Phytotoxicity in Crops: Managing Chemical Applications and Symptoms for Healthy Plant Growth

In the ever-evolving world of agriculture, we at Farmonaut understand the critical importance of maintaining healthy crops while maximizing yield. One of the most significant challenges farmers face is phytotoxicity, a condition that can severely impact plant health and crop productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of phytotoxicity, its causes, symptoms, and most importantly, how to manage and prevent it effectively.
Understanding Phytotoxicity in Agriculture
Phytotoxicity, also known as fitotoxicidad in Spanish, refers to the toxic effect that various substances can have on plants. These substances, often chemicals used in agriculture, can cause damage to crops when misapplied or used in excessive quantities. As agricultural technology experts, we’ve observed that phytotoxicity can result from a wide range of factors, including:
- Improper application of pesticides
- Overuse of fertilizers
- Incorrect mixing of agricultural chemicals
- Environmental factors such as extreme temperaturas (temperatures)
- Interactions between different químicos (chemicals) applied to crops
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and manage phytotoxicity in agricultural settings.
The Impact of Phytotoxicity on Crop Health and Yield
Phytotoxicity can have devastating effects on crop health and overall agricultural productivity. When plants are exposed to toxic substances, they may exhibit various symptoms that can lead to reduced yield or complete crop failure. Some of the most common impacts include:
- Stunted growth
- Leaf chlorosis or necrosis
- Reduced fruit or grain production
- Increased susceptibility to diseases and pests
- Poor root development
These effects can translate into significant economic losses for farmers and potentially impact food security on a broader scale. That’s why at Farmonaut, we’re committed to providing solutions that help farmers identify and mitigate phytotoxicity risks effectively.
Identifying Phytotoxicity Symptoms in Crops
Recognizing the symptoms of phytotoxicity early is crucial for implementing timely interventions. While symptoms can vary depending on the crop type and the toxic substance involved, some common signs include:
- Leaf curling or cupping
- Chlorosis (yellowing of leaves)
- Necrotic spots or patches on leaves
- Wilting or drooping of plant parts
- Abnormal growth patterns
- Reduced flowering or fruit set
It’s important to note that these symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for nutrient deficiencies or disease infections. This is where advanced technology, like our satellite-based crop monitoring system at Farmonaut, can be invaluable in accurately diagnosing phytotoxicity issues.

Common Causes of Phytotoxicity in Agricultural Settings
Understanding the root causes of phytotoxicity is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. In our experience working with farmers across various regions, we’ve identified several common causes:
1. Improper Chemical Applications
One of the most frequent causes of phytotoxicity is the misuse of agricultural chemicals. This can include:
- Applying chemicals at incorrect rates
- Using the wrong formulation for a specific crop
- Mixing incompatible chemicals
- Applying chemicals under unfavorable weather conditions
2. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions can exacerbate the risk of phytotoxicity. Factors such as:
- High temperaturas (temperatures)
- Excessive humidity
- Drought stress
- Strong sunlight
These can all increase a plant’s susceptibility to chemical damage.
3. Residual Soil Contamination
Sometimes, phytotoxicity can result from chemicals persisting in the soil from previous applications. This is particularly common with certain herbicides that have long residual effects.
4. Drift from Nearby Fields
Chemical drift from neighboring fields during spraying operations can cause unintended phytotoxicity in non-target crops.
5. Improper Use of Growth Regulators
While growth regulators can be beneficial for crop management, their misuse can lead to phytotoxic effects, especially when applied at incorrect stages of plant development.
Strategies for Preventing Phytotoxicity in Crops
At Farmonaut, we believe that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to phytotoxicity. Here are some key strategies we recommend to our farmers for minimizing the risk of chemical damage to crops:
1. Proper Chemical Selection and Application
- Always read and follow label instructions carefully
- Choose chemicals that are specifically registered for use on your crop
- Calibrate spraying equipment regularly to ensure accurate application rates
- Avoid applying chemicals during extreme weather conditions
2. Implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
By adopting IPM practices, farmers can reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides, thereby lowering the risk of phytotoxicity. This approach includes:
- Crop rotation to break pest cycles
- Use of resistant plant varieties
- Biological control methods
- Regular field monitoring for early pest detection
3. Optimize Soil Health
Healthy soils can help plants better withstand stress and reduce their susceptibility to phytotoxicity. Consider:
- Regular soil testing to ensure proper nutrient balance
- Incorporating organic matter to improve soil structure
- Maintaining optimal soil pH for nutrient availability
4. Use Precision Agriculture Techniques
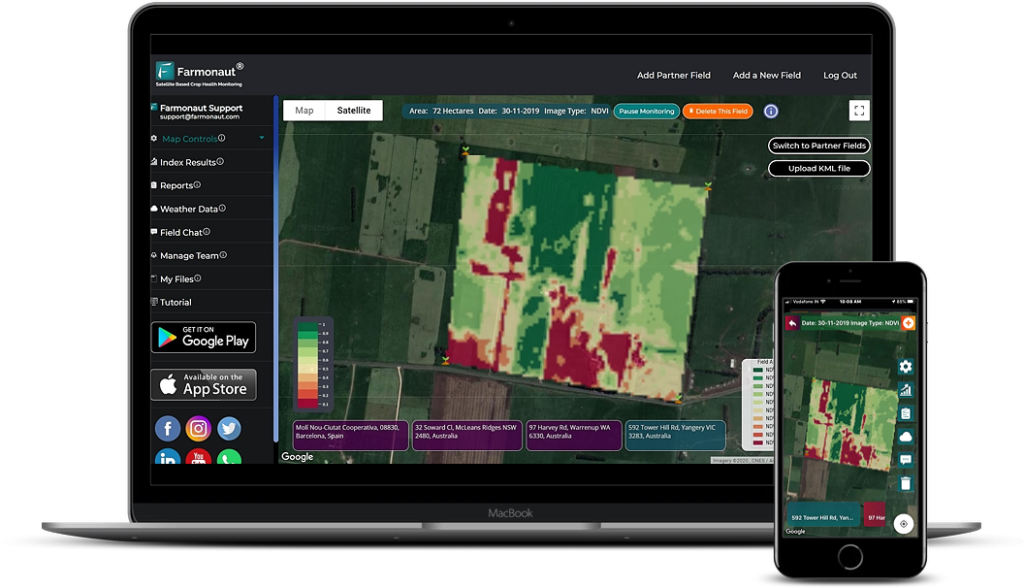
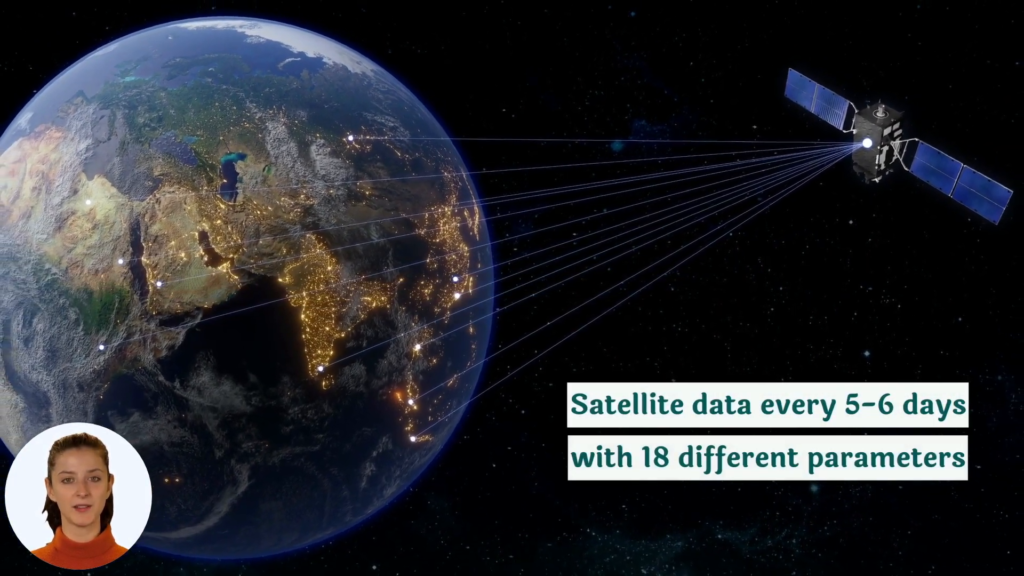
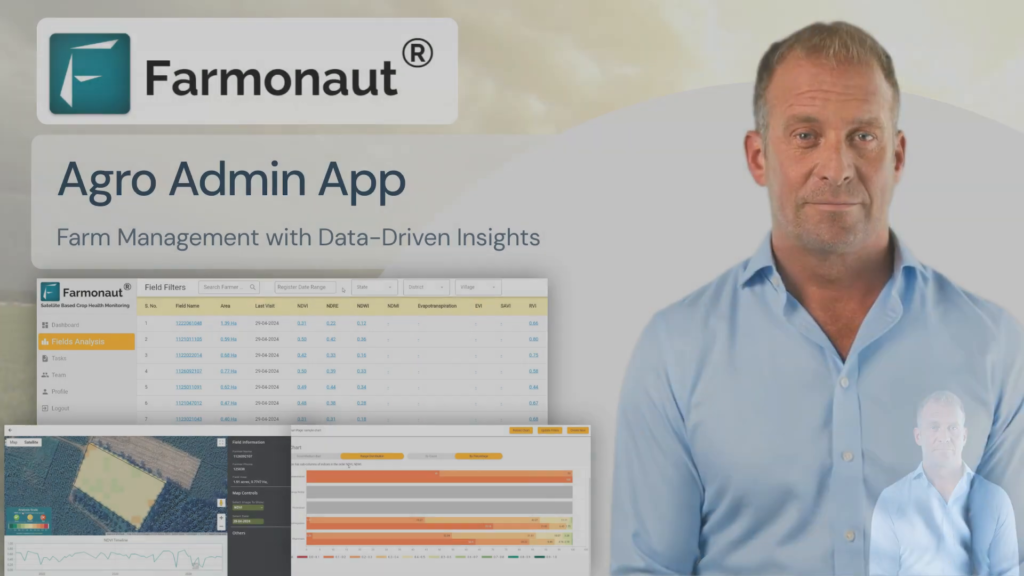
Leveraging advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut can significantly reduce the risk of phytotoxicity. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system allows for:
- Precise application of inputs based on real-time crop needs
- Early detection of stress symptoms that might indicate phytotoxicity
- Optimization of irrigation and fertilization schedules
To learn more about how our technology can help prevent phytotoxicity, visit Farmonaut’s Crop Monitoring Platform.
5. Proper Timing of Applications
Timing is crucial when it comes to chemical applications. Consider:
- Applying chemicals during the cooler parts of the day
- Avoiding applications when plants are under stress (e.g., during drought)
- Following recommended growth stage guidelines for specific chemicals
Managing Phytotoxicity: Steps to Take When Chemical Damage Occurs
Despite our best efforts, instances of phytotoxicity can still occur. When this happens, quick and appropriate action is crucial to minimize damage and potentially save the crop. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to manage phytotoxicity:
1. Identify the Problem
The first step is to accurately diagnose the issue. Look for characteristic symptoms of phytotoxicity and try to identify the potential cause. Our Farmonaut satellite monitoring system can be particularly helpful in detecting early signs of stress across large areas.
2. Stop Further Applications
If you suspect that recent chemical applications are the cause, immediately halt any further applications of the suspected product.
3. Document the Damage
Take detailed notes and photographs of the affected areas. This documentation can be crucial for insurance claims or if you need to consult with agronomists or extension services.
4. Assess the Extent of Damage
Determine how widespread the damage is and estimate its potential impact on yield. Our satellite imagery can provide a comprehensive view of affected areas, helping you make informed decisions.
5. Implement Remedial Measures
Depending on the type and extent of damage, consider the following actions:
- Flush the soil with water to dilute chemical residues (if appropriate)
- Apply activated charcoal to absorb certain chemicals
- Prune severely damaged plant parts
- Adjust fertilization and irrigation to support plant recovery
6. Monitor Recovery
Closely observe the affected crops for signs of recovery. Our Farmonaut platform can help you track plant health indices over time, providing insights into the effectiveness of your remedial actions.
7. Adjust Future Management Practices
Use the experience to refine your crop management strategies. This might involve:
- Reviewing chemical application protocols
- Investing in more precise application equipment
- Enhancing staff training on proper chemical handling
- Implementing more robust monitoring systems
The Role of Technology in Preventing and Managing Phytotoxicity
At Farmonaut, we’re at the forefront of using advanced technology to revolutionize crop management and mitigate risks like phytotoxicity. Our satellite-based monitoring system offers several key advantages in the fight against chemical damage to crops:
1. Early Detection
Our satellite imagery can detect subtle changes in crop health long before they’re visible to the naked eye. This early warning system allows farmers to identify potential phytotoxicity issues at their earliest stages, enabling prompt intervention.
2. Comprehensive Coverage
Unlike traditional scouting methods, our satellite technology can monitor vast agricultural areas quickly and efficiently. This ensures that no part of your field goes unchecked, reducing the risk of localized phytotoxicity issues going unnoticed.
3. Precise Application Guidance
By providing detailed insights into crop health and field variability, our system helps farmers optimize their chemical applications. This precision reduces the risk of over-application and subsequent phytotoxicity.
4. Historical Data Analysis
Our platform stores historical data, allowing farmers to analyze trends over time. This can be invaluable in identifying recurring patterns or risk factors associated with phytotoxicity in specific fields or crops.
5. Integration with Weather Data
By combining satellite imagery with real-time weather data, we help farmers make informed decisions about the timing of chemical applications, further reducing the risk of phytotoxicity.
To explore how our technology can help you manage phytotoxicity risks, visit our Farmonaut API documentation.
Case Studies: Successful Management of Phytotoxicity
While we don’t include specific case studies or success stories, we can share general insights from our experience working with farmers worldwide. Many of our users have successfully managed and prevented phytotoxicity issues by leveraging our technology in combination with best agricultural practices.
For instance, farmers using our satellite monitoring system have reported:
- Reduced instances of chemical overapplication
- Improved timing of pesticide and fertilizer applications
- Earlier detection and management of stress symptoms
- More efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact
These outcomes demonstrate the power of combining advanced technology with sound agricultural knowledge to address complex challenges like phytotoxicity.
The Future of Phytotoxicity Management in Agriculture
As we look to the future, we at Farmonaut are excited about the potential advancements in phytotoxicity management. Some areas we’re particularly focused on include:
1. AI-Powered Predictive Models
We’re developing machine learning algorithms that can predict the likelihood of phytotoxicity based on various factors such as weather patterns, soil conditions, and planned chemical applications.
2. Integration with IoT Devices
By connecting our satellite data with ground-based sensors, we aim to provide even more precise and real-time information on crop health and environmental conditions.
3. Automated Application Systems
We envision a future where our data feeds directly into automated spraying systems, ensuring optimal application rates and timing to minimize phytotoxicity risks.
4. Enhanced Molecular Techniques
Advances in plant genetics and molecular biology may lead to the development of crop varieties with enhanced resistance to chemical stress, further reducing the risk of phytotoxicity.
Comparing Traditional and Advanced Phytotoxicity Detection Methods
| Method | Speed | Accuracy | Coverage | Cost-effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Phytotoxicity Detection | Slow (manual scouting) | Moderate (depends on scout’s expertise) | Limited (time-consuming for large areas) | Low (labor-intensive) |
| Farmonaut Satellite System Detection | Fast (near real-time monitoring) | High (uses advanced spectral analysis) | Extensive (can cover vast areas quickly) | High (automated and scalable) |
As demonstrated in the table above, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers significant advantages in terms of speed, accuracy, coverage, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods of phytotoxicity detection.
Conclusion: Empowering Farmers in the Fight Against Phytotoxicity
Phytotoxicity remains a significant challenge in modern agriculture, but with the right knowledge, practices, and technology, it’s a challenge that can be effectively managed. At Farmonaut, we’re committed to empowering farmers with the tools and insights they need to protect their crops and optimize their yields.
By combining our advanced satellite monitoring technology with sound agricultural practices, farmers can:
- Detect potential phytotoxicity issues early
- Make more informed decisions about chemical applications
- Optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact
- Improve overall crop health and productivity
We invite you to explore how Farmonaut can help you manage phytotoxicity risks and improve your farm’s performance. Visit our website or download our mobile app to get started:
For developers interested in integrating our technology into their own solutions, check out our API documentation.
FAQs About Phytotoxicity in Crops
Q1: What is phytotoxicity?
A1: Phytotoxicity refers to the toxic effect that various substances, particularly agricultural chemicals, can have on plants. It can result in damage to crops and reduced yields.
Q2: What are common symptoms of phytotoxicity?
A2: Common symptoms include leaf curling, chlorosis (yellowing of leaves), necrotic spots, wilting, stunted growth, and reduced fruit or grain production.
Q3: How can farmers prevent phytotoxicity?
A3: Farmers can prevent phytotoxicity by following label instructions carefully, calibrating equipment regularly, avoiding applications during extreme weather, implementing integrated pest management practices, and using precision agriculture techniques like those offered by Farmonaut.
Q4: Can phytotoxicity be reversed?
A4: While severe phytotoxicity damage may be irreversible, early detection and appropriate management can help minimize the impact and allow plants to recover in some cases.
Q5: How does Farmonaut’s technology help in managing phytotoxicity?
A5: Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system provides early detection of stress symptoms, enables precise application of inputs, and offers comprehensive coverage of large agricultural areas, all of which help in preventing and managing phytotoxicity effectively.