Mastering Crop Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Common Plant Diseases and Pests
In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, protecting crops from diseases and pests remains a critical challenge for farmers worldwide. At Farmonaut, we understand the importance of early detection and effective management of these threats to ensure healthy, bountiful harvests. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore some of the most common plant diseases and pests that affect various crops, and discuss strategies for prevention and control.
The Importance of Early Detection
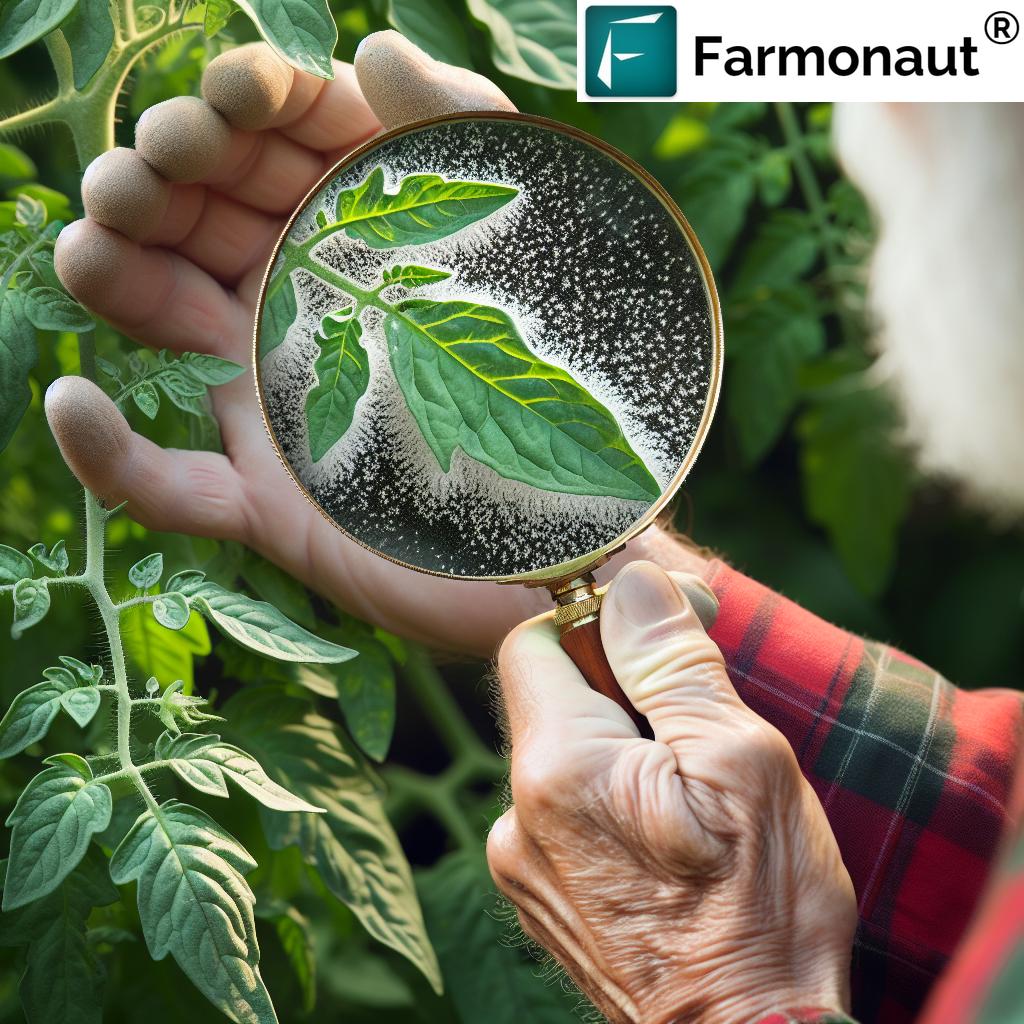
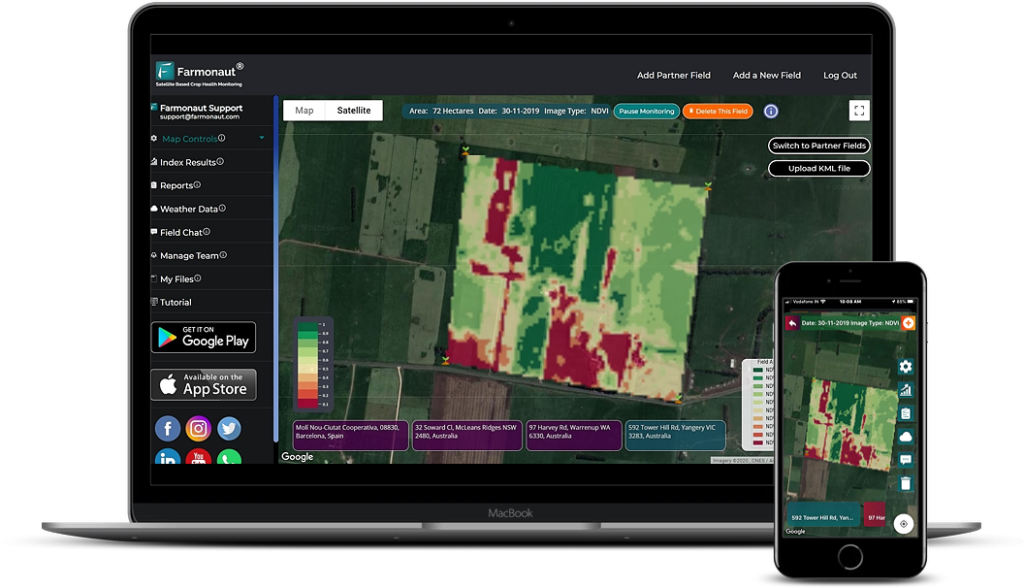
Before we delve into specific diseases and pests, it’s crucial to emphasize the significance of early detection in crop protection. Traditional scouting methods, while valuable, can be time-consuming and may miss early signs of infestation or disease. This is where advanced technologies like satellite-based crop monitoring come into play.
| Method | Coverage | Frequency | Accuracy | Cost-effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Scouting | Limited to accessible areas | Periodic, labor-dependent | Varies with expertise | Labor-intensive, time-consuming |
| Farmonaut Satellite System | Entire field coverage | Regular, automated updates | High, data-driven analysis | Highly cost-effective for large areas |
As you can see, our satellite-based crop monitoring system at Farmonaut offers significant advantages in terms of coverage, frequency, and cost-effectiveness. By providing regular, comprehensive field assessments, we enable farmers to detect and address issues before they become widespread problems.
Common Plant Diseases
Let’s explore some of the most prevalent plant diseases that farmers encounter:
1. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of crops, including cucurbits, grapes, and apples. It appears as a white or gray powdery coating on leaves, stems, and sometimes fruit. This disease thrives in humid conditions with moderate temperatures.
- Symptoms: White or grayish powdery spots on leaves and stems
- Control: Fungicides, proper plant spacing, resistant varieties
2. Leaf Spot Diseases
Leaf spot diseases can be caused by various fungi and bacteria. They manifest as discolored spots on leaves, which can lead to defoliation if left untreated.
- Symptoms: Circular or irregular spots on leaves, often with a yellow halo
- Control: Crop rotation, fungicides, improved air circulation
3. Mosaic Viruses
Mosaic viruses affect numerous crops, including tomatoes, cucurbits, and beans. They cause mottled patterns on leaves and can stunt plant growth.
- Symptoms: Mottled light and dark green patterns on leaves, stunted growth
- Control: Vector control (often aphids), resistant varieties, sanitation
4. Bacterial Canker
Bacterial canker is a serious disease affecting many fruit trees, particularly citrus. It causes lesions on leaves, stems, and fruit.
- Symptoms: Raised, corky lesions on fruits, leaves, and twigs
- Control: Copper-based sprays, pruning infected parts, quarantine measures
5. Tomato Wilt Diseases
Several pathogens can cause wilt in tomatoes, including Fusarium and Verticillium. These diseases block the plant’s vascular system, leading to wilting and eventual death.
- Symptoms: Wilting, yellowing leaves, brown discoloration in stem cross-sections
- Control: Resistant varieties, crop rotation, soil solarization
Common Crop Pests
Now, let’s turn our attention to some of the most problematic pests that farmers encounter:
1. Aphids
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap. They can reproduce rapidly and often transmit plant viruses.
- Symptoms: Curled or distorted leaves, sticky honeydew on leaves
- Control: Insecticidal soaps, natural predators, neem oil
2. Scale Insects
Scale insects, including armored scales, are small, immobile pests that attach themselves to plant parts and feed on sap.
- Symptoms: Small, bumpy scales on stems and leaves, yellowing leaves
- Control: Horticultural oils, pruning affected parts, biological control
3. Mites
Mites, such as spider mites and the olive mite (Aceria oleae), are tiny arachnids that can cause significant damage to crops.
- Symptoms: Stippling on leaves, webbing (for spider mites), leaf bronzing
- Control: Miticides, predatory mites, increasing humidity
4. Fruit Flies
Fruit flies are a major pest for many fruit crops, laying eggs in ripening fruit and causing significant economic losses.
- Symptoms: Small punctures on fruit, premature fruit drop
- Control: Traps, bait sprays, sanitation practices
5. Lace Bugs
Lace bugs are small insects that feed on the undersides of leaves, causing stippling and discoloration.
- Symptoms: Yellow or white stippling on upper leaf surfaces
- Control: Insecticidal soaps, neem oil, proper plant care
Specific Crop Diseases and Pests
Let’s take a closer look at some diseases and pests that affect specific crops:
Olive Trees
Olive trees are susceptible to several pests and diseases:
- Olive leaf spot (Spilocaea oleaginea): Causes dark spots on leaves
- Olive knot (bacterial): Results in gall-like growths on branches
- Olive fruit fly: Lays eggs in olive fruits, causing damage
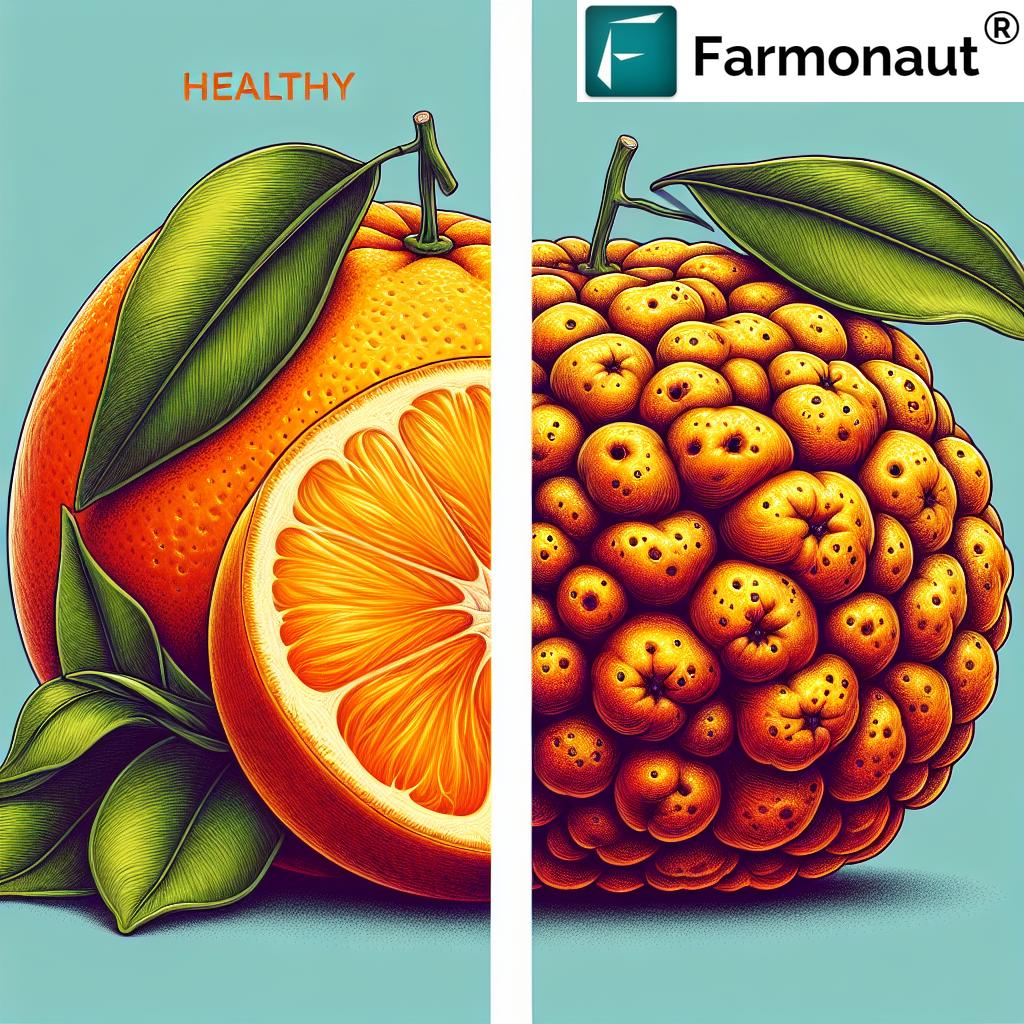
Citrus Trees
Citrus crops face several challenges:
- Citrus canker (bacterial): Causes lesions on leaves, stems, and fruit
- Citrus greening (bacterial): Leads to yellowing leaves and bitter, misshapen fruit
- Scale insects: Various species can infest citrus trees
Grapes
Grape vines are prone to several diseases:
- Powdery mildew: Affects leaves, stems, and fruit clusters
- Black rot: Causes dark lesions on leaves and fruit
- Pierce’s disease (bacterial): Leads to leaf scorching and eventual vine death
Alfalfa
Alfalfa crops can be affected by:
- Alfalfa mosaic virus: Causes mottling and stunting
- Anthracnose: Fungal disease causing stem lesions
- Alfalfa weevil: Insect pest that feeds on leaves
Bananas
Banana plantations face several threats:
- Panama disease (Fusarium wilt): Causes wilting and yellowing of leaves
- Black Sigatoka: Fungal disease affecting leaves
- Banana weevil: Insect pest that damages the plant’s rhizome
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach to crop protection. IPM combines various strategies to manage pests and diseases effectively while minimizing environmental impact:
- Prevention: Using resistant varieties, proper sanitation, and cultural practices
- Monitoring: Regular field scouting and using advanced technologies like our satellite-based crop monitoring
- Biological control: Encouraging natural predators and using biopesticides
- Chemical control: Using pesticides judiciously when necessary
- Record keeping: Maintaining detailed records of pest occurrences and control measures
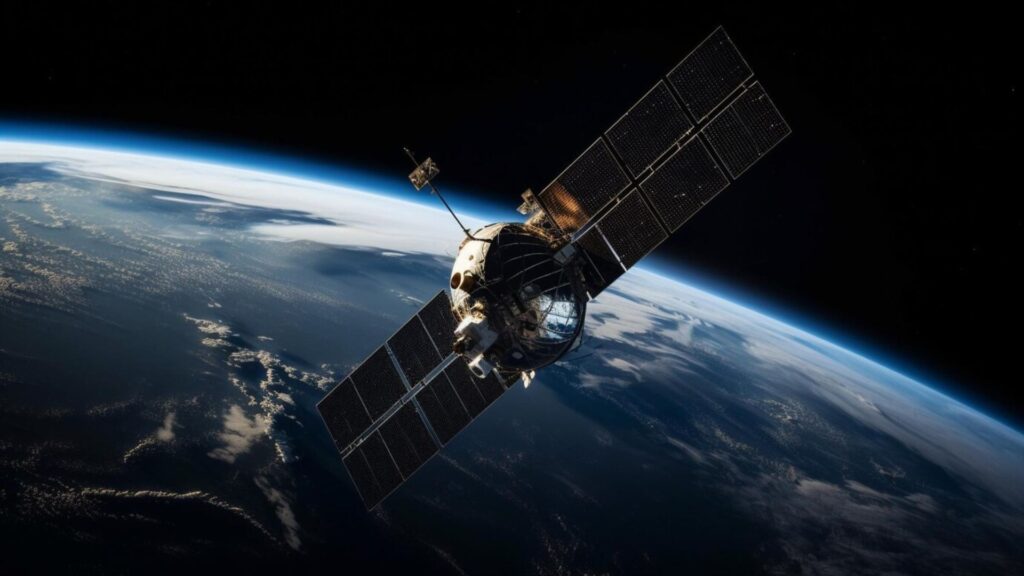
The Role of Technology in Crop Protection
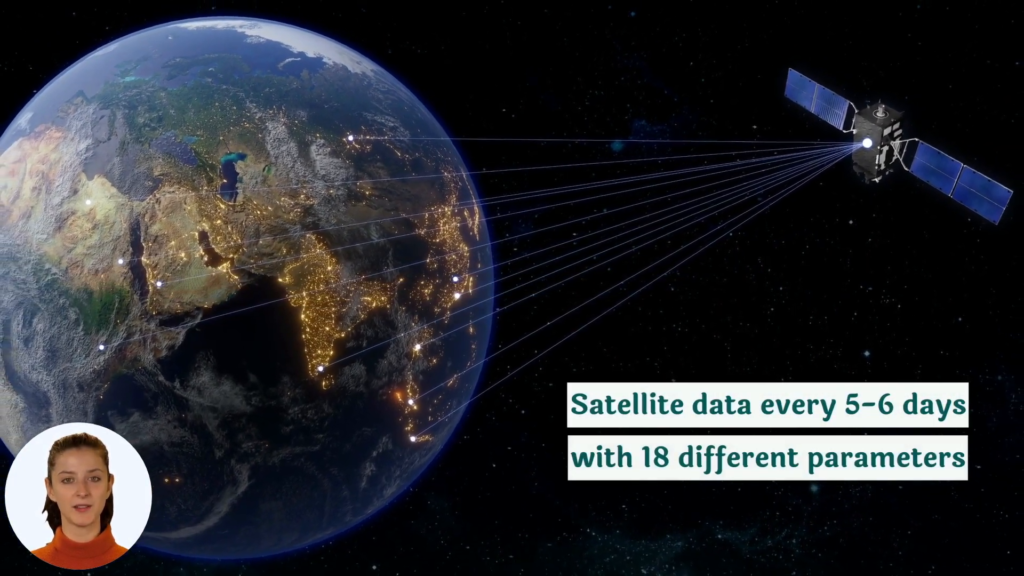
Advanced technologies play a crucial role in modern crop protection strategies. At Farmonaut, we leverage satellite imagery and artificial intelligence to provide farmers with valuable insights into crop health and potential threats.

Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers several advantages:
- Early detection of stress patterns that may indicate disease or pest infestation
- Regular, automated field assessments without the need for physical scouting
- Historical data analysis to identify trends and predict potential issues
- Integration with weather data to forecast disease-favorable conditions
To learn more about how our technology can help protect your crops, visit our crop monitoring application or explore our API services for developers.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Crop Health
While not diseases or pests, nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact crop health and make plants more susceptible to infections and infestations. Common deficiencies include:
- Nitrogen deficiency: Yellowing of older leaves, stunted growth
- Phosphorus deficiency: Purple discoloration of leaves, poor root development
- Potassium deficiency: Leaf edge scorching, weak stems
- Iron deficiency: Interveinal chlorosis, particularly in young leaves
Our satellite-based monitoring system can help detect patterns indicative of nutrient deficiencies, allowing for timely intervention and targeted fertilization strategies.
Climate Change and Crop Protection
Climate change poses new challenges for crop protection. Changing weather patterns can:
- Alter the geographic distribution of pests and diseases
- Increase the frequency of extreme weather events, stressing crops
- Change the timing of pest life cycles
- Reduce the efficacy of some pest control methods
At Farmonaut, we continuously update our models to account for these changes, providing farmers with the most relevant and up-to-date information to protect their crops in a changing climate.
The Future of Crop Protection
The field of crop protection is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and strategies emerging regularly. Some exciting developments include:
- Gene editing for disease-resistant crop varieties
- Advanced biologicals for pest control
- Precision agriculture tools for targeted treatments
- AI-powered disease diagnosis systems
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these advancements, continually improving our services to help farmers protect their crops more effectively and sustainably.
Conclusion
Effective crop protection is a complex but crucial aspect of modern agriculture. By understanding common diseases and pests, implementing integrated management strategies, and leveraging advanced technologies, farmers can significantly improve their crop health and yields.
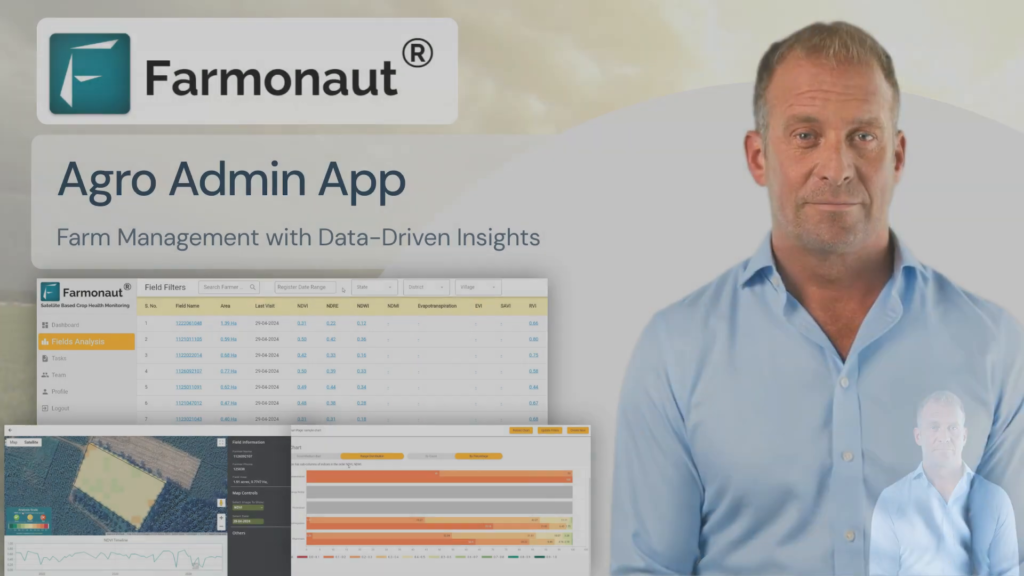
At Farmonaut, we’re dedicated to supporting farmers in this endeavor. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system, combined with AI-driven insights, provides a powerful tool for early detection and management of crop health issues.
To experience the benefits of our technology firsthand, download our app for Android or iOS, or explore our API documentation for custom integrations.
FAQs
Q: How often should I scout my fields for pests and diseases?
A: Regular scouting is crucial, ideally weekly during the growing season. However, with Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive frequent updates without physical scouting.
Q: Can organic farmers use Farmonaut’s services?
A: Absolutely! Our satellite monitoring is particularly useful for organic farmers, helping them detect issues early and implement organic control measures promptly.
Q: How accurate is satellite-based crop monitoring in detecting diseases?
A: While it can’t diagnose specific diseases, our system can detect stress patterns that often indicate disease or pest problems, prompting timely field inspections.
Q: Does Farmonaut provide pest and disease forecasting?
A: Yes, by combining satellite data with weather information, we can provide risk assessments for certain diseases based on environmental conditions.
Q: How can I get started with Farmonaut’s crop monitoring system?
A: You can sign up for our services through our website or mobile apps. Here’s a quick way to subscribe: