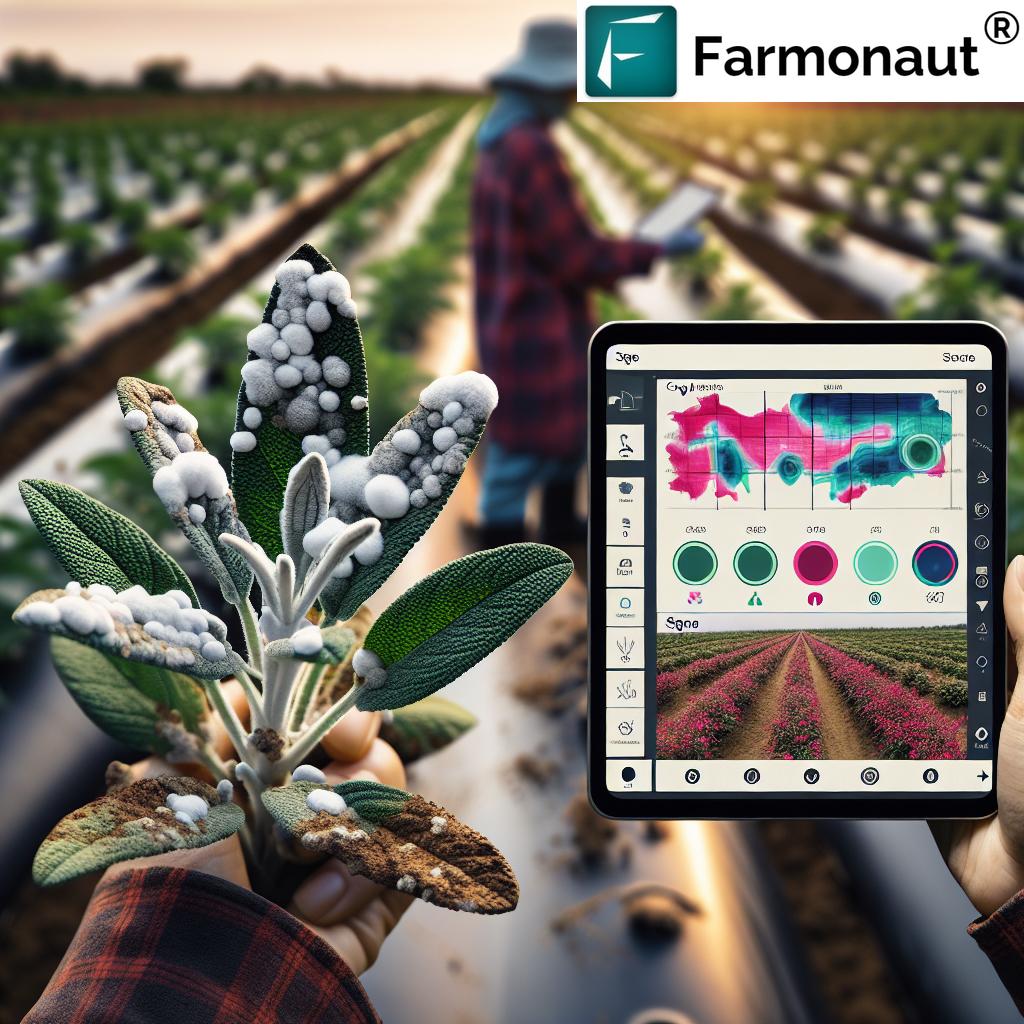
Mastering Powdery Mildew Control in Sage: Farmonaut’s Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on mastering powdery mildew control in sage. As experts in agricultural technology and plant health management, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges that herb farmers face when dealing with fungal diseases. In this extensive blog post, we’ll delve deep into the world of powdery mildew, its impact on sage crops, and the most effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that can wreak havoc on sage plants, affecting both yield and quality. As we explore this topic, we’ll cover everything from identification and prevention to organic and chemical control methods. We’ll also discuss how Farmonaut’s cutting-edge satellite technology and AI-driven insights can revolutionize your approach to sage disease control and overall crop health management.
Understanding Powdery Mildew in Sage
Before we dive into control methods, it’s crucial to understand what powdery mildew is and how it affects sage plants. Powdery mildew is caused by fungi belonging to the order Erysiphales. This fungal disease is characterized by the appearance of white or grayish powdery spots on the leaves and stems of infected plants.
Key Characteristics of Powdery Mildew:
- Appearance: White to grayish powdery coating on leaves and stems
- Favored Conditions: Warm temperatures, moderate humidity, and low light
- Spread: Spores can be dispersed by wind, water, or physical contact
- Impact: Reduced photosynthesis, stunted growth, and decreased yield
Powdery mildew in sage can cause significant damage if left unchecked. It can lead to reduced photosynthesis, nutrient deficiencies, and overall plant stress. In severe cases, it may result in leaf drop and even plant death. That’s why early detection and prompt action are crucial for effective sage disease control.
The Importance of Early Detection
When it comes to powdery mildew sage treatment, early detection is key. The sooner you identify the problem, the easier and more cost-effective it is to manage. Regular monitoring of your sage crop is essential for catching the first signs of powdery mildew infection.
Signs to Watch For:
- White, powdery spots on leaves and stems
- Yellowing or browning of leaves
- Curling or distortion of new growth
- Stunted plant growth
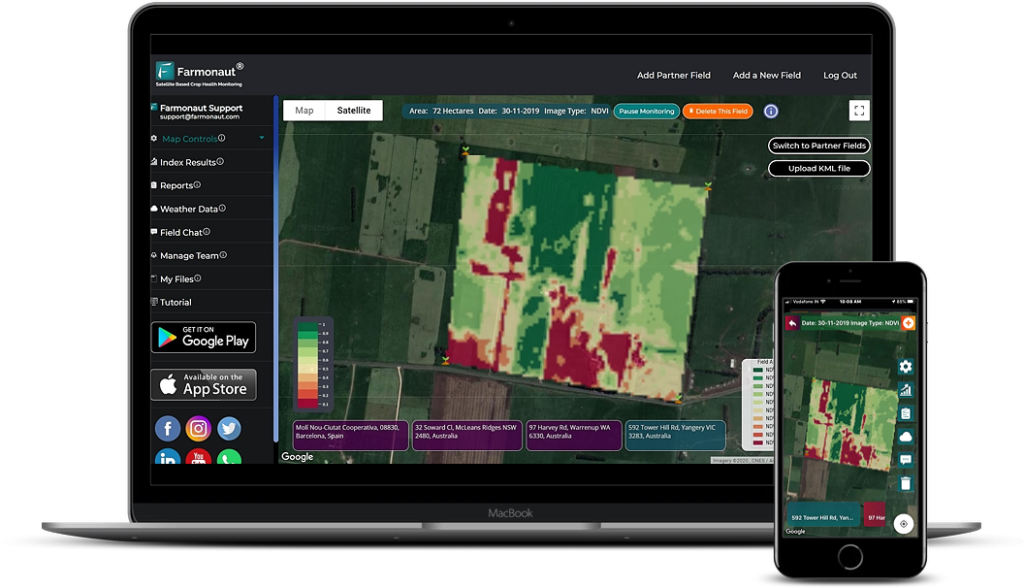
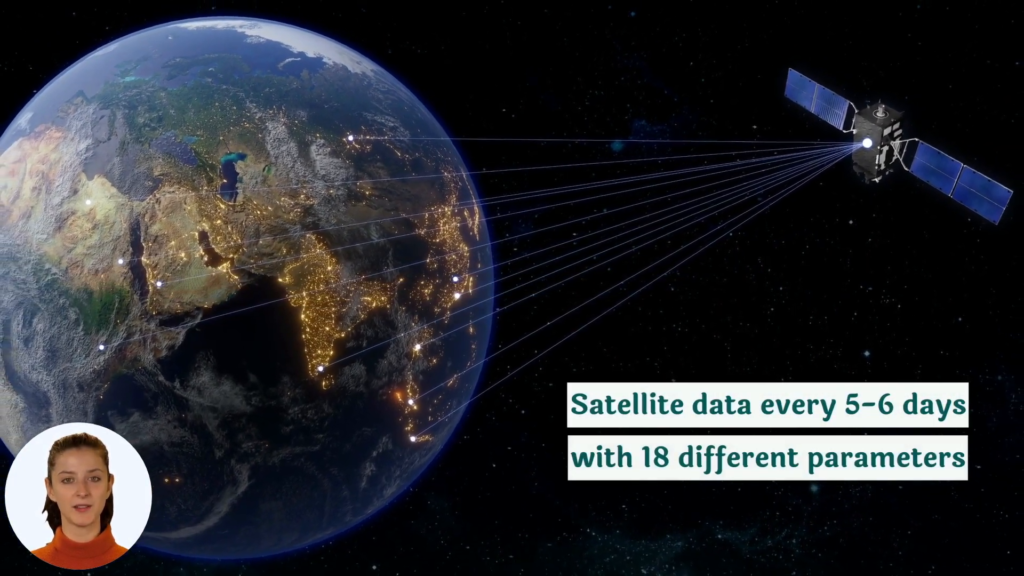
At Farmonaut, we understand the challenges of monitoring large areas of crops. That’s why our satellite-based crop health monitoring system is designed to provide real-time insights into your sage crop’s health. By analyzing multispectral satellite images, we can detect early signs of stress that may indicate powdery mildew or other issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Preventive Measures for Powdery Mildew Control
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to fungal diseases in herbs. Implementing good cultural practices can significantly reduce the risk of powdery mildew infection in your sage crop.
Key Preventive Strategies:
- Proper Spacing: Ensure adequate space between plants to improve air circulation
- Irrigation Management: Water at the base of plants and avoid overhead watering
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy infected plant debris
- Resistant Varieties: Choose powdery mildew resistant sage varieties when possible
- Crop Rotation: Practice crop rotation to reduce disease pressure
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of powdery mildew infection in your sage crop. However, even with the best prevention strategies, infections can still occur. That’s why it’s important to have a comprehensive management plan in place.
Organic Sage Pest Management Strategies
For those focused on organic herb cultivation, there are several effective strategies for managing powdery mildew without resorting to synthetic chemicals. These methods can be particularly beneficial for smaller operations or home gardeners.
Organic Control Methods:
- Milk Spray: A solution of 1 part milk to 9 parts water can be effective when applied weekly
- Neem Oil: An organic fungicide that also repels insects
- Potassium Bicarbonate: Can be used as a preventive spray or to treat mild infections
- Sulfur: Effective against powdery mildew but should be used cautiously in hot weather
- Biological Controls: Beneficial microorganisms like Bacillus subtilis can help prevent infection
These organic methods can be highly effective when used as part of an integrated pest management (IPM) approach. However, it’s important to note that organic treatments may require more frequent application and may not be as fast-acting as chemical alternatives.
Chemical Control Options for Powdery Mildew
While organic methods are preferred by many, there are situations where chemical control may be necessary, especially for large-scale commercial operations dealing with severe infestations. It’s crucial to use fungicides responsibly and in accordance with local regulations.
Common Chemical Fungicides for Powdery Mildew Control:
- Azoxystrobin: A broad-spectrum fungicide effective against various fungal diseases
- Myclobutanil: A systemic fungicide that provides both preventive and curative action
- Tebuconazole: Offers long-lasting protection against powdery mildew
- Copper-based fungicides: Can be effective but may cause phytotoxicity in some cases
When using chemical fungicides, it’s essential to rotate between different modes of action to prevent the development of fungicide resistance. Always follow the label instructions carefully and adhere to pre-harvest intervals to ensure food safety.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Herbs
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated pest management (IPM) approach to sage disease control. IPM combines various control methods to manage pests and diseases effectively while minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable herb cultivation.
Key Components of IPM for Herbs:
- Monitoring: Regular crop scouting and use of advanced technologies like satellite imaging
- Cultural Controls: Implementing best practices in planting, irrigation, and sanitation
- Biological Controls: Utilizing beneficial organisms to suppress pests and diseases
- Chemical Controls: Using pesticides judiciously and only when necessary
- Record Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of pest populations, treatments, and outcomes
By adopting an IPM approach, herb farmers can achieve effective powdery mildew control while promoting long-term sustainability and reducing reliance on chemical interventions.
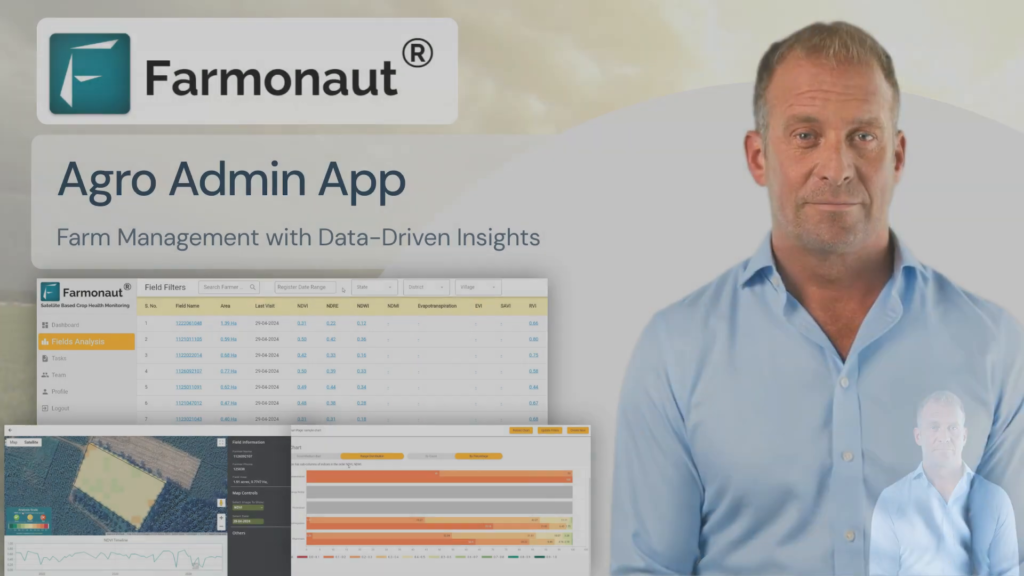
Farmonaut’s Role in Sage Plant Protection
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to revolutionizing sage crop protection through advanced technology. Our satellite-based crop health monitoring system provides valuable insights that can help you detect and manage powdery mildew more effectively.
How Farmonaut Enhances Sage Disease Control:
- Early Detection: Our satellite imagery can detect stress patterns indicative of powdery mildew before visible symptoms appear
- Precision Application: By identifying specific areas of concern, we help you target your treatments more efficiently
- Data-Driven Decisions: Our AI-powered insights help you make informed decisions about when and how to intervene
- Yield Optimization: By minimizing disease impact, we help you maximize your sage crop yield
To learn more about how Farmonaut can transform your approach to sage plant protection, visit our app page or explore our API documentation.
Powdery Mildew Detection and Management with Farmonaut
| Growth Stage | Visual Symptoms | NDVI Range | Farmonaut Alert Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early | Slight powdery patches on leaves | 0.7 – 0.8 | Low | Increase monitoring, consider preventive organic sprays |
| Mid | Widespread powdery coating, some leaf curling | 0.5 – 0.7 | Medium | Apply organic or chemical fungicides as needed, improve air circulation |
| Late | Heavy powdery coating, leaf distortion, stunted growth | < 0.5 | High | Aggressive treatment required, consider removing severely affected plants |
This table demonstrates how Farmonaut’s technology can help you detect and manage powdery mildew at different stages of infection. By providing real-time NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data, we enable you to take prompt and appropriate action to protect your sage crop.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should I monitor my sage plants for powdery mildew?
A1: We recommend monitoring your sage plants at least weekly during the growing season. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive regular updates on your crop’s health without the need for manual inspection.
Q2: Can powdery mildew spread to other herbs in my garden?
A2: Yes, powdery mildew can spread to other susceptible plants. It’s important to isolate infected plants and implement control measures promptly to prevent spread.
Q3: Are there any natural predators that can help control powdery mildew?
A3: While there are no natural predators that directly consume powdery mildew, certain beneficial microorganisms can help suppress its growth. Bacillus subtilis, for example, is a beneficial bacterium that can be used as a biocontrol agent.
Q4: How does Farmonaut’s technology detect powdery mildew before visible symptoms appear?
A4: Our satellite imagery analyzes various spectral bands to detect subtle changes in plant health. Stress caused by powdery mildew infection can be detected through changes in the plant’s reflectance patterns before visible symptoms appear to the naked eye.
Q5: Is it safe to use sulfur-based fungicides on sage?
A5: Sulfur-based fungicides can be effective against powdery mildew and are generally considered safe for use on sage. However, they should be used with caution in hot weather (above 90°F or 32°C) as they can cause leaf burn.
Conclusion: Empowering Sage Farmers with Technology
Mastering powdery mildew control in sage requires a combination of vigilance, preventive measures, and timely intervention. By leveraging Farmonaut’s advanced satellite technology and AI-driven insights, you can take your sage crop protection to the next level.
Our comprehensive approach to sage disease control and herb farming pest control enables you to:
- Detect potential issues early
- Make data-driven decisions
- Optimize resource use
- Increase crop yields
- Promote sustainable herb cultivation
Ready to revolutionize your approach to sage plant protection? Explore Farmonaut’s solutions today:
Join the future of precision agriculture with Farmonaut. Together, we can cultivate healthier, more productive sage crops and drive sustainable growth in the herb farming industry.
Subscribe to Farmonaut
Take the next step in optimizing your sage crop management. Subscribe to Farmonaut’s services and gain access to cutting-edge satellite monitoring, AI-powered insights, and expert support.
By subscribing to Farmonaut, you’re not just investing in a service – you’re investing in the future of your sage crop and the sustainability of your farming operation. Join us in revolutionizing herb farming through precision agriculture and data-driven insights.

Remember, with Farmonaut, you’re never alone in your fight against powdery mildew and other crop challenges. Our team of experts is always here to support you on your journey to mastering sage crop health management. Let’s grow together towards a more productive and sustainable future in herb cultivation.