7 Precision Agriculture Solutions That Revolutionize Farming
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Precision Agriculture in Modern Farming
- Featured Trivia
- Key Components of Precision Agriculture
- 7 Precision Agriculture Solutions Transforming Farms
- Comparative Feature-Benefit Table
- Applications of Precision Agriculture in the Field
- Farmonaut: Making Precision Farming Accessible
- Farmonaut Subscription Options
- Challenges & Considerations in Precision Agriculture
- What’s Next? Future Prospects in Precision Agriculture
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Introduction: Precision Agriculture in Modern Farming
In recent years, precision agriculture has emerged as a transformative force in the world of farming, offering farmers a powerful way to optimize resources, maximize crop yields, and minimize environmental impact. As global food demand rises and resource constraints become more apparent, innovative solutions—ranging from AI-powered crop monitoring to real-time soil health assessment—are revolutionizing the way we cultivate, manage, and harvest crops.
By harnessing smart farming technologies like GPS, IoT devices, drones, and artificial intelligence (AI), we can make more precise, data-driven decisions that boost yields, improve efficiency, and promote sustainability across our fields. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore 7 groundbreaking precision agriculture solutions that are changing the face of farming. Whether you’re a farmer, agricultural business, or simply interested in agri-tech, this post will give you a clear understanding of these innovations and their immense value.
Primary Focus Keyword: precision agriculture
Interested in integrating real-time satellite and weather data into your agricultural or research platform? Explore the Farmonaut API and view our API Developer Docs for seamless integration of precision farming intelligence.
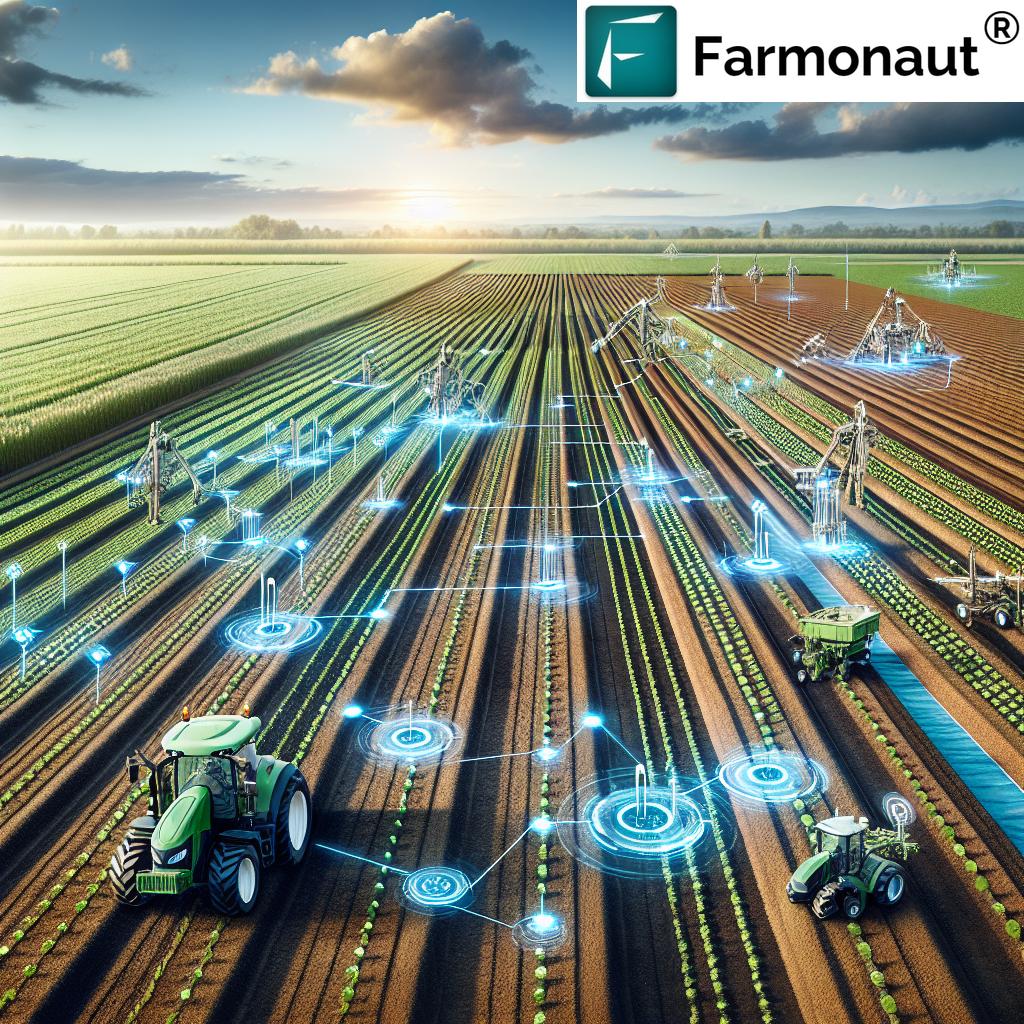
Key Components of Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture leverages a powerful suite of components and smart farming technologies designed to optimize every aspect of crop production, from sowing to harvesting. Here, we break down the essential building blocks that underpin today’s most efficient farms:
- Global Positioning System (GPS) & Geographic Information Systems (GIS): For spatial mapping, precision planting, fertilizing, and harvesting.
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): Ensures tailored application of fertilizers, pesticides, and water, matching the specific needs of each field area.
- Remote Sensing & Drones: Capture multispectral and detailed field images for real-time crop monitoring and management.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: Enable soil moisture, weather, and environmental condition monitoring around the clock.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: Analyze big data, forecast weather patterns, and suggest inputs for optimal performance.
- Automated/Autonomous Machinery: From self-driving tractors to precision sprayers for efficient, labor-saving operations.
- Software Platforms & Mobile Apps: Provide user-friendly dashboards for resource management, farm oversight, and data-driven decision-making.
Together, these components form the technological foundation that allows us to analyze and respond to field variability, making informed decisions that drive higher productivity and sustainability.
Comparative Feature-Benefit Table: Precision Agriculture Solutions
This table highlights the core technologies driving precision agriculture, providing at-a-glance insight into their yield, efficiency, and sustainability impact.
| Solution Name | Core Technology Used | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Resource Efficiency Gain (%) | Sustainability Impact (Score/Level) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS & GIS Mapping | GPS Hardware, Geographic Information Systems, Mapping Software | 10–15% | 15–25% | High |
| Variable Rate Technology (VRT) | Sensors, Application Controllers, Farm Management Software | 15–20% | 10–30% | High |
| Remote Sensing & Drones | Multispectral Cameras, UAVs, AI Image Analysis | 10–15% | 20–35% | Moderate–High |
| IoT Field Monitoring | Soil Sensors, Weather Stations, Connected Devices | 10–18% | 25–40% | High |
| AI & Machine Learning Systems | AI/ML Algorithms, Predictive Analytics Platforms | 12–20% | 10–25% | High |
| Autonomous Machinery | Robotics, GPS Navigation, Automation Software | 10–15% | 20–30% | Moderate–High |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | IoT Sensors, Automated Valves, Data Analytics | 10–18% | 20–40% | High |
7 Precision Agriculture Solutions Transforming Farms
-
1. Global Positioning System (GPS) & Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Benefits: Reduces overlaps/gaps during input application, improves seed placement, and minimizes waste.
- Use Case: Field boundary mapping for targeted fertilization and variable-rate spraying.
-
2. Variable Rate Technology (VRT) — The Power of Targeted Applications
- Map-Based VRT: Uses GIS maps (say, showing soil nutrient differences) to pre-plan application zones and rates.
- Sensor-Based VRT: Relies on real-time crop sensors and IoT devices to adjust on-the-fly as tractors traverse the field.
-
3. Remote Sensing & Drones for Crop Monitoring
- Aerial Monitoring: Detect problem areas (e.g., water stress, nutrient deficiencies) before they escalate, enabling timely intervention.
- Data-Driven Insights: Software analyzes drone imagery to generate crop health indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index).
-
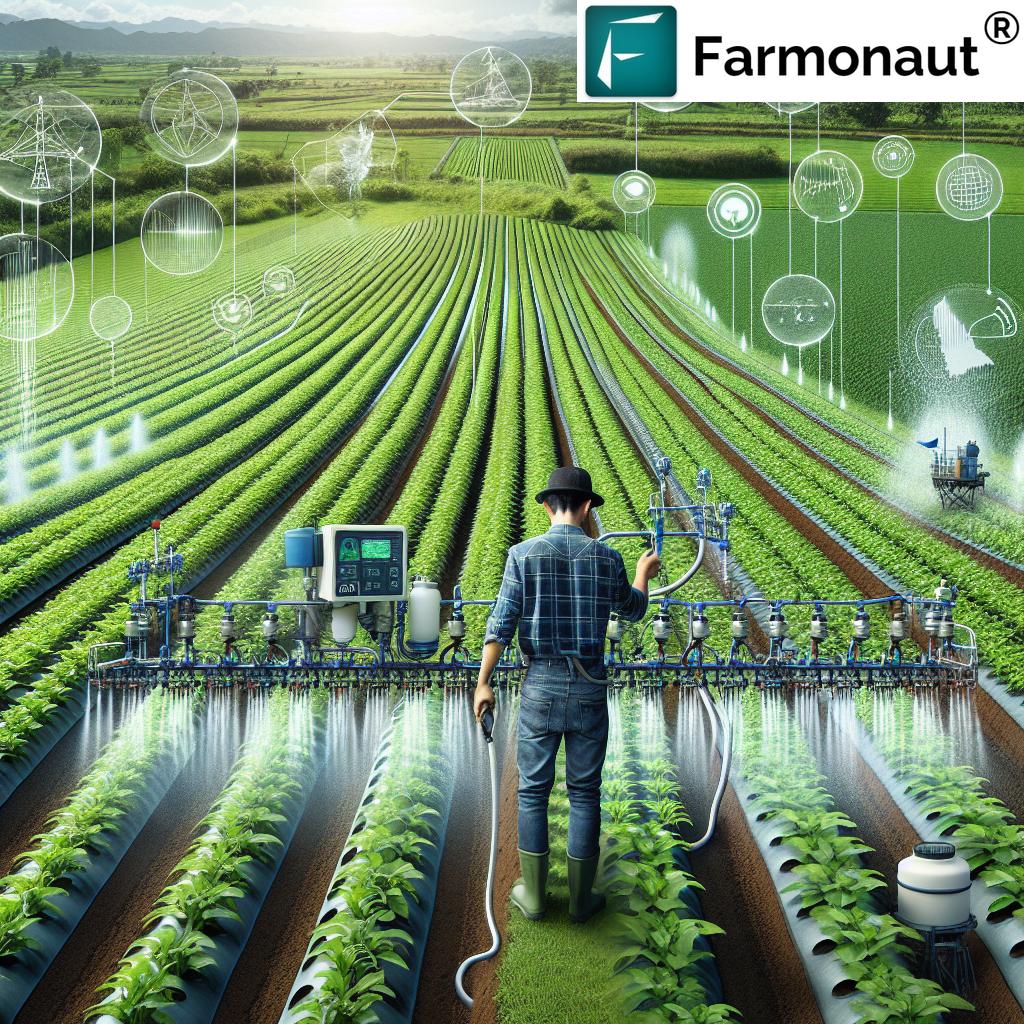
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Devices for Field Monitoring
- Automated Alerts: Receive early warnings for extreme weather or irregularities in your irrigation schedule.
- Optimized Resource Use: Reduce water and input waste by addressing variability across your farm—no more “one size fits all.”
-
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Agriculture
- Predict Pest and Disease Outbreaks: Early detection lets us apply targeted treatments, minimizing pesticide use and yield loss.
- Customized Advice: AI-powered systems like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory provide tailored crop management strategies, factoring in weather, soil, and crop stage data.
- Yield Forecasting: Plan operations and market strategies with more confidence using predictive analytics.
-
6. Autonomous Farming Equipment
- Benefits: Round-the-clock operations, improved safety, and precise input application.
- Example: Automated pesticide sprayers apply the correct dose only where needed, protecting non-target crops and reducing input waste.
-
7. Smart Irrigation Systems
- Precision Watering: Systems monitor real-time soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation based on current crop needs and weather forecasts.
- Resource Savings: Reduce water use by 20–40% while typically improving crop yields by up to 15%.
Employing GPS and GIS in farming allows us to map fields with pinpoint spatial accuracy. This means every pass of our tractors—whether planting, fertilizing, or harvesting—is precisely controlled and documented. GIS software lets us overlay spatial data like soil health, moisture, and historic yield maps to make informed decisions. Systems like John Deere’s StarFire navigation provide centimeter-level accuracy, creating an efficient and optimal approach to field management.
Why it matters: Precision starts with location. Accurate field data lets us match our practices to each area’s unique needs, improving resource management and yields.
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) allows us to apply the right fertilizers, pesticides, or irrigation at the right rates in specific field zones. Combined with GPS and sensor data, VRT modernizes how we deliver nutrients and chemicals, reducing input waste while ensuring crops get precisely what they need.
This targeted approach not only reduces chemical waste and environmental impact but also consistently improves crop yield and sustainability.
Drones, equipped with multispectral cameras and advanced sensors, give us a real-time aerial view of our crops. They can capture detailed images to assess plant health, detect pest infestations, and monitor growth rates.
This remote sensing system unlocks the potential for efficient, large-scale crop plantation & forest advisory, helping both smallholder farmers and large agribusinesses.
Dive Deeper: Explore the value of precision agriculture with drones and how fast interventions can save yields and resources.
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects our fields to the cloud, making data available 24/7 for smarter, faster decisions. Devices such as soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and crop-level sensors automatically track moisture, temperature, humidity, and environmental conditions in real time.
Field data is seamlessly integrated, supporting precision irrigation management and fertilization strategies for optimal plant growth and reduced environmental impact.
AI is at the core of modern precision farming technologies. Advanced algorithms process massive quantities of data—from satellites, soil sensors, and historical yield records—to predict outcomes and recommend tailored actions.
AI-driven recommendations are the “brains” of sustainable agriculture—fostering efficiency, productivity, and environmental stewardship.
Autonomous tractors and robotic machinery automate critical tasks such as planting, spraying, weeding, and harvesting. Guided by GPS and real-time field data, these systems perform with accuracy and consistency—significantly reducing labor costs and human error.
These advancements empower farmers to scale up operations cost-effectively, using autonomous machinery for field management.
Traditional irrigation often leads to water overuse and inefficiency. In contrast, smart irrigation systems—integrating IoT sensors, automated valves, and AI-based recommendations—deliver water exactly where and when crops need it.
Check out the potential of large-scale farm management solutions for smart irrigation and efficient field operations.
Applications of Precision Agriculture Solutions in the Field
- Crop Monitoring and Management: Real-time data from drones, satellites, and IoT sensors enables early detection of nutrient deficiencies or pest infestations, allowing prompt corrective action.
— Use the Farmonaut App for real-time crop health monitoring and field insights. - Soil Health Assessment: Advanced tools like nanosensors and remote sensing help assess soil nutrient content, moisture, and texture.
— These insights inform carbon footprint tracking and sustainable soil management strategies. - Automated and Autonomous Machinery: Carry out repetitive, labor-intensive tasks such as seeding and spraying with precision robotics, improving consistency and reducing labor costs.
— See how fleet and resource management through Farmonaut can help optimize agri-logistics and equipment usage. - Smart Irrigation: Harness IoT devices to automate irrigation scheduling, match water delivery with precise crop growth stages, and save water.
- Blockchain Traceability: Protect your crop supply chain with transparent, blockchain-backed tracking.
— Learn about blockchain-based traceability for building consumer trust and supply transparency. - Financial Services for Farmers: Access faster, data-verified crop loans and agricultural insurance using satellite-based farm verification.
— Find out more at Crop Loan and Insurance with Farmonaut.
Farmonaut: Making Precision Farming Accessible and Effective
Farmonaut stands out as a pioneer in democratizing access to precision agriculture with its advanced, satellite-powered farm management platform. Our mission is to equip every farmer, agribusiness, and policy-maker worldwide with affordable and actionable data—directly on mobile, web, or via robust APIs.
Technologies That Power Us:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multi-spectral imagery provides real-time crop health assessment, supports injury detection, monitors soil moisture, and tracks vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI, etc.).
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Delivers AI-generated, customized farm advice on weather, crop nutrition, and pest management—improving productivity while reducing input waste.
- Blockchain Product Traceability: Enables transparent supply chain tracking and fraud prevention—serving both farmers and corporate clients.
- Carbon Footprinting: Tracks and reports emission data, supporting compliance and sustainable farming practices at scale.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Monitors farm machinery use, logistics, and safety for efficient operations.
No expensive on-field hardware is needed—our system works via satellite data, making precision agriculture more affordable and scalable for smallholders and large operators alike. Our modular, subscription-based model is tailored to individual farmers, agribusinesses, and government or research organizations.
- Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting helps farms and companies monitor their carbon emissions and advance sustainable production methods.
- Farmonaut Traceability Solutions safeguard food and textile supply chains with blockchain-backed transparency.
- Fleet & Resource Management improves the monitoring of agri-logistics, helping large agribusinesses optimize fleets and machinery usage.
- Crop Loan and Insurance speeds up farmer access to credit by providing satellite-based land verification for lenders.
- Large-Scale Farm Management brings satellite-based insights to plantations, forests, and cooperatives.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Get started with precision agriculture today! Our subscription-based packages offer affordable, scalable solutions for farmers, agribusinesses, and government organizations.
Note: Our web and mobile apps empower you to monitor, manage, and optimize your farm operations from anywhere.
Challenges & Considerations in Precision Agriculture
While precision agriculture opens doors to more productive and sustainable farming, several practical and technical barriers persist:
- High Initial Investment: Advanced data systems and equipment, though cost-effective in the long run, require upfront capital.
- Technical Expertise: Farmers must become familiar with new tools, interfaces, and agricultural data analytics.
- Data Management: Handling, storing, and analyzing big data raises privacy and security concerns alongside the need for robust digital infrastructure.
- Connectivity: In rural or low-infrastructure zones, internet access may limit the immediate adoption of cloud-based and IoT solutions.
Addressing these challenges requires continuous training, financial support for farmers, improved infrastructure, and a commitment to technology adaptation at every level.
What’s Next? Future Prospects in Precision Agriculture
The future of precision agriculture is bright, as breakthroughs in AI, robotics, IoT, and nanotechnology accelerate. We expect:
- More Affordable Technologies: Satellite-based and app-driven solutions, like those from Farmonaut, are lowering barriers for farmers everywhere.
- Nanosensors: Tiny, ultra-sensitive sensors will soon deliver hyper-local data on soil health, pathogens, and water content, leading to finer control over fertilization, irrigation, and pest prevention.
- Smarter Crops: Initiatives such as Bayer’s Preceon™ Smart Corn System demonstrate the integration of genetics and smart farming for climate-resilient crops.
- Global Expansion: As awareness and accessibility increase, even smallholder farmers in remote regions will benefit from these solutions.
- Advanced Sustainability Metrics: Carbon tracking, resource management, and transparent supply chains will become the standard for sustainable food production, supported by platforms like Farmonaut.
By 2030, it is expected that the majority of global farms will use some level of precision agriculture to combat resource scarcity, climate change, and shifting market demands, ensuring food security for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture is a modern farming practice that employs advanced technologies (like GPS, IoT devices, AI, and drones) to collect and analyze field data, enabling targeted, efficient use of farm resources—for improved yields, lower costs, and less environmental impact.
Which crops benefit most from precision farming?
While all crops can benefit from data-driven farming, row crops such as corn, wheat, rice, soy, cotton, and even specialty crops like orchards and vineyards experience the highest gains due to their scale and input requirements.
How do smart irrigation systems work?
Smart irrigation systems use IoT sensors to continuously monitor soil moisture and weather. Automated controllers then adjust watering schedules and amounts, minimizing waste and ensuring crops get exactly what they need, when they need it.
Is precision farming affordable for smallholders?
Thanks to satellite-based solutions (like those from Farmonaut), precision agriculture is becoming more cost-effective. Many subscription plans are designed for small-scale farms and require no expensive hardware.
What are the main sustainability benefits?
Precision agriculture helps us reduce input waste (water, fertilizers, pesticides), improve resource efficiency, minimize environmental pollution, and ensure long-term food security.
Can I access Farmonaut’s features via mobile?
Absolutely! Farmonaut’s platform is available as a feature-rich web app, Android app, and iOS app, delivering real-time crop and field insights directly to your device.
Conclusion: The Precision Agriculture Revolution
We are living through a technological revolution in agriculture, where precision farming technologies enable us to farm smarter, not harder. By integrating AI-driven systems, drones, IoT field monitoring, and satellite innovations, we can pursue higher crop yields and greater efficiency while championing sustainability—all on a global scale.
As precision agriculture becomes increasingly accessible through platforms like Farmonaut, all farmers—from independent growers to the world’s largest agribusinesses—are empowered to manage field variability, minimize costs, and promote sustainable food production for the future.
Ready to bring your farm into the digital age? Try the Farmonaut platform and experience the power of precision agriculture firsthand.
For developers and agri-tech integrators: Seamlessly access Farmonaut Satellite & Weather API for building next-generation precision farming applications.