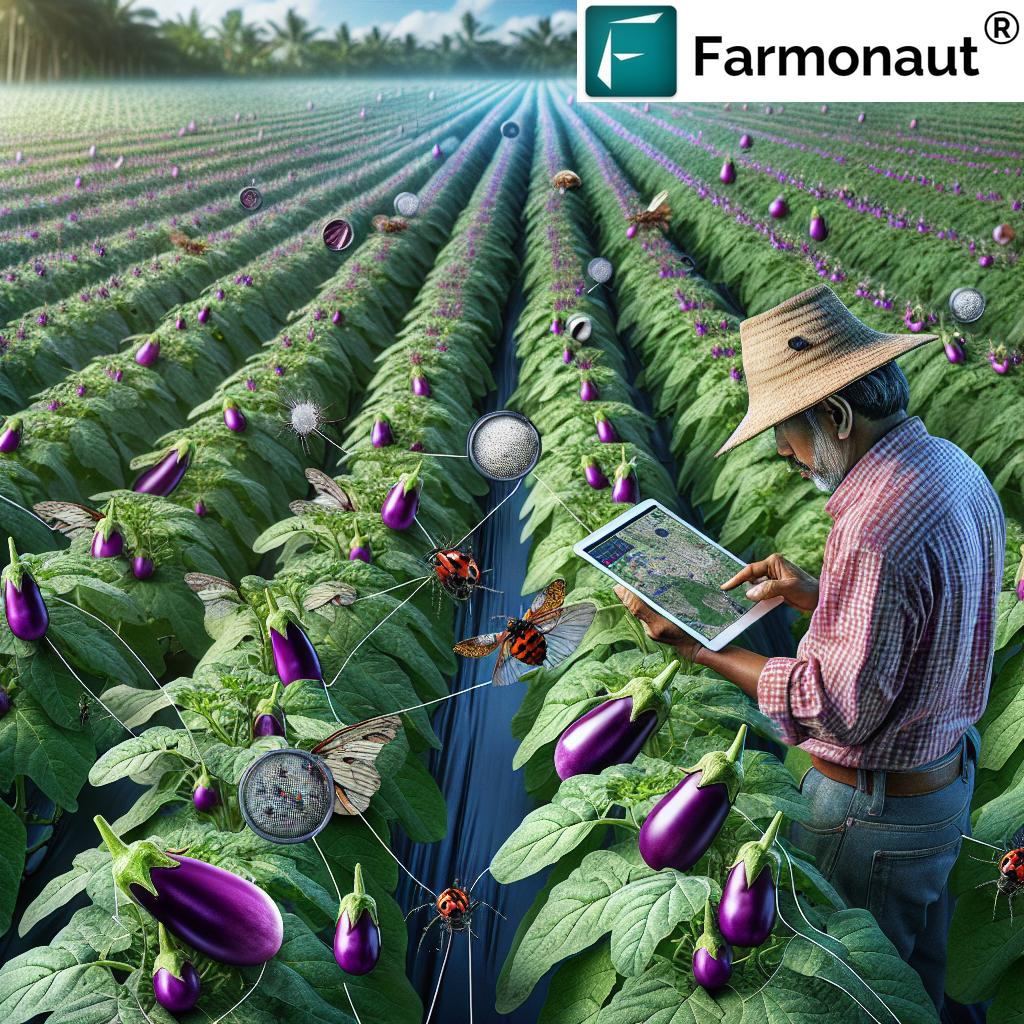
Mastering Organic Eggplant Pest Control: Effective IPM Strategies for Sustainable Crop Protection
“Organic eggplant pest control can utilize over 5 different natural insecticides, including neem oil and mineral-based solutions.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on organic eggplant pest management and integrated pest management (IPM) strategies for sustainable crop protection. In this article, we’ll explore effective techniques to identify, prevent, and combat common eggplant pests while maintaining the principles of organic farming. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or new to organic vegetable gardening, you’ll find valuable insights to help you protect your eggplants, tomatoes, and potatoes from harmful insects without relying on conventional chemical insecticides.

Understanding Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Eggplants
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that combines various strategies to minimize pest damage while reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. For eggplant growers, implementing IPM techniques can lead to healthier plants, higher yields, and a more sustainable farming practice.
- Cultural controls: Proper plant spacing, crop rotation, and sanitation
- Biological controls: Encouraging beneficial insects and natural predators
- Mechanical controls: Physical barriers and traps
- Chemical controls: Using organic and low-toxicity pesticides as a last resort
By integrating these methods, we can create a robust pest management system that protects our eggplants while minimizing environmental impact.
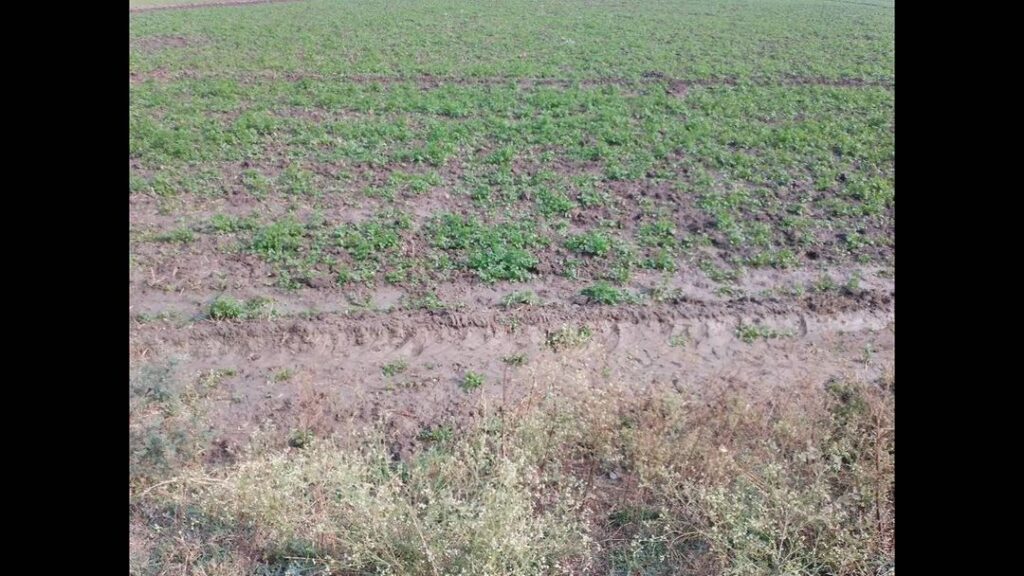
Common Eggplant Pests and Their Identification
To effectively manage pests, it’s crucial to identify them correctly. Here are some common insects that infest eggplants:
- Gargaphia solani (Eggplant Lace Bug): These small insects feed on the underside of leaves, causing yellowish or bronze discoloration.
- Colorado Potato Beetle: Recognizable by its yellow and black striped appearance, this pest can quickly defoliate eggplants.
- Flea Beetles: Tiny jumping beetles that create small holes in leaves, particularly damaging to young plants.
- Aphids: Small, soft-bodied insects that cluster on new growth and suck plant sap.
Regular monitoring of your eggplant crop is essential for early detection of these pests. Inspect the underside of leaves, stems, and fruit for signs of infestation or damage.
Organic Pest Control Methods for Eggplants
When it comes to organic eggplant pest control, we have several effective options that don’t rely on harmful chemical insecticides:
- Neem oil: A natural insecticide that disrupts pest feeding and reproduction
- Mineral-based solutions: Such as diatomaceous earth or kaolin clay, which create physical barriers against pests
- Botanical insecticides: Derived from plants like pyrethrum or rotenone (use with caution)
- Insecticidal soaps: Effective against soft-bodied insects like aphids
- Beneficial insects: Introduce ladybugs, lacewings, or predatory mites to control pest populations
These organic treatments provide effective pest control while maintaining the integrity of your organic farming practices.
Implementing IPM Strategies in Your Eggplant Field
To successfully implement IPM strategies for eggplant pest management, follow these steps:
- Monitor regularly: Inspect your plants at least twice a week for signs of pest activity or damage.
- Set action thresholds: Determine the pest population levels at which control measures become necessary.
- Use preventive measures: Implement cultural and mechanical controls to discourage pest infestations.
- Apply biological controls: Introduce or encourage natural predators of eggplant pests.
- Use organic treatments: When necessary, apply organic pesticides judiciously.
- Evaluate and adjust: Continuously assess the effectiveness of your IPM strategies and make adjustments as needed.
“Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for eggplants can increase crop yields by up to 30% compared to conventional pest control methods.”

Leveraging Technology for Effective Pest Monitoring
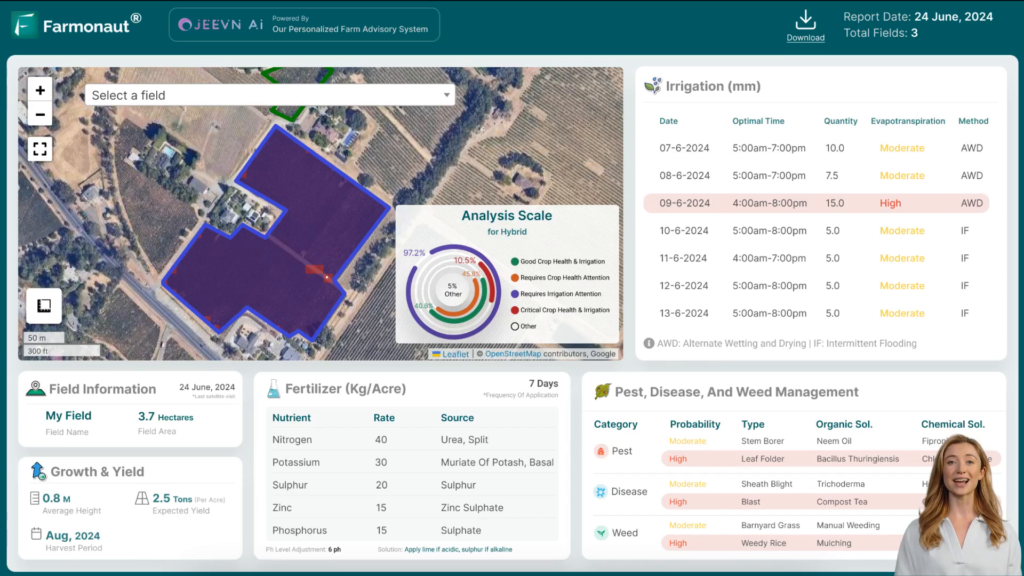
Modern technology can greatly enhance our ability to monitor and manage pests in eggplant crops. Farmonaut, a pioneering agricultural technology company, offers advanced satellite-based farm management solutions that can revolutionize pest control strategies.
By utilizing Farmonaut’s satellite imagery and AI-driven insights, farmers can:
- Detect early signs of pest infestation through vegetation health analysis
- Monitor crop health in real-time, allowing for timely intervention
- Receive personalized pest management recommendations based on field conditions
- Optimize resource allocation for pest control measures
To learn more about how Farmonaut can enhance your pest management strategies, visit their web application or download their mobile apps:
Comparison of Eggplant Pest Detection Methods
| Detection Method | Time Required | Accuracy | Early Warning Capability | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Field Inspections | 2-3 hours per acre | 70-80% | Limited | Low (labor-intensive) |
| Pheromone Traps | 1-2 hours per acre (setup + monitoring) | 75-85% | Moderate | Moderate |
| Farmonaut Satellite Monitoring | 5-10 minutes per acre | 90-95% | High (5-7 days earlier) | High (long-term savings) |
As we can see from the table, Farmonaut’s satellite-based pest detection system offers significant advantages in terms of time savings, accuracy, and early warning capabilities. This technology can be a game-changer for organic eggplant growers looking to implement effective IPM strategies.
Natural Insecticides for Organic Eggplant Pest Control
When pest populations reach action thresholds, organic growers can turn to natural insecticides as part of their IPM strategy. Here are some effective options:
- Neem oil: Derived from the neem tree, this oil disrupts insect feeding and growth.
- Pyrethrin: Extracted from chrysanthemum flowers, it’s effective against a wide range of pests.
- Spinosad: A bacterial-derived insecticide that targets caterpillars and beetles.
- Diatomaceous earth: A fine powder that damages the exoskeletons of insects.
- Garlic and hot pepper sprays: Homemade solutions that repel many common pests.
Remember to always follow label instructions and apply these natural insecticides judiciously as part of a comprehensive IPM approach.
Cultural Practices for Eggplant Pest Prevention
Implementing proper cultural practices is crucial for preventing pest infestations in eggplant crops. Consider the following techniques:
- Crop rotation: Avoid planting eggplants or related crops in the same area for consecutive seasons.
- Companion planting: Grow pest-repelling plants like marigolds or herbs near your eggplants.
- Proper spacing: Ensure adequate air circulation to reduce humidity and pest habitat.
- Timely harvesting: Remove ripe fruits promptly to discourage pest attraction.
- Soil health: Maintain healthy soil through composting and proper nutrition to boost plant resilience.
By incorporating these practices into your farming routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of pest infestations and minimize the need for interventions.
Biological Control Methods for Eggplant Pests
Biological control is a cornerstone of IPM strategies for eggplants. By encouraging or introducing natural predators, we can keep pest populations in check without resorting to chemical controls. Some effective biological control agents for eggplant pests include:
- Ladybugs: Voracious consumers of aphids and other soft-bodied insects.
- Lacewings: Both adults and larvae feed on various pests, including aphids and mites.
- Parasitic wasps: Lay eggs in or on pest insects, controlling their populations.
- Predatory mites: Effective against spider mites and other small pests.
- Nematodes: Microscopic worms that can control soil-dwelling pests.
To encourage these beneficial insects, consider planting flowering herbs and native plants nearby to provide habitat and alternative food sources.
Monitoring and Record-Keeping for Successful IPM
Effective pest management relies on diligent monitoring and accurate record-keeping. By tracking pest populations, treatment efficacy, and environmental conditions, you can make informed decisions and refine your IPM strategies over time. Consider the following monitoring techniques:
- Regular visual inspections of plants
- Use of sticky traps to capture flying insects
- Pheromone traps for specific pest species
- Soil sampling to monitor for soil-borne pests
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring system can complement these traditional methods by providing a broader view of crop health and potential pest hotspots. Learn more about their API and developer documentation to integrate this technology into your pest management workflow.
Sustainable Pest Management for Long-Term Success
Adopting sustainable pest management practices not only protects your current eggplant crop but also contributes to the long-term health of your farm ecosystem. Here are some key principles to keep in mind:
- Biodiversity: Encourage a diverse range of plants and beneficial insects on your farm.
- Soil health: Focus on building healthy, living soil to support strong, pest-resistant plants.
- Water management: Proper irrigation practices can help prevent conditions that favor pest development.
- Continuous learning: Stay informed about new organic pest control methods and IPM strategies.
- Community collaboration: Share knowledge and resources with other organic growers in your area.
By embracing these principles and utilizing advanced tools like Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, organic eggplant growers can achieve effective pest control while maintaining a sustainable and productive farming operation.
Conclusion: Embracing IPM for Healthier Eggplant Crops
Mastering organic eggplant pest control through Integrated Pest Management is a journey of continuous learning and adaptation. By combining cultural practices, biological controls, and judicious use of organic treatments, we can protect our crops while minimizing environmental impact. The integration of advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system further enhances our ability to detect and respond to pest threats promptly.
Remember that successful IPM is about creating a balanced ecosystem where pests are kept in check naturally, rather than eradicating them completely. With patience, observation, and the right tools at our disposal, we can cultivate thriving, pest-resistant eggplant crops that contribute to a more sustainable agricultural future.
FAQ Section
Q: How often should I inspect my eggplant plants for pests?
A: We recommend inspecting your eggplant plants at least twice a week, paying close attention to the underside of leaves where many pests feed and lay eggs.
Q: Can companion planting really help with pest control in eggplants?
A: Yes, companion planting can be effective. Plants like marigolds, basil, and nasturtiums can repel certain pests or attract beneficial insects that prey on eggplant pests.
Q: Is it safe to use neem oil on eggplants that are close to harvest?
A: While neem oil is generally considered safe for organic use, it’s best to avoid applying it within a week of harvest. Always follow label instructions for pre-harvest intervals.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help me with eggplant pest management?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring can detect early signs of pest infestation through vegetation health analysis, allowing for timely intervention and more targeted pest control efforts.
Q: What should I do if organic pest control methods aren’t working for my eggplant crop?
A: If organic methods are ineffective, consult with a local agricultural extension office or organic certification body for additional guidance. They may suggest alternative organic treatments or management strategies specific to your region and pest problems.