Precise Farming: 7 Powerful Technologies Transforming Yields
“Precision farming can increase crop yields by up to 20% using GPS-guided equipment and data analytics.”
What is Precision Farming?
As leaders in modern agriculture, we are part of a global evolution where technology and data intersect with traditional farming wisdom. Precision farming (also known as precision agriculture) is an advanced approach that leverages innovative technologies to optimize field-level management concerning crop farming.
By harnessing detailed data, these methods allow us to apply exact amounts of inputs—such as fertilizers, pesticides, and water—in targeted locations, at strategic times. This data-driven system ensures that every plant receives attention tailored to its precise needs, improving overall resource management, reducing waste, and boosting yields for a more sustainable agricultural future.
Today, we are witnessing an explosion in precision agriculture technologies such as GPS and GIS in agriculture, drones for crop monitoring, IoT and smart sensors, variable rate technology in farming, and machine-based automation. The adoption of these tools is key to improving crop management data, raising efficiency, and meeting our environmental sustainability in farming goals.
Why does it matter? Put simply, precision farming empowers us to optimize yields, reduce resource consumption, and promote sustainability—three pillars every farmer and agribusiness must care deeply about in the face of rising population and climate change concerns.
7 Powerful Precision Agriculture Technologies
Let’s explore the core technologies at the heart of the precision farming revolution. By diving deep into each solution, we gain clear insights on how these innovations work together to enhance yield outcomes, efficiency, and sustainability.
🌐 1. GPS and GIS in Agriculture: The Backbone of Precision
The Global Positioning System (GPS) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have radically changed how we map, monitor, and manage fields. With precision GPS-guided equipment, we can achieve near-perfect accuracy in all our operations:
- Precise mapping: Create digital field boundaries and soil zone maps
- Field variability analysis: GIS integrates spatial data to analyze soil variability, soil moisture, nutrient patterns, and yield
- Facilitating targeted interventions: By knowing exactly where and what variability exists, we direct resources where they’re needed most
- Autonomous vehicle navigation: GPS enables self-driving tractors, harvesters, and robotic weeders with pinpoint navigation
The result: fewer missed passes, less input waste, and improved resource management across all operations.
Learn how digital mapping and spatial data are impacting field operations:
Read More About Precision Mapping
🚁 2. Drones for Crop Monitoring & Remote Sensing: Aerial Intelligence
Drones are transforming farm monitoring across the globe. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors, drones offer:
- Aerial imagery and field mapping
- Timely assessment of crop health, pest infestations, and moisture conditions
- Detection of areas under stress (disease, drought, or nutrient deficiency)
- Remote evaluations: Using satellite imagery for broader insights, such as weather impacts, soil moisture variability, and yield forecasting
Leveraging drones for crop monitoring enables rapid intervention, targeted spraying, and strategic resource allocation—directly boosting yield and sustainability.
Discover More Precision Drone Techniques
🌱 3. IoT & Smart Sensors: Connecting Every Inch of the Field
The Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture enables us to deploy smart sensors in the field to collect real-time data on:
- Soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels
- Plant health and growth rates
- Weather patterns and microclimate variations
Soil moisture sensors are particularly valuable—ensuring irrigation is only applied when and where required, preventing over- or under-watering. All this data collection enables informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest management, resulting in higher farm efficiency and cost savings.
The Role of Smart Sensors in Modern Farming
Want to integrate these insights into your own digital tools? Farmonaut offers an agriculture API with full developer documentation for easy integration:
See API Developer Docs
🌾 4. Variable Rate Technology in Farming: Inputs, Right Where Needed
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) is exactly what its name promises: adjusting the rate of input application—such as fertilizers, pesticides, or water—dynamically, based on real-time field data and geo-tagged zones.
- Applies resources only when and where required, reducing environmental waste and operational costs
- Targets specific zones instead of treating the entire field uniformly
- Improves efficiency by responding to soil and crop variability
This “right rate, right place, right time” philosophy is central to modern resource efficiency and environmental sustainability in farming.
Learn How VRT Reduces Waste
“Over 70% of large farms worldwide now use precision agriculture technologies for improved efficiency and sustainability.”
🚜 5. Automated Machinery & Robotics: Farm Automation Solutions
Farm automation solutions encompass the use of autonomous tractors, robotic weeders, and smart harvesters equipped with AI. Here are the major benefits:
- Operate 24/7: Machines can run tirelessly, mitigating labor shortages and boosting productivity
- Consistency: Sowing, spraying, and harvesting tasks are executed with higher precision and accuracy
- Labor reduction: Automated tasks require fewer human hands, resulting in direct cost savings
- Data integration: Machines can collect and analyze field data in real time, enhancing subsequent operations
This new era of robotics is essential for large-scale, scalable, and resilient agriculture.
Explore Precision Robotics in Farming
Tip: Boost Operational Efficiency with Farmonaut’s Fleet Management
For agribusinesses looking to streamline logistics and optimize vehicle use, Farmonaut’s Fleet Management solution
offers real-time tracking and resource optimization features that can significantly reduce operational costs. This is especially valuable as automation and scale grow at the farm level.
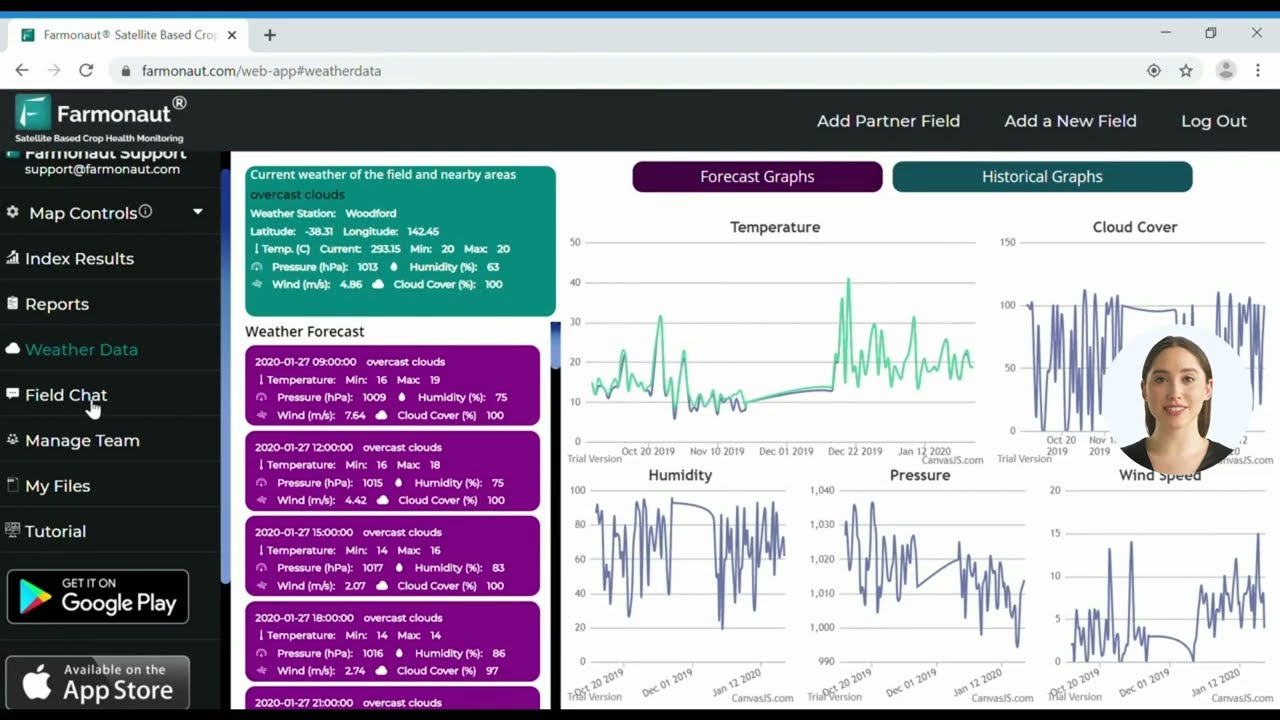
📊 6. Data Analytics & Machine Learning: Predictive Crop Management Data
Central to all precision farming innovations is the exhaustive analysis of crop management data. With today’s predictive analytics in agriculture, we can:
- Forecast yields based on historic and real-time field conditions
- Predict pest infestations and weather risks, enabling timely intervention
- Identify optimal planting and harvest times for maximum return
- Continuously refine input application rates and management strategies
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System is a standout tool, providing real-time advice, weather forecasts, and custom crop management strategies—precisely tailored to each farmer’s needs.
Such data-driven insights are rapidly becoming non-negotiable for farmers seeking to stay competitive while promoting environmental sustainability and resilience in their operations.
For Large-Scale Monitoring and Advisory
Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management app enables field technicians, cooperatives, and administrators to remotely monitor, track, and manage multiple farms or blocks simultaneously—leveraging data, productivity maps, and AI-based recommendations for better oversight and resource allocation.
🔗 7. Blockchain for Product Traceability: Trust Through Transparency
In today’s global supply chains, the demand for traceability and transparency is higher than ever before. Blockchain technology offers:
- Immutable tracking of produce throughout the supply chain (from farm to fork)
- Reduces risk of fraud and enhances consumer trust
- Supports regulatory compliance and certification in food and textiles
Farmonaut’s Product Traceability feature utilizes blockchain to provide transparent records, ensuring every stage of the journey is verifiable and secure.
Go Further: Carbon Footprinting for Sustainable Agriculture
Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting module helps agribusinesses and progressive farmers measure, reduce, and report their environmental impact.
Real-time emissions data empowers better compliance and progress toward sustainability goals, cementing your farm’s contribution to a climate-resilient future.
Comparison Table of Precision Farming Technologies
| Technology | Primary Function | Est. Yield Increase (%) | Est. Cost Savings (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-guided Equipment | Accurate field navigation & mapping | 8–12% | 10–15% | Reduces overlap, fuel use, & chemical spillover |
| Drones | Aerial crop monitoring & targeted spraying | 10–18% | 12–16% | Minimizes water/chemical waste & boosts responsiveness |
| Remote Sensing | Satellite-based health & soil analysis | 12–19% | 8–14% | Informs sustainability practices & input reduction |
| Data Analytics Platforms | Crop management & predictive analytics | 15–20% | 15–20% | Drives informed, efficient resource allocation |
| IoT Sensors | Real-time soil, moisture, weather monitoring | 10–14% | 10–15% | Ensures optimal input use, reduces runoff |
| Variable Rate Technology | Input application at varying rates | 12–18% | 12–25% | Reduces waste, minimizes chemical load |
| Autonomous Machinery | Automated fieldwork & labor savings | 11–16% | 15–20% | Consistent operations, less emissions, reduced soil compaction |
Key Benefits of Precision Farming
The adoption of precision farming methods delivers measurable improvements across every aspect of agricultural efficiency and sustainability:
- Increased Crop Yields: More accurate application of nutrients, water, and protection increases yields by up to 20%, without expanding land usage.
- Significant Cost Savings: Targeted resource use and automation result in less waste and reduced operational costs—farmers spend less and earn more.
- Environmental Sustainability in Farming: By precision targeting, we minimize chemical runoff, cut down on soil degradation, and use less water, actively promoting sustainability in our operations.
- Improved Efficiency and Farm Operations: Automation and data analytics streamline every stage, reduce the need for manual labor, and speed up production cycles.
- Enhanced Risk Management with Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics in agriculture helps us anticipate threats (like pest outbreaks or droughts) and mitigate crop loss proactively.
For those seeking to further combine sustainability with compliance and market differentiation, Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting module empowers businesses to track and report their progress on environmental goals.
Challenges in Precision Farming Adoption
While the advantages are compelling, precision farming does pose several adoption challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Investment in advanced sensors, automated machinery, and digital platforms may be prohibitive for small or resource-limited farmers.
- Technical Expertise: Using these technologies and interpreting their data requires training and digital literacy.
- Internet and Connectivity: Most advanced solutions require robust cellular or GPS connectivity, still limited in many rural or remote areas, potentially excluding smaller or geographically isolated players.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The collection, storage, and sharing of farm and crop data create new questions on data ownership, sharing, and privacy.
Farmonaut directly addresses these issues by offering affordable, user-friendly platforms compatible across devices, accessible APIs for custom needs, and an emphasis on secure, privacy-conscious data management.
Looking for remote monitoring and resource management even in large plantations? Try the Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory app by Farmonaut for real-time health monitoring and instant decision support.
Farmonaut: Making Precision Farming Accessible Worldwide
As this technology revolution unfolds, Farmonaut stands out as a leader in democratizing precision farming for farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Using multispectral satellite imagery, we provide actionable insights such as NDVI (vegetation health), soil moisture, and early warning of pest or drought-related stress.
- AI & Data-Driven Advisory: Jeevn AI delivers real-time, personalized recommendations, crop management plans, and risk alerts directly to your device—accessible on Android, iOS, web apps, and via API.
- Blockchain Traceability: Our platforms offer end-to-end product traceability for food and textile supply chains, ensuring transparency and trust from field to consumer.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Efficiently track and manage logistics, vehicles, and operation costs to ensure safe, timely deliveries.
- Carbon Footprinting: Quantify your operation’s real-time emissions and environmental impact, enabling reporting and targeted reduction efforts.
Farmonaut’s mission is simple: Harnessing advanced crop management data and remote sensing to make precision agriculture easier, more affordable, and globally accessible for every farmer on earth.
Our solutions serve a diverse audience—individual farmers, cooperatives, large agribusiness, governments, NGOs, and financial institutions—enabling more profitable, resilient, and sustainable farming for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between precision farming and traditional farming?
Precision farming optimizes input use (like water, fertilizer, and pesticides) based on detailed field data and advanced technology. Traditional farming treats each field—or even the entire farm—uniformly, without accounting for variability in soil, moisture, or crop needs.
2. How do GPS and GIS in agriculture improve efficiency?
GPS and GIS enable precise mapping and monitoring of fields, reducing overlaps and missed areas, optimizing input application, and ultimately reducing resource waste while boosting crop yields.
3. Can small-scale farmers adopt precision farming technologies affordably?
Yes, tools like Farmonaut use satellite and AI-driven solutions, bypassing the need for expensive on-field hardware, making precision farming accessible and cost-effective for farms of any size.
4. What are soil moisture sensors and why are they important?
Soil moisture sensors are devices that measure the water content in the soil. They help farmers and irrigation systems apply water efficiently, preventing both drought stress and overwatering, optimizing yields, and preserving water resources.
5. How does automation and robotics assist in farming?
Automated machinery like robotic weeders and autonomous tractors carry out tasks with precision and consistency, operate around the clock, and collect valuable data, all while reducing labor costs.
6. Is my farm’s data protected if I use digital or satellite tools?
Data privacy and ownership are core concerns for modern platforms like Farmonaut, which are designed with strict controls and transparent policies to maintain data security.
7. How can I get started with precision farming if I’m new to digital tools?
Start by downloading an intuitive app like Farmonaut and exploring its user-friendly dashboards, satellite health imagery, and basic advisory features. Most solutions offer step-by-step guides and customer support for first-time users.
Conclusion: Cultivating an Efficient, Sustainable Future with Precision Farming
Precision farming isn’t just the future—it’s the present. With the combined power of GPS, GIS, drones, IoT sensors, VRT, robotics, data analytics, and blockchain, we’re witnessing unprecedented change in how farmers manage their crops, conserve resources, and protect the environment.
Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront, breaking down adoption barriers, making precision technologies affordable, scalable, and accessible everywhere. As we continue to innovate, manage risk, and promote sustainability, we each become stewards of a smarter, healthier, and more profitable agricultural landscape.
If you’re ready to elevate your farm’s efficiency, resilience, and yield potential, we encourage you to explore Farmonaut’s suite of precision agriculture tools. Join us and millions of progressive growers on the journey toward data-driven, environmentally responsible, and future-ready farming.