Revolutionizing Environmental Management: Farmonaut’s Guide to Sustainable Farming Practices and Agricultural Licensing
“Precision agriculture technology can increase crop yields by up to 30% while reducing water usage by 50%.”
In today’s rapidly evolving agricultural landscape, environmental management in agriculture has become a critical focal point for farmers, policymakers, and agricultural technology providers alike. At Farmonaut, we understand the pressing need for sustainable farming practices that not only enhance productivity but also preserve our planet’s precious resources. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of agricultural licensing requirements, eco-friendly crop protection methods, and cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping the future of farming.
As we navigate through the complexities of modern agriculture, we’ll explore how precision agriculture technology is revolutionizing soil and water conservation techniques, paving the way for more efficient and environmentally conscious farming operations. We’ll also shed light on the importance of agricultural waste management, smart irrigation systems, and the rigorous processes involved in organic farming certification.

Our journey through sustainable agriculture will take us from the intricacies of agroecosystem management to the crucial role of environmental impact assessments and air quality regulations in farming operations. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer or managing vast agricultural enterprises, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to align your farming practices with the highest environmental protection standards.
At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced remote sensing and GIS technology to offer valuable insights into implementing these sustainable practices efficiently. Our expertise in satellite-based farm management solutions allows us to provide you with cutting-edge tools and data-driven strategies to optimize your farming operations while minimizing environmental impact.
Understanding Agricultural Licensing Requirements
Navigating the complex world of agricultural licensing is a crucial step in ensuring that your farming operations comply with environmental regulations and standards. These licensing requirements are designed to protect our ecosystems, manage hazardous substances, and promote sustainable farming practices.
- Environmental Management Agency (EMA) Registration: Many countries require farmers to register with their local EMA or equivalent agency. This registration is often the first step in the licensing process.
- Hazardous Substances Handling: If your farm operations involve the use of pesticides or other hazardous substances, you may need specific licenses for their storage, use, and disposal.
- Water Use Permits: Depending on your location and the scale of your operations, you might need permits for water extraction, especially if you’re implementing irrigation systems.
- Solid Waste Management: Proper handling and disposal of agricultural waste often requires specific permits to ensure environmental protection.
To streamline the application process, many environmental agencies now offer online portals where farmers can submit their licence applications, track the status of their submissions, and access important resources and information.
Eco-Friendly Crop Protection Methods
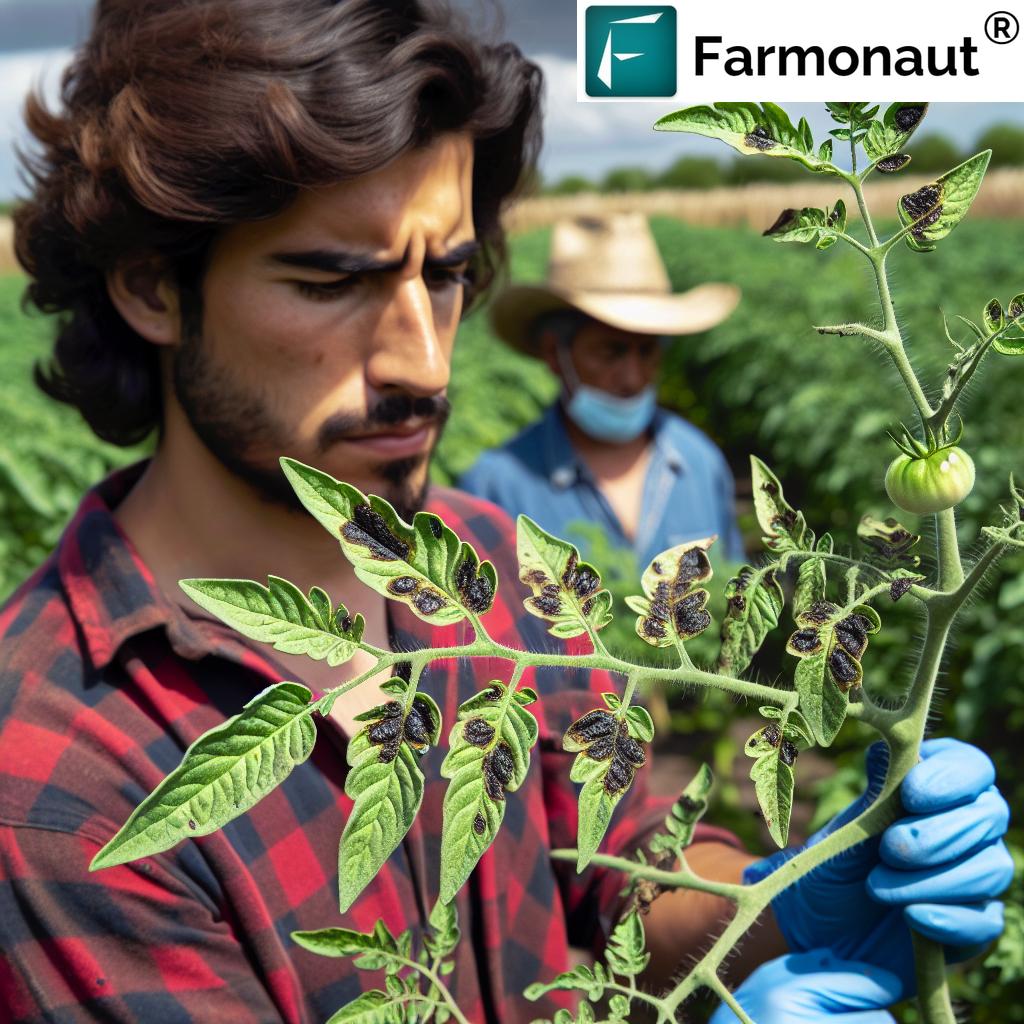
Eco-friendly crop protection is at the heart of sustainable farming practices. These methods focus on minimizing the use of harmful chemicals while effectively managing pests and diseases. Here are some key approaches:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This holistic approach combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to manage pests with minimal environmental impact.
- Biological Control: Utilizing natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to control pest populations.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops helps break pest cycles and reduces the need for chemical interventions.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops can suppress weeds, improve soil health, and reduce erosion.
- Precision Application: Using technology like GPS-guided sprayers to apply pesticides only where needed, reducing overall usage.
At Farmonaut, our satellite-based crop health monitoring system can help you identify pest and disease issues early, allowing for more targeted and eco-friendly interventions.
Precision Agriculture Technology: A Game-Changer in Soil and Water Conservation
Precision agriculture technology is revolutionizing the way we approach soil and water conservation techniques. By leveraging data-driven insights and advanced tools, farmers can optimize resource use while minimizing environmental impact.
“Organic farming certification processes can take up to 3 years, ensuring strict adherence to sustainable practices.”
- Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing: These technologies provide valuable data on crop health, soil moisture, and nutrient levels, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): VRT enables precise application of inputs like fertilizers and water based on specific field conditions.
- Soil Sensors: These devices provide real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels, optimizing irrigation and fertilization practices.
- GPS-Guided Machinery: Reduces overlap in field operations, minimizing soil compaction and optimizing resource use.
Farmonaut’s platform integrates these technologies, offering farmers a comprehensive tool for precision agriculture. Our satellite-based monitoring system provides real-time insights into crop health and soil conditions, enabling more efficient resource management.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Optimizing Water Use in Agriculture
Smart irrigation systems are a crucial component of sustainable farming practices, especially in regions facing water scarcity. These systems use advanced technologies to ensure that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, significantly reducing water waste.
- Soil Moisture Sensors: These devices provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, triggering irrigation only when necessary.
- Weather-Based Controllers: By integrating local weather data, these systems adjust irrigation schedules based on rainfall, temperature, and evapotranspiration rates.
- Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Precision Sprinklers: Advanced sprinkler systems use GPS and mapping technologies to apply water with high accuracy.
Farmonaut’s platform can integrate with smart irrigation systems, providing additional layers of data from satellite imagery to further optimize water use efficiency.
Organic Farming Certification: Ensuring Sustainable Practices
The organic farming certification process is a rigorous journey that ensures adherence to strict sustainable farming standards. This certification is crucial for farmers looking to tap into the growing market for organic produce while contributing to environmental conservation.
- Transition Period: Most certification programs require a transition period of 2-3 years, during which farmers must follow organic practices without using prohibited substances.
- Documentation: Detailed record-keeping of all farming practices, inputs used, and crop rotations is essential.
- Soil Management: Organic certification requires practices that maintain or improve soil quality without the use of synthetic fertilizers.
- Pest and Disease Management: Organic farmers must use approved natural methods for pest and disease control.
- Inspections: Regular on-site inspections by certified agencies are conducted to ensure compliance with organic standards.
Farmonaut’s technology can assist organic farmers in maintaining detailed records of their farming practices, providing valuable data for certification processes.
Agroecosystem Management: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Farming
Agroecosystem management is a comprehensive approach that views the farm as an interconnected ecosystem. This holistic perspective is essential for long-term sustainability and environmental protection.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Encouraging diverse plant and animal species on the farm to create a balanced ecosystem.
- Natural Resource Conservation: Implementing practices that conserve soil, water, and air quality.
- Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems: Combining crop and livestock production to create closed-loop nutrient cycles.
- Agroforestry: Incorporating trees and shrubs into agricultural systems to improve biodiversity and soil health.
Farmonaut’s satellite imagery and AI-powered analytics can provide valuable insights into the overall health and balance of your farm’s ecosystem, supporting informed decision-making in agroecosystem management.
Agricultural Waste Management: Turning Challenges into Opportunities
Agricultural waste management is a critical aspect of sustainable farming that addresses the proper handling, treatment, and disposal of farm-generated waste. Effective waste management not only reduces environmental impact but can also create new revenue streams through resource recovery.
- Composting: Converting organic waste into nutrient-rich compost for soil amendment.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Producing biogas from organic waste, which can be used as a renewable energy source.
- Recycling: Properly sorting and recycling materials like plastics, metals, and glass used in farming operations.
- Hazardous Waste Handling: Implementing safe storage, transportation, and disposal methods for hazardous substances like pesticide containers.
Our platform at Farmonaut can assist in mapping and monitoring waste management practices across your farm, ensuring compliance with regulations and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Environmental Impact Assessments in Agriculture
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) are crucial tools for evaluating the potential effects of agricultural projects on the environment. These assessments help in making informed decisions and implementing mitigation measures to minimize negative impacts.
- Scoping: Identifying the key environmental issues that need to be addressed.
- Baseline Studies: Gathering data on the current environmental conditions before project implementation.
- Impact Prediction: Analyzing potential environmental consequences of the proposed agricultural activities.
- Mitigation Planning: Developing strategies to avoid, minimize, or offset negative environmental impacts.
- Monitoring: Implementing long-term monitoring plans to track environmental changes and the effectiveness of mitigation measures.
Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring and data analytics capabilities can provide valuable historical and real-time environmental data to support comprehensive EIAs for agricultural projects.
Air Quality Regulations in Farming Operations
Air quality is an often-overlooked aspect of agricultural environmental management. However, farming operations can significantly impact air quality through various activities. Understanding and complying with air quality regulations is essential for sustainable farming.
- Dust Management: Implementing practices to reduce dust from tillage, harvesting, and other field operations.
- Emissions Control: Managing emissions from farm equipment, livestock operations, and crop burning activities.
- Odor Mitigation: Adopting strategies to minimize odors from livestock facilities and manure management.
- Pesticide Drift Prevention: Using proper application techniques and weather monitoring to prevent pesticide drift.
Farmonaut’s weather monitoring and forecasting capabilities can help farmers plan their activities to minimize air quality impacts, ensuring compliance with regulations.
The Role of Remote Sensing and GIS in Environmental Management
Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a pivotal role in modern environmental management for agriculture. These technologies provide farmers and environmental managers with powerful tools for monitoring, analyzing, and managing agricultural landscapes.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Satellite imagery can detect early signs of crop stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies.
- Land Use Change Detection: Tracking changes in land use over time to assess environmental impacts and compliance with regulations.
- Soil Moisture Mapping: Creating detailed maps of soil moisture levels to optimize irrigation and prevent water waste.
- Biodiversity Assessment: Monitoring habitat changes and wildlife corridors in agricultural areas.
At Farmonaut, we leverage advanced remote sensing and GIS technologies to provide farmers with actionable insights for sustainable farm management. Our platform integrates satellite data with on-ground information to create comprehensive environmental management solutions.
Comparison of Sustainable Farming Practices and Their Environmental Impact
| Sustainable Farming Practice | Environmental Benefits | Potential Challenges | Licensing/Certification Requirements | Estimated Implementation Cost | Farmonaut Technology Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Reduced resource use, minimized chemical runoff | High initial investment, technical expertise required | Varies by region, may require pesticide applicator license | High | Satellite imagery, AI-driven insights |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | Water conservation, reduced energy use | Installation complexity, ongoing maintenance | Water use permits may be required | Medium | Integration with weather data and soil moisture mapping |
| Organic Farming | Improved soil health, biodiversity enhancement | Lower yields initially, pest management challenges | Strict certification process (2-3 years) | Medium to High | Crop health monitoring, record-keeping assistance |
| Agricultural Waste Management | Reduced pollution, resource recovery | Infrastructure needs, regulatory compliance | Waste handling and disposal licenses | Medium | Mapping and monitoring of waste management practices |
Implementing Sustainable Practices: A Step-by-Step Guide
Transitioning to more sustainable farming practices can seem daunting, but with a structured approach, it’s achievable for farms of all sizes. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement sustainable practices:
- Assess Your Current Operations: Conduct a thorough evaluation of your current farming practices, identifying areas for improvement in terms of environmental impact and resource efficiency.
- Set Clear Goals: Define specific, measurable objectives for sustainability improvements, such as reducing water usage by 20% or increasing soil organic matter by 2% over five years.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the sustainable practices you’ll implement, including timelines and resource allocation.
- Invest in Technology: Consider adopting precision agriculture tools, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system, to support your sustainability efforts.
- Train Your Team: Ensure all farm staff are educated on new sustainable practices and technologies being implemented.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your sustainable practices, using data from tools like Farmonaut to make informed adjustments.
- Seek Certification: If applicable, pursue relevant certifications (e.g., organic, regenerative) to validate your sustainable practices.
- Engage with the Community: Share your sustainability journey with local communities and fellow farmers to promote wider adoption of eco-friendly practices.
Remember, implementing sustainable practices is an ongoing process. Continuous improvement and adaptation are key to long-term success.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced integration
The Future of Sustainable Farming: Emerging Trends and Technologies
As we look to the future of sustainable farming, several exciting trends and technologies are emerging that promise to further revolutionize agricultural practices:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Advanced AI algorithms will provide even more precise recommendations for crop management, pest control, and resource allocation.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology will enhance supply chain transparency, allowing consumers to trace their food from farm to table.
- Vertical Farming: Urban vertical farms will become more prevalent, reducing transportation costs and increasing food security in cities.
- Gene Editing: CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies may lead to more resilient, nutritious crops that require fewer inputs.
- Robotics and Automation: Autonomous farm equipment will reduce labor costs and increase precision in farming operations.
At Farmonaut, we’re continuously evolving our technology to stay at the forefront of these trends, ensuring that our users have access to the most advanced tools for sustainable farm management.
Check out our API Developer Docs for integration possibilities
FAQ: Sustainable Farming Practices and Agricultural Licensing
Q: What are the key benefits of implementing sustainable farming practices?
A: Sustainable farming practices offer numerous benefits, including improved soil health, reduced environmental impact, lower input costs over time, and potential premium prices for sustainably produced goods.
Q: How can I determine which sustainable practices are best for my farm?
A: The best practices for your farm depend on factors like your location, soil type, climate, and crop types. Conducting a farm assessment and consulting with agricultural experts or using tools like Farmonaut can help you identify the most suitable practices.
Q: What types of agricultural licenses might I need for my farming operation?
A: Common agricultural licenses include water use permits, pesticide applicator licenses, organic certification, and environmental compliance permits. The specific requirements vary by region and the nature of your farming activities.
Q: How can precision agriculture technology help me become more sustainable?
A: Precision agriculture technology, such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring system, can help you optimize resource use, reduce waste, and make data-driven decisions that improve both sustainability and profitability.
Q: What are some cost-effective ways to start implementing sustainable practices?
A: Start with practices that require minimal investment, such as cover cropping, crop rotation, or implementing integrated pest management. Gradually incorporate more advanced technologies as you see benefits and can invest more.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future in Agriculture
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, the journey towards sustainable farming is multifaceted, involving a careful balance of environmental stewardship, technological innovation, and regulatory compliance. By embracing sustainable practices and leveraging cutting-edge technologies like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can not only reduce their environmental impact but also enhance their productivity and profitability.
Remember, sustainable farming is not a destination but a continuous journey of improvement and adaptation. As environmental challenges evolve and new technologies emerge, staying informed and flexible in your approach will be key to long-term success.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers in this journey towards sustainability. Our satellite-based monitoring systems, AI-driven insights, and comprehensive farm management tools are designed to make sustainable farming practices more accessible and effective for farmers of all scales.
As we look to the future, the agricultural sector has a unique opportunity to lead the way in environmental stewardship while meeting the growing global demand for food. By adopting sustainable practices, staying compliant with agricultural licensing requirements, and leveraging innovative technologies, we can create a more resilient, productive, and environmentally friendly agricultural system for generations to come.