Mastering Thrips Control: Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Sustainable Crop Protection
“Thrips, measuring only 1-2mm in length, can cause up to 80% yield loss in severely infested crops.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on thrips control in agriculture! As experts in precision farming and crop protection, we at Farmonaut understand the challenges farmers face when dealing with persistent pests like thrips. In this blog post, we’ll explore effective integrated pest management (IPM) techniques for combating thrips infestations, with a particular focus on Retithrips syriacus, a common pest affecting various crops.
Whether you’re managing vineyards, fruit orchards, or other susceptible crops, this article will provide you with essential knowledge for effective thrips management and maintaining healthy, productive crops. Let’s dive into the world of these tiny yet troublesome insects and discover sustainable solutions for crop protection.
Understanding Thrips: Characteristics and Impact
Thrips are small, slender insects belonging to the order Thysanoptera. The species we’ll focus on, Retithrips syriacus, is a member of the Thripidae family and is known for its destructive impact on various crops. Let’s explore the key characteristics of these pests:
- Size: Thrips are typically 1-2 mm in length, making them difficult to spot with the naked eye.
- Color: Adult thrips are usually brown to black, while nymphs are often red.
- Life Cycle: Thrips undergo incomplete metamorphosis, with egg, nymph, and adult stages.
- Feeding Habits: They use their rasping-sucking mouthparts to feed on plant cells, causing damage to leaves and fruits.
Thrips can cause significant damage to crops, leading to reduced yields and quality. Their feeding activity results in distinctive symptoms, including:
- Silvery patches on leaves and fruits
- Distorted growth of young leaves and shoots
- Scarring and discoloration of fruits
- Transmission of plant viruses
Understanding these characteristics and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of thrips infestations.
Potential Host Plants and Crop Vulnerability
Retithrips syriacus and related thrips species can infest a wide range of crops. Some of the most common host plants include:
- Grapevines
- Pomegranate
- Persimmon
- Avocado
- Cotton
- Roses
- Myrtle
These crops are particularly vulnerable to thrips infestations, and farmers should be vigilant in monitoring and protecting them. Regular field inspections and early intervention are key to preventing widespread damage.
Integrated Pest Management: A Sustainable Approach
At Farmonaut, we advocate for integrated pest management (IPM) as the most effective and sustainable approach to thrips control. IPM combines various strategies to manage pest populations while minimizing environmental impact and preserving beneficial insects. Here are the key components of an effective IPM program for thrips:
- Monitoring and Early Detection: Regular field scouting and use of sticky traps to detect thrips populations early.
- Cultural Controls: Implementing practices that make the environment less favorable for thrips.
- Biological Controls: Utilizing natural predators and parasites of thrips.
- Chemical Controls: Using selective insecticides as a last resort, when other methods are insufficient.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of pest populations, treatments, and their efficacy.
Let’s explore each of these components in more detail.
Monitoring and Early Detection
Early detection is crucial for effective thrips management. Here are some techniques for monitoring thrips populations:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly examine plants, especially new growth, for signs of thrips damage.
- Sticky Traps: Use blue or yellow sticky traps to capture and monitor adult thrips.
- Leaf Beating: Gently tap plant parts over a white surface to dislodge and count thrips.
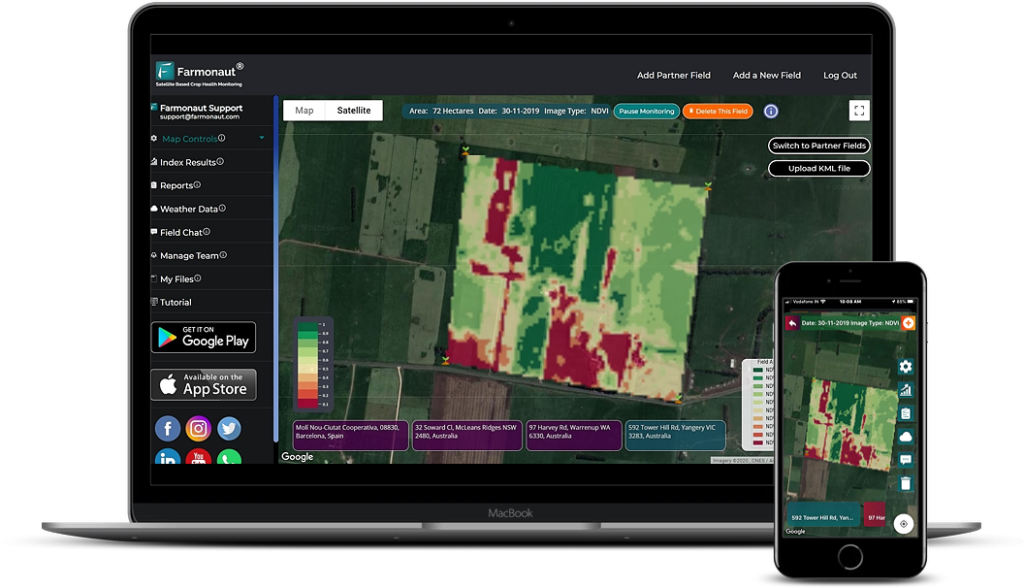
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Utilize advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite imagery to detect early signs of crop stress that may indicate pest infestations.
Regular monitoring allows for timely intervention, preventing thrips populations from reaching damaging levels.
Cultural Controls for Thrips Management
Cultural controls are preventive measures that create an environment less favorable for thrips. These practices include:
- Crop Rotation: Alternating crops to disrupt thrips life cycles.
- Weed Management: Removing weeds that can serve as alternate hosts for thrips.
- Proper Irrigation: Avoiding water stress, which can make plants more susceptible to thrips damage.
- Reflective Mulches: Using reflective materials to repel thrips from crops.
- Sanitation: Removing and destroying crop residues that may harbor thrips.
Implementing these cultural practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of severe thrips infestations.
Biological Controls: Harnessing Nature’s Defenses
Biological control involves using natural enemies of thrips to manage their populations. Some effective biological control agents include:
- Predatory Mites: Species like Amblyseius swirskii and Neoseiulus cucumeris feed on thrips.
- Predatory Bugs: Orius species are effective predators of thrips.
- Entomopathogenic Fungi: Beauveria bassiana can infect and kill thrips.
- Parasitic Wasps: Certain species parasitize thrips, reducing their populations.
Encouraging these natural enemies through habitat management and conservation can provide long-term, sustainable thrips control.
Chemical Controls: A Last Resort
While we advocate for non-chemical methods as primary control strategies, sometimes chemical interventions may be necessary. When using insecticides for thrips control, consider the following:
- Selectivity: Choose products that target thrips while minimizing harm to beneficial insects.
- Rotation: Alternate between different modes of action to prevent resistance development.
- Timing: Apply treatments when thrips are most vulnerable, typically during the nymph stage.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the ecological effects of the chosen products.
Some common insecticides used for thrips control include spinosad, imidacloprid, and neem-based products. Always follow label instructions and local regulations when applying any pesticide.
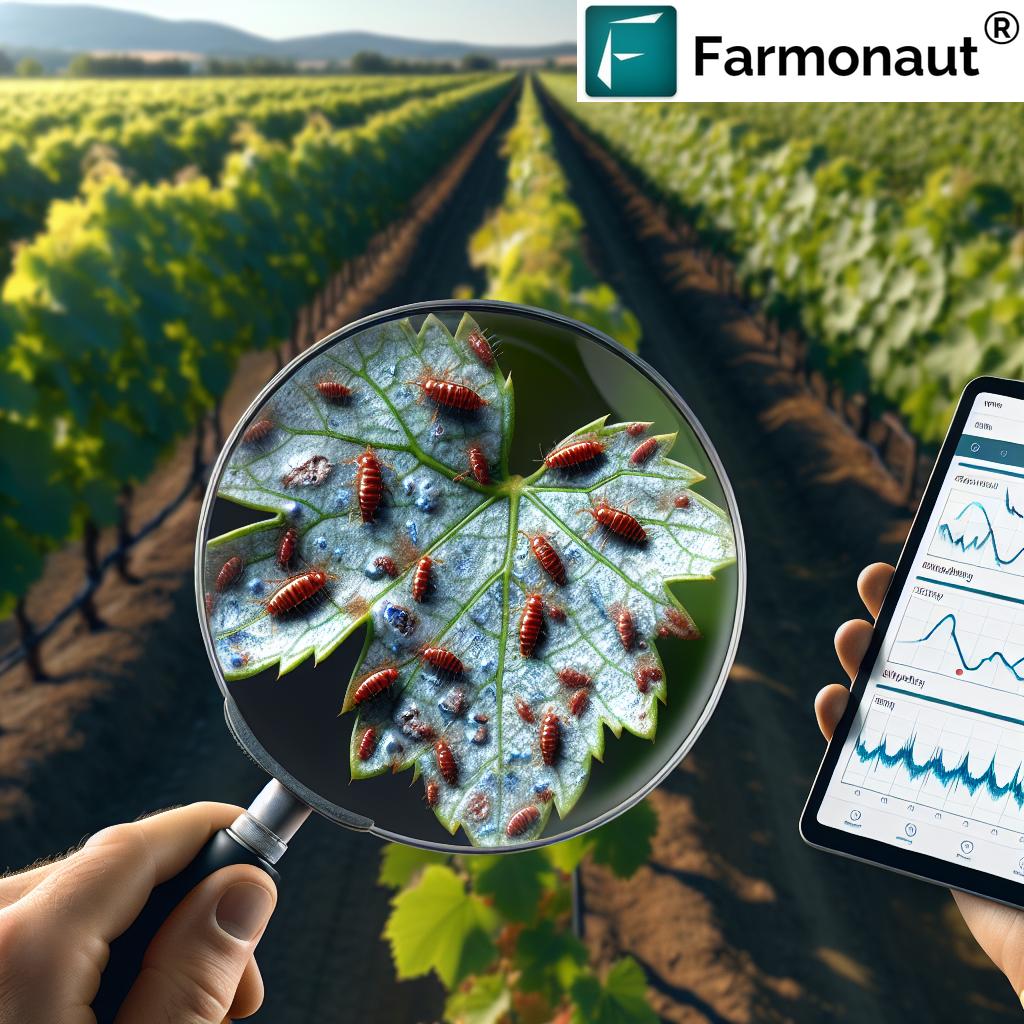

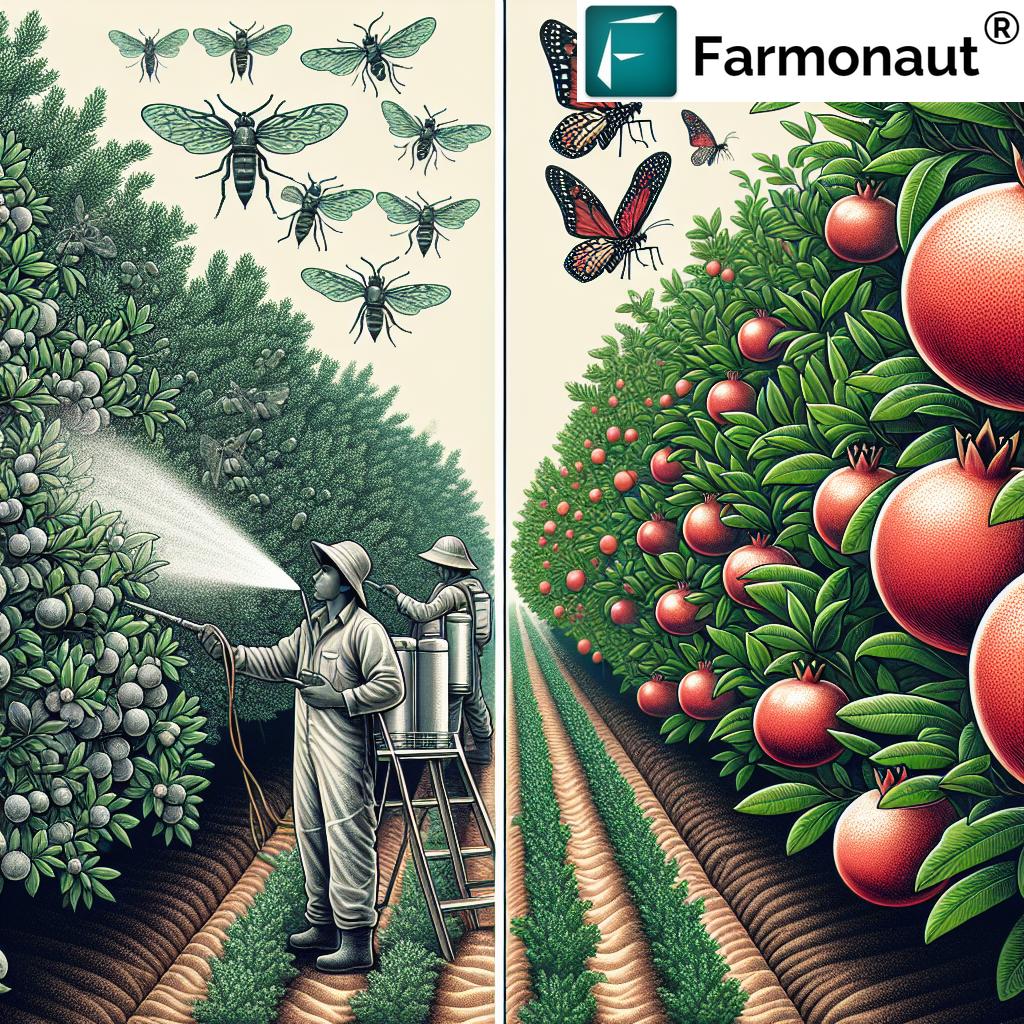
Organic vs. Conventional Thrips Control
When it comes to thrips control, farmers often debate between organic and conventional methods. Let’s compare these approaches:
Organic Thrips Control
Organic pest management relies on natural and biological methods to control thrips populations. Some effective organic strategies include:
- Neem Oil: A natural insecticide that disrupts thrips feeding and reproduction.
- Insecticidal Soaps: These products break down the protective coating of thrips, causing dehydration.
- Beneficial Insects: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs and lacewings.
- Companion Planting: Growing plants that repel thrips or attract their natural enemies.
Organic methods are often more sustainable and environmentally friendly but may require more time and effort to achieve effective control.
Conventional Thrips Control
Conventional methods typically involve the use of synthetic insecticides. Common conventional treatments include:
- Dimethoate: A systemic insecticide effective against a wide range of pests, including thrips.
- Bifenthrin: A broad-spectrum insecticide that provides quick knockdown of thrips.
- Spinosad: A naturally derived insecticide that is also approved for organic use in some formulations.
While conventional methods often provide rapid and effective control, they may have broader environmental impacts and can lead to resistance if not used judiciously.
“Regular field monitoring can reduce thrips-related crop damage by up to 60% through early detection and timely intervention.”
Integrated Approach: Combining Organic and Conventional Methods
At Farmonaut, we believe that the most effective thrips control strategy often involves an integrated approach that combines the best of both organic and conventional methods. This approach, known as Integrated Pest Management (IPM), allows farmers to:
- Minimize environmental impact
- Reduce the risk of pesticide resistance
- Preserve beneficial insects
- Achieve effective and long-term pest control
By using satellite-based crop monitoring tools like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can make informed decisions about when and where to apply specific control measures, optimizing their pest management strategies.
Thrips Control Strategies Comparison
| Control Method | Effectiveness | Sustainability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Practices | ⭐⭐⭐ | High | $ |
| Biological Control | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High | $$ |
| Organic Insecticides | ⭐⭐⭐ | Medium | $$ |
| Conventional Insecticides | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Low | $$$ |
| IPM Techniques | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | High | $$ |
Crop-Specific Thrips Management Strategies
Different crops may require tailored approaches to thrips management. Let’s explore some crop-specific strategies:
Grapevines
Thrips can cause significant damage to grapevines, affecting both leaf quality and fruit production. Key management strategies include:
- Regular monitoring of new shoot growth and flower clusters
- Using blue sticky traps for early detection
- Applying narrow-range horticultural oils during the dormant season
- Encouraging natural predators like predatory mites
Pomegranate
Pomegranate trees are particularly susceptible to thrips damage. Effective control measures include:
- Pruning to improve air circulation and reduce hiding spots for thrips
- Using reflective mulches to repel thrips
- Applying neem-based products during flowering and fruit set stages
- Implementing a robust irrigation management plan to reduce plant stress
Cotton
Thrips can severely impact cotton yields, especially during the seedling stage. Management strategies for cotton include:
- Seed treatments with systemic insecticides
- Early-season foliar sprays if populations exceed economic thresholds
- Planting resistant varieties when available
- Maintaining optimal plant nutrition to improve plant resilience
By tailoring thrips management strategies to specific crops, farmers can maximize the effectiveness of their control efforts while minimizing unnecessary interventions.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Thrips Management
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in effective pest management. At Farmonaut, we offer cutting-edge solutions that can significantly improve thrips control strategies:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Our advanced satellite imagery allows farmers to detect early signs of crop stress, which may indicate thrips infestations before they become visible to the naked eye.
- AI-Powered Advisory System: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized recommendations for thrips management based on real-time crop health data and environmental conditions.
- Mobile Apps for Field Scouting: Our user-friendly mobile applications help farmers record and track thrips populations, making it easier to implement timely control measures.
By integrating these technological tools into their pest management practices, farmers can make more informed decisions and achieve better control of thrips infestations.
Explore our satellite-based crop monitoring solutions:
Future Trends in Thrips Management
As we look to the future of thrips control in agriculture, several promising trends and technologies are emerging:
- Gene Editing: CRISPR technology may be used to develop thrips-resistant crop varieties.
- Pheromone-Based Control: Advanced pheromone traps and disruption techniques could offer more targeted thrips management.
- Nanotechnology: Nanoparticles may be used to deliver pesticides more effectively and with less environmental impact.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-driven predictive models could help farmers anticipate thrips outbreaks and optimize control measures.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, continually improving our services to help farmers tackle thrips and other pest challenges efficiently and sustainably.
Sustainable Pest Control: Balancing Efficacy and Environmental Stewardship
As we strive for effective thrips control, it’s crucial to consider the broader environmental impact of our pest management strategies. Sustainable pest control aims to achieve a balance between crop protection and ecological preservation. Here are some key considerations:
- Biodiversity Preservation: Implementing pest control methods that minimize harm to beneficial insects and other wildlife.
- Soil Health: Choosing treatments that don’t negatively impact soil microorganisms or structure.
- Water Quality: Preventing pesticide runoff and protecting water sources from contamination.
- Resistance Management: Employing strategies to prevent the development of pesticide-resistant thrips populations.
By adopting a holistic approach to thrips management, we can ensure long-term crop health while maintaining ecological balance.
The Role of Education and Community Collaboration
Effective thrips management isn’t just about individual farm practices; it’s also about community-wide efforts and knowledge sharing. Here’s how education and collaboration can enhance thrips control:
- Farmer Training Programs: Workshops and seminars on IPM techniques and new technologies.
- Community-Wide Monitoring: Collaborative efforts to track thrips populations across multiple farms.
- Information Sharing Platforms: Online forums and databases for farmers to share experiences and best practices.
- Research Partnerships: Collaboration between farmers, researchers, and technology providers to develop innovative solutions.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to fostering this collaborative approach, providing tools and platforms that facilitate knowledge sharing and community-driven pest management strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to Thrips Control
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, effective thrips management requires a multifaceted approach that combines traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology. By integrating cultural practices, biological controls, judicious use of pesticides, and advanced monitoring tools, farmers can achieve sustainable and efficient thrips control.
Remember, the key to success lies in:
- Early detection through regular monitoring
- Implementing a diverse range of control strategies
- Adapting techniques to specific crop needs and local conditions
- Leveraging technology for precision pest management
- Prioritizing sustainability and environmental stewardship
With these principles in mind, and with tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring at your disposal, you’re well-equipped to tackle the challenge of thrips control and ensure healthy, productive crops.
For more information on how Farmonaut can support your pest management efforts, visit our web app or explore our API for custom integration options. You can also find detailed information in our API Developer Docs.
FAQ: Thrips Control and Management
Q: How can I identify a thrips infestation in my crops?
A: Look for silvery patches on leaves, distorted growth, and tiny, slender insects. Use a magnifying glass to spot the 1-2mm long thrips on plant surfaces.
Q: Are there any natural predators of thrips I can introduce to my farm?
A: Yes, predatory mites like Amblyseius swirskii, predatory bugs such as Orius species, and certain parasitic wasps are effective natural enemies of thrips.
Q: How often should I monitor my crops for thrips?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial. We recommend weekly inspections during the growing season, increasing to twice weekly during peak thrips activity periods.
Q: Can thrips develop resistance to pesticides?
A: Yes, thrips can develop resistance to pesticides if the same products are used repeatedly. It’s important to rotate between different classes of insecticides and integrate non-chemical control methods.
Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help in thrips management?
A: Our satellite-based crop monitoring can detect early signs of plant stress, potentially indicating thrips infestations before they’re visible to the naked eye. This allows for timely intervention and more targeted pest control efforts.