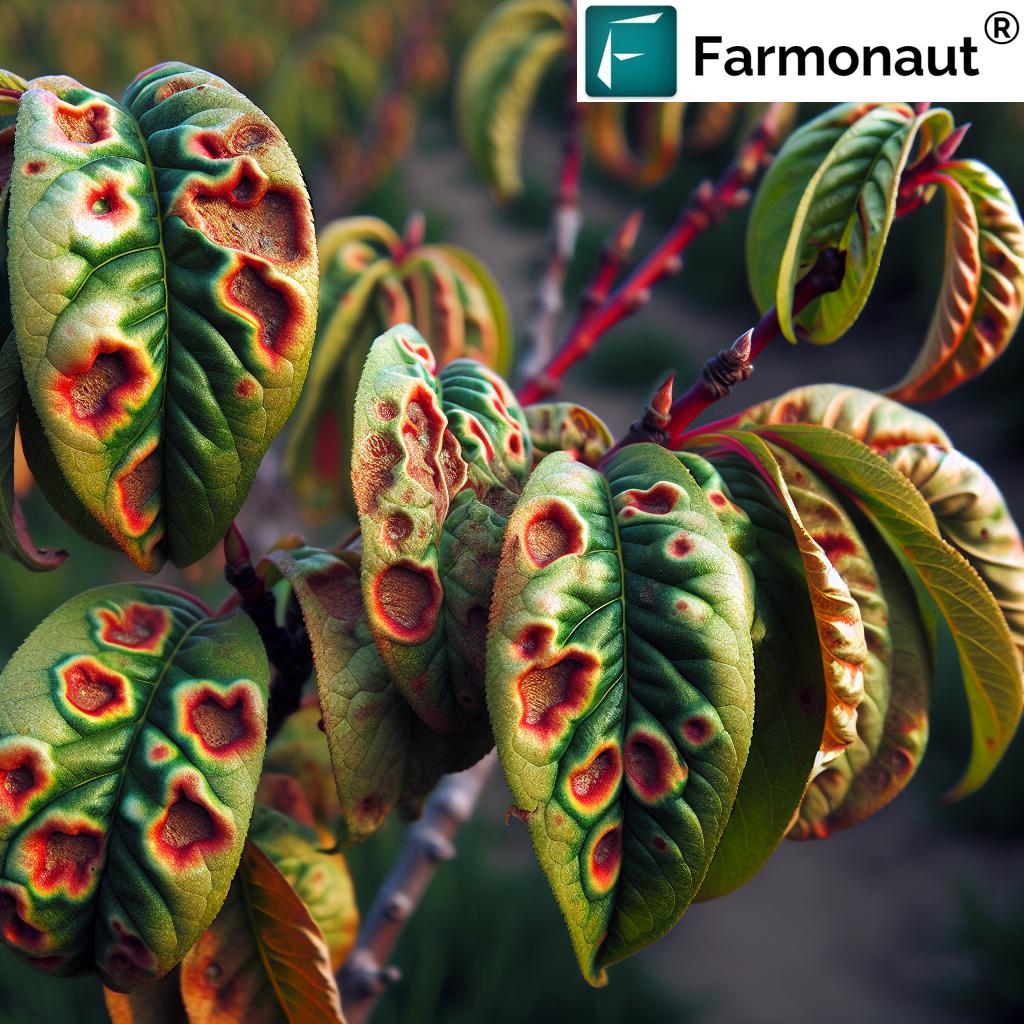
4. Leaf Spot of Guava
Leaf spot of guava can be caused by various pathogens, including fungi and bacteria. One of the most common causal agents is the fungus Pestalotiopsis psidii.
Symptoms and Identification
- Small, circular to irregular spots on leaves, often with a dark brown margin and lighter center
- Spots may coalesce, forming larger necrotic areas
- Severe infections can cause premature leaf drop
- Fruit spots may develop, reducing quality and marketability
Disease Cycle and Favorable Conditions
The pathogens responsible for guava leaf spot can survive on fallen leaves and other plant debris. They are typically spread by wind and rain splash. Warm, humid conditions favor disease development.
Impact on Crop Production
Leaf spot diseases in guava can lead to reduced photosynthetic capacity, premature defoliation, and decreased fruit yield and quality. Severe infections can impact tree health and longevity.
5. Xanthomonas Leaf Spot
Xanthomonas leaf spot is a bacterial disease that affects various crops, including vegetables and fruit trees. It is caused by different species of Xanthomonas bacteria, with the specific species varying depending on the host plant.
Symptoms and Identification
- Water-soaked lesions that turn brown or black as they age
- Lesions often have a yellow halo
- In some cases, lesions may have an angular appearance due to leaf vein boundaries
- Severe infections can lead to leaf yellowing, necrosis, and defoliation
Disease Cycle and Favorable Conditions
Xanthomonas bacteria can survive on crop debris and weed hosts. They are spread through water splash, wind-driven rain, and contaminated tools or equipment. The disease is favored by warm, humid conditions and frequent rainfall or overhead irrigation.
Impact on Crop Production
Xanthomonas leaf spot can cause significant yield losses in susceptible crops. It reduces photosynthetic capacity, can lead to defoliation, and may affect fruit quality and marketability.
6. Prevention and Management Strategies
Effective management of leaf spot diseases requires an integrated approach combining cultural, chemical, and biological control methods. Here are some key strategies:
Cultural Control
- Crop rotation with non-host plants to reduce pathogen buildup in the soil
- Proper plant spacing to improve air circulation and reduce humidity
- Removal and destruction of infected plant debris
- Use of disease-resistant varieties when available
- Avoiding overhead irrigation and working in fields when plants are wet
- Proper sanitation of tools and equipment
Chemical Control
- Application of appropriate fungicides or bactericides based on the specific pathogen
- Timing applications to coincide with environmental conditions favorable for disease development
- Rotating between different classes of fungicides to prevent resistance development
- Following all label instructions and local regulations for pesticide use
Biological Control
- Use of beneficial microorganisms that can compete with or inhibit pathogens
- Application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria to enhance plant health and disease resistance
- Incorporation of organic amendments to improve soil health and microbial diversity
7. The Role of Technology in Disease Management
Advancements in agricultural technology have revolutionized the way we approach disease management in crops. At Farmonaut, we leverage cutting-edge satellite technology and artificial intelligence to provide farmers with powerful tools for early disease detection and management.
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system uses multispectral imagery to detect changes in plant health before they become visible to the naked eye. This allows for early intervention and more targeted management strategies.
AI-Powered Disease Prediction
By analyzing historical data, weather patterns, and current crop conditions, our AI algorithms can predict the likelihood of disease outbreaks, allowing farmers to take preventive measures proactively.
Precision Agriculture
Our technology enables precise application of inputs, including fungicides and fertilizers, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact while maximizing efficacy.
8. Farmonaut’s Approach to Crop Health Monitoring
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing farmers with the most advanced and user-friendly tools for crop health monitoring and disease management. Our platform offers several key advantages:
Real-Time Monitoring
Our satellite-based system provides real-time updates on crop health, allowing for immediate response to potential issues.
Customized Alerts
Farmers receive personalized alerts based on their specific crops and local conditions, ensuring they stay informed about potential disease threats.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Our platform provides comprehensive data analysis, enabling farmers to make informed decisions about disease management strategies.
Integration with Other Farm Management Tools
Farmonaut’s crop health monitoring system integrates seamlessly with our other farm management tools, providing a holistic approach to agricultural productivity.
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (hundreds to thousands of hectares) | Limited (typically less than 100 hectares per flight) | Limited to sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Daily to weekly | As needed, but limited by battery life and regulations | Continuous, but limited to sensor locations |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (drone purchase, training) | Medium to High (sensors, network infrastructure) |
| Operational Complexity | Low (cloud-based system) | High (requires trained pilot, maintenance) | Medium (requires sensor maintenance, data management) |
| Weather Dependency | Low (can penetrate cloud cover) | High (affected by wind, rain) | Low (but sensors can be affected by extreme conditions) |
| Data Processing Time | Fast (automated processing) | Moderate to Slow (manual processing often required) | Fast (real-time data available) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability | Moderately scalable, but becomes complex with large areas |
To experience the power of Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions, visit our app or explore our API documentation. You can also download our mobile app for Android or iOS.
9. FAQs
- Q: How can I differentiate between different types of leaf spot diseases?
A: While visual symptoms can provide clues, accurate diagnosis often requires laboratory testing. Key differences include the shape, size, and color of lesions, as well as the presence of fruiting bodies or bacterial ooze. - Q: Are organic control methods effective against leaf spot diseases?
A: Organic methods can be effective when used as part of an integrated management approach. These include cultural practices, biological controls, and approved organic fungicides or bactericides. - Q: How often should I monitor my crops for leaf spot diseases?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially during periods of favorable disease conditions. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring system, you can receive daily updates on crop health. - Q: Can leaf spot diseases spread to other crop types?
A: Many leaf spot pathogens are host-specific, but some can affect multiple plant species. Proper crop rotation and sanitation practices can help prevent spread between different crops. - Q: How does climate change impact the prevalence of leaf spot diseases?
A: Climate change can alter disease patterns by affecting temperature, humidity, and precipitation. This may lead to changes in disease prevalence and severity, highlighting the importance of adaptive management strategies.
10. Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing leaf spot diseases is crucial for maintaining healthy, productive crops. By combining traditional agricultural knowledge with advanced technology like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system, farmers can stay ahead of potential disease outbreaks and optimize their crop management strategies.
We encourage you to explore our comprehensive farm management solutions and experience the benefits of precision agriculture. Subscribe to Farmonaut today and take your farming to the next level:
For more information on our satellite and weather API, please visit our developer documentation.
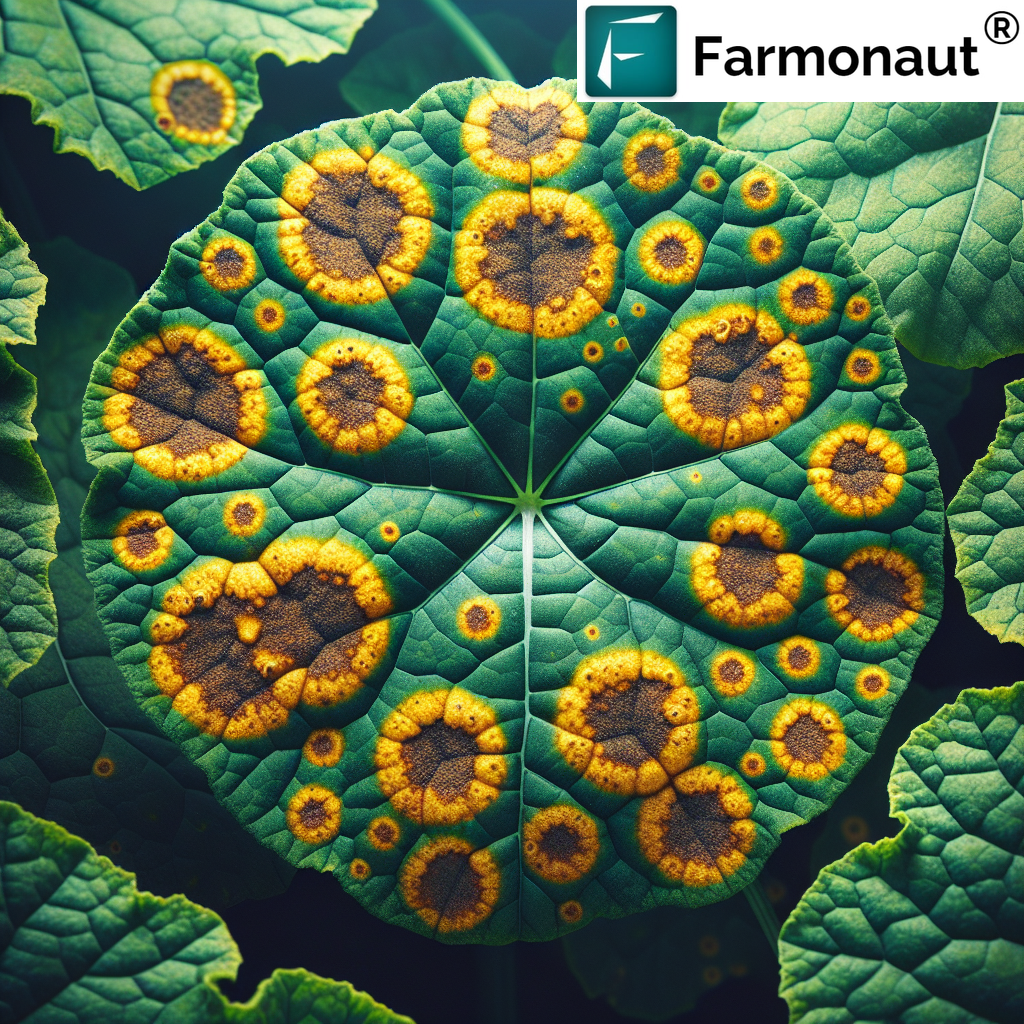

By staying informed, utilizing advanced technologies, and implementing integrated management strategies, we can work together to minimize the impact of leaf spot diseases and ensure sustainable, productive agriculture for years to come.