Maximizing Sheep Performance: Advanced Water Quality Management Techniques for Sustainable Pastoral Systems
“Sheep can tolerate water salinity up to 5,000 ppm TDS, but optimal performance occurs at levels below 3,000 ppm.”
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on water quality management for sheep in sustainable pastoral systems. As experts in precision agriculture and livestock management, we at Farmonaut understand the crucial role that water plays in sheep performance, health, and overall farm productivity. In this blog post, we’ll explore advanced techniques for optimizing water quality to maximize sheep performance while maintaining sustainable farming practices.

The Importance of Water Quality in Sheep Farming
Water is the most essential nutrient for sheep, playing a vital role in various physiological processes, including digestion, thermoregulation, and wool production. The quality of water directly impacts sheep health, growth rates, and overall farm productivity. As sustainable farming practices become increasingly important, managing water resources effectively is crucial for both animal welfare and business success.
Let’s delve into the key aspects of water quality that affect sheep performance:
- Salinity
- pH levels
- Temperature
- Cleanliness
- Contamination
Water Salinity and Sheep Performance
Salinity is one of the most critical factors affecting water quality for sheep. While sheep are relatively tolerant to saline water compared to other livestock, excessive salinity can lead to reduced water intake, decreased feed consumption, and impaired growth rates.
Here’s a breakdown of how different salinity levels impact sheep:
- 0-3,000 ppm Total Dissolved Solids (TDS): Excellent for all classes of sheep
- 3,000-5,000 ppm TDS: Satisfactory for most sheep, but may cause mild diarrhea in lambs
- 5,000-8,000 ppm TDS: Can be used with caution, but may lead to reduced performance in lactating ewes and lambs
- 8,000+ ppm TDS: Not recommended for sheep, can cause severe health issues and decreased productivity
To manage salinity effectively, we recommend regular water testing and implementing strategies such as:
- Providing alternative water sources in high-salinity areas
- Using desalination techniques for severely affected water supplies
- Strategically placing salt licks to balance mineral intake
- Monitoring sheep closely for signs of reduced water consumption or health issues
The Impact of pH Levels on Sheep Health
Water pH is another crucial factor in sheep health and performance. The ideal pH range for sheep water is between 6.5 and 8.5. Water outside this range can lead to various issues:
- Low pH (acidic water): Can cause decreased water intake, increased corrosion of water infrastructure, and potential toxicity from heavy metals
- High pH (alkaline water): May lead to digestive upset, reduced nutrient absorption, and scaling in water systems
To manage pH levels effectively:
- Regularly test water sources using pH meters or test strips
- Install water treatment systems to adjust pH if necessary
- Monitor sheep for signs of reduced water intake or digestive issues
- Consider using buffer solutions in extreme cases to stabilize pH levels
Water Temperature and Its Effects on Sheep
Water temperature plays a significant role in sheep hydration and overall performance, especially during extreme weather conditions. In hot weather, cool water is essential for maintaining body temperature and encouraging adequate water intake.
Consider the following temperature ranges:
- 7-18°C (45-65°F): Ideal temperature range for sheep water
- 18-25°C (65-77°F): Acceptable, but may lead to reduced intake in hot weather
- 25°C+ (77°F+): Can significantly reduce water consumption, leading to dehydration and heat stress
To manage water temperature effectively:
- Insulate water pipes and tanks to maintain cooler temperatures in summer
- Provide shade for water troughs in pastoral systems
- Consider using cooling systems for water supplies during extreme heat
- In winter, use heating elements to prevent freezing and ensure constant water availability
Cleanliness and Contamination: Ensuring Safe Water for Sheep
Clean, uncontaminated water is essential for sheep health and performance. Contaminated water can lead to various health issues, including parasitic infections, bacterial diseases, and reduced productivity.
Common contaminants in sheep water include:
- Algae and blue-green algae (cyanobacteria)
- Bacteria and pathogens
- Chemical pollutants (pesticides, fertilizers)
- Organic matter and sediment
To maintain clean water sources:
- Regularly clean and disinfect water troughs
- Implement filtration systems for surface water sources
- Monitor water sources for signs of algal blooms or contamination
- Fence off natural water bodies to prevent direct access and contamination
- Use approved water treatments when necessary
Precision Agriculture and Agritech Solutions for Water Quality Management
At Farmonaut, we believe in the power of technology to revolutionize water quality management in pastoral systems. Our advanced satellite-based farm management solutions can assist sheep farmers in optimizing their water resources and improving overall farm efficiency.
Here’s how precision agriculture and agritech solutions can benefit sheep farmers:
- Remote sensing technology: Monitor pasture health and soil moisture levels to optimize grazing patterns and water resource allocation
- IoT sensors: Implement real-time monitoring of water quality parameters across different pastures
- Data analytics: Use historical and real-time data to make informed decisions about water management strategies
- Automated alerts: Receive notifications about potential water quality issues before they impact sheep health
By leveraging these technologies, sheep farmers can:
- Improve water use efficiency
- Reduce the risk of water-related health issues in their flocks
- Optimize pasture management and grazing rotations
- Enhance overall farm productivity and sustainability
Understanding Sheep Water Requirements
To effectively manage water quality, it’s crucial to understand the varying water requirements of sheep based on factors such as age, reproductive stage, and climate conditions. This knowledge allows farmers to tailor their water management strategies to meet the specific needs of their flock.
| Water Quality Parameter | Optimal Range | Impact on Sheep | Management Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | 0-3,000 ppm TDS | Higher levels reduce water intake and growth rates | Regular testing, alternative water sources |
| pH | 6.5-8.5 | Affects digestive health and nutrient absorption | pH adjustment systems, buffer solutions |
| Temperature | 7-18°C (45-65°F) | Influences hydration and heat stress | Insulation, shade, cooling/heating systems |
| Cleanliness | Free from contaminants | Prevents diseases and parasitic infections | Regular cleaning, filtration, water treatments |
Here’s a breakdown of water requirements for different classes of sheep:
- Mature, dry ewes: 4-6 liters per day
- Lactating ewes: 8-12 liters per day
- Weaners: 2-4 liters per day
- Growing lambs: 3-5 liters per day
- Rams: 6-8 liters per day
These requirements can increase significantly during hot weather or when sheep are grazing on dry pastures. Understanding these needs helps farmers ensure adequate water supply and quality across different pastures and containment areas.
Strategies for Improving Water Infrastructure
Effective water quality management relies heavily on well-designed and maintained water infrastructure. Here are some key strategies for improving water systems in pastoral sheep farming:
- Strategic placement of water points: Ensure water sources are easily accessible across all pastures, ideally within 1-1.5 km of grazing areas
- Appropriate trough design: Use troughs that are easy to clean, resistant to algae growth, and suitable for different classes of sheep
- Regular maintenance: Implement a schedule for cleaning troughs, checking pipes for leaks, and repairing or replacing damaged components
- Water storage solutions: Invest in proper storage tanks to ensure a consistent water supply during dry periods or in case of infrastructure failure
- Fencing and protection: Protect water sources from contamination by wildlife and prevent erosion around water points
“Regular water testing can increase sheep farm productivity by up to 15% through improved health and wool production.”
Monitoring and Testing Water Quality
Regular monitoring and testing of water quality are essential for maintaining optimal sheep health and performance. We recommend implementing a comprehensive testing program that includes:
- Monthly pH and salinity tests
- Quarterly tests for major minerals and contaminants
- Annual comprehensive water quality analysis
Farmonaut’s technology can assist in this process by providing real-time data on various environmental factors that may impact water quality. Our satellite-based monitoring can help identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced data integration
Managing Water Quality in Different Seasons
Water quality management strategies need to adapt to seasonal changes. Here’s how to approach water management throughout the year:
Summer
- Increase water point availability to reduce competition and heat stress
- Monitor water temperature and implement cooling strategies if necessary
- Watch for signs of algal blooms in dams and natural water sources
Winter
- Prevent freezing in water systems using heating elements or insulation
- Monitor water intake, as cold water may discourage drinking
- Ensure water sources remain accessible during wet or muddy conditions
Spring and Autumn
- Conduct thorough cleaning and maintenance of water infrastructure
- Adjust water management strategies based on changing pasture conditions
- Prepare for seasonal transitions by reviewing and updating water plans
Sustainable Water Management Practices
Implementing sustainable water management practices is crucial for long-term farm viability and environmental stewardship. Consider the following approaches:
- Water harvesting: Implement systems to collect and store rainwater for use during dry periods
- Erosion control: Use vegetation and strategic landscaping to prevent soil erosion around water sources
- Efficient irrigation: If irrigating pastures, use precision techniques to minimize water waste
- Wetland preservation: Protect natural wetlands on your property to maintain water quality and biodiversity
- Water recycling: Explore options for treating and reusing wastewater from farm operations
By adopting these practices, sheep farmers can contribute to environmental conservation while ensuring a sustainable water supply for their flocks.
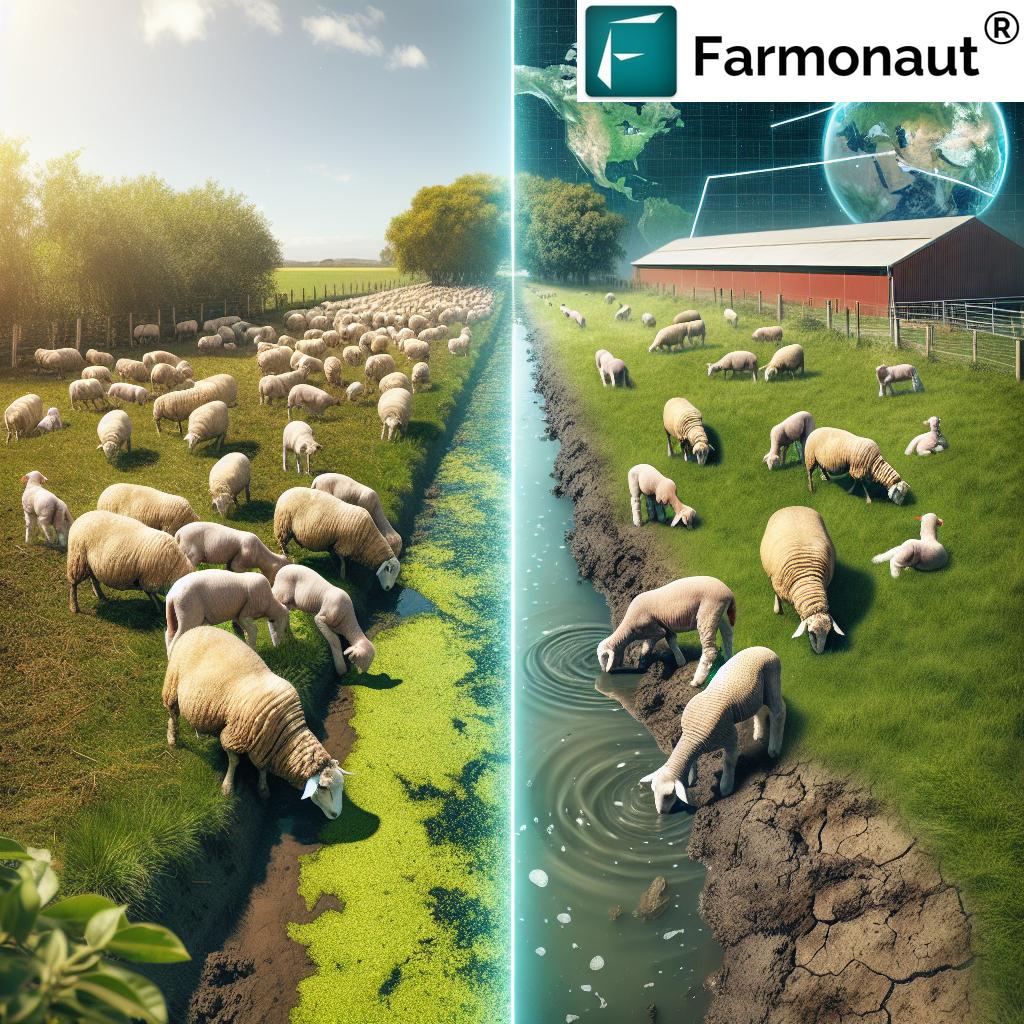

The Role of Technology in Water Quality Management
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing water quality management in sheep farming. Farmonaut’s suite of tools can significantly enhance a farmer’s ability to monitor and manage water resources effectively:
- Satellite imagery: Monitor pasture health and identify potential water-related issues across large areas
- AI-powered analytics: Predict water needs based on flock size, weather conditions, and pasture quality
- Mobile apps: Access real-time data and receive alerts about water quality issues on-the-go
- Integration with IoT devices: Connect with on-farm sensors for comprehensive water quality monitoring
Learn more about Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs
Integrating Water Quality Management with Overall Farm Management
Effective water quality management should be integrated into your overall farm management strategy. This holistic approach ensures that water-related decisions complement other aspects of sheep farming, such as:
- Grazing management: Coordinate water point placement with rotational grazing systems
- Breeding programs: Ensure optimal water quality during critical periods like lambing and lactation
- Wool production: Maintain water quality to support healthy wool growth and quality
- Disease prevention: Use water management as part of a comprehensive health strategy, including parasite control
- Feed management: Balance water quality with feed types to optimize nutrient intake and digestion
By considering water quality in relation to these other factors, farmers can maximize the overall performance and profitability of their sheep enterprise.
Economic Benefits of Proper Water Quality Management
Investing in water quality management can yield significant economic benefits for sheep farmers:
- Increased productivity: Better water quality leads to improved feed conversion rates and faster growth
- Enhanced wool quality: Optimal hydration contributes to higher quality wool production
- Reduced veterinary costs: Fewer water-related health issues mean lower medical expenses
- Improved reproductive performance: Proper hydration supports better fertility and lamb survival rates
- Long-term sustainability: Efficient water management ensures the longevity of your farming operation
By leveraging Farmonaut’s technology, farmers can make data-driven decisions that optimize water quality management and maximize these economic benefits.
Case Studies in Successful Water Quality Management
While we can’t provide specific case studies, numerous sheep farms have successfully implemented advanced water quality management techniques with remarkable results. Common outcomes include:
- 20-30% increase in lamb growth rates
- 15-25% improvement in wool quality and yield
- Significant reduction in water-related health issues
- Enhanced drought resilience and adaptability to climate variations
These success stories highlight the potential impact of implementing the strategies discussed in this blog post.
Conclusion: Elevating Sheep Performance Through Advanced Water Quality Management
In conclusion, advanced water quality management is a cornerstone of maximizing sheep performance and ensuring sustainable pastoral systems. By focusing on key parameters such as salinity, pH, temperature, and cleanliness, and leveraging cutting-edge technology like Farmonaut’s precision agriculture solutions, sheep farmers can significantly enhance their flock’s health, productivity, and overall farm efficiency.
Remember that water quality management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring, testing, and adaptation to changing conditions. By integrating these practices into your overall farm management strategy, you’ll be well-positioned to face the challenges of modern sheep farming while maximizing your operation’s potential.
We encourage you to explore Farmonaut’s range of tools and services designed to support your water quality management efforts. From satellite-based monitoring to advanced analytics, our technology can help you make informed decisions that drive your sheep farm’s success.
FAQs
- Q: How often should I test my water quality for sheep?
A: We recommend monthly pH and salinity tests, quarterly tests for major minerals and contaminants, and an annual comprehensive water quality analysis. - Q: Can sheep drink from natural water sources like streams and ponds?
A: While sheep can drink from natural sources, it’s important to monitor these for contamination and algal blooms. Providing clean, managed water sources is generally safer and more reliable. - Q: How does water quality affect wool production in sheep?
A: Good water quality supports overall sheep health, which in turn promotes better wool growth and quality. Poor water quality can lead to stress and reduced wool production. - Q: What are the signs of water quality issues in sheep?
A: Signs may include reduced water intake, diarrhea, poor weight gain, decreased wool quality, and in severe cases, health issues like urinary calculi. - Q: How can Farmonaut’s technology help with water quality management for sheep?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring and analytics can help identify potential water-related issues, optimize resource allocation, and provide data-driven insights for better decision-making in water management.